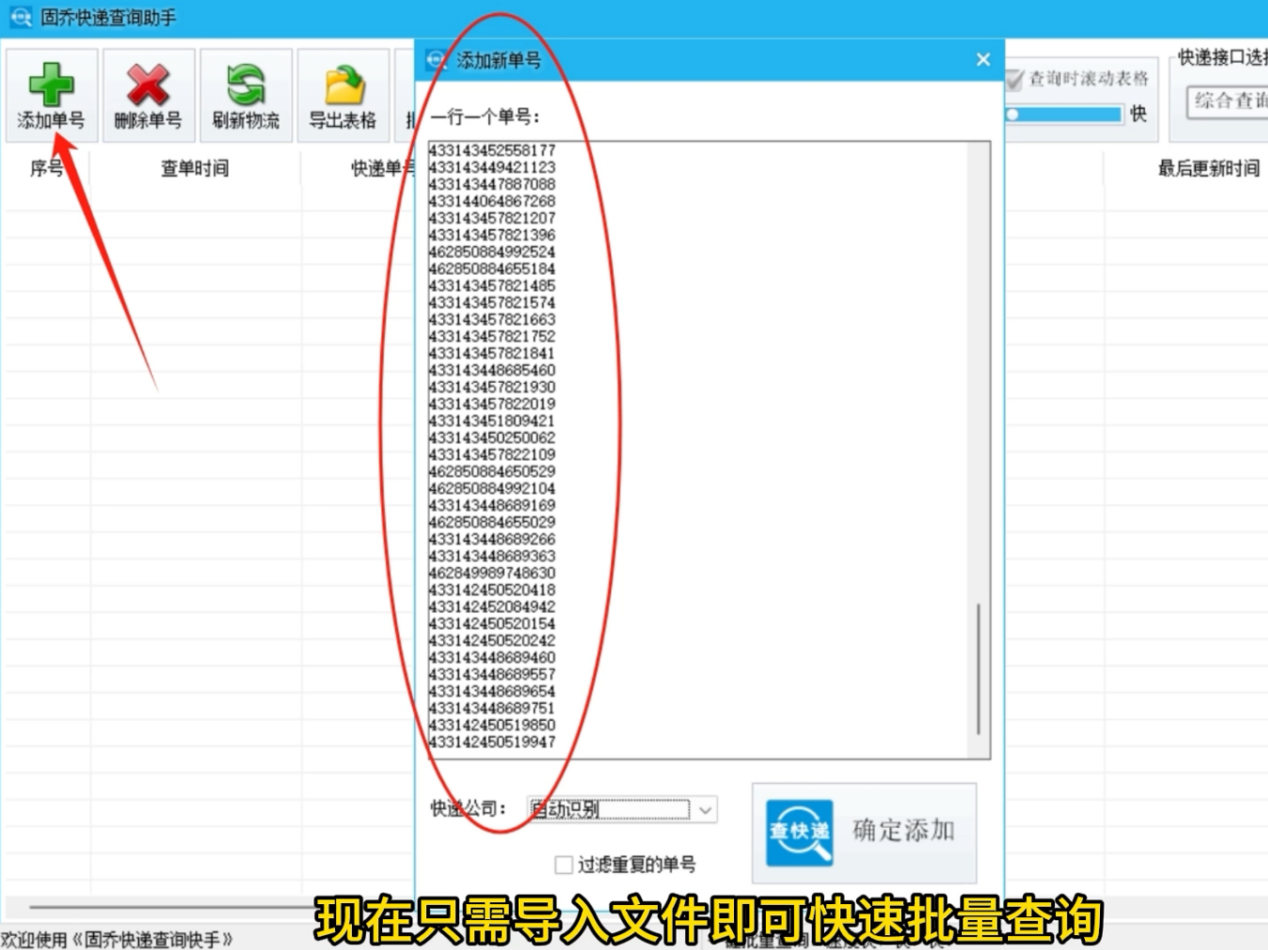
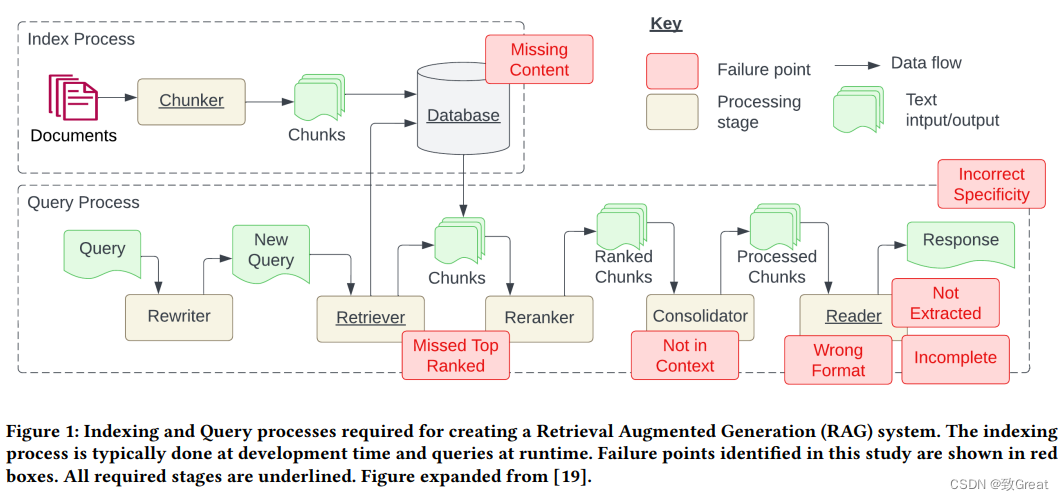
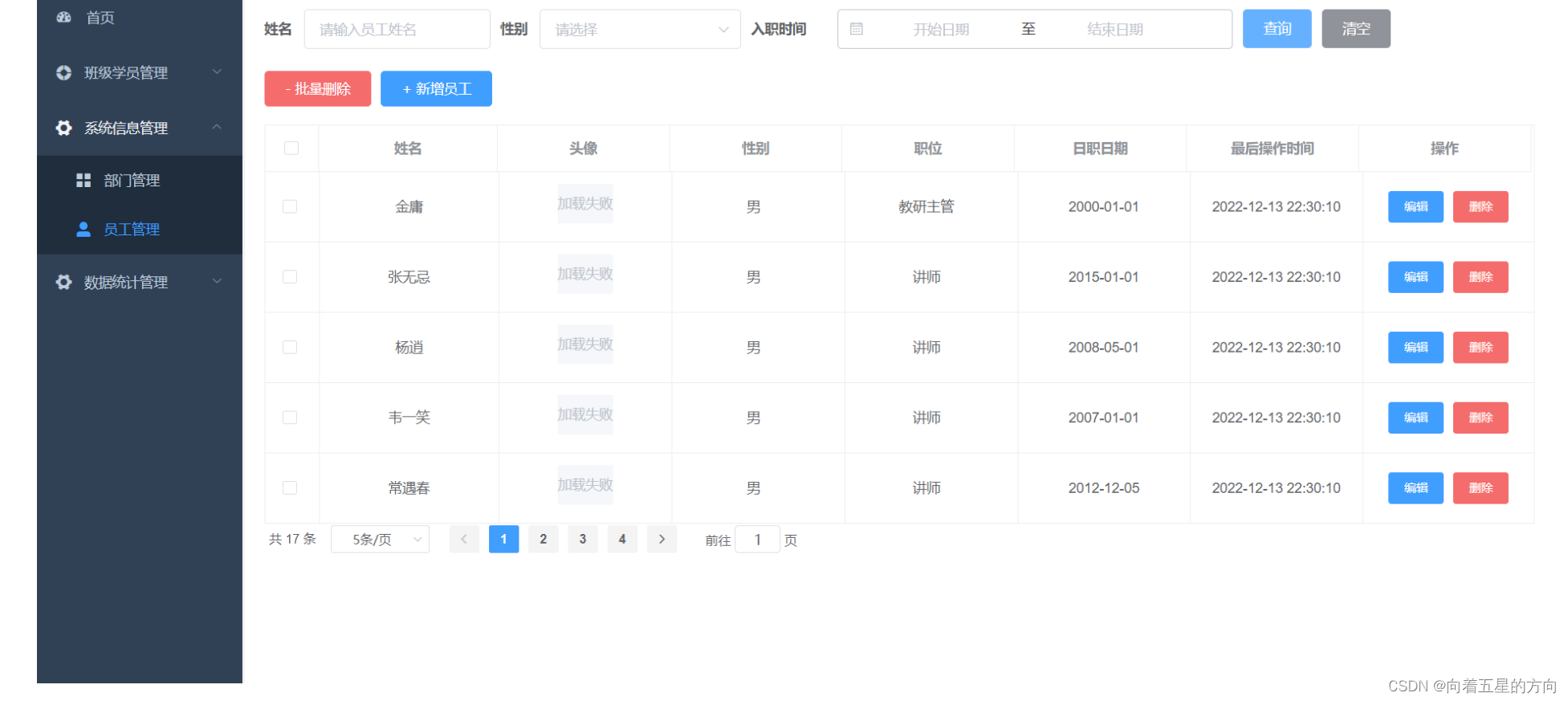
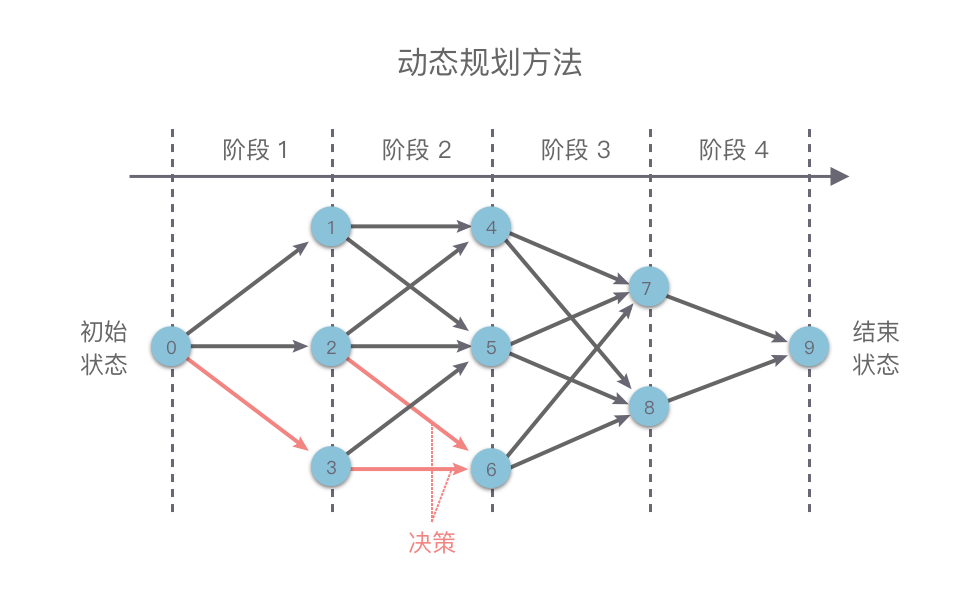
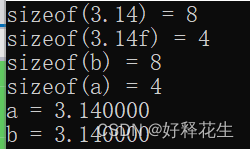
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Wheel{
public:
//成员数据
string brand; //品牌
int year; //年限
//真正的成员函数
void printWheelInfo(); //声明成员函数
};
void Wheel::printWheelInfo()
{
cout<<"我的轮胎品牌是:"<<brand<<endl;
cout<<"我的轮胎日期是:"<<std::to_string(year)<<endl;
}
//在c++中一个类包含另一个类的对象叫做组合
class Car{
public:
//成员数据
string color; //颜色
string brand; //品牌
string type; //车型
int year; //年限
Wheel wl;
Wheel *pwl;
//其实也是成员数据,指针变量,指向函数的变量,并非真正的成员函数
void (*printCarInfo)(string color,string brand,string type,int year);
void (*CarRun)(string type);
void (*CarStop)(string type);
//真正的成员函数
void realPrintCarInfo(); //声明成员函数
};
//"::" 类或者命名空间的解析符
void Car::realPrintCarInfo() //在类的外部进行成员函数的实现
{
string str = "车的品牌" + brand
+ ",型号是" + type
+ ",颜色是" + color
+ ",上市年限是" + std::to_string(year);
cout << str<<endl;
}
int main()
{
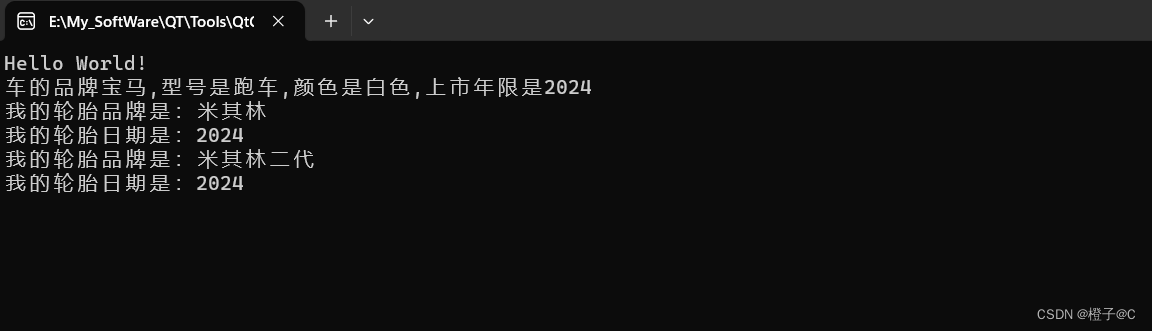
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
Car BMW3;
BMW3.color = "白色";
BMW3.brand = "宝马";
BMW3.type = "跑车";
BMW3.year = 2024;
BMW3.wl.brand = "米其林";
BMW3.wl.year = 2024;
BMW3.pwl = new Wheel;
BMW3.pwl->brand = "米其林二代";
BMW3.pwl->year = 2024;
BMW3.realPrintCarInfo();
BMW3.wl.printWheelInfo();
BMW3.pwl->printWheelInfo();
return 0;
}