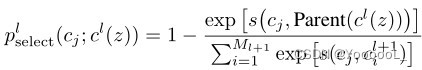手写一个单例模式,Demo,检测
- 需求分析
- 单例介绍
- 一般情况
- Demo
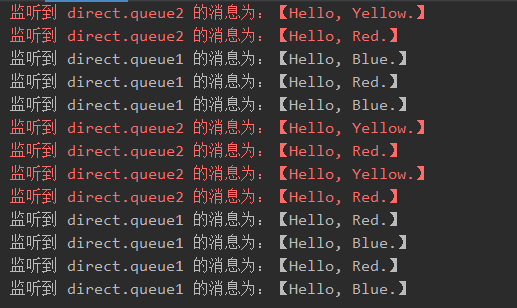
- Result
- 单例模式(饿汉式—静态常量方式(线程安全))
- Demo
- Result
- 懒汉式(线程不安全)
- Demo
- Result
- 懒汉式(加入锁机制)
- Demo
- Result
- 双检索单例
- Demo
- Result
需求分析
面试过后,感觉很久没有好好去回顾下这些设计模式了
今天出一个设计模式专栏来好好回顾下
正好最近也有充足的时间对整个知识体系和框架进行梳理和回顾
今天是设计模式专栏第二节
单例介绍
单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是 Java 中最简单的设计模式之一。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类负责创建自己的对象,同时确保只有单个对象被创建。这个类提供了一种访问其唯一的对象的方式,可以直接访问,不需要实例化该类的对象。
注意:
1、单例类只能有一个实例。
2、单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例。
3、单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例。
意图:保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点。
主要解决:一个全局使用的类频繁地创建与销毁。
何时使用:当您想控制实例数目,节省系统资源的时候。
如何解决:判断系统是否已经有这个单例,如果有则返回,如果没有则创建。
关键代码:构造函数是私有的。
应用实例:
1、一个班级只有一个班主任。
2、Windows 是多进程多线程的,在操作一个文件的时候,就不可避免地出现多个进程或线程同时操作一个文件的现象,所以所有文件的处理必须通过唯一的实例来进行。
3、一些设备管理器常常设计为单例模式,比如一个电脑有两台打印机,在输出的时候就要处理不能两台打印机打印同一个文件。
优点:
1、在内存里只有一个实例,减少了内存的开销,尤其是频繁的创建和销毁实例(比如管理学院首页页面缓存)。
2、避免对资源的多重占用(比如写文件操作)。
缺点:没有接口,不能继承,与单一职责原则冲突,一个类应该只关心内部逻辑,而不关心外面怎么样来实例化。
使用场景:
1、要求生产唯一序列号。
2、WEB 中的计数器,不用每次刷新都在数据库里加一次,用单例先缓存起来。
3、创建的一个对象需要消耗的资源过多,比如 I/O 与数据库的连接等。
注意事项:getInstance() 方法中需要使用同步锁 synchronized (Singleton.class) 防止多线程同时进入造成 instance 被多次实例化。
一般情况
Demo
public class A11172022 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// new Thread(()->{
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// }, "SingleSampleCurThread" + i + " ").start();
new Thread(()->{
SingleSample01 singleSample01 = new SingleSample01();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
}, "SingleSample01 " + i).start();
}
}
}
class SingleSample01{
private SingleSample01 singleSample;
public SingleSample01 getSingleSample(){
if (singleSample == null){
singleSample = new SingleSample01();
}
return singleSample;
}
}
Result

单例模式(饿汉式—静态常量方式(线程安全))
Demo
public class A11172022 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
}, "SingleSampleCurThread" + i + " ").start();
// new Thread(()->{
// SingleSample01 singleSample01 = new SingleSample01();
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// }, "SingleSample01 " + i).start();
}
}
}
class SingleSample{
private static SingleSample singleSample = new SingleSample();
public static SingleSample getSingleSample(){
return singleSample;
}
/*
private static SingleSample singleSample;
public static SingleSample getSingleSample(){
if (SingleSample.singleSample == null){
singleSample = new SingleSample();
}
return SingleSample.singleSample;
}*/
}
Result

懒汉式(线程不安全)
Demo
public class A11172022 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// new Thread(()->{
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// }, "SingleSampleCurThread" + i + " ").start();
new Thread(()->{
SingleSample01 singleSample01 = new SingleSample01();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
}, "SingleSample01 " + i).start();
//
}
}
}
class SingleSample01{
private static SingleSample01 singleSample;
public static SingleSample01 getSingleSample(){
if (singleSample == null){
singleSample = new SingleSample01();
}
return singleSample;
}
}
Result

懒汉式(加入锁机制)
Demo
public class A11172022 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// new Thread(()->{
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// }, "SingleSampleCurThread" + i + " ").start();
new Thread(()->{
SingleSample01 singleSample01 = new SingleSample01();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
}, "SingleSample01" + i + " ").start();
//
}
}
}
class SingleSample01{
private static SingleSample01 singleSample;
public static synchronized SingleSample01 getSingleSample(){
if (singleSample == null){
singleSample = new SingleSample01();
}
return singleSample;
}
}
Result

双检索单例
Demo
class SingleSample{
private static volatile SingleSample singleSample;
public static SingleSample getInstance(){
if(singleSample==null){
synchronized (SingleSample.class){
if (singleSample==null){
singleSample = new SingleSample();
}
}
}
return singleSample;
}
}
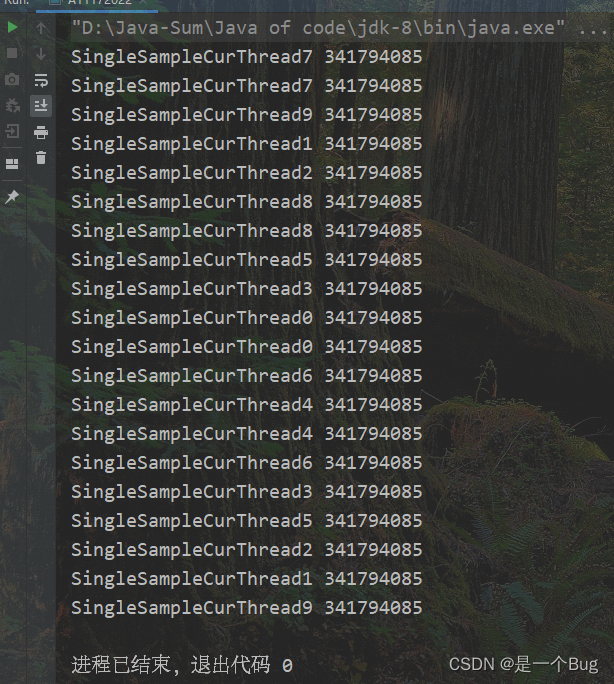
public class A11172022 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getInstance().hashCode());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + SingleSample.getInstance().hashCode());
}, "SingleSampleCurThread" + i + " ").start();
// new Thread(()->{
// SingleSample01 singleSample01 = new SingleSample01();
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + singleSample01.getSingleSample().hashCode());
// }, "SingleSample01" + i + " ").start();
//
}
}
}
Result
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计django学生学习评价与分析系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b26dd3b805044e1c88ba507f61f1e47f.png)