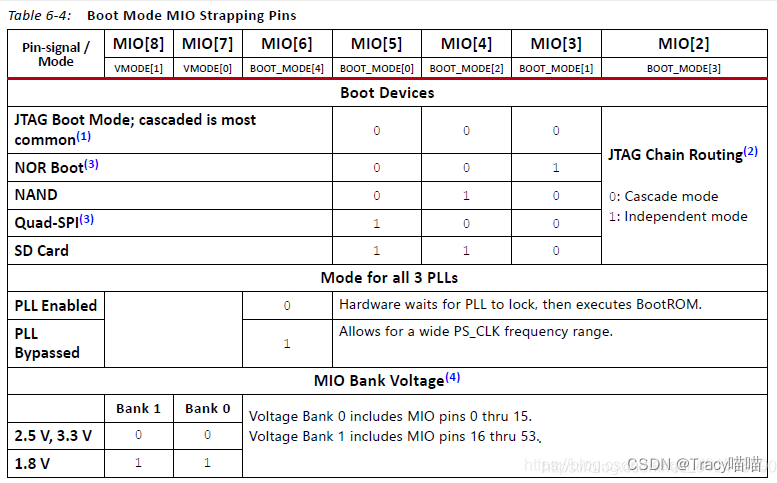
非线性方程组是一组包含非线性数学表达式的方程,即方程中含有未知数的非线性项。解这类方程组通常比解线性方程组更为复杂和困难。
非线性方程组在很多领域都有应用,例如物理学、工程学、经济学等。解决非线性方程组的方法有很多种,包括数值方法和解析方法。数值方法是通过迭代或搜索来找到近似解,而解析方法则是通过对方程进行变换或展开来找到精确解。
在处理非线性方程组时,需要注意一些问题,例如初始值的选择、解的唯一性和稳定性等。同时,也需要根据具体问题的特点选择合适的求解方法。
OpenCASCADE提供了非线性方程组的类math_FunctionSet,下面给出一个具体的例子来说明其的用法。
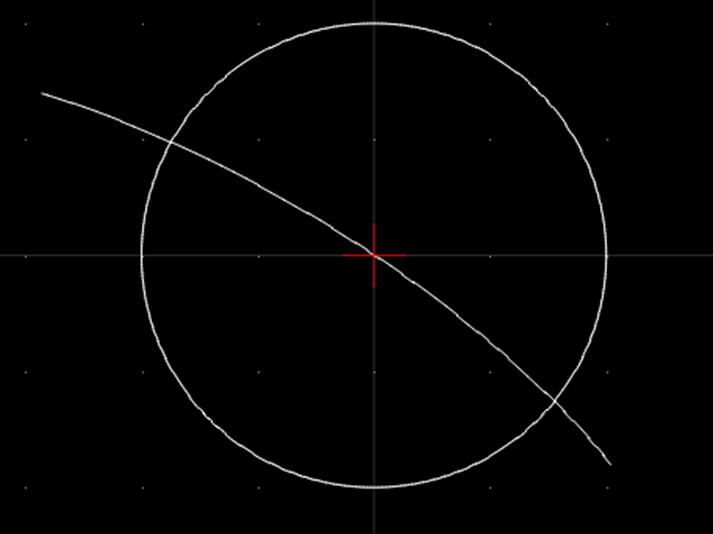
待求解方程组:

从几何上看其解就是圆心在原点,半径为2的圆与曲线的交点:
#include <math_FunctionSet.hxx>
#include <math_FunctionSetWithDerivatives.hxx>
#include <math_FunctionSetRoot.hxx>
class MyFunctionSet : public math_FunctionSetWithDerivatives
{
public:
virtual Standard_Integer NbVariables() const
{
return 2;
}
virtual Standard_Integer NbEquations() const
{
return 2;
}
virtual Standard_Boolean Value(const math_Vector& X, math_Vector& F)
{
F(1) = X(1) * X(1) + X(2) * X(2) - 4.0;
F(2) = Pow(M_E, X(1)) + X(2) - 1.0;
return Standard_True;
}
virtual Standard_Boolean Derivatives(const math_Vector& X, math_Matrix& D)
{
// matrix D is Jacobi matrix.
D(1, 1) = 2.0 * X(1);
D(1, 2) = 2.0 * X(2);
D(2, 1) = Pow(M_E, X(1));
D(2, 2) = 1.0;
return Standard_True;
}
virtual Standard_Boolean Values(const math_Vector& X, math_Vector& F, math_Matrix& D)
{
Value(X, F);
Derivatives(X, D);
return Standard_True;
}
private:
};
void test()
{
MyFunctionSet aFunctionSet;
math_FunctionSetRoot aSolver(aFunctionSet);
math_Vector aStartingPoint(1, 2);
// 1. (1.0, 1.0)
aStartingPoint(1) = 1.0;
aStartingPoint(2) = 1.0;
aSolver.Perform(aFunctionSet, aStartingPoint);
if (aSolver.IsDone())
{
aSolver.Dump(std::cout);
}
// 2. (1.0, -1.0)
aStartingPoint(1) = 1.0;
aStartingPoint(2) = -1.0;
aSolver.Perform(aFunctionSet, aStartingPoint);
if (aSolver.IsDone())
{
aSolver.Dump(std::cout);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}
math_FunctionSetRoot Status = Done
Location value = math_Vector of Length = 2
math_Vector(1) = -1.81626
math_Vector(2) = 0.837368
Number of iterations = 14
math_FunctionSetRoot Status = Done
Location value = math_Vector of Length = 2
math_Vector(1) = 1.00417
math_Vector(2) = -1.72964
Number of iterations = 6