目录
一、前言
二、我的环境
三、代码实现
1、C3模块
2、Backbone模块
一、前言
>- **🍨 本文为[🔗365天深度学习训练营](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xLjALoOD8HPZcH563En8bQ) 中的学习记录博客**
>- **🍦 参考文章:365天深度学习训练营-第P7周:YOLOv5-Backbone/C3模块实现(训练营内部成员可读)
>- **🍖 原作者:[K同学啊|接辅导、项目定制](https://mtyjkh.blog.csdn.net/)**● 难度:夯实基础⭐⭐
● 语言:Python3、Pytorch3
● 时间:1月1日-1月7日
🍺要求:
自己搭建yolov5-backbone/yolov5-c3框架
调用官方的backbone/c3网络框架
如何查看模型的参数量以及相关指标
二、我的环境
语言环境:Python3.7
编译器:jupyter notebook
深度学习环境:Pytorch1.6
三、代码实现
1、C3模块

import torch.nn.functional as F
def autopad(k, p=None): # kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))
class model_K(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model_K, self).__init__()
# 卷积模块
self.Conv = Conv(3, 32, 3, 2)
# C3模块1
self.C3_1 = C3(32, 64, 3, 2)
# 全连接网络层,用于分类
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=802816, out_features=100),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=100, out_features=4)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.Conv(x)
x = self.C3_1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = model_K().to(device)
modelC3模块:包含了3个标准Conv模块以及多个Bottleneck模块, 结构分为两支,一只使用多个Bottleneck堆叠和一个Conv模块,另外一支经过一个Conv模块,最后将两支concat操作再经过Conv模块。 Conv模块: 对输入特征进行卷积、BN、激活函数操作,这里用Silu函数作为激活函数。 Bottleneck模块: 先进行1×1 卷积将channel减小一半,再通过3×3 卷积将通道数加倍,并获取特征,其中shortcut参数控制是否进行残差连接。 Silu函数: sigmoid 加权线性单元(SiLU), 强化学习中神经网络函数逼近的激活函数, YOLOv7使用该激活函数。
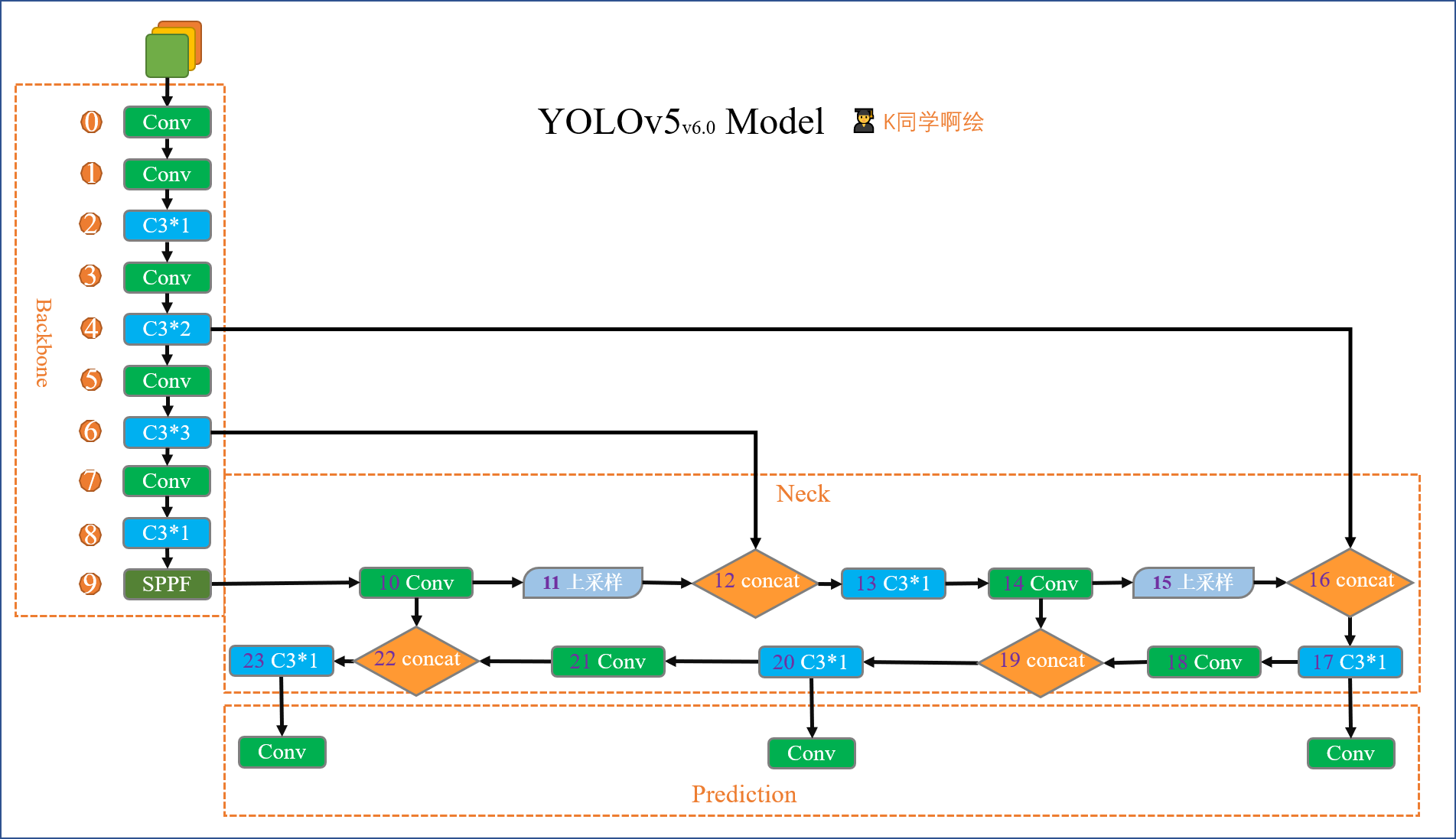
2、Backbone模块
import torch.nn.functional as F
def autopad(k, p=None): # kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))
"""
这个是YOLOv5, 6.0版本的主干网络,这里进行复现
(注:有部分删改,详细讲解将在后续进行展开)
"""
class YOLOv5_backbone(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(YOLOv5_backbone, self).__init__()
self.Conv_1 = Conv(3, 64, 3, 2, 2)
self.Conv_2 = Conv(64, 128, 3, 2)
self.C3_3 = C3(128, 128)
self.Conv_4 = Conv(128, 256, 3, 2)
self.C3_5 = C3(256, 256)
self.Conv_6 = Conv(256, 512, 3, 2)
self.C3_7 = C3(512, 512)
self.Conv_8 = Conv(512, 1024, 3, 2)
self.C3_9 = C3(1024, 1024)
self.SPPF = SPPF(1024, 1024, 5)
# 全连接网络层,用于分类
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=65536, out_features=100),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=100, out_features=4)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.Conv_1(x)
x = self.Conv_2(x)
x = self.C3_3(x)
x = self.Conv_4(x)
x = self.C3_5(x)
x = self.Conv_6(x)
x = self.C3_7(x)
x = self.Conv_8(x)
x = self.C3_9(x)
x = self.SPPF(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = YOLOv5_backbone().to(device)
model