环境介绍
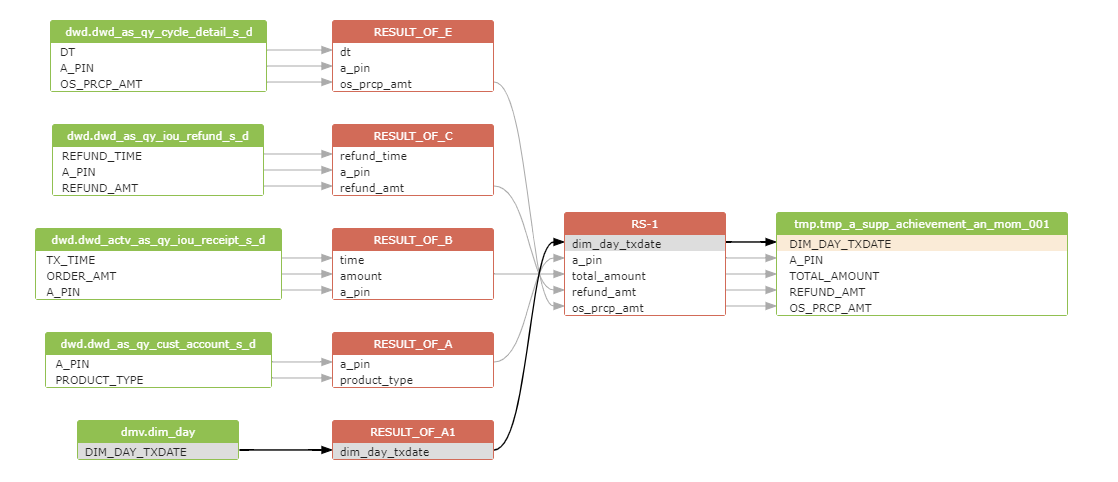
| 技术栈 | springboot+mybatis-plus+mysql+ganymed-ssh2 |
| 软件 | 版本 |
| mysql | 8 |
| IDEA | IntelliJ IDEA 2022.2.1 |
| JDK | 1.8 |
| Spring Boot | 2.7.13 |
| mybatis-plus | 3.5.3.2 |
SSH(远程连接工具)连接原理:ssh服务是一个守护进程(demon),系统后台监听客户端的连接,ssh服务端的进程名为sshd,负责实时监听客户端的请求(IP 22端口),包括公共秘钥等交换等信息。
加入依赖
<!-- shell认证支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.ethz.ganymed</groupId>
<artifactId>ganymed-ssh2</artifactId>
<version>262</version>
</dependency>测试类
@Test
void sshdemo() throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = null;
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
Connection conn=new Connection("192.168.68.133",22); //远程连接的ip 和端口
conn.connect();
if (conn.authenticateWithPassword("root", "111111")){
System.out.println("登录成功");
Session session = conn.openSession();
//获取CPU使用率
session.execCommand("df -h| awk '$NF==\"/\"{printf \"%d/%dGB 使用率(%s)\",$3,$2,$5}'");
inputStream = session.getStdout();
result = this.processStdout(inputStream);
System.out.println(result.toString());
//关闭连接
conn.close();
}else {
System.out.println("连接失败");
}
}
编写通用实体类
package com.example.domain;
import ch.ethz.ssh2.Connection;
import ch.ethz.ssh2.Session;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
@Data
public class SSHConnectionMethod {
/* 连接器 */
private Connection connect;
/* 主机(IP) */
private String host;
/* 连接端口 */
private int port;
/* 编码 */
private Charset charset;
/* 用户 */
private String user;
/* 密码 */
private String password;
/**
* 登录Centos主机方法
*/
private boolean login() {
connect = new Connection(host,port);
try {
connect.connect();
return connect.authenticateWithPassword(user, password);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 获取返回信息
*/
public StringBuilder getBackInfo(InputStream in) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
try {
int length;
while ((length = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
builder.append(new String(buf, 0, length));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return builder;
}
/**
* 执行shell命令
*/
public StringBuilder exec(String shell) throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = null;
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
try {
// 认证登录信息
if (this.login()) {
// 登陆成功
Session session = connect.openSession();
session.execCommand(shell);
inputStream = session.getStdout();
result = this.getBackInfo(inputStream);
connect.close();
}
} finally {
if (null != inputStream) {
inputStream.close();
}
}
return result;
}
}
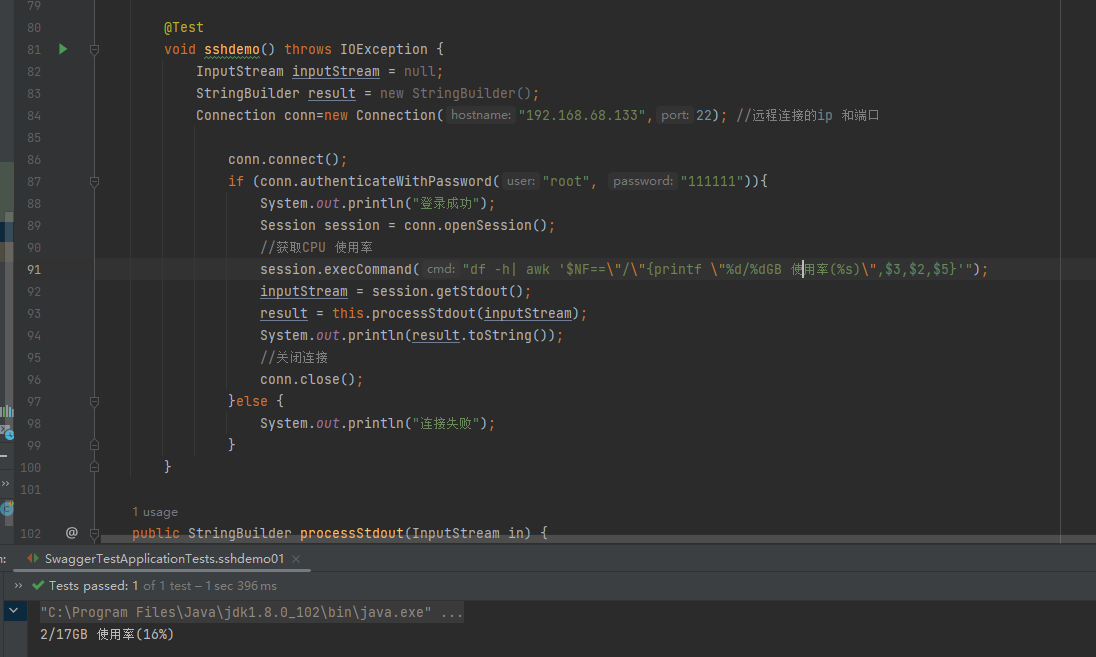
测试类
@Test
void sshdemo01()throws IOException{
SSHConnectionMethod sshConnectionMethod = new SSHConnectionMethod();
sshConnectionMethod.setHost("192.168.68.133");
sshConnectionMethod.setPort(22);
sshConnectionMethod.setUser("root");
sshConnectionMethod.setPassword("111111");
StringBuilder backResult = sshConnectionMethod.exec("df -h| awk '$NF==\"/\"{printf \"%d/%dGB 使用率(%s)\",$3,$2,$5}'");
System.out.println(backResult);
}
ssh服务端由2部分组成: openssh(提供ssh服务) openssl(提供加密的程序)
ssh的客户端可以用 XSHELL,Securecrt, Mobaxterm等工具进行连接
SSH的工作机制
服务器启动时产生一个密钥(768bit公钥),本地的ssh客户端发送连接请求到ssh服务器,服务器检查连接点客户端发送的数据和IP地址,确认合法后发送密钥(768bits)给客户端,此时客户端将本地私钥(256bit)和服务器的公钥(768bit)结合成密钥对key(1024bit),发回给服务器端,建立连接通过key-pair数据传输。
1.远程Server收到Client端用户TopGun的登录请求,Server把自己的公钥发给用户。
2.Client使用这个公钥,将密码进行加密。
3.Client将加密的密码发送给Server端。
4.远程Server用自己的私钥,解密登录密码,然后验证其合法性。
5.若验证结果,给Client相应的响应
SSH的加密技术
加密技术:传输过程,数据加密。
1.SSH1没有对客户端的秘钥进行校验,很容易被植入恶意代码
2.SSH2增加了一个确认联机正确性的Diffe_Hellman机制,每次数据的传输,Server都会检查数据来源的正确性,避免黑客入侵。
SSH2支持RSA和DSA密钥
DSA:digital signature Algorithm 数字签名
RSA:既可以数字签名又可以加密