在 Java 中,与关系型数据库进行交互是非常常见的任务之一。JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)是 Java 平台的一个标准 API,用于连接和操作各种关系型数据库。其中,PreparedStatement 是 JDBC 中的一个重要接口,用于执行预编译的 SQL 语句。
什么是 PreparedStatement
1)PreparedStatement 继承自 Statement ,是 Statement 的一种扩展;
2)PreparedStatement 特点:使用 PreparedStatement 可以执行动态参数化 sql(在 sql 语句中用占位符 ?);
3)PreparedStatement 原理:在我们调用 PreparedStatement 对象(sqlStatement)的时候,我们需要将一个半成品 sql 语句交给 sqlStatement,sqlStatement 拿着这个 sql 先发送到数据库,进行预编译(检查语法,检查权限),当我们调用 sqlStatement.setXXX() 的时候,再一起把占位符设置的动态参数值一起发送到数据库执行,不用再编译当前的sql语句,这样可以大大的节省时间,提高运行效率。
什么是 SQL 注入风险
一些黑客,将一些特殊的字符通过字符串拼接的方式注入到 sql 语句中,改变 sql 语句原有的运行逻辑,从而威胁到数据库的安全,这种现象叫做 sql 注入。
Statement 和 PreparedStatement 的区别
1)使用 Statement 执行 SQL 语句,是以字符串拼接的方式给 SQL 语句加入参数,这个时候存在 sql 注入风险;
2)使用 PreparedStatement 执行 SQL 语句,是以参数拼接(setXXX() 函数)的方式给 SQL 语句加入参数,预编译的方式能有效防止 SQL 注入;
3)PreparedStatement 和 Statement 的生命周期,都是一次数据库连接,PreparedStatement 的可重用是由于连接池管理器有缓存功能,PreparedStatement 编译时会被记录到列表,并在下次访问时返回;
4)PreparedStatement 能在一次连接中,对数据进行批量更新(Batch 功能),减少服务与数据库的交互次数,网络往返是影响性能的重要指标;
5)Statement 适用于少次或者一次的查询,PreparedStatement 适用于多次或者一次做多量的查询;
6)对于只执行一次的 SQL 语句选择 Statement 是最好的,因为只执行一次的 SQL 语句使用 PreparedStatement 反而比 Statement 更耗时;
7)PreparedStatement 代码的可读性高,可维护性好;
创建 PreparedStatement
要创建一个 PreparedStatement 对象,首先需要获得一个 Connection 对象,然后使用 prepareStatement 方法传入 SQL 语句。下面举几个具体示例:
数据准备
create database jdbc;
CREATE TABLE t1 (
c1 int,
c2 int,
c3 char(10),
PRIMARY KEY (c1),
KEY(c2)
);
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (1, 6, '3');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (2, 3, '4');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (3, 4, '1');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (4, 1, '6');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (5, 2, '2');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (6, 5, '5');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (7, 8, '9');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (8, 9, '7');
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (9, 7, '8');执行 select 语句
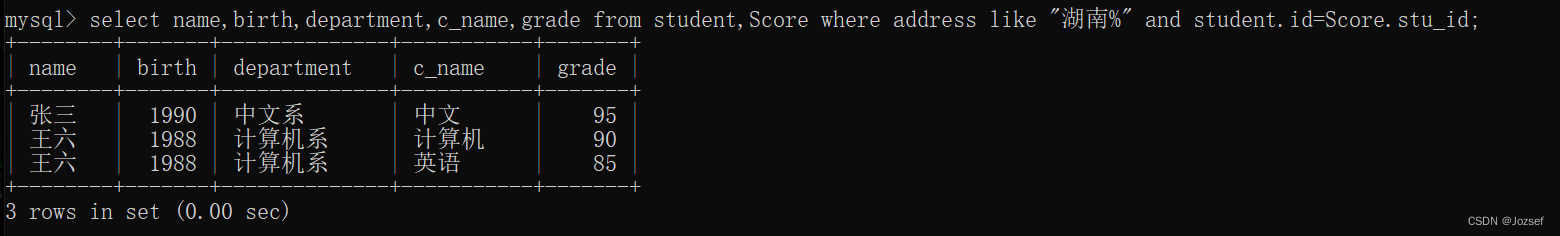
下面以执行 select 语句为例,并输出查询结果:
try {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
System.out.println("Connected to the database!");
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 2) execute SQL
try {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE c1 > ?"; // sql 查询语句使用 ? 作为占位符
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// set parameter
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 5); // 此处的 1 是指 sql 中的第 1 个参数
// execute query
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// show select result
while (resultSet.next()) {
int c1 = resultSet.getInt("c1");
int c2 = resultSet.getInt("c2");
String c3 = resultSet.getString("c3");
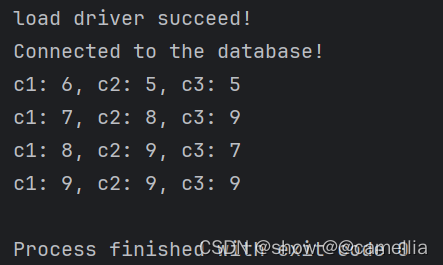
System.out.println("c1: " + c1 + ", c2: " + c2 + ", c3: " + c3);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("executeQuery fail!");
}
connection.close(); // close PreparedStatement
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
PreparedStatement 允许我们为 SQL 语句中的占位符设置参数值。有多种 setXXX 方法可用于不同数据类型的参数设置,例如 setInt、setString、setDouble 等,其中 setXXX 方法中的第一个参数是指 SQL 语句中的第几个占位符。
执行结果如下:
执行 update 语句
try {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
System.out.println("Connected to the database!");
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 2) execute SQL
try {
String sql = "UPDATE t1 SET c3 = ? WHERE c1 = ?"; // sql 查询语句使用 ? 最为占位符
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// set parameter
preparedStatement.setString(1,"9");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 9);
// execute query
int rowCount = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); // 统计更新的行数
// show select result
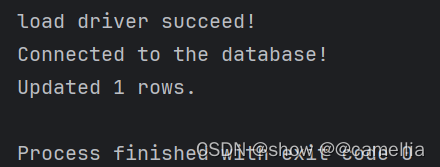
System.out.println("Updated " + rowCount + " rows.");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("executeUpdated fail!");
}
connection.close(); // close PreparedStatement
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}执行结果如下:
执行批处理
当需要批量插入或更新记录时,可以采用 Java 的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条 SQL 语句一次性提交给数据库。通常情况下,批量提交处理比单独提交处理效率要高很多,JDBC 批量处理 SQL 语句主要使用以下三个方法:
- addBatch(String):添加需要批量处理的 SQL 语句或参数;
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句;
- clearBatch():清空缓存的数据;
通常我们会遇到两种批量执行 SQL 语句的情况:
- 一个 SQL 语句的批量传参;
- 多条 SQL 语句的批量处理;
批处理的两个重要参数:
- allowMultiQueries:是否允许一次性执行多条 SQL,默认为 false;
select * from t1;select * from t1;注意:因为它允许一次执行多个查询,所以它可能导致应用程序被某些类型的 SQL 注入攻击;
- rewriteBatchedStatements:是否允许将 SQL 语句批量传给 MySQL,默认为 false;若想让 MySQL 支持批处理,可以将 ?rewriteBatchedStatements=true 写在 url 的后面;
String url = "jdbc:mysql://172.19.108.205:3306/jdbc?rewriteBatchedStatements=true";下面几种场景是往表 t1 中插入 10000 条记录,然后对比不同插入方式的耗时:
方式一:循环批量传参
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // start time
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
System.out.println("Connected to the database!");
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 2) execute SQL
try {
String insertSql = "INSERT INTO t1 (c1, c2, c3) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement insertStatement = connection.prepareStatement(insertSql);
// set parameter
for (int i =10; i <= 10000; i++) {
insertStatement.setInt(1, i);
insertStatement.setInt(2, i);
insertStatement.setString(3, Integer.toString(i));
// execute query
insertStatement.executeUpdate();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("cost time:" + (end - start));
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("executeUpdated fail!");
}
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}执行结果如下:

说明:从执行结果可知,方式一批量处理时,耗时:34886
方式二:批处理函数
使用 executeBatch 批量执行;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // start time
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
System.out.println("Connected to the database!");
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 2) execute SQL
try {
String insertSql = "INSERT INTO t1 (c1, c2, c3) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement insertStatement = connection.prepareStatement(insertSql);
// set parameter
for (int i =10; i <= 10000; i++) {
insertStatement.setInt(1, i);
insertStatement.setInt(2, i);
insertStatement.setString(3, Integer.toString(i));
insertStatement.addBatch(); // add sql
if(i % 1000 == 0) {
insertStatement.executeBatch(); // execute sql
insertStatement.clearBatch(); // clean batch
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("cost time:" + (end - start));
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("executeUpdated fail!");
}
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}执行结果如下:

说明:从执行结果可知,方式一批量处理时,耗时:2585
方式三:统一提交事务
使用 setAutoCommit(false) 关闭事务自提交,等待数据批量插入结束后,统一 commit;
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // start time
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
System.out.println("Connected to the database!");
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------- */
// 2) execute SQL
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String insertSql = "INSERT INTO t1 (c1, c2, c3) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement insertStatement = connection.prepareStatement(insertSql);
// set parameter
for (int i =10; i <= 10000; i++) {
insertStatement.setInt(1, i);
insertStatement.setInt(2, i);
insertStatement.setString(3, Integer.toString(i));
insertStatement.addBatch(); // add sql
if(i % 1000 == 0) {
insertStatement.executeBatch(); // execute sql
insertStatement.clearBatch(); // clean batch
}
}
connection.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("cost time:" + (end - start));
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("executeUpdated fail!");
}
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}执行结果如下:
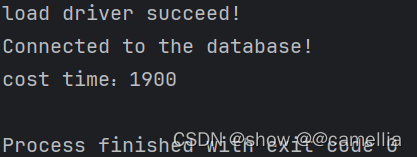
说明:从执行结果可知,方式一批量处理时,耗时:1900
如有帮助请给个👍支持下哦!谢谢!
如需完整代码请在评论区留言或从下述链接直接获取!
如需完整代码请在评论区留言或从下述链接直接获取!
如需完整代码请在评论区留言或从下述链接直接获取!
上述各场景完整代码见:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_47156401/88741460