数据结构总目录
红黑树
介绍:
- 红黑树是一种特化的AVL树(平衡二叉树),都是在进行插入和删除操作时通过特定操作保持二叉查找树的平衡,从而获得较高的查找性能。
- 红黑树是一种平衡二叉查找树的变体,它的左右子树高差有可能大于 1,所以红黑树不是严格意义上的平衡二叉树(AVL),但 对之进行平衡的代价较低, 其平均统计性能要强于 AVL
- 由于每一棵红黑树都是一颗二叉排序树,因此,在对红黑树进行查找时,可以采用运用于普通二叉排序树上的查找算法,在查找过程中不需要颜色信息
1. 图文解析
红黑树性质
- 性质一:结点是红色或黑色
- 性质二:根结点是黑色
- 性质三:空结点为叶子结点,且所有叶子结点都是黑色
- 性质四:每个红色结点的两个子结点都是黑色
- 性质五:从任一结点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色结点
1.1 存储结构
与一般二叉树相比,红黑树的结构存在父结点指针和结点颜色的标识
typedef char DataType;
typedef struct RBNode
{
int color; // 结点颜色(0:黑色 1:红色)
DataType data; // 结点数据
struct RBNode *parent; // 父结点指针,用于定位
struct RBNode *lchild, *rchild; // 左右孩子指针
}RBNode, *RBTree;
1.2 红黑树的插入操作
在红黑树的插入时,第一个问题就是新插入的结点应该为红色还是黑色呢?
- 根据性质二:如果初始红黑树为空,则插入的一定是根节点且为黑色
- 根据性质五:如果新插入的结点为黑色,那么势必会导致路径上的黑色结点数量的增加,无疑增加了插入后的调整难度
- 根据性质三:如果新插入的结点为红色,那么新结点的两个空结点一定为黑色,那么就不会增加路径上的黑色结点数量
总结:若插入的是根结点,则设置为黑色,其他情况则设置为红色
已知新插入的结点为红色,而如果父结点也为红色,就会违反性质四,则说明此时需要调整红黑树
同时在父亲结点为红色的条件下,则根据性质二,父亲结点一定不是根结点,且存在祖父结点
调整情况如下:
若父亲结点为祖父结点的左孩子结点
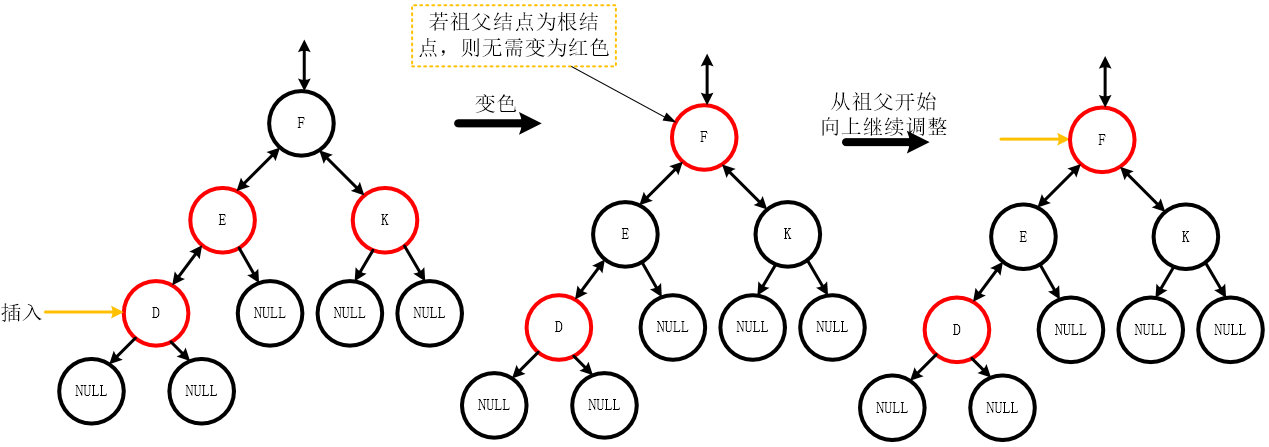
- 叔叔结点为红色
调整过程:父亲结点和叔叔结点均变为红色,祖父结点若不是根结点,则变为红色,并将祖父结点视为新插入的结点,继续向上调整
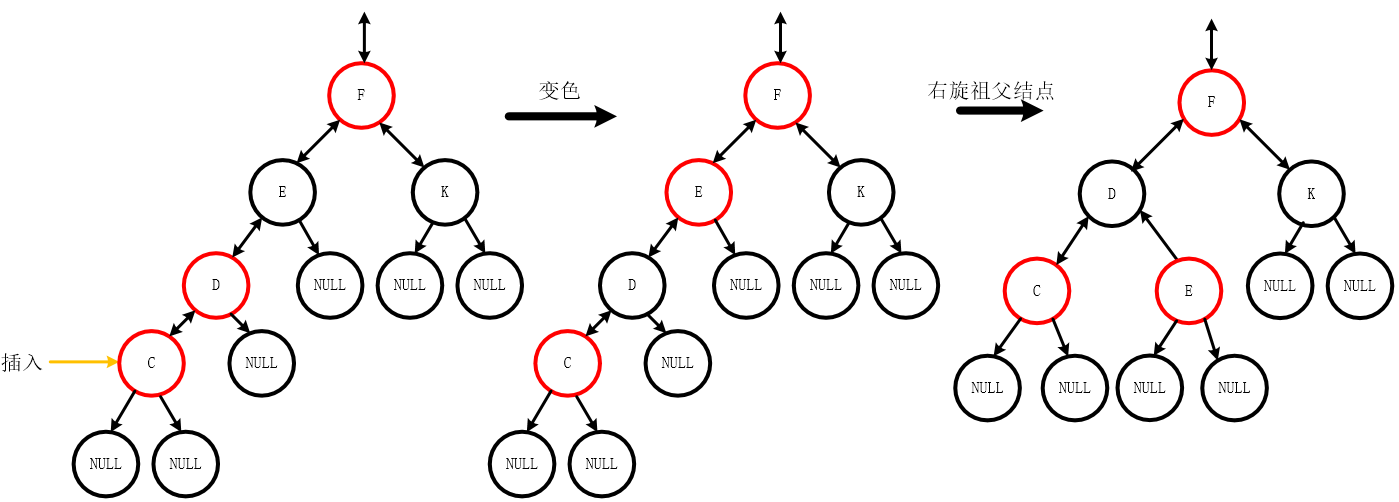
- 叔叔结点为黑色
2.1 插入的位置是父亲结点的左孩子
- 调整过程:父亲结点变为黑色,祖父结点变为红色,最后右旋祖父结点
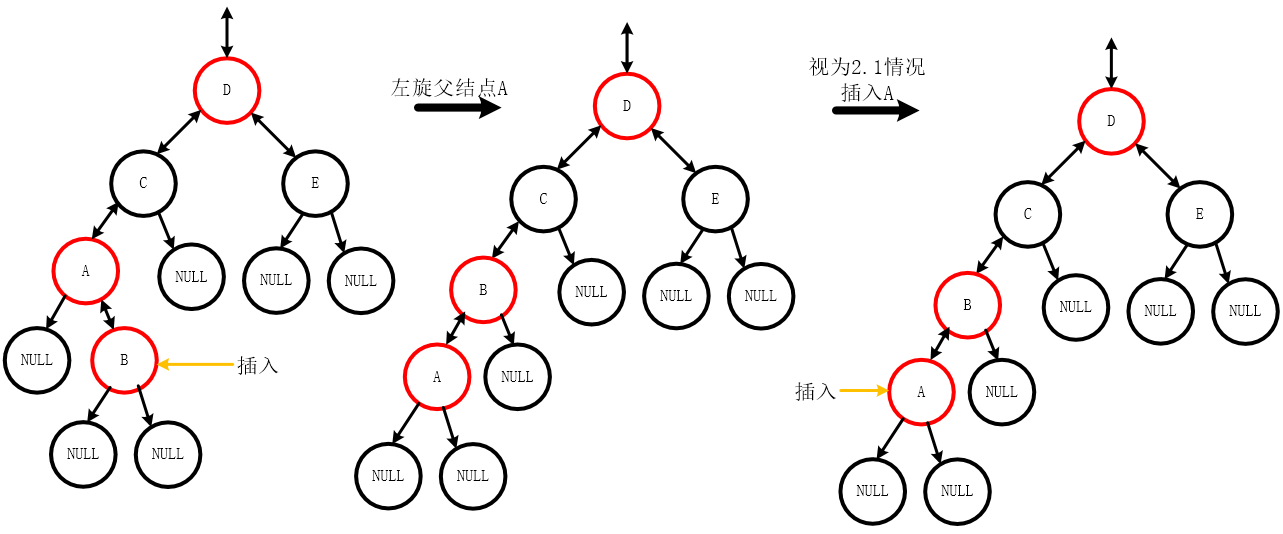
2.2 插入父亲结点的右孩子
- 调整过程:左旋父结点,而后可视为2.1的情况进行调整
若父亲结点为祖父结点的右孩子结点,其操作与以上情况对称,详细见代码
2. 源代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef char DataType;
typedef struct RBNode
{
int color; // 结点颜色(0:黑色 1:红色)
DataType data; // 结点数据
struct RBNode *parent; // 父结点指针,用于定位
struct RBNode *lchild, *rchild; // 左右孩子指针
}RBNode, *RBTree;
void InitRBTree(RBTree *T)
{
(*T) = NULL;
printf("红黑树已初始化!\n");
}
// 创建新结点
RBNode *NewNode(int color, DataType x)
{
RBNode *newNode;
newNode = (RBNode *)malloc(sizeof(RBNode));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->color = color;
newNode->parent = newNode->lchild = newNode->rchild = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 右旋转,
void RightRotate(RBNode *node, int flag)
{
RBNode *parent = node->parent;
RBNode *left = node->lchild;
node->lchild = left->rchild;
if (left->rchild)
{
left->rchild->parent = node;
}
left->rchild = node;
node->parent = left;
left->parent = parent;
if (parent)
{
// flag = 0:node为父结点左孩子
// flag = 1:node为父结点右孩子
!flag ? (parent->lchild = left) : (parent->rchild = left);
}
}
// 左旋转
void LeftRotate(RBNode *node, int flag)
{
RBNode *parent = node->parent;
RBNode *right = node->rchild;
node->rchild = right->lchild;
if (right->lchild)
{
right->lchild->parent = node;
}
right->lchild = node;
node->parent = right;
right->parent = parent;
if (parent)
{
// flag = 0:node为父结点左孩子
// flag = 1:node为父结点右孩子
!flag ? (parent->lchild = right) : (parent->rchild = right);
}
}
// 红黑树调整
void RBTreeAdjust(RBNode *node)
{
// 父结点为红色,则父结点一定不是根结点,且祖父结点一定存在
RBNode *father = node->parent;
RBNode *grandfather = father->parent;
RBNode *uncle;
if (father && father == grandfather->lchild)
{
// 父亲为祖父的左孩子
uncle = grandfather->rchild;
// printf("\t父亲(%c)为祖父(%c)的左孩子\n", father->data, grandfather->data);
if (uncle && uncle->color == 1)
{
// 若叔叔结点存在且为红色,则进行变色
// printf("\t\t叔叔(%c)为红色,进行变色\n", uncle->data);
father->color = 0;
uncle->color = 0;
grandfather->color = 1;
// 递归调整祖父结点
if (grandfather->parent && grandfather->parent->color == 1)
{
RBTreeAdjust(grandfather);
}
else if(!grandfather->parent)
{
grandfather->color = 0;
}
}
// 叔叔结点不存在,或者为黑色
else if (node == father->lchild)
{
// 若插入的结点是父亲的左孩子,则进行变色并对祖父进行右旋转
// printf("\t\t叔叔为黑色,插入位置为父亲的左孩子\n");
// printf("\t\t>> 父结点(%c)变黑色,祖父(%c)边红色, 右旋祖父\n", father->data, grandfather->data);
father->color = 0;
grandfather->color = 1;
RightRotate(grandfather, 0);
}
else
{
// 若插入的结点是父亲的右孩子,则对父亲进行左旋转
// printf("\t\t叔叔为黑色,插入位置为父亲的右孩子\n");
// printf("\t\t>> 左旋父亲结点\n");
LeftRotate(father, 0);
RBTreeAdjust(father);
}
}
else
{
// 父亲为祖父的右孩子
uncle = grandfather->lchild;
// printf("\t父亲(%c)为祖父(%c)的右孩子\n", father->data, grandfather->data);
// 以下同理,对称操作
if (uncle && uncle->color == 1)
{
// printf("\t\t叔叔(%c)为红色\n", uncle->data);
father->color = 0;
uncle->color = 0;
grandfather->color = 1;
// 递归调整祖父结点
if (grandfather->parent && grandfather->parent->color == 1)
{
RBTreeAdjust(grandfather);
}
else if(!grandfather->parent)
{
grandfather->color = 0;
}
}
else if (node == father->lchild)
{
// printf("\t\t叔叔为黑色,插入位置为父亲的左孩子\n");
// printf("\t\t>> 右旋父亲结点\n");
RightRotate(father, 1);
RBTreeAdjust(father);
}
else
{
// printf("\t\t叔叔为黑色,插入位置为父亲的右孩子\n");
// printf("\t\t>> 父结点(%c)变黑色,祖父(%c)边红色, 左旋祖父\n", father->data, grandfather->data);
father->color = 0;
grandfather->color = 1;
LeftRotate(grandfather, 1);
}
}
}
// 插入
void RBTreeInsert(RBTree *T, DataType x)
{
// 若树为空,则创建新结点作为根结点
if ((*T) == NULL)
{
// 性质二:根结点为黑色
(*T) = NewNode(0, x);
return;
}
// 根据二叉排序树的性质查找插入位置
RBNode *node = (*T), *parent;
while (node)
{
parent = node;
if (node->data > x)
{
node = node->lchild;
}
else if (node->data < x)
{
node = node->rchild;
}
else
{
printf("插入失败,存在相同数据\n");
return;
}
}
// 根据查找到的位置的父结点插入
node = NewNode(1, x);
if (parent->data > x)
{
parent->lchild = node;
}
else
{
parent->rchild = node;
}
node->parent = parent;
// 若父结点为红色,则不符合性质三:红色结点的孩子结点均为黑色
if (parent->color == 1)
{
// printf("父结点(%c)为红色,需要进行调整!\n", parent->data);
RBTreeAdjust(node);
}
}
// 先序遍历
void PreOrderTraverse(RBTree T)
{
if (T)
{
printf("%c", T->data);
T->color == 0 ? printf("[黑] ") : printf("[红] ");
PreOrderTraverse(T->lchild);
PreOrderTraverse(T->rchild);
}
}
int main()
{
RBTree T;
DataType x;
InitRBTree(&T);
while (1)
{
fflush(stdin);
printf("输入插入数据:"); // 测试数据:FEKDCABNMOP
scanf("%c", &x);
if (x == '#')
{
break;
}
RBTreeInsert(&T, x);
printf("先序遍历:");
PreOrderTraverse(T);
printf("\n\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
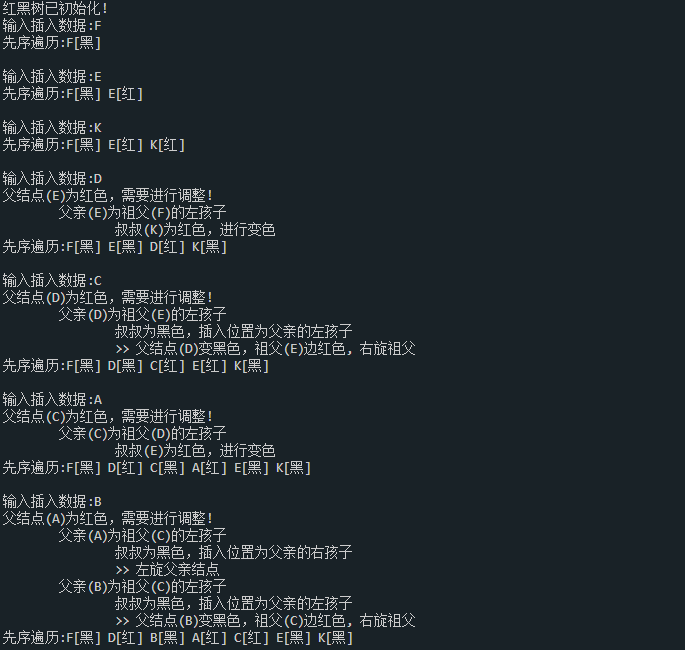
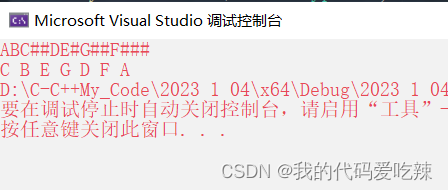
3. 测试结果