目录
1.双向循环链表的声明与定义:
2. 创建链表并对节点中的数据赋初值
3. 插入节点并链接
4.中英翻译
5. 小游戏的实现
6.菜单的实现
7. 释放内存
8.在主函数中用刚才定义的函数实现各种代码
输入样例:
实现方法:双向循环链表来实现,各个函数来实现各种功能,如game函数是实现程序小游戏的代码,translate是实现翻译的代码,将各个函数的功能在主函数中实现 。
OK,让我们开始实现吧~

1.双向循环链表的声明与定义:
//双向链表的声明
typedef struct Node
{
char data[20];
char chinese[20];
char english[20];
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
其中chinese存储中文信息,english存储英文信息,而data存储字节信息
2. 创建链表并对节点中的数据赋初值
//创建链表并对节点中的数据初始值
Node* createNode(char* chinese, char* english,char* data)
{
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
strcpy(newNode->data, data);
strcpy(newNode->chinese, chinese);
strcpy(newNode->english, english);
newNode->prev = NULL;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
3. 插入节点并链接
//插入节点并链接
void insertNode(Node** head, char* chinese, char* english,char* data)
{
Node* newNode = createNode(chinese, english,data);
if (*head == NULL)//如果节点为空,就将新创建的节点赋值给*head
{
*head = newNode;
(*head)->prev = *head;
(*head)->next = *head;
}
else//否则就执行插入链接操作
{
Node* lastNode = (*head)->prev;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = lastNode;
(*head)->prev = newNode;
lastNode->next = newNode;
}
}
4.中英翻译
//中英翻译
void translate(Node* head, char* keyword)
{
Node* current = head;
do
{
if (strcmp(current->chinese, keyword) == 0)//运用strcmp进行比较,如果相同就打印对应的翻译
{
printf("%s\n", current->english);
return;
}
if (strcmp(current->english, keyword) == 0)
{
printf("%s\n", current->chinese);
return;
}
current = current->next;//如果没找到就持续寻找下一个
} while (current != head);//注意结束标志不是NULL
printf("Translation not found.\n");
}
5. 小游戏的实现
//小游戏的实现
void game(Node* head)
{
char data[20];
char string[20];
Node* current = head;
srand(time(NULL));
int k = rand() % 11;//设置一个随机数
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
current = current->next;//通过随机数来随机指定当前链表的位置
}
printf("请输入当前英文关键字的翻译:%s->:", current->english);
scanf("%s", string);//通过随机数所指定链表的值与当前输入的值进行匹配
if (strcmp(current->chinese,string) == 0)
{
printf("你能输出它的字节大小吗(没有就写没有)->:");
scanf("%s", data);//当上一个匹配没问题,就进行字节的匹配
if (strcmp(current->data, data) == 0)
{
printf("你真是太厉害了!\n");
printf("恭喜你,挑战成功!\n");
exit(0);
}
else if (strcmp(current->data, data) != 0)
{
int count = 2;//挑战失败那再给挑战者两次机会
printf("很遗憾,挑战失败!看你表现优异,再给你两次机会吧!\n");
while (count)
{
printf("你能输出它的字节大小吗(没有就写没有)->:");
scanf("%s", data);
if (strcmp(current->data, data) == 0)
{
printf("你真是太厉害了!\n");
printf("恭喜你,挑战成功!\n");
exit(0);
}
else printf("挑战失败!\n");
count--;
}
printf("小菜鸡,再练练再来挑战吧!\n");
exit(0);
}
}
}6.菜单的实现
void menu1()
{
printf("---------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("-------------<c语言关键字翻译机>-------------------\n");
printf("-------------<输入bye退出程序>---------------------\n");
printf("-------------<强化训练输入play>--------------------\n");
printf("---------------------------------------------------\n");
}
7. 释放内存
void freeList(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
Node* current = head;
Node* next;
do
{
next = current->next;
free(current);
current = next;
} while (current != head);
}8.在主函数中用刚才定义的函数实现各种代码
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
insertNode(&head, "浮点型", "float","4");//要匹配的数据的插入
insertNode(&head, "基本整型", "int","4");
insertNode(&head, "长整型","longlong","8");
insertNode(&head, "结构体类型", "struct","没有");
insertNode(&head, "联合体类型", "union","没有");
insertNode(&head, "否则", "else","没有");
insertNode(&head, "双精度浮点型", "double","8");
insertNode(&head, "如果", "if","没有");
insertNode(&head, "开关", "switch","没有");
insertNode(&head, "循环", "while","没有");
char keyword[20];
menu1();
while (1)
{
printf("请输入中文的名词或英文的单词(输入 bye 退出)->:");
scanf("%s", keyword);
if (strcmp(keyword, "bye") == 0)
{
printf("退出程序!\n");
break;
}
if (strcmp(keyword, "play") == 0)
{
game(head);
}
translate(head, keyword);
}
freeList(head);
return 0;
}输入样例:
样例1:
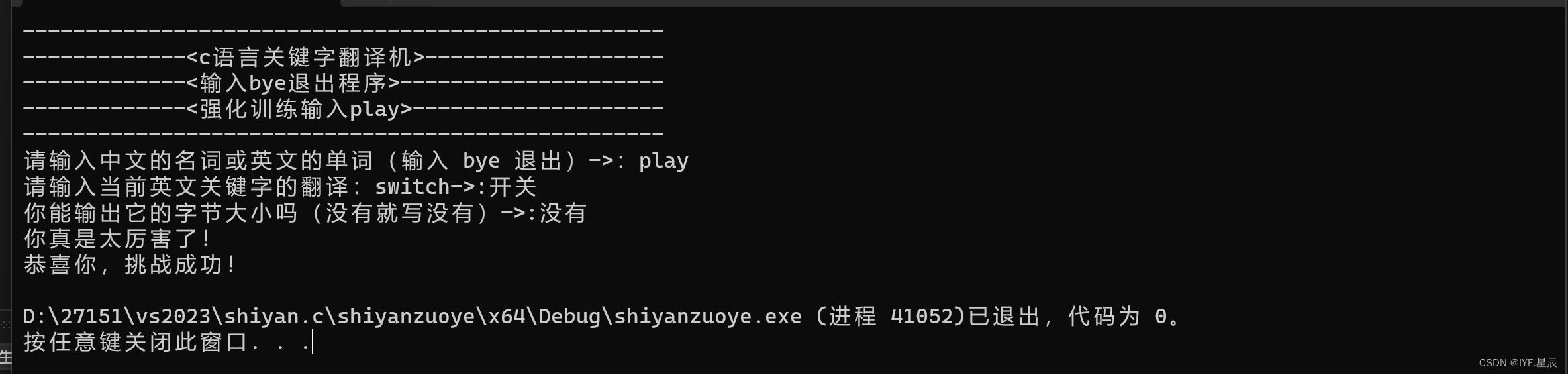
样例2:

博客到这里也是结束了,喜欢的小伙伴可以点赞加关注支持下博主,这对我真的很重要~~