配置文件入门
配置文件最重要的目的:解决硬编码问题(代码写死)
我们接下来主要介绍两个方面:常见的配置项和配置文件的使用
SpringBoot 的配置文件,有三种格式
- properties
- yaml
- yml(yaml的简写)
用的较多的是yml和properties文件
如果项目中,同时存在properties和yml配置文件,properties的优先级更高。企业开发中,通常只使用其中一个文件,但是如果同时存在时,两个文件都生效。如果两个文件中,都包含同一个配置,以properties为主。
properties配置文件说明
使用properties配置文件改变端口号:
server.port=9090
properties语法格式:
key value的形式,以 = 分割
key 的格式建议是小写,单词之间使用.分割
举例:配置数据库连接信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/testdb?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
除此之外我们还可以自定义配置
demo.key = hello,properties
读取配置文件:
@RestController
public class PropertiesController {
//读取配置文件
//如果去掉$,就会把""中的值赋值给当前变量
@Value("${demo.key}")
private String key;
@RequestMapping("/readKey")
public String readKey(){
return "读取到的配置:" + key;
}
}
yml配置文件说明
把properties配置文件中的.换成冒号+换行,key后面用冒号赋值
使用yml配置文件改变端口号:
server:
port: 9090
(Value前面)冒号后面一定要加空格,空格不可以省略。
自定义配置:
demo:
key1: hello,yml
key2: 12
key3: ""
读取配置:yml文件能够自动转化类型。
@RestController
public class YmlController {
@Value("${demo.key1}")
private String key1;
@Value("${demo.key2}")
private Integer key2;
@Value("${demo.key3}")
private String key3;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("key1:" + key1);
System.out.println("key2:" + key2);
System.out.println("key3:" + key3);
}
}
yml特殊内容配置
null:使用~
空字符串:key后面直接空着就行了,推荐用单引号或者双引号括起来
配置文件单双引号的区别
自定义配置文件:
string:
str1: Hello \n Spring Boot.
str2: 'Hello \n Spring Boot.'
str3: "Hello \n Spring Boot."
执行结果:
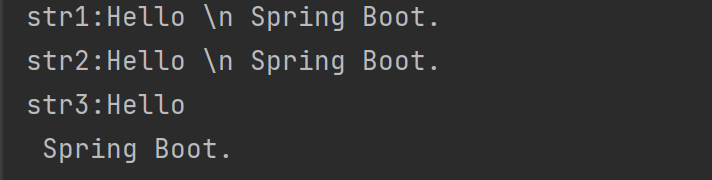
单引号会对特殊字符进行转义,双引号不会进行转义。
\n本身表示的是换行。使用单引号时,内容表示成了\n,而不是换行,所以认为是转义。使用双引号时,\n表示成了换行,也就是\n的本来含义。
yml配置对象
自定义配置文件:
student:
id: 18
name: zhangsan
age: 12
定义一个java对象:
@Data
@Component//存储到spring中
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")//读取配置文件
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
通过属性注入对象,进行使用:
@Autowired
Student student;
yml配置集合
自定义配置:
dbtypes:
name: #配置集合
- mysql
- sqlserver
- db2
map: #配置Map
k1: kk1
k2: kk2
k3: kk3
定义一个对象:
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dbtypes")
public class DBType {
private String[] name;//可以用List来接收
private Map<String,String> map;
}
获取对象并打印对象:
@RestController
public class YmlController {
@Autowired
DBType dbType;
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println(dbType + ",length:" + dbType.getName().length);
}
}
如果定义集合-后面不加空格,这部分内容会变成一个整体,统一赋值给对应属性。
两种格式的配置文件对比:
-
properties读取中文乱码,yml不会产生乱码
-
yml对中文的兼容性比较好。优先读取 properties。properties出的比较早。
-
⽀持更多的编程语⾔,不⽌是Java中可以使⽤,在Golang,Python,Ruby,JavaScript中也可以使⽤
-
yml⽀持更多的数据类型,可以简单表达对象,数组,List,Map等数据形态
-
yml不适合写复杂的配置⽂件 ,对格式有较强的要求(⼀个空格可能会引起⼀场⾎案)