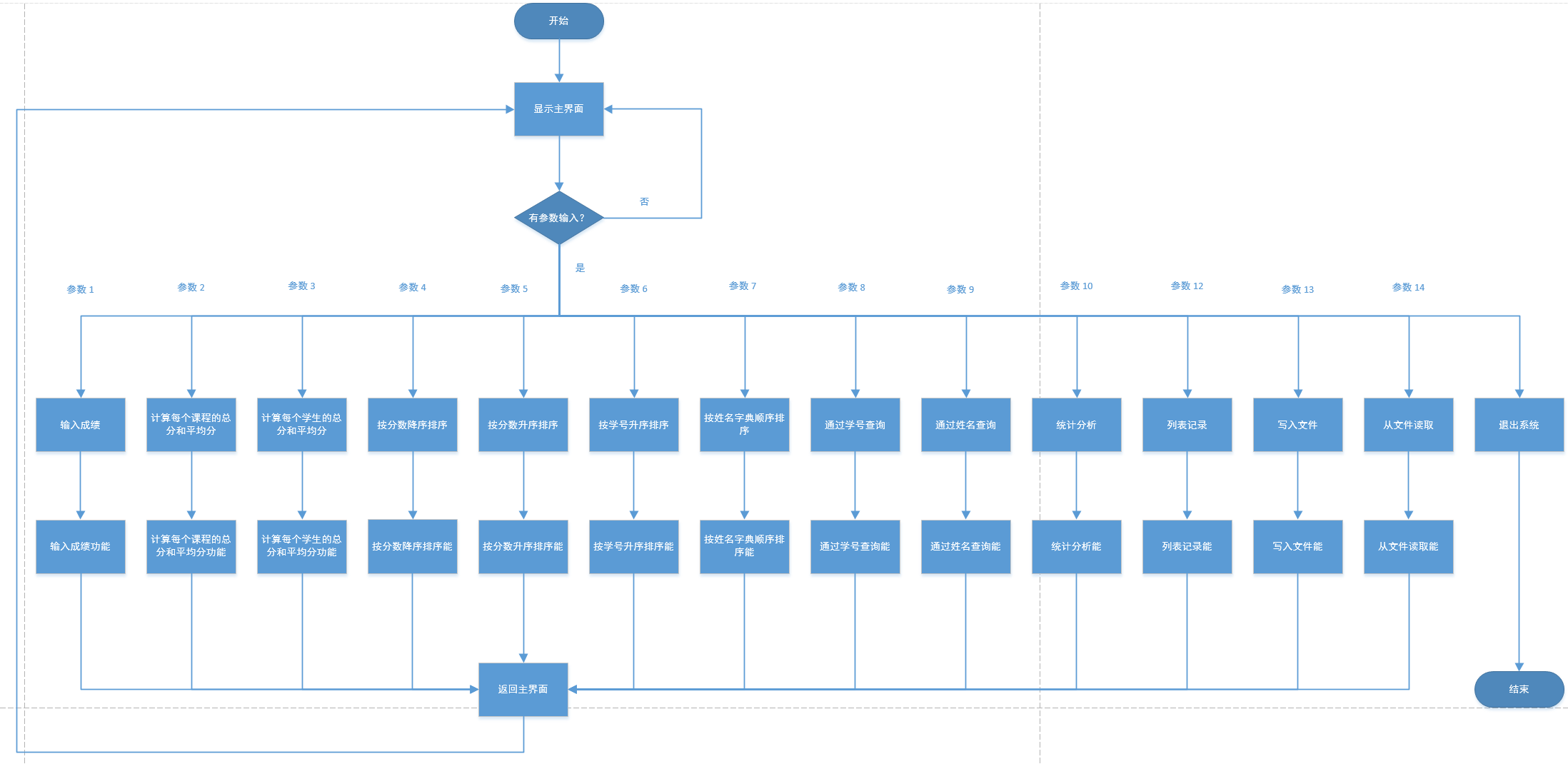
补充:xml配置
最开始(Spring 1.x),Spring都是通过xml配置控制层(controller)--业务逻辑层(service)--dao层--数据源的关系,但是比较复杂
Spring 2.x的时候,随着JDK1.5支持注解的方式,实现了 "xml + 注解" 的开发模式,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--可以配置多个数据源,用哪个就引用哪个-->
<!--mysql-->
<bean id="ds" class="com.qzcsbj.dao.impl.DataSource">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.168.168:3360/gifts?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true"/>
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
</bean>
<!--dao引用ds-->
<bean id="dao" class="com.qzcsbj.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl">
<property name="ds" ref="ds"/>
</bean>
<!--service引用dao-->
<bean id="service" class="com.qzcsbj.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="dao"/>
</bean>
<!--controller引用service-->
<bean id="controller" class="com.qzcsbj.controller.UserController">
<property name="userService" ref="service"/>
</bean>
</beans>
注解使用
引入Context的约束
输入下面后

会自动添加context的约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
配置注解
指定扫描包下所有类中的注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描注解类-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.qzcsbj.*"/>
</beans>
Component

测试:对象名是student
package com.qzcsbj.test;
import com.qzcsbj.bean.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
public class Test2 {
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student stu = context.getBean("student", Student.class);
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
结果:没有值(下图展示的是类型默认值),是因为没有注入值
![]()
也可以给对象取别的名字,后续就只能用这个自定义的对象名
@Component("stu")
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试:对象名是stu
Student stu = context.getBean("stu", Student.class);
Value
给属性赋值:@Value("属性值") 等同于 @Value(value="属性值")
@Component("stu")
public class Student {
@Value("jack")
private String name;
@Value("18")
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试
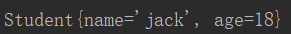
Autowired
接口
package com.qzcsbj;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
public interface Alimal {
void eat();
}
Cat实现类
package com.qzcsbj;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
@Component
public class Cat implements Alimal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("==============cat eat fish");
}
}
Dog实现类
package com.qzcsbj;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
@Component
public class Dog implements Alimal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("==========dog eat bone");
}
}
给对象属性注入值,报错
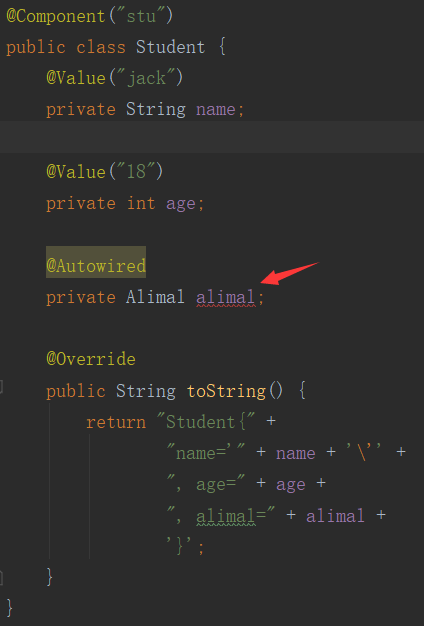
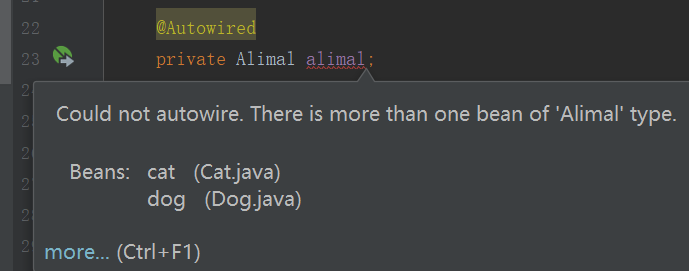
注释一个就不会报上面的错了
给Student的对象属性加上get方法
public Alimal getAlimal() {
return alimal;
}
测试
package com.qzcsbj.test;
import com.qzcsbj.bean.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
public class Test2 {
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student stu = context.getBean("stu", Student.class);
stu.getAlimal().eat();
}
}
结果
![]()
Qualifier
@Qualifier:如果匹配到多个对象,可以用Qualifier来指定要匹配哪一个对象,需要配合@Autowired使用
给Cat类加上注解:@Component
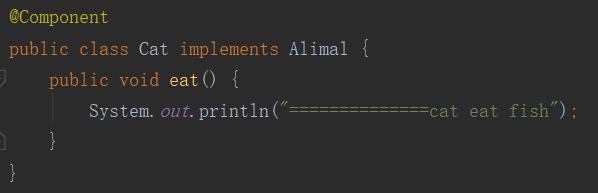
下面这种方式写,就不报错了

测试结果
![]()
Resource
@Resource:默认是根据类型自动装配一个,如果匹配多个会异常,也可以指定名字匹配,@Resource(name="obj") == @Autowired + @Qualifier("obj")
// @Autowired
// @Qualifier("cat")
@Resource(name = "cat")
private Alimal alimal;
Scope
@Scope:用于指定对象作用域,在类上添加此注解
单例:singleton
多例:prototype
@Scope(scopeName = "singleton"),或者:@Scope("singleton")
@Scope(scopeName = "prototype"),或者:@Scope("prototype")
实体类
package com.qzcsbj.bean;
import com.qzcsbj.test.Alimal;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
@Component("stu")
public class Student {
@Value("jack")
private String name;
@Value("18")
private int age;
// @Autowired
// @Qualifier("cat")
@Resource(name = "cat")
private Alimal alimal;
public Alimal getAlimal() {
return alimal;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", alimal=" + alimal +
'}';
}
}
测试
package com.qzcsbj.test;
import com.qzcsbj.bean.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @公众号 : 全栈测试笔记
* @博客 : www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong
* @微信 : ren168632201
* @描述 : <>
*/
public class Test2 {
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student stu = context.getBean("stu", Student.class);
Student stu2 = context.getBean("stu", Student.class);
System.out.println(stu==stu2);
}
}
测试结果是true,因为默认是单例
![]()
默认单例:@Scope("singleton")

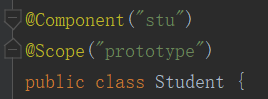
测试结果
![]()
其它注解
@Service:用于标注业务层,给业务逻辑层生成对象
@Controller:用于标注控制层,给控制层生成对象
@Repository:用于标注数据访问层,给dao层生成对象,说明:Mybatis的dao层是自动生成对象的,所以不需要这个注解
说明:不是上面任何一层,就加@Component注解;其它,上面三层也可以用@Component注解,但是用对应层的注解能见名知意。
【bak】
原文会持续更新,原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/uncleyong/p/17020010.html


![[oeasy]python0037_字符画艺术_asciiview_自制小动物_imagick_asciiart](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/26fff52e9d8d9dd0b3543f9e1a270c2c.png)