目录
- 0 前言
- 1 read命令的功能、格式、返回值和注意
-
- 1.1 命令功能
- 1.2 命令格式
- 1.3 返回值
- 1.4 注意事项
- 2 命令应用实例
-
- 2.1 一次读入多个变量值
- 2.2 不指定变量名
- 2.3 测试read命令的返回值
- 2.3 指定输入时限并进行相应处理
- 2.4 -t 指定结束符
- 2.5 -n 指定输入字符个数
- 2.6 -N 指定输入字符个数
- 2.7 -s不回显来自终端的输入
- 2.8 -e使用命令补全功能
- 2.9 -r 允许输入的值中包含的反斜杠\也作为值输出
- 2.10 -a 读取数组值
- 2.11 -u指定文件说明符
0 前言
在交互式编程中,有时我们需要用户先通过键盘来输入数据,然后程序根据用户输入的数据来做相应的处理。
在之前的学习中,我们已经使用read命令来读取用户通过键盘输入的数据,但对read命令没有做进一步的说明。
现在我们来研究一下read命令的详细用法。
1 read命令的功能、格式、返回值和注意
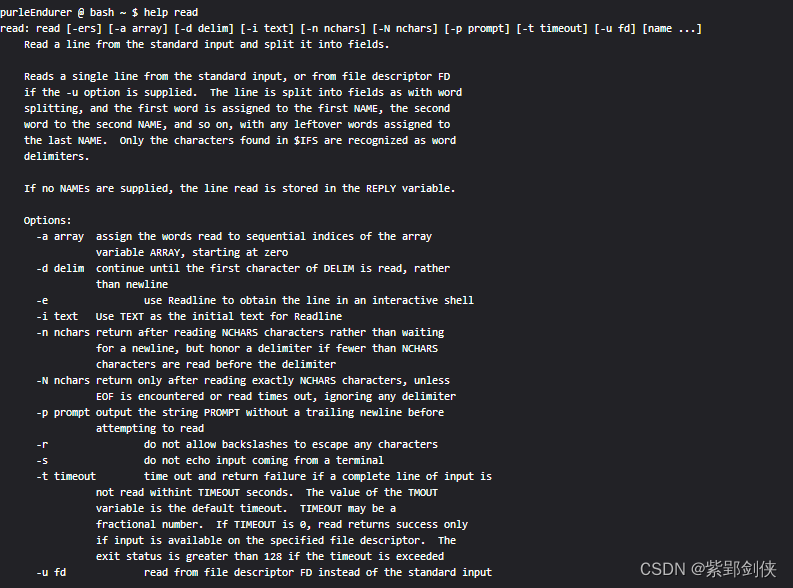
我们可以使用命令 help read 来查看seq命令的帮助信息:
purleEndurer @ bash ~ $ help read
read: read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [-i text] [-n nchars] [-N nchars] [-p prompt] [-t timeout] [-u fd] [name ...]
Read a line from the standard input and split it into fields.
Reads a single line from the standard input, or from file descriptor FD
if the -u option is supplied. The line is split into fields as with word
splitting, and the first word is assigned to the first NAME, the second
word to the second NAME, and so on, with any leftover words assigned to
the last NAME. Only the characters found in $IFS are recognized as word
delimiters.
If no NAMEs are supplied, the line read is stored in the REPLY variable.
Options:
-a array assign the words read to sequential indices of the array
variable ARRAY, starting at zero
-d delim continue until the first character of DELIM is read, rather
than newline
-e use Readline to obtain the line in an interactive shell
-i text Use TEXT as the initial text for Readline
-n nchars return after reading NCHARS characters rather than waiting
for a newline, but honor a delimiter if fewer than NCHARS
characters are read before the delimiter
-N nchars return only after reading exactly NCHARS characters, unless
EOF is encountered or read times out, ignoring any delimiter
-p prompt output the string PROMPT without a trailing newline before
attempting to read
-r do not allow backslashes to escape any characters
-s do not echo input coming from a terminal
-t timeout time out and return failure if a complete line of input is
not read withint TIMEOUT seconds. The value of the TMOUT
variable is the default timeout. TIMEOUT may be a
fractional number. If TIMEOUT is 0, read returns success only
if input is available on the specified file descriptor. The
exit status is greater than 128 if the timeout is exceeded
-u fd read from file descriptor FD instead of the standard input
Exit Status:
The return code is zero, unless end-of-file is encountered, read times out,
or an invalid file descriptor is supplied as the argument to -u.
readarray: readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s count] [-t] [-u fd] [-C callback] [-c quantum] [array]
Read lines from a file into an array variable.
A synonym for `mapfile'.
readonly: readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] ...] or readonly -p
Mark shell variables as unchangeable.
Mark each NAME as read-only; the values of these NAMEs may not be
changed by subsequent assignment. If VALUE is supplied, assign VALUE
before marking as read-only.
Options:
-a refer to indexed array variables
-A refer to associative array variables
-f refer to shell functions
-p display a list of all readonly variables and functions
An argument of `--' disables further option processing.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option is given or NAME is invalid.
purleEndurer @ bash ~ $

1.1 命令功能
从标准输入或-u 选项指定的文件描述符读取一行。该行被拆分为多个字段,就像单词拆分一样,第一个单词分配给第一个 变量,第二个单词分配给第二个 变量,依此类推,任何剩余的单词都分配给最后一个 变量。如果未提供 变量名,则读取的行存储在 REPLY 变量中。
只有在 $IFS 中找到的字符才会被识别为单词分隔符。
1.2 命令格式
read [-ers] [-a 索引数组名] [-d 结束符] [-i 文本] [-n 字符数] [-N 字符数] [-p 提示字符串] [-t 超时秒数] [-u 文件描述符] [变量名 ...]
- 选项说明
| 选项 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| -a 索引数组名 | 将读取的单词从下标零开始分配给数组名指定的 索引数组,默认是以空格为分割符 | array |
| -d 结束符 | 读取数据,直至结束符,而不是换行符 | delimiter |
| -e | 使用 Readline 在交互式 shell 中获取该行,在输入的时候可以使用命令补全功能 | |
| -i 文本 | 使用指定的文本作为 Readline 的初始文本 | initialize |
| -n 字符数 | 在读取指定的字符数后返回,除非遇到定界符、换行符或读取超时,定界符包括\t(tab键)。 | number |
| -N 字符数 | 在读取指定的字符数后返回,除非遇到 EOF 或读取超时 与 -n 不同的是,-N 会忽略任何定界符。 | number |
| -p 提示字符串 | 先输出提示字符串,再读取数据 | prompt |
| -r | 不允许反斜杠转义任何字符 | refuse |
| -s | 不回显来自终端的输入 | secrecy |
| -t 超时秒数 | 指定输入字符的等待时间。 如果在 超时秒数 内未读取完整的输入行,则超时并返回失败。 超时秒数 可以是小数。 | timeout |
| -u 文件描述符 | 从指定的文件描述符读入数据 | use |
1.3 返回值
命令正常执行时返回值为零,
如果遇到文件末尾、读取超时或提供无效文件描述符作为 -u 的参数时,返回值不为零。
如果读取超时,返回值 将 大于 128。
1.4 注意事项
- 变量名列表 应该放在 命令的最后。
- 变量名之间以空格分隔。
2 命令应用实例
2.1 一次读入多个变量值
例:提示用户输入3个整数,作为a、c、c 三个变量的值
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -p "Enter there integers:" a b c
Enter there integers:1 2 3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b c=$c
a=1 b=2 c=3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -p "Enter there integers:" a b c
Enter there integers:1 2 3 4 5 6
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b c=$c
a=1 b=2 c=3 4 5 6
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $

当我们输入1 2 3 这三个整数后,变量a的值为1,变量b的值为2,变量c的值为3。
当我们输入1 2 3 4 5 6 这六个整数后,由于我们只给了a、b、c三个变理名,所以变量a的值为1,变量b的值为2,而变量c的值为:3 4 5 6。
2.2 不指定变量名
例:提示用户输入3个整数,但没指定变量名
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $REPLY
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -p "Enter there integers:"
Enter there integers:1 2 3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $REPLY
1 2 3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $
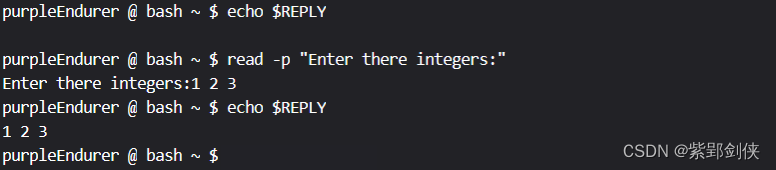
由于我们没有指定变量名,所以输入的值1 2 3保存在变量REPLY中。
2.3 测试read命令的返回值
例:提示用户输入名字,输入时间限定为10秒钟
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -t 10 -p "Enter your name:"
Enter your name:pe
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
0
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -t 10 -p "Enter your name:"
Enter your name:purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
142
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -t 10 -p "Enter your name:"
Enter your name:purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
1
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -t 10 -p "Enter your name:"
Enter your name:^C
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $?
130
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $
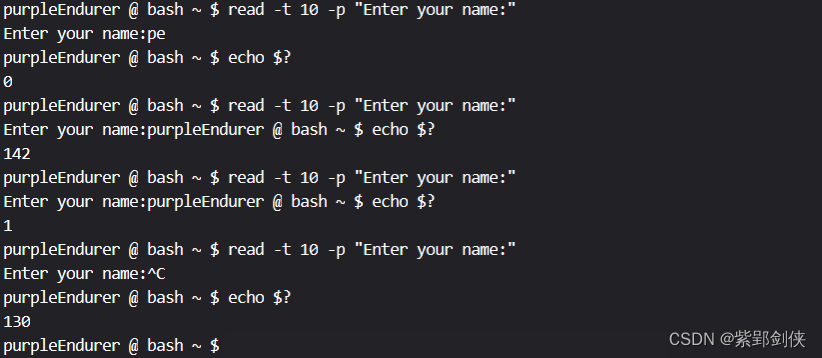
当我们在10秒钟内输入用户名pe并回车,read命令正常执行,返回值为0
当我们未在10秒钟内输入用户名,read命令返回值为142,大于128
当我们输入^D时,read命令返回值为1
当我们输入^C时,read命令返回值为130
2.3 指定输入时限并进行相应处理
例:编写一个脚本,提示用户在5秒钟内输入名字,如果用户输入名字,则对用户进行问候,否则提示用户没有输入名字。
脚本内容如下:
read -t 5 -p "Enter you name in 5 seconds:" name # 提示用户在5秒钟内输入名字并保存在变量name中
if [ $? == 0 ]; then # 如果用户在5秒钟内输入了名字,那么read命令返回值为0
echo Hello, $name. # 对用户进行问候
else
echo -e "\nYou do not enter your name." # 提示用户没有输入名字
fipurpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
read -t 5 -p "Enter you name in 5 seconds:" name
if [ $? == 0 ]; then
echo Hello, $name.
else
echo -e "\nYou do not enter your name."
fi
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cat a.sh
read -t 5 -p "Enter you name in 5 seconds:" name
if [ $? == 0 ]; then
echo Hello, $name.
else
echo -e "\nYou do not enter your name."
fi
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ . a.sh
Enter you name in 5 seconds:pe
Hello, pe.
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ . a.sh
Enter you name in 5 seconds:
You do not enter your name.
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $

2.4 -t 指定结束符
例 读取用户输入值存入变量a,指定#作为结束符
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -d '#' a
ab#purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $a
ab
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $
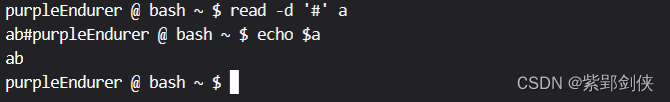
当我们输入ab#时,读取结束。变量a的值为ab。
2.5 -n 指定输入字符个数
例 读取5个字符,分别保存到变量a和b
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -n 5 a b
12345purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12345 b=
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -n 5 a b
12 34purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12 b=34
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -n 5 a b
1 234purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=1 b=234
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -n 5 a b
12
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12 b=
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -n 5 a b
123^C
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12 b=
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $
当我们输入12345时,变量a的值为12345,变量b值为空
当我们输入12空格34时,变量a的值为12,变量b值为34
当我们输入1[Tab]234时,变量a的值为1,变量b值为234
当我们输入12回车时,变量a的值为12,变量b值为空
当我们输入123^C时,read命令被终止了,所以变量a的值没有变化,仍为12,变量b值没有变化,仍为空
2.6 -N 指定输入字符个数
例 读取5个字符,分别保存到变量a和b
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -N 5 a b
12 34purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12 34 b=
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -N 5 a b
12 34purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12 34 b=
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -d '#' -N 5 a b
12#34purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo a=$a b=$b
a=12#34 b=
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $

当我们输入12[Tab]34时,变量a的值为12 34,变量b值为空
当我们输入12空格34时,变量a的值为12 34,变量b值为空
即使我们用-t '#' 选项指定#作为结束符,输入12#34,结果变量a的值为12#34,变量b值为空
- 看来使用-N选项后,空格或[Tab]不再作为字符串值的分隔符,-t选项也不起作用,这样只能将读取值存到第1个变量中了。
2.7 -s不回显来自终端的输入
例:提示用户输入密码,输入时不回显,输入完成后再显示用户输入的密码。
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -s -p "Enter your password:" p
Enter your password:purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo Your password is $p
Your password is abcd
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $
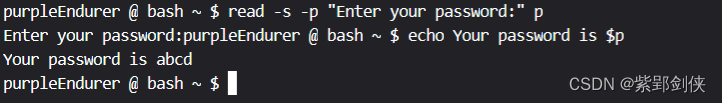
当用户输入密码abcd时并不回显,按回车键后,才显示用户输入的密码是abcd。
2.8 -e使用命令补全功能
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ ls
Code
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ read -e a
Code/
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ echo $a
Code/
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $

我们先用ls命令查看当前目录内容,存在一个名Code的文件或文件夹
然后我们用命令 read -e a 来读取输入存到变量a
在我们输入大写字符C后按Tab键启用命令补全功能,输入行的内容就变为Code/,按下回车键。
再用echo $a 查看变量a的值为Code/
2.9 -r 允许输入的值中包含的反斜杠\也作为值输出
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ read a
//\c
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo $a
//c
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ read -r a
//\c
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo $a
//\c
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $
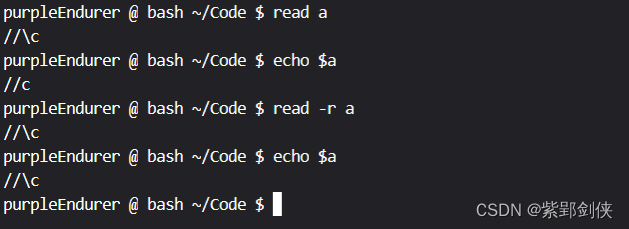
对于命令 read a,输入 //\c,存储到变量a的值为 //C,不包含反斜杠\。
对于命令 rread -r a,输入 //\c,存储到变量a的值为 //\C,包含反斜杠\。
2.10 -a 读取数组值
数组是最常用的一种数据结构,在之前的
Linux shell编程学习笔记15:定义数组、获取数组元素值和长度、数组拼接或合并_linux获取数组长度-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134009982
https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134009982
和
Linux shell编程学习笔记16:bash中的关联数组-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134053506中我们学习了Lininux Shell编程中的数组的定义和赋值的方法,其中对数组元素的赋值方法 ,我们主要介绍了在定义数组时同时进行初始化和定义数组后用赋值语句来赋值两种方法。
https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134053506中我们学习了Lininux Shell编程中的数组的定义和赋值的方法,其中对数组元素的赋值方法 ,我们主要介绍了在定义数组时同时进行初始化和定义数组后用赋值语句来赋值两种方法。
现在我们也可以用read命令来将用户输入的值存储到数组
例:从键盘读取输入存入数组a
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo ${a[*]}
1 2 3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ read -a a
1 2 3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo ${a[*]}
1 2 3
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ echo ${a[0]}
1
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $

可惜的是,read命令不能将用户输入存储到关联数组
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ declare -A A
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $ read -a A
a b c
bash: read: A: cannot convert associative to indexed array
purpleEndurer @ bash ~/Code $

我们先用命令 声明一个关联数组A
然后用命令 来读取用户输入存储到关联数组A,但是出错了:bash: read: A: cannot convert associative to indexed array
2.11 -u指定文件说明符
例:将文件a.txt和b.txt的内容逐行拼接显示。
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.txt
111
222
333
444
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ cp /dev/stdin b.txt
aaa
bbb
ccc
ddd
eee
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ while read -u3 i && read -u4 j;do echo $i $j; done 3<a.txt 4<b.txt
111 aaa
222 bbb
333 ccc
444 ddd
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $

如果我们希望在每一行前显示行号,那么我们可以增加一个变量n用来记录当前行数:
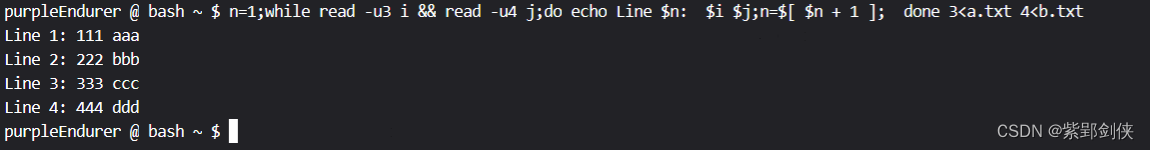
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $ n=1;while read -u3 i && read -u4 j;do echo Line $n: $i $j;n=$[ $n + 1 ]; done 3<a.txt 4<b.txt
Line 1: 111 aaa
Line 2: 222 bbb
Line 3: 333 ccc
Line 4: 444 ddd
purpleEndurer @ bash ~ $