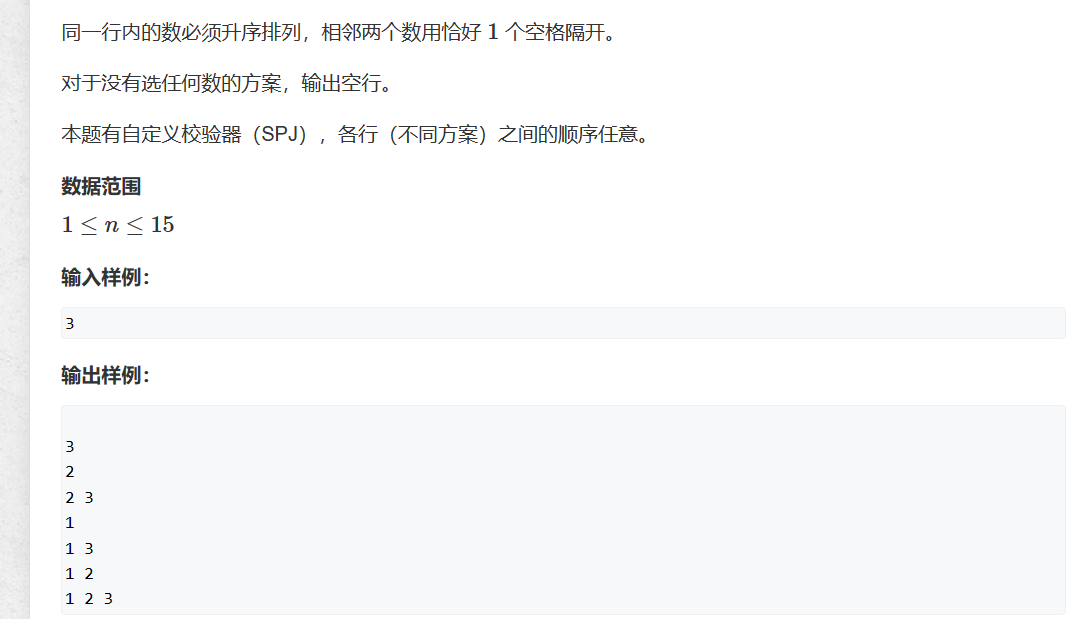
寒假刷题
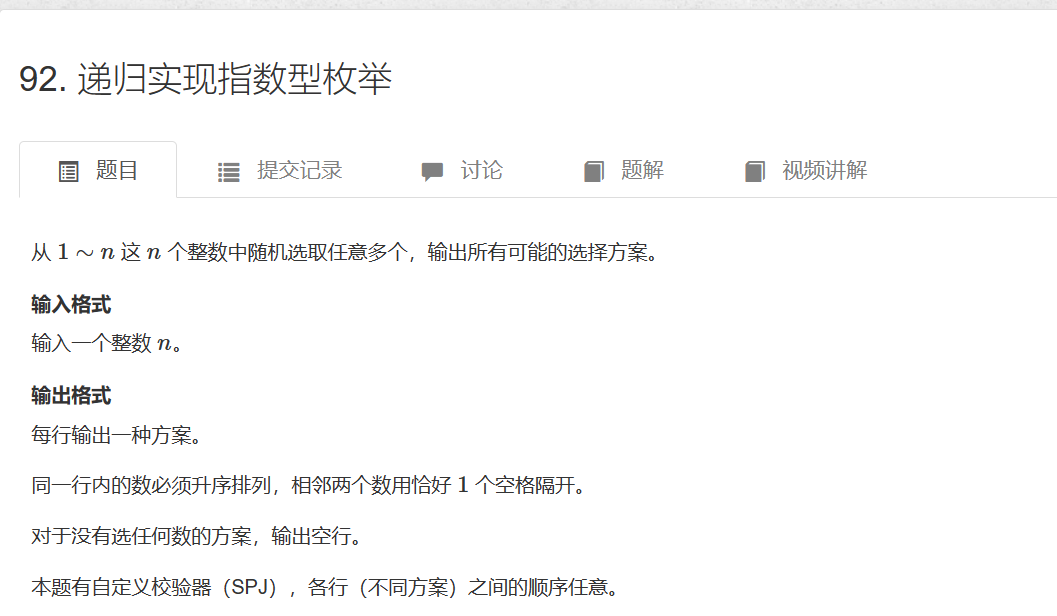
92. 递归实现指数型枚举
解法1递归
使用递归对每一个坑位进行选择,每个坑位有两种选择,填或者不填,使用st数组来记录每个坑位的状态,u来记录已经有多少坑位有了选择。

每个坑位有2钟选择,n个坑位的复杂度就是2的n次方。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 16;
int n;
int st[N];
void dfs(int u){
if(u>n)
{
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(st[i]==1)printf("%d ",i);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
st[u] = 1;
dfs(u+1);
st[u]=0;
dfs(u+1);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
坑位的下标和这个坑位的数字是存在对应关系的,所以可以用一个u来控制递归的出口。我们只关心u位置是否有数字。
st[u] = 1;
dfs(u+1);
这两句相当于是将这个位置画对勾,然后跳到下一个位置进行选择
st[u]=0;
dfs(u+1);
这两句就是这个位置不填数进入下一轮,顺便回到dfs之前的状态。(这题无所谓)
解法2二进制压缩
1-n的所有整数排列的方案可以看作一个二进制序列,例如1-3的排列中,1 3就对应二进制101。有数字用1表示,没有数字用0表示。
1-n共有2的n次方钟方案。将所有方案数枚举,然后判断位数是否是1。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 0;i < 1<<n;i ++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < n;j ++)
{
if(i >> j & 1)printf("%d ",j + 1);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
94. 递归实现排列型枚举
这题就是一个全排列问题,和上一题的区别是很明显的。上一个的每个坑位的数字是固定的,可能有或没有,这个题的每个坑位的数是不固定的,且必须有。这个题需要使用st记录是否使用过。这个st和上一个题的st代表的意义不一样。
使用循环来进行dfs。循环从1开始,到n结束。通过st[i]可以知道数字i是否被使用过。如果没被使用过就使用i,然后进入下一层搜索。使用后一定要恢复现场。

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int m,st[N],ans[N];
int n;
void dfs(int x)
{
if(x > n)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
for(int i = 1;i <=n;i ++)
{
if(!st[i])
{
st[i] = 1;
ans[x] = i;
dfs(x+1);
st[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
717. 简单斐波那契
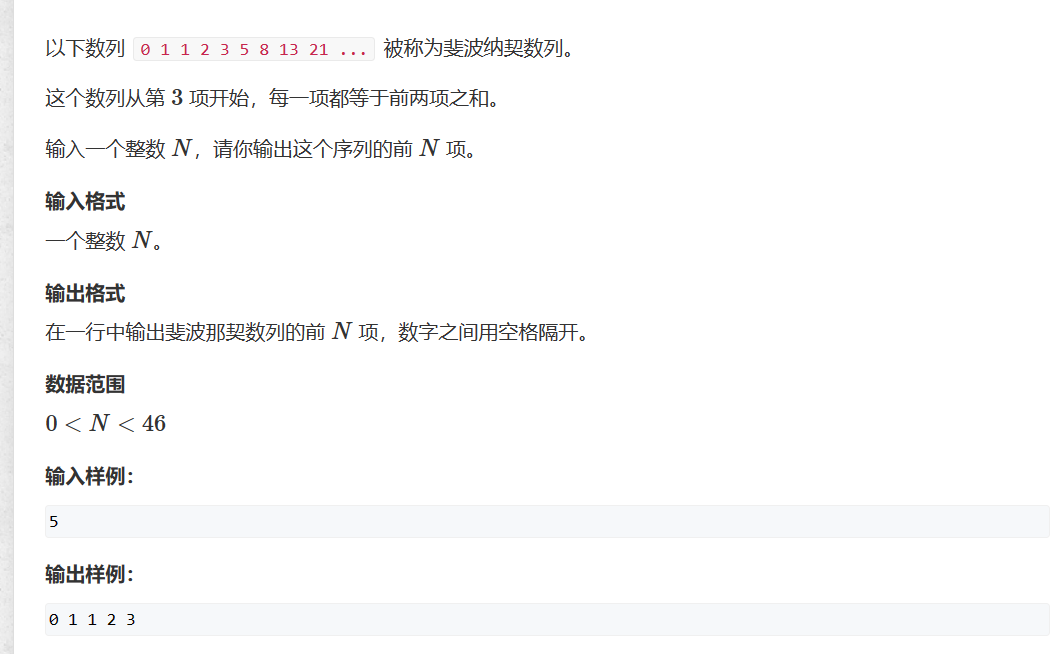
使用递推来进行求解,通过观察可以发现这个数列的第n项只与n-1和n-2项有直接关系,所以使用三个变量a b fn,依次向后轮转。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,fn;
scanf("%d",&n);
int a = 0,b = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
cout<<a<<" ";
fn = a+b;
a=b,b=fn;
}
}
95. 费解的开关

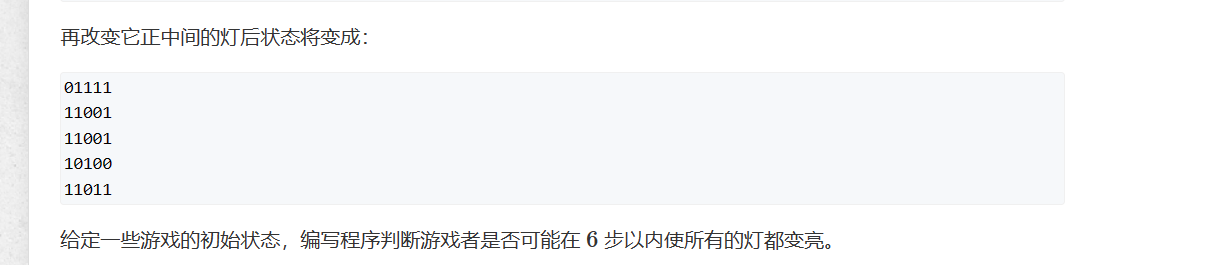

样例

改变右上角的开关


两步即可让所有的灯变亮。
观察题意可以发现能影响灯本身的除了灯自己还有灯上下左右的灯,可以枚举第一行灯的32种按法,记得备份原数组,然后从第一行按到第四行,第i行可以通过第i+1行的灯来控制,遍历完第四行后,看看第五行还有没有灭的灯,如果有的话,那这个方案就是不可行的。因为没有第六行来控制第五行。如果第五行全亮,那这个就是可以调,判断一下和ans哪个更小。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 6;
char g[N][N],backup[N][N];
int n;
int dx[] = {1,-1,0,0,0};
int dy[] = {0,0,-1,1,0};
void turn(int x,int y){
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i ++)
{
int a = x + dx[i];
int b = y + dy[i];
if(a < 0 || b < 0 || a > 4 || b > 4)continue;
g[a][b] ^= 1;
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n --)
{
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i ++)scanf("%s",g[i]);
int ans = 10;
for(int op = 0;op < 32;op ++)
{
memcpy(backup,g,sizeof g);
int step = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i ++)
{
if(op >> i & 1)
{
turn(0,i);
step ++;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < 5;j ++)
{
if(g[i][j] == '0')
{
turn(i+1,j);
step ++;
}
}
}
int drak = 0;
for(int j = 0;j < 5;j ++)
{
if(g[4][j] == '0')
{
drak = 1;
break;
}
}
if(drak == 0)ans = min(ans,step);
memcpy(g,backup,sizeof g);
}
if(ans > 6)ans = -1;
cout << ans <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
93. 递归实现组合型枚举


这题与全排列的区别就是字典序,只需要在判断是否使用过的时候加上一个判断,条件是当前的i是否大于ans数组的的最后一个元素,大于往里面添加,小于直接就跳过即可。ans数组初始化时要将元素变为-1,否则开头将无法添加。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 26;
int n,m;
int ans[N] = {-1},st[N]={0};
void dfs(int c,int m){
if(c > m)
{
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i ++)
{
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i = c ;i <= n; i ++)
{
if(!st[i]&&i > ans[c-1])
{
ans[c] = i;
st[i] = 1;
dfs(c + 1,m);
st[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
dfs(1,m);
return 0;
}
1209. 带分数

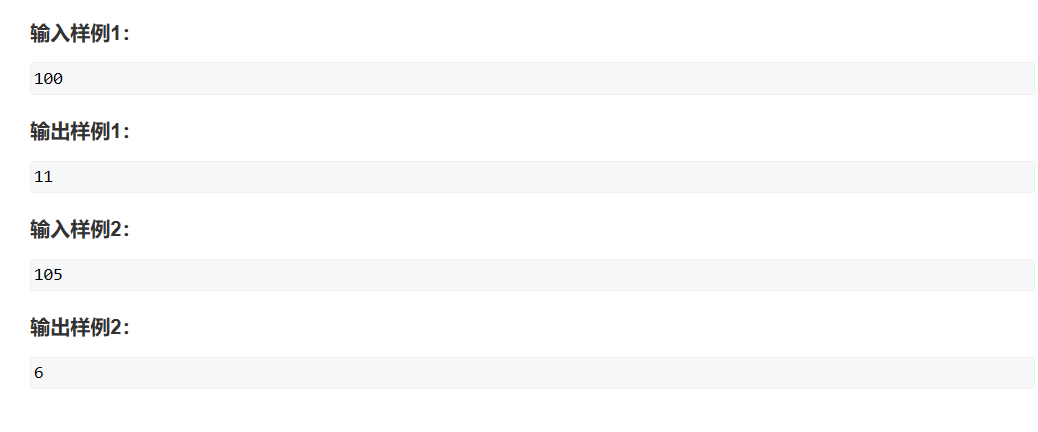
题意是
n
=
a
+
b
/
c
n = a + b/c
n=a+b/c
等式两边同时×c
c
∗
n
=
c
∗
a
+
b
c*n = c*a+b
c∗n=c∗a+b
通过dfs枚举a和c,然后计算出b,然后遍历st数组看看是否b的每一位都没有被用到。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30;
int st[N],backup[N];
int n,ans,test;
bool check(int a,int c)
{
long long b = (long long) n * c -a * c;
if(!a || !b || !c)return false;
memcpy(backup,st,sizeof st);
while(b)
{
int ge = b % 10;
if(ge == 0 || backup[ge])return false;
backup[ge] = 1;
b /= 10;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= 9;i ++)
{
if(backup[i] == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs_c(int a,int c)
{
if(check(a,c))ans ++;
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++)
{
if(st[i] == 0)
{
st[i] = 1;
dfs_c(a,c*10 + i);
st[i] = 0;
}
}
}
void dfs_a(int a)
{
if(a > n)return;
if(a)dfs_c(a,0);
for(int i = 1;i <= 9; i ++)
{
if(st[i] == 0)
{
st[i] = 1;
dfs_a(a*10 + i);
st[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
dfs_a(0);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
116. 飞行员兄弟
和费解的开关类似,只不过这个题的数量比较下,所以枚举所有行的全部可能,共65536种,对每一种方案进行操作,记录最少的方案数。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 5;
char st[N][N],backup[N][N];
vector <PII> ans;
int get(int x,int y)
{
return x*4 + y;
}
void turn(int x,int y)
{
if(st[x][y]=='+')st[x][y]='-';
else st[x][y]='+';
}
void turnall(int x,int y)
{
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++)
{
turn(x,i);
turn(i,y);
}
turn(x,y);
}
int main()
{
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++)
{
scanf("%s",st[i]);
}
for(int i = 0;i < 1 << 16;i ++)
{
vector <PII> step;
memcpy(backup,st,sizeof st);
for(int x = 0;x < 4;x ++)
{
for(int y = 0;y < 4;y ++)
{
if(i >> get(x,y) & 1)
{
turnall(x,y);
step.push_back({x,y});
}
}
}
int dark = 0;
for(int x = 0;x < 4;x ++)
{
for(int y = 0;y < 4;y ++)
{
if(st[x][y]=='+')
{
dark = 1;
break;
}
}
}
if(dark == 0)
{
if(ans.empty()||ans.size() > step.size()) ans = step;
}
memcpy(st,backup,sizeof st);
}
cout << ans.size() << endl;
for(auto p:ans)
{
cout << p.x+1<<" "<<p.y+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
1208. 翻硬币
有个初始态有个结束态。将初始态与结束态一一对比,遇到不一样的就将移动次数加一并且变换硬币状态。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int ans;
string start,aim;
void turn(int i)
{
if(start[i]=='*')start[i] = 'o';
else start[i] = '*';
}
int main()
{
cin>>start>>aim;
for(int i = 0;i < start.size() - 1;i ++)
{
if(start[i]!=aim[i])turn(i+1),ans++;
}
cout << ans <<endl;
return 0;
}