一.Activity里面的mWindow是啥
在ActivityThread的performLaunchActivity方法里面:
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
//创建一个activity
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
//LoadedApk 构建 makeApplication
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, r + ": app=" + app
+ ", appName=" + app.getPackageName()
+ ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName()
+ ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir());
if (activity != null) {
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
// Activity resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the
// application context.
appContext.getResources().addLoaders(
app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
//会在这个方法中创建Activity的PhoneWindow,并绑定对应的WindowManager。
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback,
r.assistToken);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
checkAndBlockForNetworkAccess();
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
// 设置 mLifecycleState 为 ON_CREATE
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
mLastReportedWindowingMode.put(activity.getActivityToken(),
config.windowConfiguration.getWindowingMode());
}
// 设置 mLifecycleState 为 ON_CREATE
r.setState(ON_CREATE);
// updatePendingActivityConfiguration() reads from mActivities to update
// ActivityClientRecord which runs in a different thread. Protect modifications to
// mActivities to avoid race.
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}在这个方法里面我们可以看到创建一个activity后,调用这个activity的attach方法:
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback, IBinder assistToken) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
// PhoneWindow
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(mWindowControllerCallback);
// PhoneWindow 的 callback 设置为activity
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) {
mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode);
}
if (info.uiOptions != 0) {
mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions);
}
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread();
mMainThread = aThread;
mInstrumentation = instr;
mToken = token;
mAssistToken = assistToken;
mIdent = ident;
mApplication = application;
mIntent = intent;
mReferrer = referrer;
mComponent = intent.getComponent();
mActivityInfo = info;
mTitle = title;
mParent = parent;
mEmbeddedID = id;
mLastNonConfigurationInstances = lastNonConfigurationInstances;
if (voiceInteractor != null) {
if (lastNonConfigurationInstances != null) {
mVoiceInteractor = lastNonConfigurationInstances.voiceInteractor;
} else {
mVoiceInteractor = new VoiceInteractor(voiceInteractor, this, this,
Looper.myLooper());
}
}
//设置 PhoneWindow的WindowManager
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
// 获取 WindowManagerImpl 作为windowManager
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
mCurrentConfig = config;
mWindow.setColorMode(info.colorMode);
mWindow.setPreferMinimalPostProcessing(
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_PREFER_MINIMAL_POST_PROCESSING) != 0);
setAutofillOptions(application.getAutofillOptions());
setContentCaptureOptions(application.getContentCaptureOptions());
}可以清晰的看到在ActivityThread的performLaunchActivity调用activity的attach方法,在activity的attach方法里面mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback)。所以activity里面的mWindow就是PhoneWindow。
PhoneWindow创建:
1.Activity
2.Dialog
3.Popwindow
4.Toast
二.继承自Activity的setContentView流程
总流程
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}这里的getWindow拿到的是PhoneWindow,进入PhoneWindow里面的setContentView流程:
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}我们可以看到总流程里面先执行installDecor方法,然后通过mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent)把我们的xml文件加载到这个mContentParent里面去,最后设置mContentParentExplicitlySet = true。
创建DecorView与mContentParent
首次进入mContentParent为空,走到installDecor方法里面:
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
......
}这个方法一进入就判断mDecor是否为空,肯定是空的,然后调用generateDecor创建一个DecorView:
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
// System process doesn't have application context and in that case we need to directly use
// the context we have. Otherwise we want the application context, so we don't cling to the
// activity.
Context context;
if (mUseDecorContext) {
Context applicationContext = getContext().getApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext == null) {
context = getContext();
} else {
context = new DecorContext(applicationContext, this);
if (mTheme != -1) {
context.setTheme(mTheme);
}
}
} else {
context = getContext();
}
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}回到installDecor方法里面,创建完DecorView之后mContentParent依旧为空,接下来调用generateLayout(mDecor)方法:
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
// Apply data from current theme.
TypedArray a = getWindowStyle();
......
// Inflate the window decor.
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
// System.out.println("Features: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(features));
if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title_icons;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
// System.out.println("Title Icons!");
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_PROGRESS) | (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS))) != 0
&& (features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) == 0) {
// Special case for a window with only a progress bar (and title).
// XXX Need to have a no-title version of embedded windows.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_progress;
// System.out.println("Progress!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0) {
// Special case for a window with a custom title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogCustomTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_custom_title;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) == 0) {
// If no other features and not embedded, only need a title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0) {
layoutResource = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarFullscreenDecorLayout,
R.layout.screen_action_bar);
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title;
}
// System.out.println("Title!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY)) != 0) {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple_overlay_action_mode;
} else {
// Embedded, so no decoration is needed.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple;
// System.out.println("Simple!");
}
mDecor.startChanging();
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view");
}
......
mDecor.finishChanging();
return contentParent;
}这个方法非常重要,一开始拿到窗口属性,根据我们的属性去设置窗口。我们重点看一下contentParent是怎么获取到的。
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
// System.out.println("Features: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(features));
if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title_icons;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
// System.out.println("Title Icons!");
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_PROGRESS) | (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS))) != 0
&& (features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) == 0) {
// Special case for a window with only a progress bar (and title).
// XXX Need to have a no-title version of embedded windows.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_progress;
// System.out.println("Progress!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0) {
// Special case for a window with a custom title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogCustomTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_custom_title;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) == 0) {
// If no other features and not embedded, only need a title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0) {
layoutResource = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarFullscreenDecorLayout,
R.layout.screen_action_bar);
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title;
}
// System.out.println("Title!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY)) != 0) {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple_overlay_action_mode;
} else {
// Embedded, so no decoration is needed.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple;
// System.out.println("Simple!");
}这段代码是根据属性去拿对应的xml文件,我们拿一个最简单的R.layout.screen_simple来看看:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundInsidePadding="false"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</LinearLayout>
拿到xml后通过 mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource)把我们的xml加载到DecorView里面:
void onResourcesLoaded(LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutResource) {
if (mBackdropFrameRenderer != null) {
loadBackgroundDrawablesIfNeeded();
mBackdropFrameRenderer.onResourcesLoaded(
this, mResizingBackgroundDrawable, mCaptionBackgroundDrawable,
mUserCaptionBackgroundDrawable, getCurrentColor(mStatusColorViewState),
getCurrentColor(mNavigationColorViewState));
}
mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater);
final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
if (mDecorCaptionView != null) {
if (mDecorCaptionView.getParent() == null) {
addView(mDecorCaptionView,
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mDecorCaptionView.addView(root,
new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
} else {
// Put it below the color views.
addView(root, 0, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) root;
initializeElevation();
}接下来我们在通过findViewById的方式,拿到contentParent。contentParent是通过这一行代码拿到的:
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);我们清晰的可以看到contentParent就是我们前面R.layout.screen_simple里面id为content的那个FrameLayout。
总结
1.在ActivityThread的performLaunchActivity里面调用Activity的attach方法,创建PhoneWindow。
2.在PhoneWindow里面调用setContentView的installDecor方法里面的generateDecor创建一个DecorView
3.在PhoneWindow里面调用setContentView的installDecor方法里面的generateLayout方法,根据属性选择对应的xml文件,并且把xml文件加载到DecorView里面,并且通过findViewById的方式,从xml里面拿到contentParent。
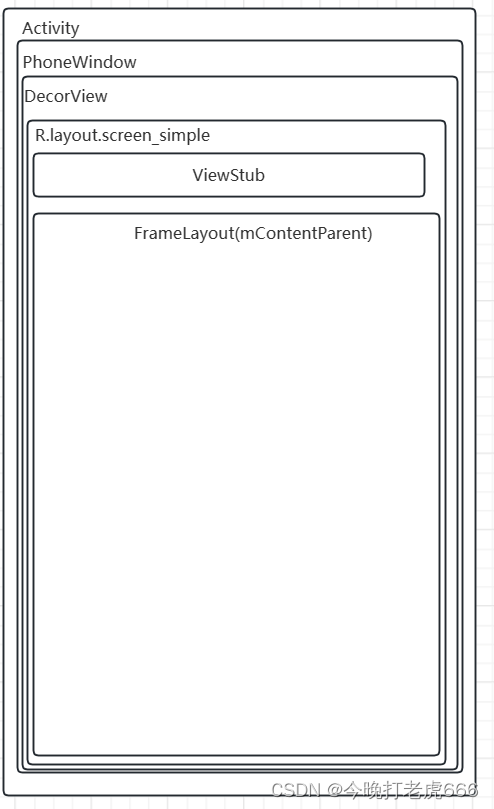
4.在PhoneWindow里面调用setContentView的mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent),把我们自己的xml文件加载到mContentParent里面。
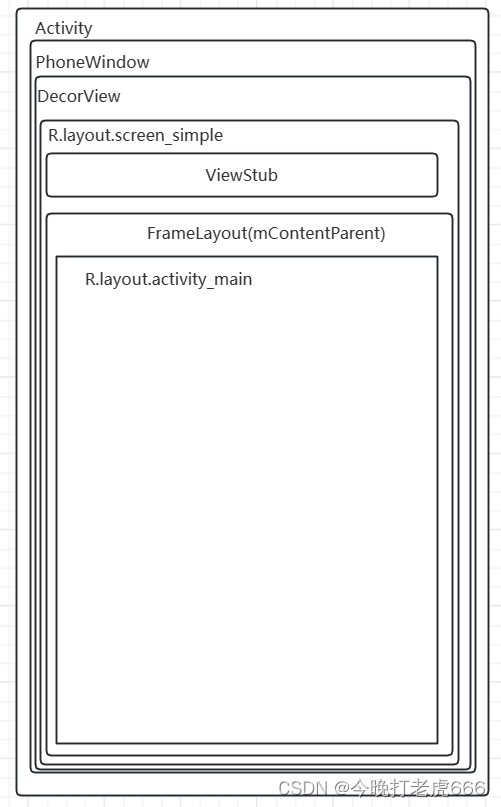
三.继承自AppCompatActivity的setContentView
总流程
@Override
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
initViewTreeOwners();
getDelegate().setContentView(layoutResID);
}
@NonNull
public AppCompatDelegate getDelegate() {
if (mDelegate == null) {
mDelegate = AppCompatDelegate.create(this, this);
}
return mDelegate;
}
@NonNull
public static AppCompatDelegate create(@NonNull Activity activity,
@Nullable AppCompatCallback callback) {
return new AppCompatDelegateImpl(activity, callback);
}这里的setContentView最后会调到AppCompatDelegateImpl的setContentView里面:
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor();
ViewGroup contentParent = mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);
mAppCompatWindowCallback.bypassOnContentChanged(mWindow.getCallback());
}这里我们可以看到关键的就是ensureSubDecor方法了,通过这个方法去创建mSubDecor,然后拿到contentParent,通过LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent)把我们的布局文件加到contentParent里面去。
ensureSubDecor()
private void ensureSubDecor() {
if (!mSubDecorInstalled) {
mSubDecor = createSubDecor();
......
}
}在这个方法里面createSubDecor才是真正创建mSubDecor的方法:
private ViewGroup createSubDecor() {
TypedArray a = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme);
......
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowNoTitle, false)) {
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
} else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.AppCompatTheme_windowActionBar, false)) {
// Don't allow an action bar if there is no title.
requestWindowFeature(FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR);
}
......
// Now let's make sure that the Window has installed its decor by retrieving it
ensureWindow();
mWindow.getDecorView();
final LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(mContext);
ViewGroup subDecor = null;
if (!mWindowNoTitle) {
if (mIsFloating) {
// If we're floating, inflate the dialog title decor
subDecor = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(
R.layout.abc_dialog_title_material, null);
// Floating windows can never have an action bar, reset the flags
mHasActionBar = mOverlayActionBar = false;
} else if (mHasActionBar) {
/**
* This needs some explanation. As we can not use the android:theme attribute
* pre-L, we emulate it by manually creating a LayoutInflater using a
* ContextThemeWrapper pointing to actionBarTheme.
*/
TypedValue outValue = new TypedValue();
mContext.getTheme().resolveAttribute(R.attr.actionBarTheme, outValue, true);
Context themedContext;
if (outValue.resourceId != 0) {
themedContext = new ContextThemeWrapper(mContext, outValue.resourceId);
} else {
themedContext = mContext;
}
// Now inflate the view using the themed context and set it as the content view
subDecor = (ViewGroup) LayoutInflater.from(themedContext)
.inflate(R.layout.abc_screen_toolbar, null);
mDecorContentParent = (DecorContentParent) subDecor
.findViewById(R.id.decor_content_parent);
mDecorContentParent.setWindowCallback(getWindowCallback());
/**
* Propagate features to DecorContentParent
*/
if (mOverlayActionBar) {
mDecorContentParent.initFeature(FEATURE_SUPPORT_ACTION_BAR_OVERLAY);
}
if (mFeatureProgress) {
mDecorContentParent.initFeature(Window.FEATURE_PROGRESS);
}
if (mFeatureIndeterminateProgress) {
mDecorContentParent.initFeature(Window.FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS);
}
}
} else {
if (mOverlayActionMode) {
subDecor = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(
R.layout.abc_screen_simple_overlay_action_mode, null);
} else {
subDecor = (ViewGroup) inflater.inflate(R.layout.abc_screen_simple, null);
}
}
if (subDecor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"AppCompat does not support the current theme features: { "
+ "windowActionBar: " + mHasActionBar
+ ", windowActionBarOverlay: "+ mOverlayActionBar
+ ", android:windowIsFloating: " + mIsFloating
+ ", windowActionModeOverlay: " + mOverlayActionMode
+ ", windowNoTitle: " + mWindowNoTitle
+ " }");
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
// If we're running on L or above, we can rely on ViewCompat's
// setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(subDecor, new OnApplyWindowInsetsListener() {
@Override
public WindowInsetsCompat onApplyWindowInsets(View v,
WindowInsetsCompat insets) {
final int top = insets.getSystemWindowInsetTop();
final int newTop = updateStatusGuard(insets, null);
if (top != newTop) {
insets = insets.replaceSystemWindowInsets(
insets.getSystemWindowInsetLeft(),
newTop,
insets.getSystemWindowInsetRight(),
insets.getSystemWindowInsetBottom());
}
// Now apply the insets on our view
return ViewCompat.onApplyWindowInsets(v, insets);
}
});
} else if (subDecor instanceof FitWindowsViewGroup) {
// Else, we need to use our own FitWindowsViewGroup handling
((FitWindowsViewGroup) subDecor).setOnFitSystemWindowsListener(
new FitWindowsViewGroup.OnFitSystemWindowsListener() {
@Override
public void onFitSystemWindows(Rect insets) {
insets.top = updateStatusGuard(null, insets);
}
});
}
if (mDecorContentParent == null) {
mTitleView = (TextView) subDecor.findViewById(R.id.title);
}
// Make the decor optionally fit system windows, like the window's decor
ViewUtils.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows(subDecor);
final ContentFrameLayout contentView = (ContentFrameLayout) subDecor.findViewById(
R.id.action_bar_activity_content);
final ViewGroup windowContentView = (ViewGroup) mWindow.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
if (windowContentView != null) {
// There might be Views already added to the Window's content view so we need to
// migrate them to our content view
while (windowContentView.getChildCount() > 0) {
final View child = windowContentView.getChildAt(0);
windowContentView.removeViewAt(0);
contentView.addView(child);
}
// Change our content FrameLayout to use the android.R.id.content id.
// Useful for fragments.
windowContentView.setId(View.NO_ID);
contentView.setId(android.R.id.content);
// The decorContent may have a foreground drawable set (windowContentOverlay).
// Remove this as we handle it ourselves
if (windowContentView instanceof FrameLayout) {
((FrameLayout) windowContentView).setForeground(null);
}
}
// Now set the Window's content view with the decor
mWindow.setContentView(subDecor);
contentView.setAttachListener(new ContentFrameLayout.OnAttachListener() {
@Override
public void onAttachedFromWindow() {}
@Override
public void onDetachedFromWindow() {
dismissPopups();
}
});
return subDecor;
}在这个方法里面,先拿到自定义属性,然后根据属性设置requestWindowFeature。ensureWindow()这个方法是确保mWindow变量是acticity里面的PhoneWindow:
private void ensureWindow() {
// We lazily fetch the Window for Activities, to allow DayNight to apply in
// attachBaseContext
if (mWindow == null && mHost instanceof Activity) {
attachToWindow(((Activity) mHost).getWindow());
}
if (mWindow == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("We have not been given a Window");
}
}
private void attachToWindow(@NonNull Window window) {
......
mWindow = window;
......
}这边调一遍是因为在AppCompatDelegateImpl的onCreate方法里面也会调一遍ensureWindow,但不知道谁先谁后。
接下来调用mWindow.getDecorView(),这个mWindow就是PhoneWindow咯,实际上调用的是PhoneWindow的getDecorView方法:
public final @NonNull View getDecorView() {
if (mDecor == null || mForceDecorInstall) {
installDecor();
}
return mDecor;
}我们发现getDecorView方法里面不正是继承Activity的时候也调用的吗?它的作用是创建一个DecorView,根据属性拿到对应的xml文件,把xml文件加载到DecorView里面去,然后再通过findViewById的方式去拿到xml里面的content赋值给mContentParent。
现在再回到createSubDecor方法里面,现在我们创建好DecorView,帮DecorView添加好布局,并且拿到了DecorView里面的content赋值给mContentParent。
接下来根据各种属性去拿subDecor对应的xml文件,我们拿一个R.layout.abc_screen_simple文件来看一下:
<androidx.appcompat.widget.FitWindowsLinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/action_bar_root"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.ViewStubCompat
android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/abc_action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<include layout="@layout/abc_screen_content_include" />
</androidx.appcompat.widget.FitWindowsLinearLayout>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.ContentFrameLayout
android:id="@id/action_bar_activity_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</merge>接下来执行这两行代码:
final ContentFrameLayout contentView = (ContentFrameLayout) subDecor.findViewById(
R.id.action_bar_activity_content);
final ViewGroup windowContentView = (ViewGroup) mWindow.findViewById(android.R.id.content);这一下我们就可以清晰的判断出contentView是R.layout.abc_screen_simple里面的ContentFrameLayout,而windowContentView是DecorView的xml的content,也是activity里面的mContentParent。
接下来做一个关键操作:
if (windowContentView != null) {
// There might be Views already added to the Window's content view so we need to
// migrate them to our content view
while (windowContentView.getChildCount() > 0) {
final View child = windowContentView.getChildAt(0);
windowContentView.removeViewAt(0);
contentView.addView(child);
}
// Change our content FrameLayout to use the android.R.id.content id.
// Useful for fragments.
windowContentView.setId(View.NO_ID);
contentView.setId(android.R.id.content);
// The decorContent may have a foreground drawable set (windowContentOverlay).
// Remove this as we handle it ourselves
if (windowContentView instanceof FrameLayout) {
((FrameLayout) windowContentView).setForeground(null);
}
}这段代码里面判断DecorView的xml的content里面有没有子View,有的话全部移除,加入到contentView里面。然后把DecorView的xml的content对应的id设置为View.NO_ID,把contentView的id设置为android.R.id.content。这里其实就是把DecorView的xml的conten拥有的所以东西拿给contentView了。
接下来会调用mWindow.setContentView(subDecor):
@Override
public void setContentView(View view) {
setContentView(view, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
@Override
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
view.setLayoutParams(params);
final Scene newScene = new Scene(mContentParent, view);
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mContentParent.addView(view, params);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
mContentParentExplicitlySet = true;
}这时候明显mContentParent是不为空的,所以会调用mContentParent.addView(view, params),这一行代码把我们创建好的subDecor加入到DectorView的xml的content上。
接下来回到setContentView方法上面:
@Override
public void setContentView(int resId) {
ensureSubDecor();
ViewGroup contentParent = mSubDecor.findViewById(android.R.id.content);
contentParent.removeAllViews();
LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent);
mAppCompatWindowCallback.bypassOnContentChanged(mWindow.getCallback());
}通过findViewById的方式找到mSubDecor的xml里面的R.id.content,其实就是R.layout.abc_screen_simple里面的ContentFrameLayout,原来的id是R.id.action_bar_activity_content。
最后通过LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent),把我们的xml文件加载到content里面。
总结
1.创建一个AppCompatDelegateImpl
2.调用AppCompatDelegateImpl的setContentView方法里面的ensureSubDecor的createSubDecor
3.调用PhoneWindow的getDecorView的installDecor
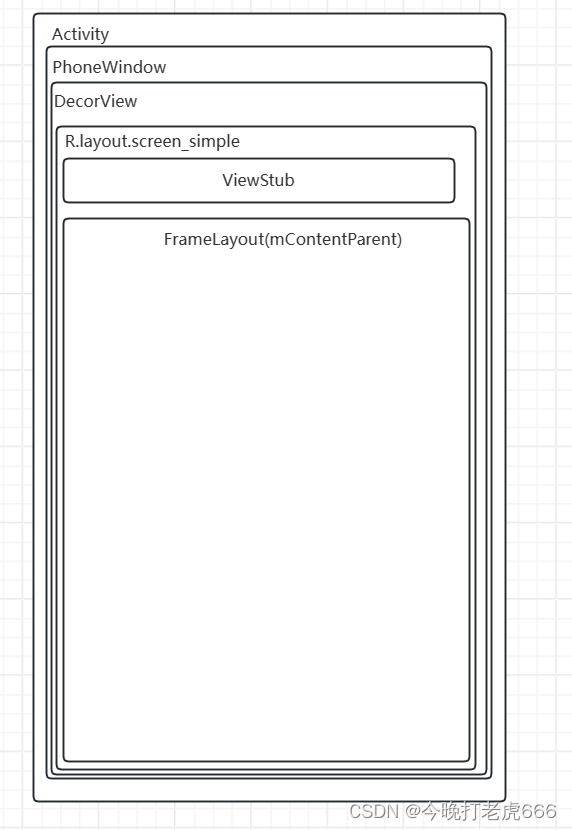
4.给subDecor设置xml文件
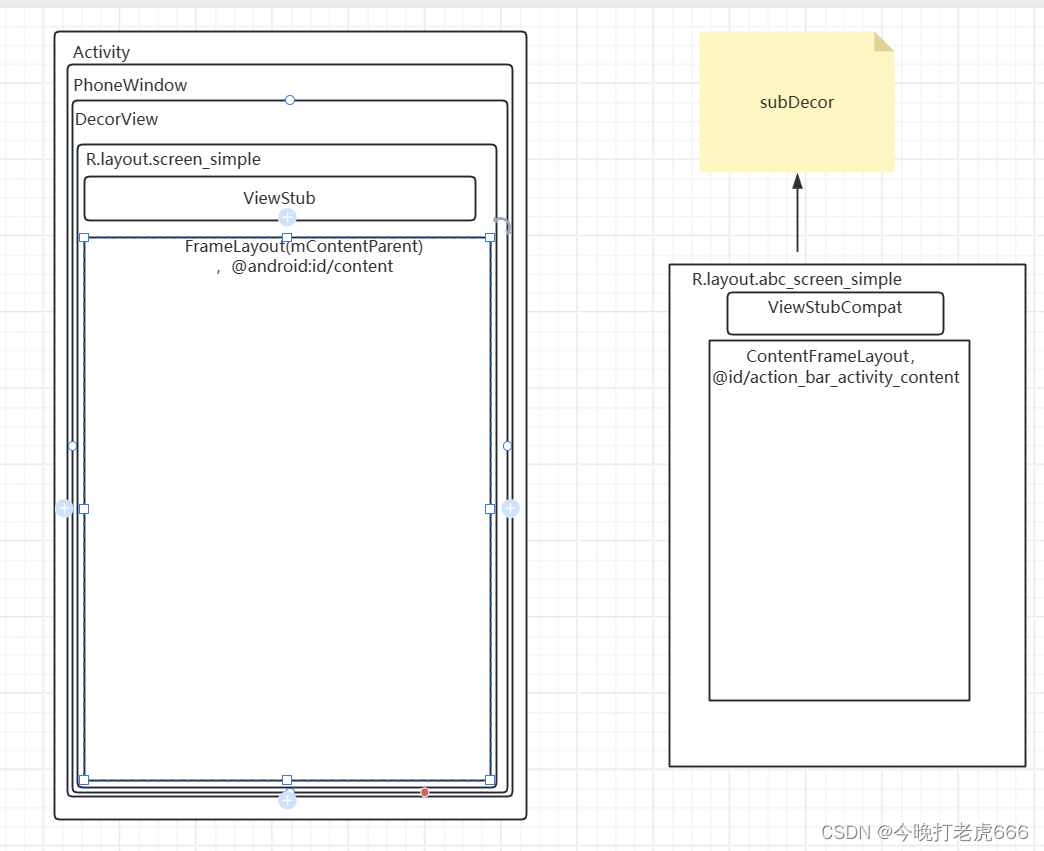
5. 把DecorView的FrameLayout的id设置为View.NO_ID,subDecor的ContentFrameLayout的id设置为android.R.id.content。
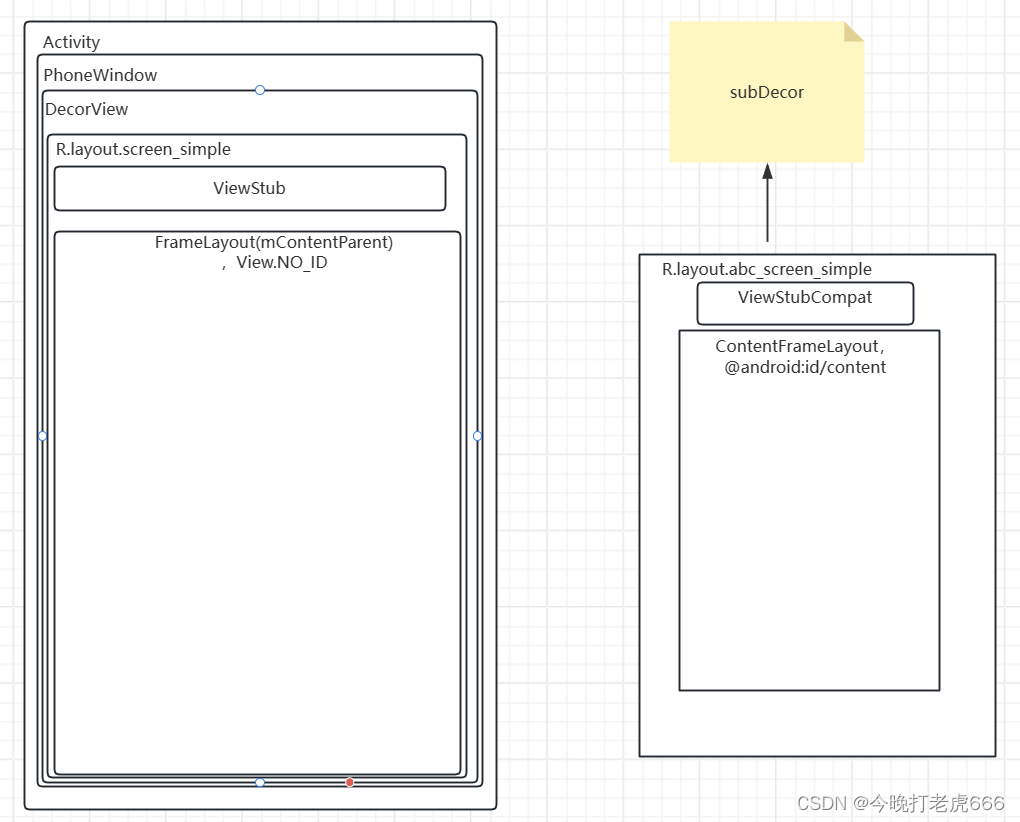
6.通过调用PhoneWindow的setContentView方法,把subDecor加入到DecorView的FrameLayout中。

7.通过LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(resId, contentParent),把我们的xml文件加入到content中

AppCompatActivity为什么需要对Activity的setContentView再包一层
其实一切都是为了兼容性。AppCompatActivity有自己的主题,是androidX引入的,为了兼容之前的android版本,这里使用了门面模式。
requestWindowFeature的正确设置
1.在setContentView方法后面设置窗口属性会报错
public class MainActivity2 extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
}
}2.正常应该要这样设置,在setContentView方法前面
public class MainActivity2 extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}原因就是在PhoneWindow的requestFeature方法里面,mContentParentExplicitlySet为true的话,就会抛出异常:"requestFeature() must be called before adding content"。而mContentParentExplicitlySet这个参数在PhoneWindow的setContentView结束后就设置为true了。
@Override
public boolean requestFeature(int featureId) {
if (mContentParentExplicitlySet) {
throw new AndroidRuntimeException("requestFeature() must be called before adding content");
}
final int features = getFeatures();
final int newFeatures = features | (1 << featureId);
if ((newFeatures & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0 &&
(newFeatures & ~CUSTOM_TITLE_COMPATIBLE_FEATURES) != 0) {
// Another feature is enabled and the user is trying to enable the custom title feature
// or custom title feature is enabled and the user is trying to enable another feature
throw new AndroidRuntimeException(
"You cannot combine custom titles with other title features");
}
if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) != 0 && featureId == FEATURE_ACTION_BAR) {
return false; // Ignore. No title dominates.
}
if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0 && featureId == FEATURE_NO_TITLE) {
// Remove the action bar feature if we have no title. No title dominates.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
if (featureId == FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS &&
getContext().getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_WATCH)) {
throw new AndroidRuntimeException("You cannot use indeterminate progress on a watch.");
}
return super.requestFeature(featureId);
}3.继承自AppCompatActivity需要使用supportRequestWindowFeature