📢作者: 小小明-代码实体
📢博客主页:https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322
📢欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 欢迎讨论!
本手册目录:
文章目录
- 前言
- Markdown导入数据库python脚本
- SQL Schema批量导入
- 基本配置
- 参考资料
- 基本语句
- delete删除操作
- update更新操作
- case when的应用
- union all应用
- 区间统计
- 基本字符串处理函数
- 字符串拼接与分组拼接
- 正则表达式
- like模糊匹配
- instr函数
- with rollup的使用
- 日期操作
- date_sub函数
- datediff函数
- timestampdiff函数
- weekday计算星期几
- date_format日期格式化
- 日期区间拆分为年份
- 窗口函数
- 排名函数
- 偏移分析窗口函数
- 统计分析函数
- count也支持窗口函数
- window子句ROWS与RANGE的区别
- 窗口函数可以执行在group by之后
- 排名函数执行在order by上
- 排名函数实现多列分别排序
- 窗口函数相减为负数会报错
- 判断连续性
- 是否连续相等
- 是否连续为某个固定值
- 数字是否连续递增
- 数字连续递增区间
- 日期是否连续按年递增
- 日期是否连续按天递增
- 日期是否连续按月递增
- 操作技巧
- 向下填充连续的空值
- 取topn对应的行
- 一个聚合中求出多个类别的个数
- 奇偶行两两交换
- 一组数字查询中位数
- 给定数字的频率查询中位数
- 共同好友
- 共同关注者
- 页面推荐1
- 页面推荐2
- 好友推荐
- 重叠区间合并
- 自连接
- 司机成为乘客的次数
- 二叉树节点类型
- 任意两点之间的距离
- 矩形面积
- 二级关注者
- 每个帖子的评论数
- 每位经理的下属员工数量
- 向公司CEO汇报工作的所有人
- 生成序列并统计
- 生成固定值
- 生成数字序列
- 分配问题
- 每辆车的乘客人数1
- 每辆车的乘客人数2
- 职员招聘人数1
- 职员招聘人数2
- 函数与存储过程
- 自定义函数
- 自定义函数对比存储过程
- 透视/逆透视(行转列、列转行)
- 无主键顺序行转列
- 透视表(行转列)
- 逆透视(列转行)
- 动态行转列
- 动态列转行
- 其他
- 行程和用户
- 部门与公司比较平均工资
- 活跃业务
- 报告的记录
- 显示价格最高的发票的详情
- 游戏玩法分析
- 好友申请:总体通过率
- 好友申请:谁有最多的好友
- 产品销售分析1
- 产品销售分析4
- Hopper 公司查询1
- Hopper 公司查询2
- Hopper 公司查询3
前言
本人写SQL断断续续也有5年多了,对于刷题这种事情一直都是非常不屑的态度“写SQL这么简单的事情也需要刷?不是看一眼就会了吗?”
直到我最近我真的刷了力扣的SQL题,才发现其实还是有很多不熟悉的技巧。最近花了近一个多月的时间,刷完了LeetCode上220道SQL数据库的题,感觉收获还是很多,下面在二刷后整理了本手册。
本手册主干:
力扣刷题地址:https://leetcode.cn/problemset/database/
以《176. 第二高的薪水》为例看看题目格式:
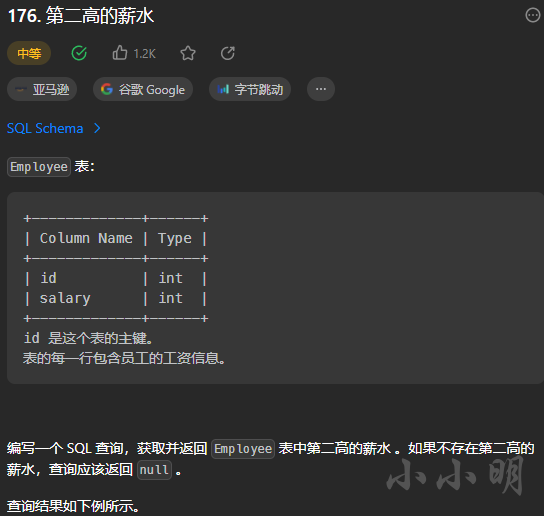
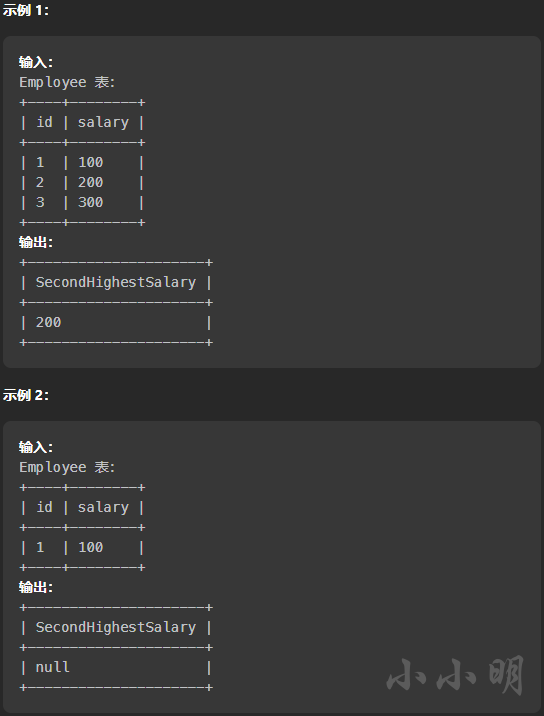
Markdown导入数据库python脚本
力扣的SQL绝大部分会员可见,为了保证各题的数据能够很方便的导入本地数据库,我编写了一个Python脚本,以上述题目为例代码如下:
from urllib.parse import quote_plus
import pandas as pd
import re
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.types import *
from sqlalchemy import types
def md2sql(sql_text, type_md, tbname, db_config):
host = db_config["host"]
database = db_config["database"]
user_name = db_config["user_name"]
password = quote_plus(db_config["password"])
port = db_config["port"]
engine = create_engine(
f'mysql+pymysql://{user_name}:{password}@{host}:{port}/{database}')
dtypes = {}
if type_md and type_md.strip():
type_txt = " ".join(dir(types))
lines = type_md.strip().splitlines()
for line in lines:
if "---" in line or "Column Name" in line:
continue
k, v = re.split(" *\| *", line.strip(" |"), maxsplit=1)
a, b = re.split("(?=\(|$)", v, 1)
dtypes[k.lower()] = eval(re.search(a, type_txt, re.I).group(0) + b)
lines = [line for line in sql_text.strip().splitlines() if "---" not in line]
header = [c.lower() for c in re.split(" *\| *", lines[0])[1:-1]]
data = []
for line in lines[1:]:
row = [None if e.lower() == "null" else e
for e in re.split(" *\| *", line.strip(" |"))]
data.append(row)
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=header)
with engine.connect() as conn:
print(tbname)
df.to_sql(name=tbname.lower(), con=conn, if_exists='replace', index=False,
dtype=dtypes)
table = pd.read_sql_table(tbname.lower(), conn)
return table
db_config = {
"host": "localhost",
"database": "leetcode",
"user_name": "root",
"password": '123456',
"port": 3306
}
type_md = """
+-------------+------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+------+
| id | int |
| salary | int |
+-------------+------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+--------+
| id | salary |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
+----+--------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df)
将上述脚本保存为md2sql.py。
根据自己本地数据库的实际情况修改参数。后面要导入其他表时,也只需要修改前3个参数。
导入上述数据后,测试一下如下SQL语句:
select (select distinct salary from employee order by salary desc limit 1,1) SecondHighestSalary;
SecondHighestSalary
---------------------
200
顺利通过。
SQL Schema批量导入
此外LeetCode还提供了SQL Schema导入语句:
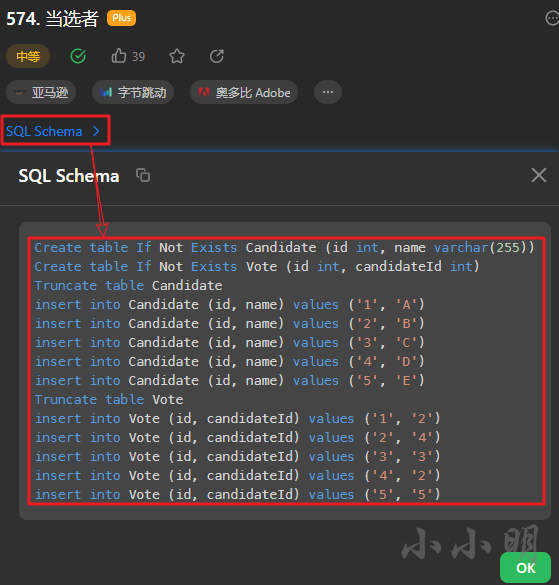
只不过这些语句没有;结尾,无法直接批量执行,但是我们依然可以使用python脚本批量逐条执行:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from urllib.parse import quote_plus
host = 'localhost'
database = 'leetcode'
user_name = 'root'
password = '123456'
port = 3306
engine = create_engine(
f'mysql+pymysql://{user_name}:{quote_plus(password)}@{host}:{port}/{database}')
def SQL_Schema_import(sql_txt):
with engine.connect() as conn:
n = 0
for line in sql_txt.strip().splitlines():
result = conn.execute(line.replace("'None'", "null"))
n += result.rowcount
print(f"共插入{n}条数据(原有数据已被覆盖)")
sql_txt = """
Create table If Not Exists Candidate (id int, name varchar(255))
Create table If Not Exists Vote (id int, candidateId int)
Truncate table Candidate
insert into Candidate (id, name) values ('1', 'A')
insert into Candidate (id, name) values ('2', 'B')
insert into Candidate (id, name) values ('3', 'C')
insert into Candidate (id, name) values ('4', 'D')
insert into Candidate (id, name) values ('5', 'E')
Truncate table Vote
insert into Vote (id, candidateId) values ('1', '2')
insert into Vote (id, candidateId) values ('2', '4')
insert into Vote (id, candidateId) values ('3', '3')
insert into Vote (id, candidateId) values ('4', '2')
insert into Vote (id, candidateId) values ('5', '5')
"""
SQL_Schema_import(sql_txt)
从SQL Schema复制的SQL无法自动修改同名表的Schema,若已存在Schema不同的同名表,只能手动删除表后再执行上述代码或者自行添加自动删除的代码。
本文个别题使用SQL Schema这种导入形式,但由于Markdown形式更清晰,所以整体上还是都使用了Markdown的导入形式。
基本配置
若我们直接引用未聚合的字段,例如:
select
a.id,name,group_concat(b.id) ids
from Candidate a join vote b
on a.id=b.candidateId
group by a.id;
会报出如下错误:
Expression #2 of SELECT list is not in GROUP BY clause and contains nonaggregated column ‘leetcode.a.name’ which is not functionally dependent on columns in GROUP BY clause; this is incompatible with sql_mode=only_full_group_by
要直接引用未参与聚合的字段,我们可以使用聚合函数:
select
a.id,
any_value(name) name,
group_concat(b.id) ids
from Candidate a join vote b
on a.id=b.candidateId
group by a.id;
另外就是修改mysql的配置,修改my.ini配置文件的 [mysqld] 配置:
# 可以直接引用未聚合字段
sql_mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
另外就是我们创建自定义函数时,可能会报出如下错误:
This function has none of DETERMINISTIC, NO SQL, or READS SQL DATA in its declaration and binary logging is enabled (you *might* want to use the less safe log_bin_trust_function_creators variable)
这时除了临时修改:
set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=TRUE;
还可以修改my.ini配置文件的 [mysqld] 配置:
# 可以创建自定义函数
log_bin_trust_function_creators=1
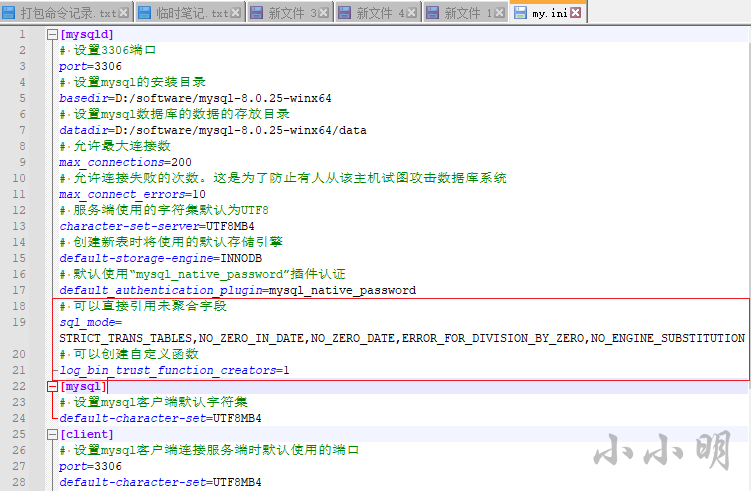
重启后即可生效。
参考资料
MySQL语法查询网站:https://www.begtut.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html
该网站可以查看MySQL按关键字分类的语法:
MySQL8.0的安装
本手册全部在MySQL8.0版本测试,可以参考以下方法安装:
不卸载原有mysql直接安装mysql8.0
https://xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net/article/details/113204880
MySQL视频教程推荐:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1iq4y1u7vj/
对应的资料下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1v44IeG8kwqbVrpwAGRPytw?pwd=1234
基本语句
delete删除操作
示例:196. 删除重复的电子邮箱
数据:
type_md = """
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| id | int |
| email | varchar(20) |
+-------------+---------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+------------------+
| id | email |
+----+------------------+
| 1 | john@example.com |
| 2 | bob@example.com |
| 3 | john@example.com |
+----+------------------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Person", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
要求: 删除 所有重复的电子邮件,只保留一个id最小的唯一电子邮件。
我们需要先查找出重复的且id不是最小的记录:
select p1.* from person p1 join person p2
on p1.email=p2.email and p1.id>p2.id
然后将select修改为delete即可:
delete p1.* from person p1 join person p2
on p1.email=p2.email and p1.id>p2.id;
不使用自连接的方法:
delete from person where id not in(
select * from (select min(id) from person group by email) t
)
需要嵌套一层子查询,是因为直接删除会报出如下错误:You can't specify target table 'person' for update in FROM clause
update更新操作
示例:627. 变更性别
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| sex | ENUM('m','f') |
| salary | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | name | sex | salary |
+----+------+-----+--------+
| 1 | A | m | 2500 |
| 2 | B | f | 1500 |
| 3 | C | m | 5500 |
| 4 | D | f | 500 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Salary", db_config)
print(df)
使用 单个 update 语句交换所有的 'f' 和 'm' (即,将所有 'f' 变为 'm' ,反之亦然)
update salary set sex=if(sex="f","m","f");
case when的应用
示例:1440. 计算布尔表达式的值
数据:
type_md = """
| name | varchar(5) |
| value | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| name | value |
| ---- | ----- |
| x | 66 |
| y | 77 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Variables", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| left_operand | varchar(5) |
| operator | enum('<','>','=') |
| right_operand | varchar(5) |
"""
sql_text = """
| left_operand | operator | right_operand |
| ------------ | -------- | ------------- |
| x | > | y |
| x | < | y |
| x | = | y |
| y | > | x |
| y | < | x |
| x | = | x |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Expressions", db_config)
print(df)
查询表 Expressions 的布尔表达式。
select
e.*,
case when(
case operator
when ">" then l.value>r.value
when "=" then l.value=r.value
when "<" then l.value<r.value
end
) then "true" else "false"
end as value
from expressions e
join variables l on e.left_operand=l.name
join variables r on e.right_operand=r.name;
以上SQL展示了case when的两种写法,结果:
left_operand operator right_operand value
------------ -------- ------------- --------
x = x true
y < x false
y > x true
x = y false
x < y true
x > y false
union all应用
示例:1783. 大满贯数量
数据:
type_md = """
| player_id | int |
| player_name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| player_id | player_name |
| --------- | ----------- |
| 1 | Nadal |
| 2 | Federer |
| 3 | Novak |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Players", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| year | int |
| Wimbledon | int |
| Fr_open | int |
| US_open | int |
| Au_open | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| year | Wimbledon | Fr_open | US_open | Au_open |
| ---- | --------- | ------- | ------- | ------- |
| 2018 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 2020 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Championships", db_config)
print(df)
查询出每一个球员赢得大满贯比赛的次数。结果不包含没有赢得比赛的球员的ID 。
select
a.player_id,player_name,count(1) grand_slams_count
from(
select Wimbledon player_id from Championships
union all
select Fr_open from Championships
union all
select US_open from Championships
union all
select Au_open from Championships
) a join players using(player_id)
group by a.player_id,player_name
player_id player_name grand_slams_count
--------- ----------- -------------------
1 Nadal 7
2 Federer 5
示例:1212. 查询球队积分
数据:
type_md = """
| team_id | int |
| team_name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| team_id | team_name |
| ------- | ----------- |
| 10 | Leetcode FC |
| 20 | NewYork FC |
| 30 | Atlanta FC |
| 40 | Chicago FC |
| 50 | Toronto FC |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Teams", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| match_id | int |
| host_team | int |
| guest_team | int |
| host_goals | int |
| guest_goals | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| match_id | host_team | guest_team | host_goals | guest_goals |
| -------- | --------- | ---------- | ---------- | ----------- |
| 1 | 10 | 20 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | 30 | 10 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 10 | 50 | 5 | 1 |
| 4 | 20 | 30 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 50 | 30 | 1 | 0 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Matches", db_config)
print(df)
在所有比赛之后计算所有球队的比分。积分奖励方式如下:
- 如果球队赢了比赛(即比对手进更多的球),就得 3 分。
- 如果双方打成平手(即,与对方得分相同),则得 1 分。
- 如果球队输掉了比赛(例如,比对手少进球),就 不得分 。
查询每个队的 team_id,team_name 和 num_points。
返回的结果根据 num_points 降序排序,如果有两队积分相同,那么这两队按 team_id 升序排序。
select
b.team_id,
any_value(b.team_name) team_name,
ifnull(sum(num_points),0) num_points
from(
select
host_team team_id,
if(host_goals>guest_goals,3,host_goals=guest_goals) num_points
from Matches
union all
select
guest_team team_id,
if(host_goals<guest_goals,3,host_goals=guest_goals) num_points
from Matches
) a right join teams b on a.team_id=b.team_id
group by b.team_id
order by num_points desc,b.team_id;
team_id team_name num_points
------- ----------- ------------
10 Leetcode FC 7
20 NewYork FC 3
50 Toronto FC 3
30 Atlanta FC 1
40 Chicago FC 0
区间统计
示例:1435. 制作会话柱状图
数据:
type_md = """
| session_id | int |
| duration | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| session_id | duration |
| ---------- | -------- |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 199 |
| 3 | 299 |
| 4 | 580 |
| 5 | 1000 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Sessions", db_config)
print(df)
统计访问时长区间分别为 “[0-5>”, “[5-10>”, “[10-15>” 和 “15 or more” (单位:分钟)的会话数量。
select '[0-5>' bin, sum(duration<300) total from Sessions
union all
select '[5-10>', sum(300<=duration and duration<600) from Sessions
union all
select '[10-15>', sum(600<=duration and duration<900) from Sessions
union all
select '15 or more', sum(duration>=900) from Sessions;
bin total
---------- --------
[0-5> 3
[5-10> 1
[10-15> 0
15 or more 1
不使用union:
select
a.bin,
count(b.bin) total
from(values row("[0-5>"),row("[5-10>"),row("[10-15>"),row("15 or more")) a(bin)
left join(
select
case
when duration<300 then '[0-5>'
when duration<600 then '[5-10>'
when duration<900 then '[10-15>' else '15 or more'
end `bin`
from sessions
) b using(`bin`)
group by a.bin;
示例:1907. 按分类统计薪水
数据:
type_md = """
| account_id | int |
| income | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| account_id | income |
| ---------- | ------ |
| 3 | 108939 |
| 2 | 12747 |
| 8 | 87709 |
| 6 | 91796 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Accounts", db_config)
print(df)
查询,来报告每个工资类别的银行账户数量。 工资类别如下:
"Low Salary":所有工资 严格低于20000美元。"Average Salary": 包含 范围内的所有工资[$20000, $50000]。"High Salary":所有工资 严格大于50000美元。
结果表 必须 包含所有三个类别。 如果某个类别中没有帐户,则报告 0 。
select "Low Salary" category,count(1) accounts_count from accounts where income<20000
union all
select "Average Salary" category,count(1) from accounts where income between 20000 and 50000
union all
select "High Salary" category,count(1) from accounts where income>50000;
或
select "Low Salary" category,sum(income<20000) accounts_count from accounts
union all
select "Average Salary" category,sum(income between 20000 and 50000) from accounts
union all
select "High Salary" category,sum(income>50000) from accounts;
category accounts_count
-------------- ----------------
Low Salary 1
Average Salary 0
High Salary 3
不使用union:
select
a.bin,
count(b.bin) total
from(values row("Low Salary"),row("Average Salary"),row("High Salary")) a(bin)
left join(
select
case
when income<20000 then 'Low Salary'
when income<50000 then 'Average Salary'
else 'High Salary'
end `bin`
from accounts
) b using(`bin`)
group by a.bin;
基本字符串处理函数
这里我们展示lower/trim/left/upper/right/length/concat等函数的使用。
示例:1543. 产品名称格式修复
数据:
type_md = """
| sale_id | int |
| product_name | varchar(20) |
| sale_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| sale_id | product_name | sale_date |
| ------- | ------------ | ---------- |
| 1 | LCPHONE | 2000-01-16 |
| 2 | LCPhone | 2000-01-17 |
| 3 | LcPhOnE | 2000-02-18 |
| 4 | LCKeyCHAiN | 2000-02-19 |
| 5 | LCKeyChain | 2000-02-28 |
| 6 | Matryoshka | 2000-03-31 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Sales", db_config)
print(df)
写一个 SQL 语句报告每个月的销售情况:
product_name是小写字母且不包含前后空格sale_date格式为('YYYY-MM')total是产品在本月销售的次数
返回结果以 product_name 升序 排列,如果有排名相同,再以 sale_date 升序 排列。
select
lower(trim(product_name)) product_name,
left(sale_date,7) sale_date,
count(1) total
from sales
group by 1,2
order by 1,2;
product_name sale_date total
------------ --------- --------
lckeychain 2000-02 2
lcphone 2000-01 2
lcphone 2000-02 1
matryoshka 2000-03 1
示例:1667. 修复表中的名字
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | name |
| ------- | ----- |
| 1 | aLice |
| 2 | bOB |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Users", db_config)
print(df)
修复名字,使得只有第一个字符是大写的,其余都是小写的。返回按 user_id 排序的结果表。
select
user_id,
concat(upper(left(name,1)),lower(right(name,length(name)-1))) name
from users
order by user_id;
user_id name
------- --------
1 Alice
2 Bob
示例:2504. 拼接名字和职业
数据:
type_md = """
| person_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| profession | ENUM('Doctor', 'Singer', 'Actor', 'Player', 'Engineer', 'Lawyer') |
"""
sql_text = """
| person_id | name | profession |
| --------- | ----- | ---------- |
| 1 | Alex | Singer |
| 3 | Alice | Actor |
| 2 | Bob | Player |
| 4 | Messi | Doctor |
| 6 | Tyson | Engineer |
| 5 | Meir | Lawyer |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Person", db_config)
print(df)
查询每个人的名字,后面是他们职业的第一个字母,用括号括起来。
返回按 person_id 降序排列 的结果表。
select person_id,concat(name,"(",left(profession,1),")") name
from person
order by person_id desc;
person_id name
--------- ----------
6 Tyson(E)
5 Meir(L)
4 Messi(D)
3 Alice(A)
2 Bob(P)
1 Alex(S)
字符串拼接与分组拼接
示例:2118. 建立方程
数据:
type_md = """
| power | int |
| factor | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| power | factor |
| ----- | ------ |
| 2 | 1 |
| 1 | -4 |
| 0 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Terms", db_config)
print(df)
要求将以上表拼接成+1X^2-4X+2=0形式的字符串。
我的思路是先按列拼接每行的组成元素:
select
concat(if(factor>0,"+",""),factor) a,
if(power>0,"X","") b,
if(power>1,concat("^",power),"") c
from terms;
a b c
------ ------ --------
+1 X ^2
-4 X
+2
然后整体拼接:
select
concat(group_concat(a,b,c order by power desc separator ""),"=0") equation
from(
select
power,
concat(if(factor>0,"+",""),factor) a,
if(power>0,"X","") b,
if(power>1,concat("^",power),"") c
from terms
) a;
equation
--------------
+1X^2-4X+2=0
group_concat内部需要根据power排序,所以子查询中增加power字段,separator指定了连接符。
case when写法:
select
concat(group_concat(a,b order by power desc separator ""),"=0") equation
from(
select
power,
concat(if(factor>0,"+",""),factor) a,
case power
when 0 then ""
when 1 then "X"
else concat('X^',power)
end b
from terms
) a;
正则表达式
示例:1517. 查找拥有有效邮箱的用户
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| mail | varchar(100) |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | name | mail |
| ------- | --------- | ----------------------- |
| 1 | Winston | winston@leetcode.com |
| 2 | Jonathan | jonathanisgreat |
| 3 | Annabelle | bella-@leetcode.com |
| 4 | Sally | sally.come@leetcode.com |
| 5 | Marwan | quarz#2020@leetcode.com |
| 6 | David | david69@gmail.com |
| 7 | Shapiro | .shapo@leetcode.com |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Users", db_config)
print(df)
查询拥有有效邮箱的用户。
有效的邮箱包含符合下列条件的前缀名和域名:
- 前缀名是包含字母(大写或小写)、数字、下划线
'_'、句点'.'和横杠'-'的字符串。前缀名必须以字母开头。 - 域名是
'@leetcode.com'。
select * from users
where mail regexp "^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_.-]*@leetcode\\.com$";
user_id name mail
------- --------- -------------------------
1 Winston winston@leetcode.com
3 Annabelle bella-@leetcode.com
4 Sally sally.come@leetcode.com
示例:1527. 患某种疾病的患者
数据:
type_md = """
| patient_id | int |
| patient_name | varchar(20) |
| conditions | varchar(50) |
"""
sql_text = """
| patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
| ---------- | ------------ | ------------ |
| 1 | Daniel | YFEV COUGH |
| 2 | Alice | |
| 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
| 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
| 5 | Alain | DIAB201 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Patients", db_config)
print(df)
查询患有 I 类糖尿病的患者的全部信息。I 类糖尿病的代码总是包含前缀 DIAB1 。
select * from Patients where conditions regexp "(^| )DIAB1";
patient_id patient_name conditions
---------- ------------ --------------
3 Bob DIAB100 MYOP
4 George ACNE DIAB100
正则表达式的语法可参考:
正则表达式速查表与Python实操手册
https://xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net/article/details/112691043
示例:2199. 找到每篇文章的主题
数据:
type_md = """
| topic_id | int |
| word | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| topic_id | word |
| -------- | -------- |
| 1 | handball |
| 1 | football |
| 3 | WAR |
| 2 | Vaccine |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Keywords", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| post_id | int |
| content | varchar(200) |
"""
sql_text = """
| post_id | content |
| ------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| 1 | We call it soccer They call it football hahaha |
| 2 | Americans prefer basketball while Europeans love handball and football |
| 3 | stop the war and play handball |
| 4 | warning I planted some flowers this morning and then got vaccinated |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Posts", db_config)
print(df)
表: Keywords每一行都包含一个主题的 id 和一个用于表达该主题的词。可以用多个词来表达同一个主题,也可以用一个词来表达多个主题。
表: Posts每一行都包含一个帖子的 ID 及其内容。内容仅由英文字母和空格组成。
编写一个 SQL 查询,根据以下规则查找每篇文章的主题:
- 如果帖子没有来自任何主题的关键词,那么它的主题应该是
"Ambiguous!"。 - 如果该帖子至少有一个主题的关键字,其主题应该是其主题的 id 按升序排列并以逗号 ‘,’ 分隔的字符串。字符串不应该包含重复的 id。
select
post_id,
ifnull(group_concat(distinct topic_id order by topic_id),"Ambiguous!") topic
from posts p left join keywords k
on content regexp concat("(^| )",word,"( |$)")
group by post_id;
post_id topic
------- ------------
1 1
2 1
3 1,3
4 Ambiguous!
5 1,2
like模糊匹配
like的匹配模式中,有两种占位符:
_:匹配对应的单个字符
%:匹配多个字符
针对上一题,使用like实现需要考虑三种情况(keyword居中,起始,末尾)。参考解法:
select
post_id,
ifnull(group_concat(distinct topic_id order by topic_id),"Ambiguous!") topic
from posts p left join keywords k
on content like concat(word," %")
or content like concat("% ",word," %")
or content like concat("% ",word)
group by post_id;
instr函数
针对上题还有种办法是使用instr函数,确保文章首尾都有空格后,则可以判断首尾带空格的词汇是否存在于文章中:
select
post_id,
ifnull(group_concat(distinct topic_id order by topic_id),"Ambiguous!") topic
from posts p left join keywords k
on instr(concat(' ',content,' '),concat(' ',word,' '))>0
group by post_id;
with rollup的使用
Hive中支持 GROUPING SETS,GROUPING__ID,CUBE,ROLLUP等函数,MySQL则只支持rollup。下面演示一下roll up的使用。
示例:615. 平均工资:部门与公司比较
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| employee_id | int |
| amount | int |
| pay_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | employee_id | amount | pay_date |
|----|-------------|--------|------------|
| 1 | 1 | 9000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 2 | 2 | 6000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 3 | 3 | 10000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 4 | 1 | 7000 | 2017-02-28 |
| 5 | 2 | 6000 | 2017-02-28 |
| 6 | 3 | 8000 | 2017-02-28 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "salary", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| department_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | department_id |
|-------------|---------------|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df)
该题正常解法请查看最后一章的《部门与公司比较平均工资》
mysql支持rollup,我们可以使用一个分组查询即可同时获取每个月部门和公司的平均工资:
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month,
department_id,
avg(amount) amount
from salary a join employee b
using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7),department_id
with rollup;
结果:
pay_month department_id amount
--------- ------------- -----------
2017-02 1 7000.0000
2017-02 2 7000.0000
2017-02 (NULL) 7000.0000
2017-03 1 9000.0000
2017-03 2 8000.0000
2017-03 (NULL) 8333.3333
(NULL) (NULL) 7666.6667
GROUPING() 函数可以检查超级聚合中,聚合字段是否为空:
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month,
department_id,
avg(amount) amount,
grouping(left(pay_date,7)) e1,
grouping(department_id) e2
from salary a join employee b
using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7),department_id
with rollup;
pay_month department_id amount e1 e2
--------- ------------- --------- ------ --------
2017-02 1 7000.0000 0 0
2017-02 2 7000.0000 0 0
2017-02 (NULL) 7000.0000 0 1
2017-03 1 9000.0000 0 0
2017-03 2 8000.0000 0 0
2017-03 (NULL) 8333.3333 0 1
(NULL) (NULL) 7666.6667 1 1
然后我们分解结果进行表连接:
with cte as (
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month,
department_id,
avg(amount) v
from salary a join employee b
using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7),department_id
with rollup
)
select
a.pay_month,a.department_id,
case
when a.v>b.v then "higher"
when a.v<b.v then "lower"
else "same"
end comparison
from(
select * from cte where pay_month is not null and department_id is not null
) a join (
select * from cte where pay_month is not null and department_id is null
) b using(pay_month);
pay_month department_id comparison
--------- ------------- ------------
2017-02 1 same
2017-02 2 same
2017-03 1 higher
2017-03 2 lower
日期操作
date_sub函数
示例:1107. 每日新用户统计
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| activity | enum('login','logout','jobs','groups','homepage') |
| activity_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | activity | activity_date |
+---------+----------+---------------+
| 1 | login | 2019-05-01 |
| 1 | homepage | 2019-05-01 |
| 1 | logout | 2019-05-01 |
| 2 | login | 2019-06-21 |
| 2 | logout | 2019-06-21 |
| 3 | login | 2019-01-01 |
| 3 | jobs | 2019-01-01 |
| 3 | logout | 2019-01-01 |
| 4 | login | 2019-06-21 |
| 4 | groups | 2019-06-21 |
| 4 | logout | 2019-06-21 |
| 5 | login | 2019-03-01 |
| 5 | logout | 2019-03-01 |
| 5 | login | 2019-06-21 |
| 5 | logout | 2019-06-21 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Traffic", db_config)
print(df)
查询从今天起最多 90 天内,每个日期该日期首次登录的用户数。假设今天是 2019-06-30.
思路:
- 过滤出每个用户的登录数据
- 标记这是每个用户第几次登录
- 过滤第一次登录并判断登录时间是否在一个月之内
- 分组计数
select
login_date,count(user_id) user_count
from(
select
user_id,activity_date login_date,
row_number() over(partition by user_id order by activity_date) rn
from traffic
where activity="login"
) a
where a.rn=1 and login_date>=subdate('2019-06-30', 90)
group by login_date;
login_date user_count
---------- ------------
2019-05-01 1
2019-06-21 2
注意:
subdate(‘2019-06-30’, 90)等价于date_sub(‘2019-06-30’, interval 90 day)
adddate(‘2019-06-30’, 90)等价于date_add(‘2019-06-30’, interval 90 day)
示例:1098. 小众书籍
数据:
type_md = """
| book_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| available_from | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| book_id | name | available_from |
| ------- | ---------------- | -------------- |
| 1 | Kalila And Demna | 2010-01-01 |
| 2 | 28 Letters | 2012-05-12 |
| 3 | The Hobbit | 2019-06-10 |
| 4 | 13 Reasons Why | 2019-06-01 |
| 5 | The Hunger Games | 2008-09-21 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "books", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| order_id | int |
| book_id | int |
| quantity | int |
| dispatch_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| order_id | book_id | quantity | dispatch_date |
| -------- | ------- | -------- | ------------- |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 2018-07-26 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 2018-11-05 |
| 3 | 3 | 8 | 2019-06-11 |
| 4 | 4 | 6 | 2019-06-05 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 2019-06-20 |
| 6 | 5 | 9 | 2009-02-02 |
| 7 | 5 | 8 | 2010-04-13 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Orders", db_config)
print(df)
筛选出过去一年中订单总量 少于10本 的 书籍 。
注意:不考虑 上架(available from)距今 不满一个月 的书籍。并且 假设今天是 2019-06-23 。
首先我们查询每本书过去一年的订单:
select
a.book_id,name,available_from,quantity,dispatch_date
from books a left join orders b
on a.book_id=b.book_id and dispatch_date>=date_sub('2019-06-23', interval 1 year)
book_id name available_from quantity dispatch_date
------- ---------------- -------------- -------- ---------------
1 Kalila And Demna 2010-01-01 1 2018-11-05
1 Kalila And Demna 2010-01-01 2 2018-07-26
2 28 Letters 2012-05-12 (NULL) (NULL)
3 The Hobbit 2019-06-10 8 2019-06-11
4 13 Reasons Why 2019-06-01 5 2019-06-20
4 13 Reasons Why 2019-06-01 6 2019-06-05
5 The Hunger Games 2008-09-21 (NULL) (NULL)
然后过滤掉上架不满一个月的书籍:
select
a.book_id,name,available_from,quantity,dispatch_date
from books a left join orders b
on a.book_id=b.book_id and dispatch_date>=date_sub('2019-06-23', interval 1 year)
where available_from <= date_sub('2019-06-23', interval 1 month);
最终就可以找出小众书籍:
select
a.book_id,
any_value(a.name) `name`
from books a left join orders b
on a.book_id=b.book_id and dispatch_date>=date_sub('2019-06-23', interval 1 year)
where available_from <= date_sub('2019-06-23', interval 1 month)
group by a.book_id
having ifnull(sum(quantity),0)<10;
datediff函数
上面的问题同样可以使用datediff函数来进行判断,datediff用于计算两个日期之间相差的天数。
示例:1142. 过去30天的用户活动 II
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| session_id | int |
| activity_date | date |
| activity_type | enum('open_session', 'end_session', 'scroll_down', 'send_message') |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | session_id | activity_date | activity_type |
| ------- | ---------- | ------------- | ------------- |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | open_session |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | scroll_down |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | end_session |
| 2 | 4 | 2019-07-20 | open_session |
| 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | send_message |
| 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | end_session |
| 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | open_session |
| 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | send_message |
| 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | end_session |
| 3 | 5 | 2019-07-21 | open_session |
| 3 | 5 | 2019-07-21 | scroll_down |
| 3 | 5 | 2019-07-21 | end_session |
| 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | open_session |
| 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | end_session |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Activity", db_config)
print(df)
查询以查找截至 2019-07-27(含)的 30 天内每个用户的平均会话数,四舍五入到小数点后两位。只统计那些会话期间用户至少进行一项活动的有效会话。
总会话数 除以 总用户数,即可得到每个用户的平均会话数:
select
round(
ifnull(
count(distinct session_id)/count(distinct user_id)
,0)
,2) average_sessions_per_user
from activity
where datediff("2019-07-27",activity_date)<30;
timestampdiff函数
语法:timestampdiff(unit, begin, end)
unit支持的参数:
- 秒:second
- 分钟:minute
- 小时:hour
- 天:day
- 周:week
- 月:month
- 季:quarter
- 年:year
相对于datediff函数timestampdiff支持任意单位。
示例:2394. 开除员工
数据:
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| needed_hours | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | needed_hours |
| ----------- | ------------ |
| 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 12 |
| 3 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employees", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| in_time | datetime |
| out_time | datetime |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | in_time | out_time |
| ----------- | ------------------- | ------------------- |
| 1 | 2022-10-01 09:00:00 | 2022-10-01 17:00:00 |
| 1 | 2022-10-06 09:05:04 | 2022-10-06 17:09:03 |
| 1 | 2022-10-12 23:00:00 | 2022-10-13 03:00:01 |
| 2 | 2022-10-29 12:00:00 | 2022-10-29 23:58:58 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Logs", db_config)
print(df)
表: Employees每一行都包含员工的 id 和他们获得工资所需的最低工作时数。employee_id 是该表的主键。
表: Logs每一行都显示了员工的工作时间。in_time 是员工开始工作的时间,out_time 是员工结束工作的时间。out_time 可以是 in_time 之后的一天,意味着该员工在午夜之后工作。
个员工每个月必须工作一定的小时数。员工在工作段中工作。员工工作的小时数可以通过员工在所有工作段中工作的分钟数的总和来计算。每个工作段的分钟数是四舍五入的。
- 例如,如果员工在一个时间段中工作了
51分2秒,我们就认为它是52分钟。查询没有达到工作所需时间的员工的 id。
首先统计每个员工工作的分钟数和所需的最低分钟数:
select
a.employee_id,
sum(ceil(timestampdiff(second,in_time,out_time)/60)) t,
any_value(needed_hours*60) needed_minutes
from employees a left join logs b using(employee_id)
group by a.employee_id
employee_id t needed_minutes
----------- ------ ----------------
1 1205 1200
2 719 720
3 (NULL) 120
然后找出不达标的员工:
select
employee_id
from(
select
a.employee_id,
sum(ceil(timestampdiff(second,in_time,out_time)/60)) t,
any_value(needed_hours*60) needed_minutes
from employees a left join logs b using(employee_id)
group by a.employee_id
) a
where t is null or t<needed_minutes;
employee_id
-------------
2
3
weekday计算星期几
weekday对一个日期返回0-6的数字,分别表示从周一到周日。
示例:2298. 周末任务计数
数据:
type_md = """
| task_id | int |
| assignee_id | int |
| submit_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| task_id | assignee_id | submit_date |
| ------- | ----------- | ----------- |
| 1 | 1 | 2022-06-13 |
| 2 | 6 | 2022-06-14 |
| 3 | 6 | 2022-06-15 |
| 4 | 3 | 2022-06-18 |
| 5 | 5 | 2022-06-19 |
| 6 | 7 | 2022-06-19 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Tasks", db_config)
print(df)
task_id 是此表的主键,每一行都包含任务 ID、委托人 ID 和提交日期。
查询:
- 在周末 (周六,周日) 提交的任务的数量
weekend_cnt - 工作日内提交的任务数
working_cnt。
select
sum(weekday(submit_date) in (5,6)) weekend_cnt,
sum(weekday(submit_date) between 0 and 4) working_cnt
from tasks;
weekend_cnt working_cnt
----------- -------------
3 3
示例:1479. 周内每天的销售情况
数据:
type_md = """
| order_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| item_id | varchar(20) |
| quantity | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| order_id | customer_id | order_date | item_id | quantity |
| -------- | ----------- | ---------- | ------- | -------- |
| 1 | 1 | 2020-06-01 | 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 1 | 2020-06-08 | 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 2 | 2020-06-02 | 1 | 5 |
| 4 | 3 | 2020-06-03 | 3 | 5 |
| 5 | 4 | 2020-06-04 | 4 | 1 |
| 6 | 4 | 2020-06-05 | 5 | 5 |
| 7 | 5 | 2020-06-05 | 1 | 10 |
| 8 | 5 | 2020-06-14 | 4 | 5 |
| 9 | 5 | 2020-06-21 | 3 | 5 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Orders", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| item_id | varchar(20) |
| item_name | varchar(20) |
| item_category | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| item_id | item_name | item_category |
| ------- | -------------- | ------------- |
| 1 | LC Alg. Book | Book |
| 2 | LC DB. Book | Book |
| 3 | LC SmarthPhone | Phone |
| 4 | LC Phone 2020 | Phone |
| 5 | LC SmartGlass | Glasses |
| 6 | LC T-Shirt XL | T-shirt |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Items", db_config)
print(df)
查询 周内每天 每个商品类别下订购了多少单位,返回结果 按商品类别排序 。
首先统计周内每天每类商品的销售额:
select
item_category category,
weekday(order_date) week,
sum(ifnull(quantity,0)) q
from items left join orders using(item_id)
group by 1,2
category week q
-------- ------ --------
Book 4 10
Book 1 5
Book 0 20
Phone 6 10
Phone 2 5
Phone 3 1
Glasses 4 5
T-shirt (NULL) 0
然后进行透视得到结果:
select
category,
sum(if(week=0,q,0)) Monday,
sum(if(week=1,q,0)) Tuesday,
sum(if(week=2,q,0)) Wednesday,
sum(if(week=3,q,0)) Thursday,
sum(if(week=4,q,0)) Friday,
sum(if(week=5,q,0)) Saturday,
sum(if(week=6,q,0)) Sunday
from(
select
item_category category,
weekday(order_date) week,
sum(ifnull(quantity,0)) q
from items left join orders using(item_id)
group by 1,2
) a
group by 1
order by 1;
category Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday
-------- ------ ------- --------- -------- ------ -------- --------
Book 20 5 0 0 10 0 0
Glasses 0 0 0 0 5 0 0
Phone 0 0 5 1 0 0 10
T-shirt 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
date_format日期格式化
语法 DATE_FORMAT(date,format)
date参数是合法的日期。format规定日期/时间的输出格式。 可以使用的格式有:
格式 描述
%a 缩写星期名
%b 缩写月名
%c 月,数值
%D 带有英文前缀的月中的天
%d 月的天,数值(00-31)
%e 月的天,数值(0-31)
%f 微秒
%H 小时 (00-23)
%h 小时 (01-12)
%I 小时 (01-12)
%i 分钟,数值(00-59)
%j 年的天 (001-366)
%k 小时 (0-23)
%l 小时 (1-12)
%M 月名
%m 月,数值(00-12)
%p AM 或 PM
%r 时间,12-小时(hh:mm:ss AM 或 PM)
%S 秒(00-59)
%s 秒(00-59)
%T 时间, 24-小时 (hh:mm:ss)
%U 周 (00-53) 星期日是一周的第一天
%u 周 (00-53) 星期一是一周的第一天
%V 周 (01-53) 星期日是一周的第一天,与 %X 使用
%v 周 (01-53) 星期一是一周的第一天,与 %x 使用
%W 星期名
%w 周的天 (0=星期日, 6=星期六)
%X 年,其中的星期日是周的第一天,4 位,与 %V 使用
%x 年,其中的星期一是周的第一天,4 位,与 %v 使用
%Y 年,4 位
%y 年,2 位
示例:1853. 转换日期格式
sql_txt = """
Create table If Not Exists Days (day date)
Truncate table Days
insert into Days (day) values ('2022-04-12')
insert into Days (day) values ('2021-08-09')
insert into Days (day) values ('2020-06-26')
"""
SQL_Schema_import(sql_txt)
将Days表中的每一个日期转化为"day_name, month_name day, year"格式的字符串。
select date_format(day,"%W, %M %e, %Y") day from days
day
-------------------------
Tuesday, April 12, 2022
Monday, August 9, 2021
Friday, June 26, 2020
日期区间拆分为年份
示例:1384. 按年度列出销售总额
数据:
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | product_name |
| ---------- | ------------ |
| 1 | LC Phone |
| 2 | LC T-Shirt |
| 3 | LC Keychain |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Product", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| period_start | date |
| period_end | date |
| average_daily_sales | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | period_start | period_end | average_daily_sales |
| ---------- | ------------ | ---------- | ------------------- |
| 1 | 2019-01-25 | 2019-02-28 | 100 |
| 2 | 2018-12-01 | 2020-01-01 | 10 |
| 3 | 2019-12-01 | 2020-01-31 | 1 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Sales", db_config)
print(df)
查询每个产品每年的总销售额,并包含 product_id, product_name 以及 report_year 等信息。
销售年份介于 2018 年到 2020 年之间,结果需要按 product_id 和 report_year 排序。
对于这题难点在于如何按年拆分日期,首先我们先生成2018 年到 2020 年日期序列(相关基础见生成序列并统计一节):
select yr from(values row(2018), row(2019), row(2020)) yr_t(yr);
yr
--------
2018
2019
2020
使用makedate函数,即可基于该年创建日期:
select
yr,makedate(yr,1),makedate(yr+1,1)
from(values row(2018), row(2019), row(2020)) yr_t(yr);
yr makedate(yr,1) makedate(yr+1,1)
------ -------------- ------------------
2018 2018-01-01 2019-01-01
2019 2019-01-01 2020-01-01
2020 2020-01-01 2021-01-01
makedate的第二个参数为dayofyear,表示第几天,但每一年的总天数是不确定的,所以为了表示2018年,使用[2018-01-01,2019-01-01)。
下面我们将销售数据拆分到每一年:
select
product_id,
yr report_year,
average_daily_sales,
period_start,period_end,
greatest(period_start,makedate(yr,1)) start_date,
least(adddate(period_end,1),makedate(yr+1,1)) end_date
from (values row(2018), row(2019), row(2020)) yr_t(yr)
join sales on yr between year(period_start) and year(period_end)
order by 1,2;
然后我们可以看到拆分效果:
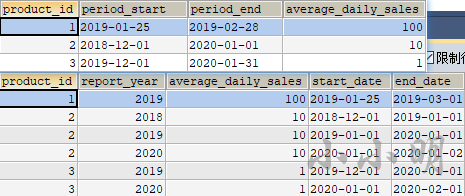
可以看到,区间被完美的拆分到每个年份中。
最终结果:
select
a.product_id,
b.product_name,
report_year,
average_daily_sales*datediff(end_date,start_date) total_amount
from(
select
product_id,
convert(yr,char) report_year,
average_daily_sales,
greatest(period_start,makedate(yr,1)) start_date,
least(adddate(period_end,1),makedate(yr+1,1)) end_date
from (values row(2018), row(2019), row(2020)) yr_t(yr)
join sales on yr between year(period_start) and year(period_end)
) a join product b using(product_id)
order by product_id,report_year;
product_id product_name report_year total_amount
---------- ------------ ----------- --------------
1 LC Phone 2019 3500
2 LC T-Shirt 2018 310
2 LC T-Shirt 2019 3650
2 LC T-Shirt 2020 10
3 LC Keychain 2019 31
3 LC Keychain 2020 31
注意:convert(yr,char)是因为原题要求报告年份为字符串类型。
窗口函数
排名函数
示例:178. 分数排名
数据:
type_md = """
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| id | int |
| score | decimal(10,2) |
+-------------+---------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+-------+
| id | score |
+----+-------+
| 1 | 3.50 |
| 2 | 3.65 |
| 3 | 4.00 |
| 4 | 3.85 |
| 5 | 4.00 |
| 6 | 3.65 |
+----+-------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Scores", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
注意:明显需要保留2位小数,所以需要给decimal类型指定长度,手工将decimal修改为decimal(10,2)
看看四种排名窗口的效果:
select
*,
row_number() over(order by score) rn1,
rank() over(order by score) rn2,
dense_rank() over(order by score) rn3,
ntile(2) over(order by score) rn4,
ntile(4) over(order by score) rn5
from scores;
结果:
id score rn1 rn2 rn3 rn4 rn5
------ ------ ------ ------ ------ ------ --------
1 3.50 1 1 1 1 1
2 3.65 2 2 2 1 1
6 3.65 3 2 2 1 2
4 3.85 4 4 3 2 2
3 4.00 5 5 4 2 3
5 4.00 6 5 4 2 4
解释:
- row_number():会保持序号递增不重复,相同数值按出现顺序排名。
- rank():相同数值排名相同,在名次中会留下空位。
- dense_rank():相同数值排名相同,在名次中不会留下空位。
- ntile(group_num):将所有记录分成group_num个组,每组序号一样。如果切片不均匀,默认增加前面切片的分布。
注意:排名函数均不支持WINDOW子句。(即ROWS BETWEEN语句)
还有两种不常用的排名函数:
select
*,
round(cume_dist() over(order by score),2) rn1,
rank() over(order by score) `rank`,
round(percent_rank() over(order by score),2) rn2
from scores;
结果:
id score rn1 rank rn2
------ ------ ------ ------ --------
1 3.50 0.17 1 0
2 3.65 0.5 2 0.2
6 3.65 0.5 2 0.2
4 3.85 0.67 4 0.6
3 4.00 1 5 0.8
5 4.00 1 5 0.8
解释:
- CUME_DIST:小于等于当前值的行数/分组内总行数
- PERCENT_RANK:(分组内当前行的RANK值-1)/(分组内总行数-1)
偏移分析窗口函数
偏移分析函数的基本用法:
LAG,LEAD,FIRST_VALUE,LAST_VALUE这四个窗口函数属于偏移分析函数,不支持WINDOW子句。
LAG(col,n,DEFAULT) 用于统计窗口内往上第n行值
第一个参数为列名,第二个参数为往上第n行(可选,默认为1),第三个参数为默认值(当往上第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)。
LEAD(col,n,DEFAULT) 用于统计窗口内往下第n行值
第一个参数为列名,第二个参数为往下第n行(可选,默认为1),第三个参数为默认值(当往下第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)。
FIRST_VALUE取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,第一个值。
LAST_VALUE取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,最后一个值。
在使用偏移分析函数的过程中,要特别注意ORDER BY子句。
197. 上升的温度
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| recordDate | date |
| temperature | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | recordDate | temperature |
| -- | ---------- | ----------- |
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Weather", db_config)
print(df)
编写一个 SQL 查询,查找与昨天的日期相比温度更高的所有日期的 id 。
select
id
from(
select id,Temperature,lag(Temperature) over(order by recordDate) last_t from Weather
) a
where a.Temperature>a.last_t;
id
--------
2
4
示例:1939. 主动请求确认消息的用户
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| time_stamp | datetime |
| action | ENUM('confirmed','timeout') |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | time_stamp | action |
| ------- | ------------------- | --------- |
| 3 | 2021-01-06 03:30:46 | timeout |
| 3 | 2021-01-06 03:37:45 | timeout |
| 7 | 2021-06-12 11:57:29 | confirmed |
| 7 | 2021-06-13 11:57:30 | confirmed |
| 2 | 2021-01-22 00:00:00 | confirmed |
| 2 | 2021-01-23 00:00:00 | timeout |
| 6 | 2021-10-23 14:14:14 | confirmed |
| 6 | 2021-10-24 14:14:13 | timeout |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Confirmations", db_config)
print(df)
Confirmations表每一行都表示 ID 为 user_id 的用户在 time_stamp 请求了确认消息,并且该确认消息已被确认(‘confirmed’)或已过期(‘timeout’)。
查找在 24 小时窗口内(含)两次请求确认消息的用户的 ID。
可以先查询每个用户的下次确认时间:
select
user_id,
time_stamp,
lead(time_stamp) over(partition by user_id order by time_stamp) next
from Confirmations
user_id time_stamp next
------- ------------------- ---------------------
2 2021-01-22 00:00:00 2021-01-23 00:00:00
2 2021-01-23 00:00:00 (NULL)
3 2021-01-06 03:30:46 2021-01-06 03:37:45
3 2021-01-06 03:37:45 (NULL)
6 2021-10-23 14:14:14 2021-10-24 14:14:13
6 2021-10-24 14:14:13 (NULL)
7 2021-06-12 11:57:29 2021-06-13 11:57:30
7 2021-06-13 11:57:30 (NULL)
然后判断两次相隔的时间是否在一天之内即可:
select
distinct user_id
from(
select
user_id,
time_stamp,
lead(time_stamp) over(partition by user_id order by time_stamp) next
from Confirmations
) a
where next<=adddate(time_stamp,1);
user_id
---------
2
3
6
示例:1709. 访问日期之间最大的空档期
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| visit_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | visit_date |
| ------- | ---------- |
| 1 | 2020-11-28 |
| 1 | 2020-10-20 |
| 1 | 2020-12-3 |
| 2 | 2020-10-5 |
| 2 | 2020-12-9 |
| 3 | 2020-11-11 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "UserVisits", db_config)
print(df)
假设今天的日期是 '2021-1-1' 。
编写 SQL 语句,对于每个 user_id ,求出每次访问及其下一个访问(若该次访问是最后一次,则为今天)之间最大的空档期天数 window 。
返回结果表,按用户编号 user_id 排序。
首先求出每次访问到下次访问的空档天数:
select
user_id,visit_date,
lead(visit_date,1,"2021-1-1") over(partition by user_id order by visit_date) next_date,
datediff(lead(visit_date,1,"2021-1-1") over(partition by user_id order by visit_date),visit_date) w
from uservisits
user_id visit_date next_date w
------- ---------- ---------- --------
1 2020-10-20 2020-11-28 39
1 2020-11-28 2020-12-03 5
1 2020-12-03 2021-1-1 29
2 2020-10-05 2020-12-09 65
2 2020-12-09 2021-1-1 23
3 2020-11-11 2021-1-1 51
然后统计每个用户的最大空档天数:
select
user_id,
max(w) biggest_window
from(
select
user_id,
datediff(lead(visit_date,1,"2021-1-1") over(partition by user_id order by visit_date),visit_date) w
from uservisits
) a
group by 1
order by 1;
user_id biggest_window
------- ----------------
1 39
2 65
3 51
统计分析函数
统计分析函数的基本用法:
SUM、AVG、MIN、MAX这四个窗口函数属于统计分析函数,支持WINDOW子句。
示例:1204. 最后一个能进入电梯的人
数据:
type_md = """
| person_id | int |
| person_name | varchar(20) |
| weight | int |
| turn | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| person_id | person_name | weight | turn |
| --------- | ----------- | ------ | ---- |
| 5 | Alice | 250 | 1 |
| 4 | Bob | 175 | 5 |
| 3 | Alex | 350 | 2 |
| 6 | John Cena | 400 | 3 |
| 1 | Winston | 500 | 6 |
| 2 | Marie | 200 | 4 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Queue", db_config)
print(df)
有一群人在等着上公共汽车。巴士有1000 公斤的重量限制,所以可能会有一些人不能上。
查询 最后一个 能进入电梯且不超过重量限制的 person_name 。数据确保队列中第一位的人可以进入电梯,不会超重。
首先计算每个人进入电梯后的累积重量:
select
person_name,
sum(weight) over(order by turn) weight
from Queue;
person_name weight
----------- --------
Alice 250
Alex 600
John Cena 1000
Marie 1200
Bob 1375
Winston 1875
然后筛选并取最大:
select
person_name
from(
select
person_name,
sum(weight) over(order by turn) weight
from Queue
) a
where weight<=1000
order by weight desc limit 1;
很明显John Cena是最后一个体重合适并进入电梯的人。
示例:2066. 账户余额
数据:
type_md = """
| account_id | int |
| day | date |
| type | ENUM('Deposit','Withdraw') |
| amount | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| account_id | day | type | amount |
| ---------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ |
| 1 | 2021-11-07 | Deposit | 2000 |
| 1 | 2021-11-09 | Withdraw | 1000 |
| 1 | 2021-11-11 | Deposit | 3000 |
| 2 | 2021-12-07 | Deposit | 7000 |
| 2 | 2021-12-12 | Withdraw | 7000 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Transactions", db_config)
print(df)
交易类型(type)字段包括了两种行为:存入 (‘Deposit’), 取出(‘Withdraw’).
查询用户每次交易完成后的账户余额,所有用户在进行交易前的账户余额都为0。数据保证所有交易行为后的余额不为负数。
返回的结果按照 账户(account_id), 日期( day ) 进行升序排序 。
select
account_id,day,
sum(if(type="Deposit",amount,-amount)) over(partition by account_id order by day) balance
from transactions
order by 1,2;
account_id day balance
---------- ---------- ---------
1 2021-11-07 2000
1 2021-11-09 1000
1 2021-11-11 4000
2 2021-12-07 7000
2 2021-12-12 0
count也支持窗口函数
示例:1369. 获取最近第二次的活动
数据:
type_md = """
| username | varchar(20) |
| activity | varchar(20) |
| startDate | Date |
| endDate | Date |
"""
sql_text = """
| username | activity | startDate | endDate |
| -------- | -------- | ---------- | ---------- |
| Alice | Travel | 2020-02-12 | 2020-02-20 |
| Alice | Dancing | 2020-02-21 | 2020-02-23 |
| Alice | Travel | 2020-02-24 | 2020-02-28 |
| Bob | Travel | 2020-02-11 | 2020-02-18 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "UserActivity", db_config)
print(df)
查询每一位用户 最近第二次 的活动,如果用户仅有一次活动,返回该活动
数据保证一个用户不能同时多项活动。
首先标记每个用户的第几次活动和总活动次数:
select
*,
rank() over(partition by username order by startDate desc) rk,
count(1) over(partition by username) cnt
from UserActivity;
username activity startdate enddate rk cnt
-------- -------- ---------- ---------- ------ --------
Alice Travel 2020-02-24 2020-02-28 1 3
Alice Dancing 2020-02-21 2020-02-23 2 3
Alice Travel 2020-02-12 2020-02-20 3 3
Bob Travel 2020-02-11 2020-02-18 1 1
最后再过滤:
select
username,activity,startDate,endDate
from(
select
*,
rank() over(partition by username order by startDate desc) rk,
count(1) over(partition by username) cnt
from UserActivity
) a
where a.rk=2 or a.cnt=1;
username activity startDate endDate
-------- -------- ---------- ------------
Alice Dancing 2020-02-21 2020-02-23
Bob Travel 2020-02-11 2020-02-18
示例:1972. 同一天的第一个电话和最后一个电话
数据:
type_md = """
| caller_id | int |
| recipient_id | int |
| call_time | datetime |
"""
sql_text = """
| caller_id | recipient_id | call_time |
| --------- | ------------ | ------------------- |
| 8 | 4 | 2021-08-24 17:46:07 |
| 4 | 8 | 2021-08-24 19:57:13 |
| 5 | 1 | 2021-08-11 05:28:44 |
| 8 | 3 | 2021-08-17 04:04:15 |
| 11 | 3 | 2021-08-17 13:07:00 |
| 8 | 11 | 2021-08-17 22:22:22 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Calls", db_config)
print(df)
(caller_id, recipient_id, call_time) 是Calls表的主键。
查询在任意一天的第一个电话和最后一个电话都是和同一个人的,拨打者和接收者均记录。
首先标记每个通话者每天的的通话序号:
select
u1,u2,date(call_time) dt,call_time,
row_number() over(partition by u1,date(call_time) order by call_time) rn,
count(1) over(partition by u1,date(call_time)) num
from(
select caller_id u1,recipient_id u2,call_time from calls
union all
select recipient_id,caller_id,call_time from calls
) a;
u1 u2 dt call_time rn num
------ ------ ---------- ------------------- ------ --------
1 5 2021-08-11 2021-08-11 05:28:44 1 1
3 8 2021-08-17 2021-08-17 04:04:15 1 2
3 11 2021-08-17 2021-08-17 13:07:00 2 2
4 8 2021-08-24 2021-08-24 17:46:07 1 2
4 8 2021-08-24 2021-08-24 19:57:13 2 2
5 1 2021-08-11 2021-08-11 05:28:44 1 1
8 3 2021-08-17 2021-08-17 04:04:15 1 2
8 11 2021-08-17 2021-08-17 22:22:22 2 2
8 4 2021-08-24 2021-08-24 17:46:07 1 2
8 4 2021-08-24 2021-08-24 19:57:13 2 2
11 3 2021-08-17 2021-08-17 13:07:00 1 2
11 8 2021-08-17 2021-08-17 22:22:22 2 2
然后后过滤出每个用户每天首次和最后一次通话的对象:
select
u1,u2,dt
from(
select
u1,u2,date(call_time) dt,
row_number() over(partition by u1,date(call_time) order by call_time) rn,
count(1) over(partition by u1,date(call_time)) num
from(
select caller_id u1,recipient_id u2,call_time from calls
union all
select recipient_id,caller_id,call_time from calls
) a
) b
where rn=1 or rn=num;
u1 u2 dt
------ ------ ------------
1 5 2021-08-11
3 8 2021-08-17
3 11 2021-08-17
4 8 2021-08-24
4 8 2021-08-24
5 1 2021-08-11
8 3 2021-08-17
8 11 2021-08-17
8 4 2021-08-24
8 4 2021-08-24
11 3 2021-08-17
11 8 2021-08-17
最后找出某天某个用户的首次和最后一次通话对象一致的用户:
select
distinct u1 user_id
from(
select
u1,u2,date(call_time) dt,
row_number() over(partition by u1,date(call_time) order by call_time) rn,
count(1) over(partition by u1,date(call_time)) num
from(
select caller_id u1,recipient_id u2,call_time from calls
union all
select recipient_id,caller_id,call_time from calls
) a
) b
where rn=1 or rn=num
group by u1,dt
having count(distinct u2)=1;
user_id
---------
1
4
5
8
window子句ROWS与RANGE的区别
window子句:
如果指定ORDER BY,不指定ROWS BETWEEN,默认为从起点到当前行,相当于:
ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW
或
ROWS UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
如果不指定ORDER BY,则将分组内所有值累加,相当于:
ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
分组内当前行+往前3行:
ROWS BETWEEN 3 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW
或
ROWS 3 PRECEDING
分组内往前3行到往后1行:
ROWS BETWEEN 3 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING
分组内当前行+往后所有行:
ROWS BETWEEN CURRENT ROW AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
WINDOW子句各项含义:
- PRECEDING:往前
- FOLLOWING:往后
- CURRENT ROW:当前行
- UNBOUNDED:起点
- UNBOUNDED PRECEDING:表示从前面的起点
- UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING:表示到后面的终点
ROWS是以实际的数据行排序,RANGE是逻辑上的排序,例如order by指定月份字段时,如果存在缺失月份,也会被考虑进去。
示例:1321. 餐馆营业额变化增长
数据:
type_md = """
| customer_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| visited_on | date |
| amount | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| customer_id | name | visited_on | amount |
| ----------- | ------- | ---------- | ------ |
| 1 | Jhon | 2019-01-01 | 100 |
| 2 | Daniel | 2019-01-02 | 110 |
| 3 | Jade | 2019-01-03 | 120 |
| 4 | Khaled | 2019-01-04 | 130 |
| 5 | Winston | 2019-01-05 | 110 |
| 6 | Elvis | 2019-01-06 | 140 |
| 7 | Anna | 2019-01-07 | 150 |
| 8 | Maria | 2019-01-08 | 80 |
| 9 | Jaze | 2019-01-09 | 110 |
| 1 | Jhon | 2019-01-10 | 130 |
| 3 | Jade | 2019-01-10 | 150 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Customer", db_config)
print(df)
(customer_id, visited_on) 是该表的主键,
visited_on 表示 customer_id 的顾客访问餐馆的日期,amount 表示消费总额。
现在需要分析营业额变化增长(每天至少有一位顾客)。
查询计算以 7 天(某日期 + 该日期前的 6 天)为一个窗口的顾客消费平均值。average_amount 要保留两位小数,查询结果按 visited_on 排序。
首先查询每天的营业额,以及近7天的累积营业额:
select
visited_on,
sum(amount) amount,
sum(sum(amount)) over(order by visited_on rows 6 preceding) accu_amount,
rank() over(order by visited_on) rn
from customer
group by visited_on
visited_on amount accu_amount rn
---------- ------ ----------- --------
2019-01-01 100 100 1
2019-01-02 110 210 2
2019-01-03 120 330 3
2019-01-04 130 460 4
2019-01-05 110 570 5
2019-01-06 140 710 6
2019-01-07 150 860 7
2019-01-08 80 840 8
2019-01-09 110 840 9
2019-01-10 280 1000 10
然后计算7日平均:
select
visited_on,amount,
round(amount/least(rn,7),2) average_amount
from(
select
visited_on,
sum(sum(amount)) over(order by visited_on rows 6 preceding) amount,
rank() over(order by visited_on) rn
from customer
group by visited_on
) a;
visited_on amount average_amount
---------- ------ ----------------
2019-01-01 100 100.00
2019-01-02 210 105.00
2019-01-03 330 110.00
2019-01-04 460 115.00
2019-01-05 570 114.00
2019-01-06 710 118.33
2019-01-07 860 122.86
2019-01-08 840 120.00
2019-01-09 840 120.00
2019-01-10 1000 142.86
不过题目只需要具备7天窗口的数据:
select
visited_on,amount,
round(amount/7,2) average_amount
from(
select
visited_on,
sum(sum(amount)) over(order by visited_on rows 6 preceding) amount,
rank() over(order by visited_on) rn
from customer
group by visited_on
) a
where rn>=7;
visited_on amount average_amount
---------- ------ ----------------
2019-01-07 860 122.86
2019-01-08 840 120.00
2019-01-09 840 120.00
2019-01-10 1000 142.86
示例:579. 查询员工的累计薪水
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| Month | int |
| Salary | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | month | salary |
| -- | ----- | ------ |
| 1 | 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 1 | 20 |
| 1 | 2 | 30 |
| 2 | 2 | 30 |
| 3 | 2 | 40 |
| 1 | 3 | 40 |
| 3 | 3 | 60 |
| 1 | 4 | 60 |
| 3 | 4 | 70 |
| 1 | 7 | 90 |
| 1 | 8 | 90 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df)
题目要求查询每个员工除最近一个月(即最大月)之外,剩下每个月的近三个月的累计薪水(不足三个月也要计算)。
我们看看rows和range的区别:
select
id,month,salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by id order by month rows 2 preceding) s1,
sum(salary) over(partition by id order by month range 2 preceding) s2
from employee;
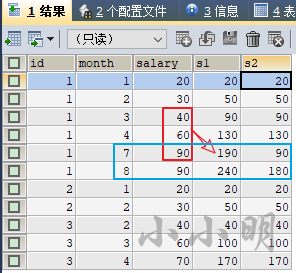
可以清楚看到range是逻辑上窗口,不连续的月默认为空;rows则严格按照数据行为准。
结果要求按 Id 升序, Month 降序显示。
那么就非常简单了:
select
id,month,salary
from(
select
id,month,
sum(salary) over(partition by id order by month rows 2 preceding) salary,
max(month) over(partition by id) mn
from employee
) a
where month<>mn
order by id,month desc;
结果:
id month salary
------ ------ --------
1 1 20
1 2 50
1 3 90
1 4 130
1 7 190
2 1 20
3 2 40
3 3 100
或者使用rank过滤最近一个月:
select
id,month,salary
from(
select
id,month,
sum(salary) over(partition by id order by month rows 2 preceding) salary,
rank() over(partition by id order by month desc) rk
from employee
) a
where rk>1
order by id,month desc;
窗口函数可以执行在group by之后
示例:574. 当选者
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | name |
| -- | ---- |
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | D |
| 5 | E |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Candidate", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| id | int |
| candidateId | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | candidateId |
| -- | ----------- |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 5 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Vote", db_config)
print(df)
Candidate表示候选对象的id和名称的信息,Vote每一行决定了在选举中获得第i张选票的候选人。
现在要求查询出获得最多选票的候选人,我们可以先查询出每个候选人获取的选票:
select
name, count(b.id) cnt
from Candidate a join Vote b on a.id=b.candidateid
group by candidateid;
name cnt
------ --------
B 2
D 1
C 1
E 1
然后我们可以直接在聚合函数的基础上使用窗口函数,而无需使用子查询:
select
name, rank() over(order by count(b.id) desc) rn
from Candidate a join Vote b on a.id=b.candidateid
group by candidateid;
name rn
------ --------
B 1
D 2
C 2
E 2
但是mysql的having不支持对窗口函数的结果进行操作,此时我们必须使用子查询得到结果:
select name from(
select
name, rank() over(order by count(b.id) desc) rn
from Candidate a join Vote b on a.id=b.candidateid
group by candidateid
) t
where rn=1;
name
--------
B
当然对于本题而言,题目限制了测试数据能够确保确保 只有一个候选人赢得选举。那么更简单的写法是:
select
name
from Candidate a join Vote b on a.id=b.candidateid
group by candidateid
order by count(b.id) desc limit 1;
但是当可能存在多个候选人同票获得第一的情况,则只能使用窗口函数。
示例:2474. 购买量严格增加的客户
数据:
type_md = """
| order_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| price | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| order_id | customer_id | order_date | price |
| -------- | ----------- | ---------- | ----- |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | 1100 |
| 2 | 1 | 2019-11-01 | 1200 |
| 3 | 1 | 2020-05-26 | 3000 |
| 4 | 1 | 2021-08-31 | 3100 |
| 5 | 1 | 2022-12-07 | 4700 |
| 6 | 2 | 2015-01-01 | 700 |
| 7 | 2 | 2017-11-07 | 1000 |
| 8 | 3 | 2017-01-01 | 900 |
| 9 | 3 | 2018-11-07 | 900 |
| 11 | 6 | 2021-04-16 | 6700 |
| 10 | 6 | 2019-10-11 | 5400 |
| 23 | 6 | 2020-09-21 | 4700 |
| 17 | 6 | 2022-05-13 | 2100 |
| 18 | 6 | 2019-04-21 | 9600 |
| 15 | 6 | 2020-12-27 | 900 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Orders", db_config)
print(df)
order_id 是该表的主键。每行包含订单的 id、订购该订单的客户 id、订单日期和价格。
查询 总购买量 每年严格增加的客户 id。
- 客户在一年内的 总购买量 是该年订单价格的总和。如果某一年客户没有下任何订单,我们认为总购买量为
0。 - 对于每个客户,要考虑的第一个年是他们 第一次下单 的年份。
- 对于每个客户,要考虑的最后一年是他们 最后一次下单 的年份。
首先统计每个客户每年和上一年的总购买量:
select
customer_id,
lag(year(order_date)) over(partition by customer_id order by year(order_date)) ly,
year(order_date) y,
lag(sum(price)) over(partition by customer_id order by year(order_date)) lp,
sum(price) price
from orders
group by customer_id,year(order_date);
customer_id ly y lp price
----------- ------ ------ ------ --------
1 (NULL) 2019 (NULL) 2300
1 2019 2020 2300 3000
1 2020 2021 3000 3100
1 2021 2022 3100 4700
2 (NULL) 2015 (NULL) 700
2 2015 2017 700 1000
3 (NULL) 2017 (NULL) 900
3 2017 2018 900 900
6 (NULL) 2019 (NULL) 15000
6 2019 2020 15000 5600
6 2020 2021 5600 6700
6 2021 2022 6700 2100
要找出每年严格增加的客户,我们可先找出某年未严格增加的客户:
select
distinct customer_id
from(
select
customer_id,
lag(year(order_date)) over(partition by customer_id order by year(order_date)) ly,
year(order_date) y,
lag(sum(price)) over(partition by customer_id order by year(order_date)) lp,
sum(price) price
from orders
group by customer_id,year(order_date)
) a
where ly is not null and (ly+1!=y or lp>=price);
customer_id
-------------
2
3
6
然后一个外连接过滤得到答案:
select
distinct customer_id
from orders left join (
select
distinct customer_id
from(
select
customer_id,
lag(year(order_date)) over(partition by customer_id order by year(order_date)) ly,
year(order_date) y,
lag(sum(price)) over(partition by customer_id order by year(order_date)) lp,
sum(price) price
from orders
group by customer_id,year(order_date)
) a
where ly is not null and (ly+1!=y or lp>=price)
) b using(customer_id)
where b.customer_id is null;
customer_id
-------------
1
排名函数执行在order by上
示例:2308. 按性别排列表格
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| gender | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | gender |
| ------- | ------ |
| 4 | male |
| 7 | female |
| 2 | other |
| 5 | male |
| 3 | female |
| 8 | male |
| 6 | other |
| 1 | other |
| 9 | female |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Genders", db_config)
print(df)
user_id 是该表的主键。gender 的值是 ‘female’, ‘male’,‘other’ 之一。该表中的每一行都包含用户的 ID 及其性别。
重新排列 Genders 表,使行按顺序在 'female', 'other' 和 'male' 之间交替。同时每种性别按照 user_id 升序进行排序。
select
user_id,gender
from genders
order by
rank() over(partition by gender order by user_id),
rank() over(order by length(gender) desc);
user_id gender
------- --------
3 female
1 other
4 male
7 female
2 other
5 male
9 female
6 other
8 male
由于要求的 'female', 'other' 和 'male' 的交替顺序具备字符长度递减的特征,所以我们可以使用长度排序,若不具备这样的特征,则只能使用if或case when进行映射:
select
user_id,gender
from genders
order by
rank() over(partition by gender order by user_id),
if(gender="male",2,if(gender="other",1,0));
或:
select
user_id,gender
from genders
order by
rank() over(partition by gender order by user_id),
case gender
when "female" then 0
when "other" then 1
else 2
end;
排名函数实现多列分别排序
示例:2159. 分别排序两列
数据:
type_md = """
| first_col | int |
| second_col | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| first_col | second_col |
| --------- | ---------- |
| 4 | 2 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 1 | 4 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Data", db_config)
print(df)
编写 SQL 使:
first_col按照 升序 排列。second_col按照 降序 排列。
思路:给要排序的多列分别生成编号,然后对编号进行表连接。
with cte as(
select
first_col,second_col,
row_number() over(order by first_col) rk1,
row_number() over(order by second_col desc) rk2
from data
)
select a.first_col,b.second_col
from cte a join cte b on a.rk1=b.rk2
order by a.rk1;
first_col second_col
--------- ------------
1 4
2 3
3 2
4 1
窗口函数相减为负数会报错
这是因为窗口函数的结果为无符号整数类型UNSIGNED,这时应该使用cast(expression as data_type),将其转换为整数类型,常见的类型有:
- 可带参数 : CHAR()
- 日期 : DATE
- 时间: TIME
- 日期时间型 : DATETIME
- 浮点数 : DECIMAL
- 整数 : SIGNED
- 无符号整数 : UNSIGNED
示例:2175. 世界排名的变化
数据:
type_md = """
| team_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| points | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| team_id | name | points |
| ------- | ----------- | ------ |
| 3 | Algeria | 1431 |
| 1 | Senegal | 2132 |
| 2 | New Zealand | 1402 |
| 4 | Croatia | 1817 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "TeamPoints", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| team_id | int |
| points_change | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| team_id | points_change |
| ------- | ------------- |
| 3 | 399 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 4 | 13 |
| 1 | -22 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "PointsChange", db_config)
print(df)
表TeamPoints:team_id 是主键,每一行代表一支国家队在全球排名中的得分。没有两支队伍代表同一个国家。
表PointsChange:team_id 是这张表的主键。每一行代表一支国家队在世界排名中的得分的变化。0:代表分数没有改变;正数:代表分数增加;负数:代表分数降低。TeamPoints 表中出现的每一个 team_id 均会在这张表中出现。
每支国家队的分数应根据其相应的 points_change 进行更新。查询来计算在分数更新后,每个队伍的全球排名的变化。
首先查询每支国家队之前的排名和分数变化的排名:
select
a.team_id,a.name,
rank() over(order by points desc,name) rn1,
rank() over(order by points+points_change desc,name) rn2
from teampoints a join pointschange b using(team_id);
team_id name rn1 rn2
------- ----------- ------ --------
1 Senegal 1 1
3 Algeria 3 2
4 Croatia 2 3
2 New Zealand 4 4
由于rank函数的返回值是unsigned类型,如果我们直接使用rn1-rn2直接相减会得到错误:BIGINT UNSIGNED value is out of range
此时我们需要转换类型后再相减:
select
team_id,name,
cast(rn1 as signed)-cast(rn2 as signed) rank_diff
from(
select
a.team_id,a.name,
rank() over(order by points desc,name) rn1,
rank() over(order by points+points_change desc,name) rn2
from teampoints a join pointschange b using(team_id)
) c;
team_id name rank_diff
------- ----------- -----------
1 Senegal 0
3 Algeria 1
4 Croatia -1
2 New Zealand 0
顺利得到最终答案。
判断连续性
是否连续相等
示例:180. 连续出现的数字
数据:
type_md = """
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| id | int |
| num | varchar(20) |
+-------------+---------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+-----+
| Id | Num |
+----+-----+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 |
+----+-----+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Logs", db_config)
print(df)
lag+sum判断连续性:
select
num,count(1) cnt
from(
select
id, num,
sum(t) over(order by id) g
from(
select
id, num,
num!=lag(num,1,0) over(order by id) t
from logs
) a
) b
group by num,g;
结果:
num cnt
------ --------
1 3
2 1
1 1
2 2
双row_number序号排名判断连续性:
select
num,count(1) cnt
from(
select
id, num,
row_number() over(order by id) -
row_number() over(partition by num order by id) g
from logs
) a
group by num,g;
与上述结果一致。
题目要求查找所有至少连续出现三次的数字,只需:
select
distinct num ConsecutiveNums
from(
select
id, num,
row_number() over(order by id) -
row_number() over(partition by num order by id) g
from logs
) a
group by num,g
having count(1)>=3;
显然后者更简单。
示例:603. 连续空余座位
数据:
type_md = """
| seat_id | int |
| free | smallint |
"""
sql_text = """
| seat_id | free |
+---------+------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Cinema", db_config)
print(df)
每一行表示第i个座位是否空闲。1表示空闲,0表示被占用。
查询所有连续可用的座位,按 seat_id 升序排序:
select
seat_id
from(
select
seat_id,count(1) over(partition by rn1-rn2) g
from(
select
seat_id,free,
row_number() over(order by seat_id) rn1,
row_number() over(partition by free order by seat_id) rn2
from cinema
) a where free=1
) b
where g>1 order by seat_id;
当然针对本题只需判断一次连续,简易解法为:
select
distinct a.seat_id
from cinema a join cinema b
on abs(a.seat_id-b.seat_id)=1
and a.free=1 and b.free=1
order by a.seat_id;
seat_id
---------
3
4
5
是否连续为某个固定值
示例:2173. 最多连胜的次数
数据:
type_md = """
| player_id | int |
| match_day | date |
| result | enum('Win','Draw','Lose') |
"""
sql_text = """
| player_id | match_day | result |
| --------- | ---------- | ------ |
| 1 | 2022-01-17 | Win |
| 1 | 2022-01-18 | Win |
| 1 | 2022-01-25 | Win |
| 1 | 2022-01-31 | Draw |
| 1 | 2022-02-08 | Win |
| 2 | 2022-02-06 | Lose |
| 2 | 2022-02-08 | Lose |
| 3 | 2022-03-30 | Win |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Matches", db_config)
print(df)
选手的 连胜数 是指连续获胜的次数,且没有被平局或输球中断。
写一个SQL 语句来计算每个参赛选手最多的连胜数。
本题本质上是求每个选手最大的连续为Win的次数。
如果需要求分组内连续性,可以使用如下代码:
select
player_id,result,
row_number() over(partition by player_id order by match_day) -
row_number() over(partition by player_id,result order by match_day) g
from matches;
player_id result g
--------- ------ --------
1 Win 0
1 Win 0
1 Win 0
1 Win 1
1 Draw 3
2 Lose 0
2 Lose 0
3 Win 0
但是本题只需要求每个选手的连续win:
select
player_id,result,
sum(result!="Win") over(partition by player_id order by match_day) g
from matches;
player_id result g
--------- ------ --------
1 Win 0
1 Win 0
1 Win 0
1 Draw 1
1 Win 1
2 Lose 1
2 Lose 2
3 Win 0
然后求得每个选手的连胜数:
select
player_id,sum(result="Win") cnt
from(
select
player_id,result,
sum(result!="Win") over(partition by player_id order by match_day) g
from matches
) a
group by player_id,g;
player_id cnt
--------- --------
1 3
1 1
2 0
2 0
3 1
最终求得每个用户的最大连胜数:
select
player_id,max(cnt) longest_streak
from(
select
player_id,sum(result="Win") cnt
from(
select
player_id,result,
sum(result!="Win") over(partition by player_id order by match_day) g
from matches
) a
group by player_id,g
) b
group by 1;
player_id longest_streak
--------- ----------------
1 3
2 0
3 1
数字是否连续递增
示例:601. 体育馆的人流量
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| visit_date | date |
| people | int |
"""
sql_text = """
+------+------------+-----------+
| id | visit_date | people |
+------+------------+-----------+
| 1 | 2017-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2017-01-02 | 109 |
| 3 | 2017-01-03 | 150 |
| 4 | 2017-01-04 | 99 |
| 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
| 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
| 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
| 8 | 2017-01-09 | 188 |
+------+------------+-----------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Stadium", db_config)
print(df)
要求:找出人数大于等于100,并且id连续3行以上的记录。
我们可以在过滤后,给每行一个连续性判断的标记:
select
id,visit_date,people,
id-rank() over(order by id) g
from stadium
where people>=100;
id visit_date people g
------ ---------- ------ --------
2 2017-01-02 109 1
3 2017-01-03 150 1
5 2017-01-05 145 2
6 2017-01-06 1455 2
7 2017-01-07 199 2
8 2017-01-09 188 2
可以看到,连续的id都被标记了相同组号,接下来我们继续找到拥有三条记录以上的组:
select
id,visit_date,people
from(
select
id,visit_date,people,
count(1) over(partition by g) n
from(
select
id,visit_date,people,
id-rank() over(order by id) g
from stadium
where people>=100
) a
) b
where n>=3;
结果:
id visit_date people
------ ---------- --------
5 2017-01-05 145
6 2017-01-06 1455
7 2017-01-07 199
8 2017-01-09 188
数字连续递增区间
示例:1285. 找到连续区间的开始和结束数字
数据:
type_md = """
| log_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| log_id |
| ------ |
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 7 |
| 8 |
| 10 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Logs", db_config)
print(df)
查询得到 Logs 表中的连续区间的开始数字和结束数字,结果按照 start_id 排序。
select
min(log_id) start_id,max(log_id) end_id
from(
select
log_id,
log_id-rank() over(order by log_id) g
from logs
) a
group by g;
start_id end_id
-------- --------
1 3
7 8
10 10
日期是否连续按年递增
这本质上依然是一个数字递增的问题,因为日期取年份是数字。
示例:2292. 连续两年有 3 个及以上订单的产品
数据:
type_md = """
| order_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| quantity | int |
| purchase_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| order_id | product_id | quantity | purchase_date |
| -------- | ---------- | -------- | ------------- |
| 1 | 1 | 7 | 2020-03-16 |
| 2 | 1 | 4 | 2020-12-02 |
| 3 | 1 | 7 | 2020-05-10 |
| 4 | 1 | 6 | 2021-12-23 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 2021-05-21 |
| 6 | 1 | 6 | 2021-10-11 |
| 7 | 2 | 6 | 2022-10-11 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Orders", db_config)
print(df)
order_id 是该表的主键。每一行都包含订单 ID、购买的产品 ID、数量和购买日期。
查询连续两年订购三次或三次以上的所有产品的 id。
首先筛选某年订购三次以上的产品,并进行连续年份标记:
select
product_id,
year(purchase_date),
year(purchase_date)-rank() over(partition by product_id order by year(purchase_date)) g
from orders
group by product_id,year(purchase_date)
having count(1)>=3;
product_id year(purchase_date) g
---------- ------------------- --------
1 2020 2019
1 2021 2019
最后,判断是否能够连续2年以上:
select
distinct product_id
from (
select
product_id,
year(purchase_date)-rank() over(partition by product_id order by year(purchase_date)) g
from orders
group by product_id,year(purchase_date)
having count(1)>=3
) a
group by product_id,g
having count(1)>1;
product_id
------------
1
日期是否连续按天递增
示例:1225. 报告系统状态的连续日期
数据:
type_md = """
| fail_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| fail_date |
+-------------------+
| 2018-12-28 |
| 2018-12-29 |
| 2019-01-04 |
| 2019-01-05 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Failed", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| success_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| success_date |
+-------------------+
| 2018-12-30 |
| 2018-12-31 |
| 2019-01-01 |
| 2019-01-02 |
| 2019-01-03 |
| 2019-01-06 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Succeeded", db_config)
print(df)
查询 2019-01-01 到 2019-12-31 期间任务连续同状态 period_state 的起止日期(start_date 和 end_date)。即如果任务失败了,就是失败状态的起止日期,如果任务成功了,就是成功状态的起止日期。
首先我们合并两张表:
select success_date d,"succeeded" period_state from Succeeded
union all
select fail_date d,"failed" period_state from failed
d period_state
---------- --------------
2018-12-30 succeeded
2018-12-31 succeeded
2019-01-01 succeeded
2019-01-02 succeeded
2019-01-03 succeeded
2019-01-06 succeeded
2018-12-28 failed
2018-12-29 failed
2019-01-04 failed
2019-01-05 failed
然后过滤并赋予连续编号:
select
d,period_state,
subdate(d, rank() over(partition by period_state order by d)) g
from(
select success_date d,"succeeded" period_state from Succeeded
union all
select fail_date d,"failed" period_state from failed
) a
where year(d)=2019
d period_state g
---------- ------------ ------------
2019-01-04 failed 2019-01-03
2019-01-05 failed 2019-01-03
2019-01-01 succeeded 2018-12-31
2019-01-02 succeeded 2018-12-31
2019-01-03 succeeded 2018-12-31
2019-01-06 succeeded 2019-01-02
然后分组获取区间:
select
period_state,
min(d) start_date,
max(d) end_date
from(
select
d,period_state,
subdate(d, rank() over(partition by period_state order by d)) g
from(
select success_date d,"succeeded" period_state from Succeeded
union all
select fail_date d,"failed" period_state from failed
) a
where year(d)=2019
) b
group by period_state,g
order by start_date;
period_state start_date end_date
------------ ---------- ------------
succeeded 2019-01-01 2019-01-03
failed 2019-01-04 2019-01-05
succeeded 2019-01-06 2019-01-06
日期是否连续按月递增
查询一个月份的上个月以及下个月:
select period_add("202212",-1) p_m,"202212" m,period_add("202212",1) n_m;
p_m m n_m
------ ------ --------
202211 202212 202301
示例:1843. 可疑银行账户
数据:
type_md = """
| account_id | int |
| max_income | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| account_id | max_income |
| ---------- | ---------- |
| 3 | 21000 |
| 4 | 10400 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Accounts", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| transaction_id | int |
| account_id | int |
| type | ENUM('Creditor','Debtor') |
| amount | int |
| day | datetime |
"""
sql_text = """
| transaction_id | account_id | type | amount | day |
| -------------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | ------------------- |
| 2 | 3 | Creditor | 107100 | 2021-06-02 11:38:14 |
| 4 | 4 | Creditor | 10400 | 2021-06-20 12:39:18 |
| 11 | 4 | Debtor | 58800 | 2021-07-23 12:41:55 |
| 1 | 4 | Creditor | 49300 | 2021-05-03 16:11:04 |
| 15 | 3 | Debtor | 75500 | 2021-05-23 14:40:20 |
| 10 | 3 | Creditor | 102100 | 2021-06-15 10:37:16 |
| 14 | 4 | Creditor | 56300 | 2021-07-21 12:12:25 |
| 19 | 4 | Debtor | 101100 | 2021-05-09 15:21:49 |
| 8 | 3 | Creditor | 64900 | 2021-07-26 15:09:56 |
| 7 | 3 | Creditor | 90900 | 2021-06-14 11:23:07 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Transactions", db_config)
print(df)
表: Accounts每行包含一个银行账户每月最大收入的信息。account_id 是表主键。
表: Transactions,其中’Creditor’表示用户向其账户存入资金,'Debtor’表示用户从其账户取出资金。amount 是转账的存取金额。
查询所有的可疑账户,如果一个账户在连续两个及以上月份中总收入超过最大收入(max_income ),那么这个账户可疑。 账户当月总收入是当月存入资金总数(即transactions 表中type字段的'Creditor')。返回的结果表以transaction_id 排序。
首先查询每个账户每个月的收入:
select
a.account_id,
date_format(day,"%Y%m") month,
sum(amount) sum_amount
from Transactions
where type="Creditor"
group by 1,2;
account_id month sum_amount
---------- ------ ------------
3 202106 300100
4 202106 10400
4 202105 49300
4 202107 56300
3 202107 64900
过滤出超过最大收入的数据:
select
a.account_id,
date_format(day,"%Y%m") month
from Transactions a join accounts b using(account_id)
where type="Creditor"
group by account_id,month
having sum(amount)>max(max_income);
account_id month
---------- --------
3 202106
4 202105
4 202107
3 202107
然后进行连续标记:
select
account_id,month,
period_add(month,-rank() over(partition by account_id order by month)) g
from(
select
a.account_id,
date_format(day,"%Y%m") month
from Transactions a join accounts b using(account_id)
where type="Creditor"
group by account_id,month
having sum(amount)>max(max_income)
) c
account_id month m
---------- ------ --------
3 202106 202105
3 202107 202105
4 202105 202104
4 202107 202105
最终结果:
select
distinct account_id
from(
select
account_id,month,
period_add(month,-rank() over(partition by account_id order by month)) m
from(
select
a.account_id,
date_format(day,"%Y%m") month
from Transactions a join accounts b using(account_id)
where type="Creditor"
group by account_id,month
having sum(amount)>max(max_income)
) c
) d
group by account_id,m
having count(1)>=2
order by account_id;
account_id
------------
3
操作技巧
向下填充连续的空值
示例:2388. 将表中的空值更改为前一个值
type_md = """
| id | int |
| drink | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | drink |
| -- | ---------------- |
| 9 | Mezcal Margarita |
| 6 | null |
| 7 | null |
| 3 | Americano |
| 1 | Daiquiri |
| 2 | null |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "CoffeeShop", db_config)
print(df)
将 drink 的 null 值替换为前面最近一行不为 null 的 drink。表第一行的 drink 保证不为 null。
使用变量实现:
select
id,@t:=if(drink is null,@t,drink) drink
from coffeeshop;
id drink
------ ------------------
9 Mezcal Margarita
6 Mezcal Margarita
7 Mezcal Margarita
3 Americano
1 Daiquiri
2 Daiquiri
取topn对应的行
示例:
- 184. 部门工资最高的员工
- 185. 部门工资前三高的所有员工
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| salary | int |
| departmentId | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | name | salary | departmentId |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | Joe | 85000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
| 5 | Janet | 69000 | 1 |
| 6 | Randy | 85000 | 1 |
| 7 | Will | 70000 | 1 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
type_md = """
| id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | name |
+----+-------+
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Department", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
思路:只需要给每个工资一个排名然后过滤,则可以获取工资最高的。
select
b.name Department,a.name Employee,a.Salary
from(
select
name,
salary,
departmentId,
rank() over(partition by departmentId order by salary desc) rn
from Employee e
) a
join Department b on a.departmentId=b.id
where a.rn=1;
不使用窗口函数的思路:先计算每个部门的最高工资然后直接过滤:
select
b.name Department,a.name Employee,a.Salary
from Employee a join Department b on a.departmentId=b.id
where (a.DepartmentId,a.salary) in (
select DepartmentId,max(salary) salary from Employee e
group by e.departmentId
);
注意:in语句可以使用多个字段。
要求部门工资前三高的所有员工还是使用窗口函数最佳:
select
b.name Department,a.name Employee,a.Salary
from(
select
name,
salary,
departmentId,
dense_rank() over(partition by departmentId order by salary desc) rn
from Employee e
) a
join Department b on a.departmentId=b.id
where a.rn<=3;
Department Employee Salary
---------- -------- --------
IT Max 90000
Sales Henry 80000
一个聚合中求出多个类别的个数
示例:578. 查询回答率最高的问题
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| action | ENUM("show","answer","skip") |
| question_id | int |
| answer_id | int |
| q_num | int |
| timestamp | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | action | question_id | answer_id | q_num | timestamp |
| -- | ------ | ----------- | --------- | ----- | --------- |
| 5 | show | 285 | null | 1 | 123 |
| 5 | answer | 285 | 124124 | 1 | 124 |
| 5 | show | 369 | null | 2 | 125 |
| 5 | skip | 369 | null | 2 | 126 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "SurveyLog", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
每一行表示用户对 question_id 的问题在 timestamp 时间进行了 action 操作。
如果用户对应的操作是 “answer” ,answer_id 将会是对应答案的 id ,否则,值为 null 。
查询回答率最高的问题,如果有多个问题具有相同的最大 回答率 ,返回
question_id最小的那个。每个问题的回答率=该问题的回答次数/该问题的显示次数。
下面我们看看如何在一个分组中,同时求出每个问题的回答次数和显示次数:
select
question_id,
sum(action='answer') answer_num,
sum(action='show') show_num
from surveylog
group by question_id;
question_id answer_num show_num
----------- ---------- ----------
285 1 1
369 0 1
这样要求解该问题就简单了:
select
question_id
from surveylog group by question_id
order by sum(action='answer')/sum(action='show') desc,question_id
limit 1;
question_id
-------------
285
示例:1322. 广告效果
数据:
type_md = """
| ad_id | int |
| user_id | int |
| action | enum('Clicked','Viewed','Ignored') |
"""
sql_text = """
| ad_id | user_id | action |
| ----- | ------- | ------- |
| 1 | 1 | Clicked |
| 2 | 2 | Clicked |
| 3 | 3 | Viewed |
| 5 | 5 | Ignored |
| 1 | 7 | Ignored |
| 2 | 7 | Viewed |
| 3 | 5 | Clicked |
| 1 | 4 | Viewed |
| 2 | 11 | Viewed |
| 1 | 2 | Clicked |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Ads", db_config)
print(df)
该表每一行表示用户对广告采取的行为 (action)。
现在需要查询每一条广告的 ctr ,广告效果用点击通过率(Click-Through Rate:CTR)计算公式如下:
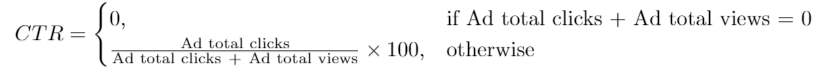
ctr 要保留两位小数。结果需要按 ctr 降序、按 ad_id 升序 进行排序。
select
ad_id,
round(ifnull(sum(action="Clicked")/
(sum(action="Clicked")+sum(action="Viewed")),0)*100,2) ctr
from ads group by ad_id
order by ctr desc,ad_id;
ad_id ctr
------ --------
1 66.67
3 50.00
2 33.33
5 0.00
示例:1205. 每月交易II
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| country | varchar(20) |
| state | enum('approved','declined') |
| amount | int |
| trans_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | country | state | amount | trans_date |
| --- | ------- | -------- | ------ | ---------- |
| 101 | US | approved | 1000 | 2019-05-18 |
| 102 | US | declined | 2000 | 2019-05-19 |
| 103 | US | approved | 3000 | 2019-06-10 |
| 104 | US | declined | 4000 | 2019-06-13 |
| 105 | US | approved | 5000 | 2019-06-15 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Transactions", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
type_md = """
| trans_id | int |
| trans_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| trans_id | trans_date |
| -------- | ---------- |
| 102 | 2019-05-29 |
| 101 | 2019-06-30 |
| 105 | 2019-09-18 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Chargebacks", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
Transactions 表包含approved(已批准)、declined(已拒绝)两种状态。
Chargebacks 表包含有关放置在事务表中的某些事务的传入退单的基本信息。
查询每个月和每个国家/地区的信息:已批准交易的数量及其总金额、退单的数量及其总金额。
首先先交易表中补充退单数据:
select * from transactions
union all
select
trans_id,country,
"Chargeback" state,
amount,c.trans_date
from transactions t join Chargebacks c
on t.id=c.trans_id;
id country state amount trans_date
------ ------- ---------- ------ ------------
101 US approved 1000 2019-05-18
102 US declined 2000 2019-05-19
103 US approved 3000 2019-06-10
104 US declined 4000 2019-06-13
105 US approved 5000 2019-06-15
101 US Chargeback 1000 2019-06-30
102 US Chargeback 2000 2019-05-29
105 US Chargeback 5000 2019-09-18
然后可以一次性统计:
select
substr(trans_date,1,7) month,
country,
sum(state="approved") approved_count,
sum(if(state="approved",amount,0)) approved_amount,
sum(state="Chargeback") chargeback_count,
sum(if(state="Chargeback",amount,0)) chargeback_amount
from(
select * from transactions
union all
select trans_id,country,"Chargeback" state,amount,c.trans_date
from transactions t join Chargebacks c
on t.id=c.trans_id
) a
group by substr(trans_date,1,7),country
having approved_count or chargeback_count;
结果:
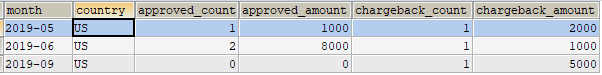
奇偶行两两交换
示例:626. 换座位
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| student | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | student |
+----+---------+
| 1 | Abbot |
| 2 | Doris |
| 3 | Emerson |
| 4 | Green |
| 5 | Jeames |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Seat", db_config)
print(df)
每两个连续的学生的座位号进行交换,如果学生的数量是奇数,则最后一个学生的id不交换。最终按 id 升序 返回。
奇偶变换的公式为(id+1)^1-1:
select id,(id+1)^1-1 id2,student from seat;
id id2 student
------ ------ ---------
1 2 Abbot
2 1 Doris
3 4 Emerson
4 3 Green
5 6 Jeames
但是要求最后一个id为奇数时,id不变。这时我们可以自连接找出那些变换后匹配不上的id:
select
*
from seat a left join seat b
on a.id=((b.id+1)^1)-1;
id student id student
------ ------- ------ ---------
1 Abbot 2 Doris
2 Doris 1 Abbot
3 Emerson 4 Green
4 Green 3 Emerson
5 Jeames (NULL) (NULL)
这时就可以轻松交换id:
select
ifnull(b.id,a.id) id,
a.student
from seat a left join seat b
on a.id=((b.id+1)^1)-1
order by id;
id student
------ ---------
1 Doris
2 Abbot
3 Green
4 Emerson
5 Jeames
由于id是已经排序的,我们也可以直接交换学生:
select
a.id,
ifnull(b.student,a.student) student
from seat a left join seat b
on a.id=((b.id+1)^1)-1;
注意:ifnull的功能是第一个参数空时取第二个,如果有3个以上的数据需要获取第一个非空数据可以使用coalesce。
当然我们还可以使用窗口函数进行最大id判断:
select
if(id1=m_id and id1%2=1,id1,id2) id,
student
from(
select
id id1,
(id+1)^1-1 id2,
max(id) over() m_id,
student
from seat
) a
order by id;
或者直接判断:
select
case
when id%2=0 then id-1
when id=(select max(id) from seat) then id
else id+1
end id,
student
from seat
order by id;
均顺利实现交换。
一组数字查询中位数
示例:569. 员工薪水中位数
数据:
type_md = """
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| id | int |
| company | varchar(10) |
| salary | int |
+--------------+---------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+---------+--------+
| id | company | salary |
+----+---------+--------+
| 1 | A | 2341 |
| 2 | A | 341 |
| 3 | A | 15 |
| 4 | A | 15314 |
| 5 | A | 451 |
| 6 | A | 513 |
| 7 | B | 15 |
| 8 | B | 13 |
| 9 | B | 1154 |
| 10 | B | 1345 |
| 11 | B | 1221 |
| 12 | B | 234 |
| 13 | C | 2345 |
| 14 | C | 2645 |
| 15 | C | 2645 |
| 16 | C | 2652 |
| 17 | C | 65 |
+----+---------+--------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
要求找出每个公司的工资中位数。
对于一组从小到大排序的数据,长度为n:
- 如果n为偶数,则第
n/2和n/2+1个值为中位数 - 如果n为奇数,则第
(n+1)/2个值为中位数
下面div表示整除符号:当n为偶数时,(n+1) div 2=n/2;当n为奇数时,(n+2) div 2=(n+1)/2。
所以不管n为偶数还是奇数,都可以抽象成(n+1) div 2和(n+2) div 2两种情况,只不过n为奇数时,两个值相等。基于此,我们可以通过窗口函数求解该问题:
select
id, company, salary
from(
select
id, company, salary,
row_number() over(partition by company order by salary) rn,
count(id) over(partition by company) n
from employee
) a
where rn in ((n+1) div 2,(n+2) div 2);
结果:
id company salary
------ ------- --------
5 A 451
6 A 513
12 B 234
9 B 1154
14 C 2645
中位数 还可以认为是将半数较高值和半数较低值分隔开的值。
那么只需一个数的正序排名和倒序排名均大于n/2时也可以满足条件:
select
id, company, salary
from(
select
id, company, salary,
row_number() over(partition by company order by salary) rn1,
row_number() over(partition by company order by salary desc) rn2,
count(id) over(partition by company) n
from employee
) a
where rn1>=n/2 and rn2>=n/2;
结果:
id company salary
------ ------- --------
6 A 513
5 A 451
9 B 1154
12 B 234
15 C 2645
给定数字的频率查询中位数
示例:571. 给定数字的频率查询中位数
数据:
type_md = """
+-------------+------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+------+
| num | int |
| frequency | int |
+-------------+------+
"""
sql_text = """
+-----+-----------+
| num | frequency |
+-----+-----------+
| 0 | 7 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 |
+-----+-----------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Numbers", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
这张表的每一行表示某个数字在该数据库中的出现频率。解压 Numbers 表,报告数据库中所有数字的 中位数。
原题还要求多个中位数取平均值,结果四舍五入至 一位小数 :
select
round(avg(num),1) median
from(
select
num,frequency,
sum(frequency) over(order by num) rn1,
sum(frequency) over(order by num desc) rn2,
sum(frequency) over() n
from numbers
) a
where rn1>=n/2 and rn2>=n/2;
结果:
median
--------
0.0
共同好友
示例:1949. 坚定的友谊
数据:
type_md = """
| user1_id | int |
| user2_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user1_id | user2_id |
| -------- | -------- |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 1 | 7 |
| 3 | 7 |
| 1 | 6 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Friendship", db_config)
print(df)
(user1_id, user2_id) 是这个表的主键。每一行都表示用户 user1_id 和 user2_id 是朋友。user1_id < user2_id。
如果 x 和 y 为朋友且他们至少有三个共同的朋友 ,那么 x 和 y 之间的友谊就是坚定的。
查询所有坚定的友谊。
注意,结果表不应该包含重复,并且 user1_id < user2_id。
首先,我们生成每个用户所有的好友的两两组合:
with cte as (
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
)
select
a.u1 user_id,a.u2 f1,b.u2 f2
from cte a join cte b using(u1)
where a.u2<b.u2 and a.u2<>b.u2
order by 1;
结果仅展示用户3开始的好友组合:
user_id f1 f2
------- ------ --------
......
3 6 7
3 1 2
3 1 6
3 1 7
3 2 6
3 2 7
4 1 2
5 1 2
6 1 2
6 1 3
6 2 3
7 1 3
然后我们需要确保好友的组合间存在好友关系:
with cte as (
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
)
select
a.u2 user1,b.u2 user2,
a.u1 common_friend_id
from cte a join cte b using(u1)
join cte c on a.u2=c.u1 and b.u2=c.u2
where a.u2<b.u2 and a.u2<>b.u2
order by 1,2;
user1 user2 common_friend_id
------ ------ ------------------
1 2 3
1 2 4
1 2 5
1 2 6
1 3 2
1 3 7
1 3 6
1 4 2
1 5 2
1 6 2
1 6 3
1 7 3
2 3 1
2 3 6
2 4 1
2 5 1
2 6 1
2 6 3
3 6 1
3 6 2
3 7 1
由于user1和user2是好友,而且都是common_friend_id的好友,所以common_friend_id是user1和user2的共同好友。然后可以得到共同好友列表:
with cte as (
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
)
select
a.u2 user1_id,b.u2 user2_id,
group_concat(a.u1 order by a.u1) common_friend_list,
count(a.u1) common_friend_num
from cte a join cte b using(u1)
join cte c on a.u2=c.u1 and b.u2=c.u2
where a.u2<b.u2 and a.u2<>b.u2
group by 1,2
order by 1,2;
user1_id user2_id common_friend_list common_friend_num
-------- -------- ------------------ -------------------
1 2 3,4,5,6 4
1 3 2,6,7 3
1 4 2 1
1 5 2 1
1 6 2,3 2
1 7 3 1
2 3 1,6 2
2 4 1 1
2 5 1 1
2 6 1,3 2
3 6 1,2 2
3 7 1 1
下面我们找出所有共同好友数量大于3的坚定友谊:
with cte as (
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
)
select
a.u2 user1_id,b.u2 user2_id,
count(a.u1) common_friend
from cte a join cte b using(u1)
join cte c on a.u2=c.u1 and b.u2=c.u2
where a.u2<b.u2 and a.u2<>b.u2
group by 1,2
having common_friend>=3;
user1_id user2_id common_friend
-------- -------- ---------------
1 2 4
1 3 3
共同关注者
示例:1951. 查询具有最多共同关注者的所有两两结对组
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| follower_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | follower_id |
| ------- | ----------- |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 7 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 7 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 7 | 5 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Relations", db_config)
print(df)
(user_id, follower_id) 是Relations表的主键,每一行表示这个user_id的用户和他的关注者
找到具有最多共同关注者的所有两两结对组。如果有两个以上用户的共同关注者是最大的,则都返回。
结果表每一行应该包含user1_id和 user2_id,其中user1_id < user2_id。
首先两两配对,找出其共同关注者:
select
a.user_id user1_id,b.user_id user2_id,
follower_id
from relations a join relations b using(follower_id)
where a.user_id<b.user_id;
user1_id user2_id follower_id
-------- -------- -------------
1 2 3
2 7 3
1 7 3
1 2 4
2 7 4
1 7 4
1 7 5
然后统计共同关注者的数量并排序取最大,但题目要求多个最大值都返回,所以这里使用窗口函数标记共同关注者的数量排序序号:
select
a.user_id user1_id,b.user_id user2_id,
rank() over(order by count(follower_id) desc) rk
from relations a join relations b using(follower_id)
where a.user_id<b.user_id
group by 1,2;
user1_id user2_id rk
-------- -------- --------
1 7 1
1 2 2
2 7 2
然后过滤出排序第一的即可:
select
user1_id,user2_id
from(
select
a.user_id user1_id,b.user_id user2_id,
rank() over(order by count(follower_id) desc) rn
from relations a join relations b using(follower_id)
where a.user_id<b.user_id
group by 1,2
) a
where rn=1;
user1_id user2_id
-------- ----------
1 7
页面推荐1
示例:1264. 页面推荐
数据:
type_md = """
| user1_id | int |
| user2_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user1_id | user2_id |
+----------+----------+
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 6 | 1 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Friendship", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| page_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | page_id |
+---------+---------+
| 1 | 88 |
| 2 | 23 |
| 3 | 24 |
| 4 | 56 |
| 5 | 11 |
| 6 | 33 |
| 2 | 77 |
| 3 | 77 |
| 6 | 88 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Likes", db_config)
print(df)
Friendship表的每一行代表着 user1_id 和 user2_id 之间存在着朋友关系。
Likes表的每一行代表着 user_id 喜欢 page_id。
要向user_id = 1 的用户,推荐其朋友们喜欢的页面。不要推荐该用户已经喜欢的页面。
首先我们查询其好友:
select
greatest(user1_id,user2_id) user_id
from Friendship where user1_id=1 or user2_id=1
user_id
---------
2
3
4
6
然后查询好友喜欢的页面:
select
user_id,page_id
from(
select
greatest(user1_id,user2_id) user_id
from Friendship where user1_id=1 or user2_id=1
) a join likes b using(user_id);
user_id page_id
------- ---------
2 23
3 24
4 56
6 33
2 77
3 77
6 88
最后过滤掉自己喜欢的页面即可:
select
distinct b.page_id recommended_page
from(
select
greatest(user1_id,user2_id) user_id
from Friendship where user1_id=1 or user2_id=1
) a join likes b using(user_id)
left join (select page_id from likes where user_id=1) c
using(page_id) where c.page_id is null;
recommended_page
------------------
23
24
56
33
77
注意:greatest可以从多个值中获取最大值;least则可以从多个值中获取最小值。
页面推荐2
示例:1892. 页面推荐Ⅱ
还是上面的数据,下面要求向所有用户推荐页面。如果页面被user_id的 至少一个朋友喜欢 ,而 不被user_id喜欢 , 推荐 一个页面到user_id。
查询针对每个用户的所有可能的 页面建议 。结果包含以下列:
user_id: 系统向其提出建议的用户的ID。page_id: 推荐为user_id的页面ID。.friends_likes:user_id对应page_id的好友数。
首先我们查询每个用户的好友和他喜欢的页面:
select
u1,u2,l1.page_id
from(
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
)a join likes l1 on a.u1=l1.user_id
order by 1,2;
u1 u2 page_id
------ ------ ---------
1 2 88
1 3 88
1 4 88
1 6 88
2 1 23
2 1 77
2 3 23
2 3 77
2 4 23
2 4 77
2 5 23
......
然后我们查询每个好友喜欢的页面是否包含当前页面:
select
u1,u2,l1.page_id p1,l2.page_id p2
from(
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
) a join likes l1 on a.u1=l1.user_id
left join likes l2 on a.u2=l2.user_id and l1.page_id = l2.page_id
order by 1,2;
u1 u2 p1 p2
------ ------ ------ --------
1 2 88 (NULL)
1 3 88 (NULL)
1 4 88 (NULL)
1 6 88 88
2 1 23 (NULL)
2 1 77 (NULL)
2 3 23 (NULL)
2 3 77 77
2 4 23 (NULL)
2 4 77 (NULL)
2 5 23 (NULL)
2 5 77 (NULL)
......
由于左连接保留了,每个好友未喜欢的页面,所以我们可以基于此进行推荐:
select
u2 user_id,l1.page_id page_id,
count(u1) friends_likes
from(
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
) a join likes l1 on a.u1=l1.user_id
left join likes l2 on a.u2=l2.user_id and l1.page_id = l2.page_id
where isnull(l2.page_id)
group by 1,2;
user_id page_id friends_likes
------- ------- ---------------
1 23 1
1 24 1
1 33 1
1 56 1
1 77 2
2 11 1
2 24 1
2 56 1
2 88 1
3 23 1
3 88 1
4 23 1
4 77 1
4 88 1
5 23 1
5 77 1
好友推荐
示例:1917. Leetcodify 好友推荐
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| song_id | int |
| day | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | song_id | day |
| ------- | ------- | ---------- |
| 1 | 10 | 2021-03-15 |
| 1 | 11 | 2021-03-15 |
| 1 | 12 | 2021-03-15 |
| 2 | 10 | 2021-03-15 |
| 2 | 11 | 2021-03-15 |
| 2 | 12 | 2021-03-15 |
| 3 | 10 | 2021-03-15 |
| 3 | 11 | 2021-03-15 |
| 3 | 12 | 2021-03-15 |
| 4 | 10 | 2021-03-15 |
| 4 | 11 | 2021-03-15 |
| 4 | 13 | 2021-03-15 |
| 5 | 10 | 2021-03-16 |
| 5 | 11 | 2021-03-16 |
| 5 | 12 | 2021-03-16 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Listens", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| user1_id | int |
| user2_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user1_id | user2_id |
| -------- | -------- |
| 1 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Friendship", db_config)
print(df)
表 Listens中的每一行表示用户 user_id 在 day 这一天收听的歌曲 song_id。
表 Friendship中的每一行表示 user1_id 和 user2_id 是好友。user1_id < user2_id。
将符合下列条件的用户 x 推荐给用户 y :
- 用户
x和y不是好友,且 - 用户
x和y在同一天收听了相同的三首或更多不同歌曲。
注意,好友推荐是单向的,这意味着如果用户 x 和用户 y 需要互相推荐给对方,结果表需要将用户 x 推荐给用户 y 并将用户 y 推荐给用户 x。另外,结果表不得出现重复项。
首先查询每天听了同一首歌的用户,然后分组过滤:
select
a.user_id u1,b.user_id u2,a.day,
group_concat(distinct a.song_id) song_list
from listens a join listens b using(song_id,day)
where a.user_id!=b.user_id
group by 1,2,3
having count(distinct a.song_id)>=3
u1 u2 day song_list
------ ------ ---------- -----------
1 2 2021-03-15 10,11,12
1 3 2021-03-15 10,11,12
2 1 2021-03-15 10,11,12
2 3 2021-03-15 10,11,12
3 1 2021-03-15 10,11,12
3 2 2021-03-15 10,11,12
上面已经过滤出了,在同一天收听了相同歌曲三首以上的用户。然后我们需要过滤掉已经是好友的用户:
select
a.user_id,b.user_id recommended_id
from listens a join listens b using(song_id,day)
where a.user_id!=b.user_id
and not exists(
select 1 from friendship
where (user1_id=a.user_id and user2_id=b.user_id)
or (user2_id=a.user_id and user1_id=b.user_id)
)
group by 1,2,a.day
having count(distinct a.song_id)>=3;
user_id recommended_id
------- ----------------
1 3
2 3
3 1
3 2
但是这种exists的写法,在面对超过千条数据时,会执行非常慢。力扣中也提示超时无法通过:
因此我们改写成外连接的形式:
select
distinct a.u1 user_id,a.u2 recommended_id
from (
select
a.user_id u1,b.user_id u2
from listens a join listens b using(song_id,day)
where a.user_id!=b.user_id
group by 1,2,a.day
having count(distinct a.song_id)>=3
) a left join (
select user1_id u1,user2_id u2 from friendship
union all
select user2_id,user1_id from friendship
) b using(u1,u2)
where b.u1 is null;
顺利通过:
示例:1919. 兴趣相同的朋友
基于上面的数据给Friendship表增加2条数据:
type_md = """
| user1_id | int |
| user2_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user1_id | user2_id |
| -------- | -------- |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 2 | 5 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Friendship", db_config)
print(df)
获取到兴趣相同的朋友。需满足下述条件:
- 用户
x和y是好友,并且 - 用户
xandy在同一天内听过相同的歌曲,且数量大于等于三首.
结果表需满足 user1_id < user2_id。
根据前面的思路,比前一题简单:
select
distinct user1_id, user2_id
from(
select
a.user_id user1_id,
b.user_id user2_id
from listens a join listens b using(song_id,day)
where a.user_id!=b.user_id
group by 1,2,a.day
having count(distinct a.song_id)>=3
) a join friendship b using(user1_id,user2_id);
user1_id user2_id
-------- ----------
1 2
重叠区间合并
纯Python解决的类似问题:
Pandas基础|用户游览日志时间合并排序
https://xxmdmst.blog.csdn.net/article/details/112387087
以下我们看看SQL如何实现。
示例:2494. 合并在同一个大厅重叠的活动
数据:
type_md = """
| hall_id | int |
| start_day | date |
| end_day | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| hall_id | start_day | end_day |
| ------- | ---------- | ---------- |
| 1 | 2023-01-13 | 2023-01-14 |
| 1 | 2023-01-14 | 2023-01-17 |
| 1 | 2023-01-18 | 2023-01-25 |
| 2 | 2022-12-09 | 2022-12-23 |
| 2 | 2022-12-13 | 2022-12-17 |
| 3 | 2022-12-01 | 2023-01-30 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "HallEvents", db_config)
print(df)
每一行表示活动的开始日期和结束日期,以及活动举行的大厅。
合并在 同一个大厅举行 的所有重叠活动。如果两个活动 至少有一天 相同,那么它们就是重叠的。
首先我们查询每个大厅,到目前为止举行过的活动的最大结束日期,和上一个最大结束日期:
select
*,
lag(cur_max_end_day) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) pre_end_day
from(
select
*,max(end_day) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) cur_max_end_day
from hallevents
) a;
hall_id start_day end_day cur_max_end_day pre_end_day
------- ---------- ---------- --------------- -------------
1 2023-01-13 2023-01-14 2023-01-14 (NULL)
1 2023-01-14 2023-01-17 2023-01-17 2023-01-14
1 2023-01-18 2023-01-25 2023-01-25 2023-01-17
2 2022-12-09 2022-12-23 2022-12-23 (NULL)
2 2022-12-13 2022-12-17 2022-12-23 2022-12-23
3 2022-12-01 2023-01-30 2023-01-30 (NULL)
对于起始日期小于等于上一条最大结束日期的,说明需要参与合并,于是我们可以对需要合并的活动赋予相同的分组编号:
select
hall_id,start_day,end_day,
sum(ifnull(start_day>pre_end_day,1)) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) g
from(
select
hall_id,start_day,end_day,
lag(cur_max_end_day) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) pre_end_day
from(
select
*,max(end_day) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) cur_max_end_day
from hallevents
) a
) b;
hall_id start_day end_day g
------- ---------- ---------- --------
1 2023-01-13 2023-01-14 1
1 2023-01-14 2023-01-17 1
1 2023-01-18 2023-01-25 2
2 2022-12-09 2022-12-23 1
2 2022-12-13 2022-12-17 1
3 2022-12-01 2023-01-30 1
可以看到存在重叠的区间都被赋予了相同的分组编号,于是我们可以轻松完成合并了:
select
hall_id,
min(start_day) start_day,
max(end_day) end_day
from(
select
hall_id,start_day,end_day,
sum(ifnull(start_day>pre_end_day,1)) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) g
from(
select
hall_id,start_day,end_day,
lag(cur_max_end_day) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) pre_end_day
from(
select
*,max(end_day) over(partition by hall_id order by start_day) cur_max_end_day
from hallevents
) a
) b
) c
group by hall_id,g;
hall_id start_day end_day
------- ---------- ------------
1 2023-01-13 2023-01-17
1 2023-01-18 2023-01-25
2 2022-12-09 2022-12-23
3 2022-12-01 2023-01-30
自连接
司机成为乘客的次数
示例:2238. 司机成为乘客的次数
数据:
type_md = """
| ride_id | int |
| driver_id | int |
| passenger_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| ride_id | driver_id | passenger_id |
| ------- | --------- | ------------ |
| 1 | 7 | 1 |
| 2 | 7 | 2 |
| 3 | 11 | 1 |
| 4 | 11 | 7 |
| 5 | 11 | 7 |
| 6 | 11 | 3 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Rides", db_config)
ride_id 是该表的主键。查询每个司机的 ID 和他们作为乘客的次数。
select
a.driver_id,count(distinct b.ride_id) cnt
from rides a left join rides b
on a.driver_id=b.passenger_id
group by a.driver_id;
driver_id cnt
--------- --------
7 2
11 0
如果不希望在最后计数时对ride_id去重,则需要先对司机id去重:
select
a.driver_id,count(b.ride_id) cnt
from (
select distinct driver_id from rides
) a left join rides b
on a.driver_id=b.passenger_id
group by a.driver_id;
二叉树节点类型
示例:608. 树节点
type_md = """
| id | int |
| p_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | p_id |
+----+------+
| 1 | null |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Cinema", db_config)
print(df)
树中每个节点属于以下三种类型之一:
- Leaf:如果这个节点没有任何孩子节点。
- Root:如果这个节点是整棵树的根,即没有父节点。
- Inner:如果这个节点既不是叶子节点也不是根节点。
现在要求查询出每个节点的类型。
已知每个节点的父节点,那我们首先查询出每个节点的子节点:
select
a.id,a.p_id pid,b.id cid
from tree a left join tree b
on a.id=b.p_id;
结果:
id pid cid
------ ------ --------
1 (NULL) 3
1 (NULL) 2
2 1 5
2 1 4
3 1 (NULL)
4 2 (NULL)
5 2 (NULL)
然后就可以轻松判断是否存在子节点从而获取答案:
select distinct
a.id,
case
when a.p_id is null then "Root"
when b.id is null then "Leaf"
else "Inner"
end as `Type`
from tree a left join tree b
on a.id=b.p_id;
id Type
------ --------
1 Root
2 Inner
3 Leaf
4 Leaf
5 Leaf
任意两点之间的距离
示例:612. 平面上的最近距离
数据:
type_md = """
| x | int |
| y | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| x | y |
+----+----+
| -1 | -1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| -1 | -2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Point2D", db_config)
print(df)
下面我们需要计算任意两点间的距离:
select
a.x x1,a.y y1,b.x x2,b.y y2,
round(sqrt(pow(a.x-b.x,2)+pow(a.y-b.y,2)),2) `distance`
from Point2D a join Point2D b
on (a.x<=b.x and a.y!=b.y) or (a.x<b.x and a.y=b.y);
结果:
x1 y1 x2 y2 distance
------ ------ ------ ------ ----------
-2 -1 -1 -1 1
-1 -2 -1 -1 1
-2 -1 0 0 2.24
-1 -2 0 0 2.24
-1 -1 0 0 1.41
-2 -1 -1 -2 1.41
-1 -1 -1 -2 1
那么找出最短距离只需聚合一下:
select
min(round(sqrt(pow(a.x-b.x,2)+pow(a.y-b.y,2)),2)) shortest
from Point2D a join Point2D b
on (a.x<=b.x and a.y!=b.y) or (a.x<b.x and a.y=b.y);
如果判断条件为:
a.x!=b.x or a.y!=b.y
可以避免每个点与自己求距离。如果每个点只计算比自己x 坐标大的点,那么就可以进一步减少重复计算,条件为:
(a.x<=b.x and a.y<b.y) or (a.x<=b.x and a.y>b.y) or (a.x<b.x and a.y=b.y)
合并后就是上面SQL的判断条件。
矩形面积
示例:1459. 矩形面积
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| x_value | int |
| y_value | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | x_value | y_value |
| -- | ------- | ------- |
| 1 | 2 | 7 |
| 2 | 4 | 8 |
| 3 | 2 | 10 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Points", db_config)
print(df)
查询任意两点可以形成的所有 边与坐标轴平行 且 面积不为零 的矩形。
结果表中的每一行包含三列 (p1, p2, area) 如下:
p1和p2是矩形两个对角的id- 矩形的面积由列
area表示
按照面积 area 大小降序排列;如果面积相同的话, 则按照 p1 升序排序;若仍相同,则按 p2 升序排列。
select
a.id p1,
b.id p2,
abs(a.x_value-b.x_value)*abs(a.y_value-b.y_value) area
from points a,points b
where a.id<b.id having area>0
order by area desc,p1,p2;
结果:
p1 p2 area
------ ------ --------
2 3 4
1 2 2
可视化:
二级关注者
示例:614. 二级关注者
数据:
type_md = """
| followee | char |
| follower | char |
"""
sql_text = """
| followee | follower |
+-------------+------------+
| A | B |
| B | C |
| B | D |
| D | E |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "follow", db_config)
print(df)
followee, follower ,分别表示被关注者和关注者。
查询每一个关注者,关注他的关注者的数目。
表连接:
select
a.followee follower,
count(a.follower) num
from follow a join (select distinct follower from follow) b
on a.followee=b.follower
group by a.followee
order by a.followee;
in语句:
select
followee follower,count(followee) num
from follow
where followee in (select distinct follower from follow)
group by followee
order by 1;
exists语句:
select
followee follower,count(followee) num
from follow a
where exists(select 1 from follow where follower=a.followee)
group by followee
order by 1;
结果:
follower num
-------- --------
B 2
D 1
补充:not in与not exsist的区别
not in 的写法是 where (x,y) not in (select x,y from table)
not exsist 的写法是 where not exsist(select 1 from table where x=x,y=y)
IN适合于外表大而内表小的情况;EXISTS适合于外表小而内表大的情况
not in最好改写为 外连接+is null 的形式。
每个帖子的评论数
示例:1241. 每个帖子的评论数
数据:
type_md = """
| sub_id | int |
| parent_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| sub_id | parent_id |
| ------ | --------- |
| 1 | null |
| 2 | null |
| 1 | null |
| 12 | null |
| 3 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 9 | 1 |
| 10 | 2 |
| 6 | 7 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Submissions", db_config)
print(df)
Submissions表每行可以是一个帖子或对该帖子的评论。
parent_id 是 null 表示是帖子,否则为评论,parent_id 是对应的帖子id。
要求查询每个帖子的评论数。
首先我们查询每个帖子的评论ID:
select
a.sub_id,b.sub_id
from(
select distinct sub_id from submissions where parent_id is null
) a left join (
select distinct sub_id,parent_id from Submissions where parent_id is not null
) b on a.sub_id=b.parent_id;
sub_id sub_id
------ --------
1 3
1 4
1 9
2 5
2 10
12 (NULL)
然后聚合统计:
select
a.sub_id post_id,
count(b.sub_id) number_of_comments
from(
select distinct sub_id from submissions where parent_id is null
) a left join (
select distinct sub_id,parent_id from Submissions where parent_id is not null
) b on a.sub_id=b.parent_id
group by a.sub_id
order by post_id;
post_id number_of_comments
------- --------------------
1 3
2 2
12 0
每位经理的下属员工数量
示例:1731. 每位经理的下属员工数量
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| name | varchar(20) |
| reports_to | int |
| age | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | name | reports_to | age |
| ----------- | ------- | ---------- | --- |
| 9 | Hercy | null | 43 |
| 6 | Alice | 9 | 41 |
| 4 | Bob | 9 | 36 |
| 2 | Winston | null | 37 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employees", db_config)
print(df)
我们将至少有一个其他员工需要向他汇报的员工,视为一个经理。
编写SQL查询需要听取汇报的所有经理的ID、名称、直接向该经理汇报的员工人数,以及这些员工的平均年龄,其中该平均年龄需要四舍五入到最接近的整数。
返回的结果集需要按照 employee_id 进行排序。
select
a.reports_to employee_id,
b.name,
count(b.employee_id) reports_count,
round(avg(a.age)) average_age
from employees a join employees b on a.reports_to=b.employee_id
group by 1,2
order by employee_id;
employee_id name reports_count average_age
----------- ------ ------------- -------------
9 Hercy 2 39
向公司CEO汇报工作的所有人
示例:1270. 向公司CEO汇报工作的所有人
数据:
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| employee_name | varchar(20) |
| manager_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | employee_name | manager_id |
| ----------- | ------------- | ---------- |
| 1 | Boss | 1 |
| 3 | Alice | 3 |
| 2 | Bob | 1 |
| 4 | Daniel | 2 |
| 7 | Luis | 4 |
| 8 | John | 3 |
| 9 | Angela | 8 |
| 77 | Robert | 1 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employees", db_config)
print(df)
employee_id 表示职工的 ID,employee_name 表示职工的名字,manager_id 表示该职工汇报工作的直线经理。这个公司 CEO 是 employee_id = 1 的人。
查询出所有直接或间接向公司 CEO 汇报工作的职工的 employee_id 。由于公司规模较小,经理之间的间接关系不超过 3 个经理。
由于间接关系不超过3个,所以我们可以使用3次自连接解决该问题。
查询CEO的直属下级:
select * from employees
where employee_id<>1 and manager_id=1;
employee_id employee_name manager_id
----------- ------------- ------------
2 Bob 1
77 Robert 1
查询CEO下级的下级:
select
a.employee_id,a.employee_name,
b.*
from employees a
join employees b on a.manager_id=b.employee_id
where a.employee_id<>1 and b.manager_id=1;
employee_id employee_name employee_id employee_name manager_id
----------- ------------- ----------- ------------- ------------
2 Bob 1 Boss 1
4 Daniel 2 Bob 1
77 Robert 1 Boss 1
那么查询全部与CEO存在管理关系的呢?
select
a.employee_id e1,
b.employee_id e2,
c.employee_id e3,
c.manager_id m
from employees a
join employees b on a.manager_id=b.employee_id
join employees c on b.manager_id=c.employee_id
where a.employee_id<>1 and c.manager_id=1;
e1 e2 e3 m
------ ------ ------ --------
2 1 1 1
4 2 1 1
7 4 2 1
77 1 1 1
所以本题:
select a.employee_id from employees a
join employees b on a.manager_id=b.employee_id
join employees c on b.manager_id=c.employee_id
where a.employee_id<>1 and c.manager_id=1;
生成序列并统计
生成固定值
可以通过以下方法生成固定值的表:
select * from(
values row("desktop"),row("mobile"),row("both")
) t(platform);
platform
----------
desktop
mobile
both
示例:1990. 统计实验的数量
数据:
type_md = """
| experiment_id | int |
| platform | enum('Android', 'IOS', 'Web') |
| experiment_name | enum('Reading', 'Sports', 'Programming') |
"""
sql_text = """
| experiment_id | platform | experiment_name |
| ------------- | -------- | --------------- |
| 4 | IOS | Programming |
| 13 | IOS | Sports |
| 14 | Android | Reading |
| 8 | Web | Reading |
| 12 | Web | Reading |
| 18 | Web | Programming |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Experiments", db_config)
print(df)
experiment_id 是Experiments表的主键,查询给定三个实验平台中每种实验完成的次数。要求每一对(实验平台、实验名称)都应包含在输出中,包括平台上实验次数是零的。
select
b.platform,a.experiment_name,
count(c.experiment_id) num_experiments
from (values row('Programming'),row('Sports'),row('Reading')) a(experiment_name)
join (values row('Android'),row('IOS'),row('Web')) b(platform)
left join experiments c using(platform,experiment_name)
group by 1,2;
platform experiment_name num_experiments
-------- --------------- -----------------
Android Reading 1
Android Sports 0
Android Programming 0
IOS Reading 0
IOS Sports 1
IOS Programming 1
Web Reading 2
Web Sports 0
Web Programming 1
示例:1127. 用户购买平台
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| spend_date | date |
| platform | enum('desktop','mobile') |
| amount | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | spend_date | platform | amount |
| ------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ |
| 1 | 2019-07-01 | mobile | 100 |
| 1 | 2019-07-01 | desktop | 100 |
| 2 | 2019-07-01 | mobile | 100 |
| 2 | 2019-07-02 | mobile | 100 |
| 3 | 2019-07-01 | desktop | 100 |
| 3 | 2019-07-02 | desktop | 100 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Spending", db_config)
print(df)
这张表的主键是 (user_id, spend_date, platform),记录了用户支出的时间、平台和金额。
查找每天 仅 使用手机端用户、仅 使用桌面端用户和 同时 使用桌面端和手机端的用户人数和总支出金额。
如果不展示每一天的所有平台会比较简单:
select
spend_date,platform,
sum(amount) total_amount,
count(user_id) total_users
from(
select
user_id,
spend_date,
if(count(platform)=2,"both",any_value(platform)) platform,
sum(amount) amount
from spending
group by user_id,spend_date
) a
group by spend_date,platform
order by spend_date,platform;
spend_date platform total_amount total_users
---------- -------- ------------ -------------
2019-07-01 both 200 1
2019-07-01 desktop 100 1
2019-07-01 mobile 100 1
2019-07-02 desktop 100 1
2019-07-02 mobile 100 1
但是题目要求每天的三种情况都需要展示。
一般情况下面我们可能会使用3个union来生成每天的三种情况:
select distinct spend_date, 'desktop' platform from spending
union all
select distinct spend_date, 'mobile' from spending
union all
select distinct spend_date, 'both' from spending;
另一种方案是使用values生成三种情况再与每一天做笛卡尔积:
select
spend_date,platform
from(
select distinct spend_date from spending
) a,(values row("desktop"),row("mobile"),row("both")) b(platform);
spend_date platform
---------- ----------
2019-07-01 both
2019-07-01 mobile
2019-07-01 desktop
2019-07-02 both
2019-07-02 mobile
2019-07-02 desktop
然后可以基于此进行左连接:
select
a.spend_date,b.platform,
ifnull(sum(amount),0) total_amount,
count(user_id) total_users
from(
select distinct spend_date from spending
) a join (values row("both"),row("mobile"),row("desktop")) b(platform)
left join (
select
user_id,
spend_date,
if(count(platform)=2,"both",any_value(platform)) platform,
sum(amount) amount
from spending
group by user_id,spend_date
) c using(spend_date,platform)
group by a.spend_date,b.platform;
spend_date platform total_amount total_users
---------- -------- ------------ -------------
2019-07-01 desktop 100 1
2019-07-01 mobile 100 1
2019-07-01 both 200 1
2019-07-02 desktop 100 1
2019-07-02 mobile 100 1
2019-07-02 both 0 0
生成数字序列
MySQL可以使用recursive递归临时表生成序列,例如我们需要生成1-100的顺序递增序列:
with recursive nums(n) as(
select 1
union all
select n+1 from nums
where n<100
)
select n from nums;
示例:1613. 找到遗失的ID
数据:
type_md = """
| customer_id | int |
| customer_name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| customer_id | customer_name |
| ----------- | ------------- |
| 1 | Alice |
| 4 | Bob |
| 5 | Charlie |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Customers", db_config)
print(df)
找到所有遗失的顾客id. 遗失的顾客id是指那些不在 Customers 表中, 值却处于 1 和表中最大 customer_id 之间的id.
注意: 最大的 customer_id 值不会超过 100.
返回结果按 ids 升序排列。
with recursive nums(n) as(
select 1
union all
select n+1 from nums
where n<(select max(customer_id) from customers limit 1)
)
select n ids from nums
left join customers a on nums.n=a.customer_id
where a.customer_id is null;
ids
--------
2
3
示例:1767. 寻找没有被执行的任务对
数据:
type_md = """
| task_id | int |
| subtasks_count | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| task_id | subtasks_count |
| ------- | -------------- |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Tasks", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| task_id | int |
| subtask_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| task_id | subtask_id |
| ------- | ---------- |
| 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Executed", db_config)
print(df)
表:Tasks,task_id 表示的为主任务的id,每一个task_id被分为了多个子任务(subtasks),subtasks_count表示为子任务的个数(n),它的值表示了子任务的索引从1到n。
本表保证2 <=subtasks_count<= 20。
表: Executed,每一行表示标记为task_id的主任务与标记为subtask_id的子任务被成功执行。对于每一个task_id,subtask_id <= subtasks_count。
查询没有被执行的(主任务,子任务)对,即没有被执行的(task_id, subtask_id)。
首先生成每个任务的所有子任务id:
with recursive nums(n) as(
select 1
union all
select n+1 from nums
where n<20
)
select
task_id,
n subtask_id
from nums,tasks
where n<=subtasks_count
task_id subtask_id
------- ------------
3 1
2 1
1 1
3 2
2 2
1 2
3 3
1 3
3 4
然后判断其中没有被执行的任务:
with recursive nums(n) as(
select 1 union all
select n+1 from nums
where n<20
)
select
a.*
from (
select
task_id, n subtask_id
from tasks,nums
where n<=subtasks_count
) a left join Executed b using(task_id,subtask_id)
where b.task_id is null;
task_id subtask_id
------- ------------
2 1
1 1
2 2
1 3
示例:1336. 每次访问的交易次数
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| visit_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | visit_date |
| ------- | ---------- |
| 1 | 2020-01-01 |
| 2 | 2020-01-02 |
| 12 | 2020-01-01 |
| 19 | 2020-01-03 |
| 1 | 2020-01-02 |
| 2 | 2020-01-03 |
| 1 | 2020-01-04 |
| 7 | 2020-01-11 |
| 9 | 2020-01-25 |
| 8 | 2020-01-28 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Visits", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| transaction_date | date |
| amount | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | transaction_date | amount |
| ------- | ---------------- | ------ |
| 1 | 2020-01-02 | 120 |
| 2 | 2020-01-03 | 22 |
| 7 | 2020-01-11 | 232 |
| 1 | 2020-01-04 | 7 |
| 9 | 2020-01-25 | 33 |
| 9 | 2020-01-25 | 66 |
| 8 | 2020-01-28 | 1 |
| 9 | 2020-01-25 | 99 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Transactions", db_config)
print(df)
表: Visits(user_id, visit_date) 是该表的主键,每行表示 user_id 在 visit_date 访问了银行
表: Transactions每一行表示 user_id 在 transaction_date 完成了一笔 amount 数额的交易,产生交易记录当天必然会在Visits表留下访问记录。
查询以下两列:
transactions_count:客户在一次访问中的交易次数visits_count:在transactions_count交易次数下相应的访问的客户数量(相同用户多天访问记录多次)
要求transactions_count 的值从 0 到所有用户一次访问中的 max(transactions_count),按 transactions_count 排序
首先查询每个用户每天的交易次数:
select
a.user_id,a.visit_date,
count(b.user_id) transactions_count
from visits a left join transactions b on a.user_id=b.user_id
and a.visit_date=b.transaction_date
group by a.user_id,a.visit_date
user_id visit_date transactions_count
------- ---------- --------------------
1 2020-01-01 0
2 2020-01-02 0
12 2020-01-01 0
19 2020-01-03 0
1 2020-01-02 1
2 2020-01-03 1
1 2020-01-04 1
7 2020-01-11 1
9 2020-01-25 3
8 2020-01-28 1
然后统计每种交易次数下,相应的访问用户数:
select
transactions_count,
count(user_id) visits_count
from(
select
a.user_id,a.visit_date,
count(b.user_id) transactions_count
from visits a left join transactions b on a.user_id=b.user_id
and a.visit_date=b.transaction_date
group by a.user_id,a.visit_date
) a
group by transactions_count;
transactions_count visits_count
------------------ --------------
0 4
1 5
3 1
题目要求包含0次到最大次的所有次数,可以使用可以使用recursive递归临时表生成序列。为了获取max(transactions_count),将上表作为临时表:
with cte as (
select
transactions_count n,
count(user_id) visits_count
from(
select
a.user_id,a.visit_date,
count(b.user_id) transactions_count
from visits a left join transactions b on a.user_id=b.user_id
and a.visit_date=b.transaction_date
group by a.user_id,a.visit_date
) a
group by transactions_count
)
select
a.n transactions_count,
ifnull(cte.visits_count,0) visits_count
from(
with recursive nums(n) as (
select 0 union all
select n+1 from nums
where n<(select max(n) from cte limit 1)
)
select n from nums
) a left join cte using(n)
order by transactions_count;
transactions_count visits_count
------------------ --------------
0 4
1 5
2 0
3 1
分配问题
每辆车的乘客人数1
示例:2142. 每辆车的乘客人数 I
数据:
type_md = """
| bus_id | int |
| arrival_time | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| bus_id | arrival_time |
| ------ | ------------ |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 7 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Buses", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| passenger_id | int |
| arrival_time | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| passenger_id | arrival_time |
| ------------ | ------------ |
| 11 | 1 |
| 12 | 5 |
| 13 | 6 |
| 14 | 7 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Passengers", db_config)
print(df)
- 表
Buses每一行表示公交车到站时间。不会出现两辆公交车会同时到达。bus_id 是该表的主键。 - 表
Passengers每一行表示乘客到站的时间信息。passenger_id 是该表的主键。
如果一辆公交车在时间
tbus到站,乘客在时间tpassenger到站,其中tpassenger <= tbus,该乘客之前没有赶上任何公交车,则该乘客将搭乘该公交车。编写一个 SQL 来查询使用每条总线的用户数量。
返回按
bus_id升序排序 的结果表。
我们可以根据每位乘客的到站时间是否在一辆公交车的上一辆到站时间和自己到站时间的范围,划分乘客坐上了哪辆公交车。
首先我们看看每辆车搭载的乘客:
select
*
from(
select
bus_id,
lag(arrival_time,1,0) over(order by arrival_time) pre_time,
arrival_time
from buses
) a left join passengers b
on b.arrival_time between pre_time and a.arrival_time;
bus_id pre_time arrival_time passenger_id arrival_time
------ -------- ------------ ------------ --------------
1 0 2 11 1
2 2 4 (NULL) (NULL)
3 4 7 14 7
3 4 7 13 6
3 4 7 12 5
由于所有乘客和公交车的到站时间都大于0,所以可以给第一辆到站公交车的上一辆赋值为0。
然后可以统计每辆车搭载的乘客数:
select
bus_id,count(distinct passenger_id) passengers_cnt
from(
select
bus_id,
lag(arrival_time,1,0) over(order by arrival_time) pre_time,
arrival_time
from buses
) a left join passengers b
on b.arrival_time between pre_time and a.arrival_time
group by bus_id
order by bus_id;
bus_id passengers_cnt
------ ----------------
1 1
2 0
3 3
每辆车的乘客人数2
示例:2153. 每辆车的乘客人数 II
相对于上题,给每辆公交车增加了容量限制。数据:
type_md = """
| bus_id | int |
| arrival_time | int |
| capacity | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| bus_id | arrival_time | capacity |
| ------ | ------------ | -------- |
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | 10 |
| 3 | 7 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Buses", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| passenger_id | int |
| arrival_time | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| passenger_id | arrival_time |
| ------------ | ------------ |
| 11 | 1 |
| 12 | 1 |
| 13 | 5 |
| 14 | 6 |
| 15 | 7 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Passengers", db_config)
print(df)
由于存在容量限制,我们无法按照上题的思路实现。现在我们首先查询每辆车到达时累积到达的乘客数量以及,当前车辆的容量限制:
select
bus_id,capacity,
count(distinct passenger_id) cnt
from buses a left join passengers b
on a.arrival_time>=b.arrival_time
group by bus_id
order by a.arrival_time;
bus_id capacity cnt
------ -------- --------
1 1 2
2 10 2
3 2 5
然后使用@go变量表示当前坐上车的乘客,@gone变量表示已经坐上车的全部乘客。最终实现:
select
bus_id,passengers_cnt
from(
select
bus_id,
@go:=if(capacity>cnt-@gone,cnt-@gone,capacity) passengers_cnt,
@gone:=@go+@gone t
from(
select
bus_id,capacity,
count(distinct passenger_id) cnt
from buses a left join passengers b on a.arrival_time>=b.arrival_time
group by bus_id
order by a.arrival_time
) num,(select @go:=0,@gone:=0) var
) t
order by bus_id;
bus_id passengers_cnt
------ ----------------
1 1
2 1
3 2
职员招聘人数1
示例:2004. 职员招聘人数
数据:
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| experience | enum('Senior','Junior') |
| salary | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | experience | salary |
| ----------- | ---------- | ------ |
| 1 | Junior | 10000 |
| 9 | Junior | 10000 |
| 2 | Senior | 20000 |
| 11 | Senior | 20000 |
| 13 | Senior | 50000 |
| 4 | Junior | 40000 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Candidates", db_config)
print(df)
一家公司想雇佣新员工。公司的工资预算是 70000 美元。公司的招聘标准是:
- 雇佣最多的高级员工。
- 在雇佣最多的高级员工后,使用剩余预算雇佣最多的初级员工。
编写一个SQL查询,查找根据上述标准雇佣的高级员工和初级员工的数量。
首先统计不同类型员工,工资从小到大的累计:
select
experience,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary) ss
from candidates;
experience ss
---------- --------
Senior 40000
Senior 40000
Senior 90000
Junior 20000
Junior 20000
Junior 60000
然后我们需要尽可能多的雇佣高级员工,统计雇佣数量和剩余金额:
select
"Senior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates,
70000-max(ss) remain
from (
select
experience,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary) ss
from candidates
) a where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000;
experience accepted_candidates remain
---------- ------------------- --------
Senior 2 30000
然后我们使用剩余预算尽可能多的雇佣初级员工:
with a as(
select
experience,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary,employee_id) ss
from candidates
),b as(
select
"Senior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates,
70000-ifnull(max(ss),0) remain
from a where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000
)
select
"Junior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates
from a where experience="Junior"
and ss<=(select remain from b limit 1)
experience accepted_candidates
---------- ---------------------
Junior 2
最后合并结果:
with a as(
select
experience,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary,employee_id) ss
from candidates
),b as(
select
"Senior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates,
70000-ifnull(max(ss),0) remain
from a where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000
)
select experience,accepted_candidates from b
union all
select
"Junior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates
from a where experience="Junior"
and ss<=(select remain from b limit 1);
experience accepted_candidates
---------- ---------------------
Senior 2
Junior 2
另一种写法:
with cte as(
select
experience,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary,employee_id) ss
from candidates
)
select
"Senior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates
from cte where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000
union all
select
"Junior" experience,
count(1) accepted_candidates
from cte where experience="Junior"
and ss<=70000-(
select ifnull(max(ss),0) from cte
where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000 limit 1
);
职员招聘人数2
示例:2010. 职员招聘人数 II
数据:
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| experience | enum('Senior','Junior') |
| salary | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | experience | salary |
| ----------- | ---------- | ------ |
| 1 | Junior | 10000 |
| 9 | Junior | 15000 |
| 2 | Senior | 20000 |
| 11 | Senior | 16000 |
| 13 | Senior | 50000 |
| 4 | Junior | 40000 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Candidates", db_config)
print(df)
一家公司想雇佣新员工。公司的工资预算是 70000 美元。公司的招聘标准是:
- 雇佣最多的高级员工。
- 在雇佣最多的高级员工后,使用剩余预算雇佣最多的初级员工。
查询雇用职员的 ID。
根据上题相同的思路即可:
with cte as(
select
experience,employee_id,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary,employee_id) ss
from candidates
)
select
employee_id
from cte where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000
union all
select
employee_id
from cte where experience="Junior"
and ss<=70000-(
select ifnull(max(ss),0) from cte
where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000 limit 1
);
或
with a as(
select
experience,employee_id,
sum(salary) over(partition by experience order by salary,employee_id) ss
from candidates
),b as(
select
employee_id,ss
from a where experience="Senior" and ss<=70000
)
select employee_id from b
union all
select
employee_id
from a where experience="Junior"
and ss<=70000-(
select ifnull(max(ss),0) from b
);
结果:
employee_id
-------------
2
11
1
9
函数与存储过程
自定义函数
示例:177. 第N高的薪水
数据:
type_md = """
+-------------+------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+------+
| id | int |
| salary | int |
+-------------+------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+--------+
| id | salary |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
+----+--------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df)
针对上面的问题,下面我们需要编写存储过程创建一个函数能够获得第N高的工资:
delimiter $$
create function getNthHighestSalary(N int) returns int
begin
set N=N-1;
return (
select distinct salary from employee order by salary desc limit N,1
);
end$$
然后就可以轻松得到第N高的薪水:
select getNthHighestSalary(1) salary;
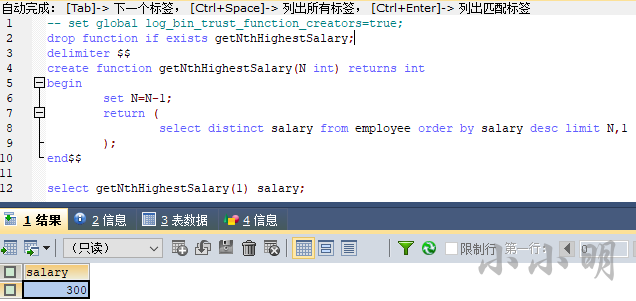
select getNthHighestSalary(2) salary;
salary
--------
200
自定义函数对比存储过程
示例:2205. 有资格享受折扣的用户数量
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| time_stamp | datetime |
| amount | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | time_stamp | amount |
| ------- | ------------------- | ------ |
| 1 | 2022-04-20 09:03:00 | 4416 |
| 2 | 2022-03-19 19:24:02 | 678 |
| 3 | 2022-03-18 12:03:09 | 4523 |
| 3 | 2022-03-30 09:43:42 | 626 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Purchases", db_config)
print(df)
(user_id, time_stamp) 是该表的主键。
每一行都包含 ID 为 user_id 的用户的购买时间和支付金额的信息。
如果用户在时间间隔 [startDate, endDate] 内购买了至少 minAmount 金额的商品,则有资格获得折扣。若要将日期转换为时间,两个日期都应该被视为一天的 开始 (即 endDate = 2022-03-05 应该被视为时间 2022-03-05 00:00:00)。
编写一个 SQL 来查询有资格享受折扣的用户数量。
首先我们看看自定义函数的实现,创建自定义函数:
delimiter $$
create function getUserIDs(startDate date, endDate date, minAmount int) returns int
begin
return (
select
count(distinct user_id) user_cnt
from purchases where amount>=minAmount
and time_stamp between startDate and endDate
order by user_id
);
end$$
执行查询:
select getUserIDs("2022-03-08", "2022-03-20", 1000) user_cnt;
user_cnt
----------
1
示例:2230. 查找可享受优惠的用户
与上题同样的数据。编写一个 SQL 查询来报告符合折扣条件的用户的 id。
由于返回的结果存在多行,所以不能使用函数。
看看存储过程的实现,创建存储过程:
delimiter $$
create procedure getUserIDs(startDate date, endDate date, minAmount int)
begin
select
distinct user_id
from purchases where amount>=minAmount
and time_stamp between startDate and endDate
order by user_id;
end$$
执行:
call getUserIDs("2022-03-08", "2022-03-20", 1000);
user_id
---------
3
透视/逆透视(行转列、列转行)
无主键顺序行转列
示例:618. 学生地理信息报告
数据:
type_md = """
| name | varchar(20) |
| continent | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| name | continent |
+--------+-----------+
| Jane | America |
| Pascal | Europe |
| Xi | Asia |
| Jack | America |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Student", db_config)
print(df)
对大洲(continent)列透视操作,使得每个学生按照姓名的字母顺序依次排列在对应的大洲下面。输出的标题应依次为美洲(America)、亚洲(Asia)和欧洲(Europe)。
题目限制了测试数据中,美洲的学生必定最多,SQL写法如下:
select
America,Asia,Europe
from(
select row_number() over(order by name) id,name America from student where continent="America"
) a left join (
select row_number() over(order by name) id,name Asia from student where continent="Asia"
) b on a.id=b.id left join (
select row_number() over(order by name) id,name Europe from student where continent="Europe"
) c on a.id=c.id;
结果:
America Asia Europe
------- ------ --------
Jack Xi Pascal
Jane (NULL) (NULL)
透视表(行转列)
示例:1179. 重新格式化部门表
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| revenue | int |
| month | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | revenue | month |
| -- | ------- | ----- |
| 1 | 8000 | Jan |
| 2 | 9000 | Jan |
| 3 | 10000 | Feb |
| 1 | 7000 | Feb |
| 1 | 6000 | Mar |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Department", db_config)
print(df)
重新格式化表,使得新的表中有一个部门 id 列和一些对应 每个月 的收入(revenue)列。
select
id,
sum(if(month='Jan',revenue,null)) as Jan_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Feb',revenue,null)) as Feb_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Mar',revenue,null)) as Mar_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Apr',revenue,null)) as Apr_Revenue,
sum(if(month='May',revenue,null)) as May_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Jun',revenue,null)) as Jun_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Jul',revenue,null)) as Jul_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Aug',revenue,null)) as Aug_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Sep',revenue,null)) as Sep_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Oct',revenue,null)) as Oct_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Nov',revenue,null)) as Nov_Revenue,
sum(if(month='Dec',revenue,null)) as Dec_Revenue
from department group by id;
结果:

逆透视(列转行)
示例:1795. 每个产品在不同商店的价格
数据:
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| store1 | int |
| store2 | int |
| store3 | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | store1 | store2 | store3 |
| ---------- | ------ | ------ | ------ |
| 0 | 95 | 100 | 105 |
| 1 | 70 | null | 80 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Products", db_config)
print(df)
重构 Products 表,查询每个产品在不同商店的价格,使得输出的格式变为(product_id, store, price) 。如果这一产品在商店里没有出售,则不输出这一行。
select product_id,"store1" store,store1 price from products where store1 is not null
union all
select product_id,"store2" store,store2 from products where store2 is not null
union all
select product_id,"store3" store,store3 from products where store3 is not null;
product_id store price
---------- ------ --------
0 store1 95
1 store1 70
0 store2 100
0 store3 105
1 store3 80
动态行转列
示例:2252. 表的动态旋转
数据:
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| store | varchar(20) |
| price | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | store | price |
| ---------- | -------- | ----- |
| 1 | Shop | 110 |
| 1 | LC_Store | 100 |
| 2 | Nozama | 200 |
| 2 | Souq | 190 |
| 3 | Shop | 1000 |
| 3 | Souq | 1900 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Products", db_config)
print(df)
与前面透视表的区别在于,要求能够根据Products表的store列的内容自动生成列,store列的内容不确定。
这里我们使用存储过程,拼接SQL字符串并执行,最终实现:
drop procedure if exists PivotProducts;
delimiter $$
create procedure PivotProducts()
begin
set group_concat_max_len = 10240;
with tmp as (
select distinct store from products
order by store
)
select
concat('select product_id,',
group_concat("sum(if(store='",store,"',price,null)) ",store),
" from products group by product_id")
into @sql from tmp;
prepare statement from @sql;
execute statement;
end$$
然后我们调用:
product_id LC_Store Nozama Shop Souq
---------- -------- ------ ------ --------
1 100 (NULL) 110 (NULL)
2 (NULL) 200 (NULL) 190
3 (NULL) (NULL) 1000 1900
下面我们将其升级到能够针对任何表格:
drop procedure if exists PivotTable;
delimiter $$
create procedure PivotTable(tbname text,idx text,col text,v text,aggfunc text)
begin
set group_concat_max_len = 10240;
drop table if exists tmp;
set @sql=concat("create temporary table tmp(select distinct ",
col," t from ",tbname," order by ",col,")");
prepare stmt from @sql;
execute stmt;
deallocate prepare stmt;
select
concat('select ',idx,',',
group_concat(aggfunc,"(if(",col,"='",t,"',",v,",null)) ",t),
" from ",tbname," group by ",idx)
into @sql from tmp;
prepare stmt from @sql;
execute stmt;
end$$
调用:
call PivotTable("products","product_id","store","price","sum");
能够得到上面一致的结果。
针对前面的部门表试试:
call PivotTable("department","id","month","revenue","sum");
id Feb Jan Mar
------ ------ ------ --------
1 7000 8000 6000
2 (NULL) 9000 (NULL)
3 10000 (NULL) (NULL)
动态列转行
示例:2253. 动态取消表的旋转
数据:
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| LC_Store | int |
| Nozama | int |
| Shop | int |
| Souq | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | LC_Store | Nozama | Shop | Souq |
| ---------- | -------- | ------ | ---- | ---- |
| 1 | 100 | null | 110 | null |
| 2 | null | 200 | null | 190 |
| 3 | null | null | 1000 | 1900 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Products", db_config)
print(df)
相当于上题的逆过程。
存储过程创建代码:
drop procedure if exists UnpivotProducts;
delimiter $$
create procedure UnpivotProducts() # 列转行
begin
set group_concat_max_len = 10240;
select
group_concat("select product_id,'",column_name,"' store,",
column_name," price from products where ",
column_name," is not null" separator ' union all '
) into @sql
from (
select column_name from information_schema.columns
where table_schema = database() and table_name = "products"
and column_name <> "product_id"
) t;
prepare statement from @sql;
execute statement;
end$$
调用该过程:
call UnpivotProducts();
product_id store price
---------- -------- --------
1 lc_store 100
2 nozama 200
1 shop 110
3 shop 1000
2 souq 190
3 souq 1900
同样将该过程升级到可以处理任何表:
drop procedure if exists MeltTable;
delimiter $$
create procedure MeltTable(tbname text,idx text,col_name text,val_name text) # 列转行
begin
set group_concat_max_len = 10240;
select
group_concat("select ",idx,",'",column_name,"' ",col_name,",",
column_name," ",val_name," from ",tbname," where ",
column_name," is not null" separator ' union all '
) into @sql
from (
select column_name from information_schema.columns
where table_schema = database() and table_name = tbname
and column_name <> idx
) t;
prepare statement from @sql;
execute statement;
end$$
调用:
call MeltTable("products","product_id","store","price");
product_id store price
---------- -------- --------
1 lc_store 100
2 nozama 200
1 shop 110
3 shop 1000
2 souq 190
3 souq 1900
其他
行程和用户
示例:262. 行程和用户
数据:
type_md = """
+-------------+----------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+----------+
| id | int |
| client_id | int |
| driver_id | int |
| city_id | int |
| status | enum('completed','cancelled_by_driver','cancelled_by_client') |
| request_at | date |
+-------------+----------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----+-----------+-----------+---------+---------------------+------------+
| id | client_id | driver_id | city_id | status | request_at |
+----+-----------+-----------+---------+---------------------+------------+
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | completed | 2013-10-01 |
| 2 | 2 | 11 | 1 | cancelled_by_driver | 2013-10-01 |
| 3 | 3 | 12 | 6 | completed | 2013-10-01 |
| 4 | 4 | 13 | 6 | cancelled_by_client | 2013-10-01 |
| 5 | 1 | 10 | 1 | completed | 2013-10-02 |
| 6 | 2 | 11 | 6 | completed | 2013-10-02 |
| 7 | 3 | 12 | 6 | completed | 2013-10-02 |
| 8 | 2 | 12 | 12 | completed | 2013-10-03 |
| 9 | 3 | 10 | 12 | completed | 2013-10-03 |
| 10 | 4 | 13 | 12 | cancelled_by_driver | 2013-10-03 |
+----+-----------+-----------+---------+---------------------+------------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Trips", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
type_md = """
+-------------+----------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+----------+
| users_id | int |
| banned | enum('Yes','No') |
| role | enum('client','driver','partner') |
+-------------+----------+
"""
sql_text = """
+----------+--------+--------+
| users_id | banned | role |
+----------+--------+--------+
| 1 | No | client |
| 2 | Yes | client |
| 3 | No | client |
| 4 | No | client |
| 10 | No | driver |
| 11 | No | driver |
| 12 | No | driver |
| 13 | No | driver |
+----------+--------+--------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Users", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
要求:
取消率 的计算方式如下:(被司机或乘客取消的非禁止用户生成的订单数量) / (非禁止用户生成的订单总数)。
写一段 SQL 语句查出 "2013-10-01" 至 "2013-10-03" 期间非禁止用户(乘客和司机都必须未被禁止)的取消率。非禁止用户即 banned 为 No 的用户,禁止用户即 banned 为 Yes 的用户。
返回结果表中的数据可以按任意顺序组织。其中取消率 Cancellation Rate 需要四舍五入保留 两位小数 。
解答:
select
request_at day,round(avg(status!="completed"),2) `Cancellation Rate`
from Trips a
join Users b on a.client_id =b.users_id and b.banned="No"
join Users c on a.driver_id =c.users_id and c.banned="No"
where a.request_at between '2013-10-01' and '2013-10-03'
group by request_at;
day Cancellation Rate
---------- -------------------
2013-10-03 0.50
2013-10-01 0.33
2013-10-02 0.00
部门与公司比较平均工资
示例:615. 平均工资:部门与公司比较
数据:
type_md = """
| id | int |
| employee_id | int |
| amount | int |
| pay_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| id | employee_id | amount | pay_date |
|----|-------------|--------|------------|
| 1 | 1 | 9000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 2 | 2 | 6000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 3 | 3 | 10000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 4 | 1 | 7000 | 2017-02-28 |
| 5 | 2 | 6000 | 2017-02-28 |
| 6 | 3 | 8000 | 2017-02-28 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "salary", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| employee_id | int |
| department_id | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| employee_id | department_id |
|-------------|---------------|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Employee", db_config)
print(df)
求出在每一个工资发放日,每个部门的平均工资与公司的平均工资的比较结果 (高 / 低 / 相同)。
先求出每个工资发放月份,每个部门的总工资和人数,以及全公司的总工资和人数:
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month,
department_id,
sum(amount) d1,
count(1) n1,
sum(sum(amount)) over(partition by left(pay_date,7)) d2,
sum(count(1)) over(partition by left(pay_date,7)) n2
from salary a join employee b
using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7),department_id
pay_month department_id d1 n1 d2 n2
--------- ------------- ------ ------ ------ --------
2017-02 1 7000 1 21000 3
2017-02 2 14000 2 21000 3
2017-03 1 9000 1 25000 3
2017-03 2 16000 2 25000 3
然后直接判断,为了使代码清晰一点,这里在子查询中进行判断:
select
pay_month,department_id,
case
when d1/n1>d2/n2 then "higher"
when d1/n1<d2/n2 then "lower"
else "same"
end comparison
from(
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month,
department_id,
sum(amount) d1,
count(1) n1,
sum(sum(amount)) over(partition by left(pay_date,7)) d2,
sum(count(1)) over(partition by left(pay_date,7)) n2
from salary a join employee b
using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7),department_id
) a;
方法二:分别在两个查询中计算出部门和公司的平均工资,再进行表连接。
select
pay_month,department_id,
case
when v1>v2 then "higher"
when v1<v2 then "lower"
else "same"
end comparison
from(
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month, department_id,
avg(amount) v1
from salary a join employee b using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7),department_id
) a join (
select
left(pay_date,7) pay_month, avg(amount) v2
from salary a join employee b using(employee_id)
group by left(pay_date,7)
) b using(pay_month);
结果:
pay_month department_id comparison
--------- ------------- ------------
2017-03 1 higher
2017-03 2 lower
2017-02 1 same
2017-02 2 same
活跃业务
示例:1126. 查询活跃业务
数据:
type_md = """
| business_id | int |
| event_type | varchar(20) |
| occurences | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| business_id | event_type | occurences |
| ----------- | ---------- | ---------- |
| 1 | reviews | 7 |
| 3 | reviews | 3 |
| 1 | ads | 11 |
| 2 | ads | 7 |
| 3 | ads | 6 |
| 1 | page views | 3 |
| 2 | page views | 12 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Events", db_config)
print(df)
Events表的每一行记录了某种类型的事件在某些业务中发生的次数。
题目:查询所有活跃的业务。如果一个业务的某个事件类型的发生次数大于此事件类型在所有业务中的平均发生次数,并且该业务至少有两个这样的事件类型,那么该业务就可被看做是活跃业务。
select
a.business_id
from events a join (
select event_type,avg(occurences) avg_num
from Events
group by event_type
) b using(event_type)
group by a.business_id
having sum(a.occurences>b.avg_num)>=2;
也可以使用窗口函数,省略掉一次连接:
select
business_id
from (
select
*,
avg(occurences) over(partition by event_type) avg_num
from events
) a
group by business_id
having sum(occurences>avg_num)>=2;
business_id
-------------
1
报告的记录
示例:1132. 报告的记录 II
数据:
type_md = """
| user_id | int |
| post_id | int |
| action_date | date |
| action | enum('view','like','reaction','comment','report','share') |
| extra | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| user_id | post_id | action_date | action | extra |
| ------- | ------- | ----------- | ------ | ------ |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | view | null |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | like | null |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | share | null |
| 2 | 2 | 2019-07-04 | view | null |
| 2 | 2 | 2019-07-04 | report | spam |
| 3 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | view | null |
| 3 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | report | spam |
| 4 | 3 | 2019-07-02 | view | null |
| 4 | 3 | 2019-07-02 | report | spam |
| 5 | 2 | 2019-07-03 | view | null |
| 5 | 2 | 2019-07-03 | report | racism |
| 5 | 5 | 2019-07-03 | view | null |
| 5 | 5 | 2019-07-03 | report | racism |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Actions", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| post_id | int |
| remove_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| post_id | remove_date |
| ------- | ----------- |
| 2 | 2019-07-20 |
| 3 | 2019-07-18 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Removals", db_config)
print(df)
post_id表示帖子id,remove_date表示帖子被移除的日期。
查询在被报告为垃圾广告的帖子中,被移除的帖子的每日平均占比,四舍五入到小数点后 2 位。
首先,我们查询被报告为垃圾广告的帖子:
select distinct post_id,action_date from Actions where extra="spam"
post_id action_date
------- -------------
2 2019-07-04
4 2019-07-04
3 2019-07-02
然后查看这些帖子是否被移除:
select
*
from(
select distinct post_id,action_date from Actions where extra="spam"
) a
left join removals b using(post_id);
post_id action_date remove_date
------- ----------- -------------
2 2019-07-04 2019-07-20
4 2019-07-04 (NULL)
3 2019-07-02 2019-07-18
然后统计每日的垃圾广告帖子的移除率:
select
action_date,avg(remove_date is not null) daily_percent
from(
select distinct post_id,action_date from Actions where extra="spam"
) a
left join removals b using(post_id)
group by action_date;
action_date daily_percent
----------- ---------------
2019-07-04 0.5000
2019-07-02 1.0000
最终平均每日移除率为:
select
round(avg(daily_percent)*100,2) average_daily_percent
from(
select
action_date,avg(remove_date is not null) daily_percent
from(
select distinct post_id,action_date from Actions where extra="spam"
) a
left join removals b using(post_id)
group by action_date
) c;
average_daily_percent
-----------------------
75.00
显示价格最高的发票的详情
示例:2362. 生成发票
数据:
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| price | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | price |
| ---------- | ----- |
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Products", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| invoice_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| quantity | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| invoice_id | product_id | quantity |
| ---------- | ---------- | -------- |
| 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | 4 |
| 4 | 1 | 10 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Purchases", db_config)
print(df)
表:Products中的每一行显示了一个产品的 ID 和一个单位的价格。product_id 是该表的主键。
表 Purchases中的每一行都显示了从发票中的一种产品订购的数量。(invoice_id, product_id) 是该表的主键。
查询显示价格最高的发票的详细信息。如果两个或多个发票具有相同的价格,则返回 invoice_id 最小的发票的详细信息。
首先查询每件商品的总价格和对应信息:
select
invoice_id,b.product_id,quantity,
quantity*price price
from products a join purchases b using(product_id);
invoice_id product_id quantity price
---------- ---------- -------- --------
1 1 2 200
3 2 1 200
2 2 3 600
2 1 4 400
4 1 10 1000
然后查询总价格最高的发票:
select
invoice_id
from products a join purchases b using(product_id)
group by invoice_id
order by sum(quantity*price) desc,invoice_id limit 1;
invoice_id
------------
2
最后基于前面的信息表筛选:
select
product_id,quantity,price
from(
select
invoice_id
from products a join purchases b using(product_id)
group by invoice_id
order by sum(quantity*price) desc,invoice_id limit 1
) a join (
select
invoice_id,b.product_id,quantity,
quantity*price price
from products a join purchases b using(product_id)
) b using(invoice_id);
product_id quantity price
---------- -------- --------
1 4 400
2 3 600
明显查询总价格最高的发票,也可以基于第一步生成的完整详情表操作,使用临时表:
with cte as(
select
invoice_id,b.product_id,quantity,
quantity*price price
from products a join purchases b using(product_id)
)
select
product_id,quantity,price
from(
select invoice_id from cte group by invoice_id order by sum(price) desc,invoice_id limit 1
) a join cte using(invoice_id);
游戏玩法分析
示例:511. 游戏玩法分析 I
数据:
type_md = """
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| player_id | int |
| device_id | int |
| event_date | date |
| games_played | int |
+--------------+---------+
"""
sql_text = """
+-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+
| player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played |
+-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+
| 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 2016-05-02 | 6 |
| 2 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2016-03-02 | 0 |
| 3 | 4 | 2018-07-03 | 5 |
+-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Activity", db_config)
print(df.to_markdown(index=False))
- 获取每位玩家 第一次登陆平台的日期
select
player_id, min(event_date) first_login
from Activity group by player_id;
player_id first_login
--------- -------------
1 2016-03-01
2 2017-06-25
3 2016-03-02
示例:512. 游戏玩法分析 II
- 描述每一个玩家首次登陆的设备名称
select
player_id,device_id
from(
select
player_id, device_id,
rank() over(partition by player_id order by event_date) rn
from Activity
) a
where rn=1;
player_id device_id
--------- -----------
1 2
2 3
3 1
示例:534. 游戏玩法分析 III
- 报告每组玩家到目前为止玩了多少游戏,即在此日期之前玩家所玩的游戏总数
select
player_id, event_date,
sum(games_played) over(partition by player_id order by event_date) games_played_so_far
from Activity
player_id event_date games_played_so_far
--------- ---------- ---------------------
1 2016-03-01 5
1 2016-05-02 11
2 2017-06-25 1
3 2016-03-02 0
3 2018-07-03 5
示例:550. 游戏玩法分析 IV
- 计算玩家首次登录的第二天再次登录比率,即首次登录第二天仍然登录的玩家数量/玩家总数
select
round(avg(b.player_id is not null),2) fraction
from(
select
player_id,adddate(min(event_date),1) event_date
from activity
group by player_id
) a left join activity b using (player_id,event_date);
修改一处数据后的执行结果:
fraction
----------
0.33
示例:1097. 游戏玩法分析 V
- 安装日第一天留存率
玩家的 安装日期 定义为该玩家的第一个登录日。
玩家的 第一天留存率 为:假定安装日期为 X 的玩家的数量为 N ,其中在 X 之后的一天重新登录的玩家数量为 M ,M/N 就是第一天留存率,四舍五入到小数点后两位。
查询所有安装日期、当天安装游戏的玩家数量和玩家的第一天留存率。
此题再修改一处数据:
此题只需要在上一题基础上分组即可:
select
a.min_date install_dt,
count(a.player_id) installs,
round(avg(b.player_id is not null),2) Day1_retention
from(
select
player_id,min(event_date) min_date
from Activity
group by player_id
) a left join Activity b on a.player_id=b.player_id
and datediff(b.event_date,a.min_date)=1
group by a.min_date;
结果:
install_dt installs Day1_retention
---------- -------- ----------------
2016-03-01 2 0.50
2017-06-25 1 0.00
好友申请:总体通过率
示例:I:总体通过率
数据:
type_md = """
| sender_id | int |
| send_to_id | int |
| request_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
+-----------+------------+--------------+
| sender_id | send_to_id | request_date |
+-----------+------------+--------------+
| 1 | 2 | 2016/06/01 |
| 1 | 3 | 2016/06/01 |
| 1 | 4 | 2016/06/01 |
| 2 | 3 | 2016/06/02 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016/06/09 |
+-----------+------------+--------------+
"""
md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "FriendRequest", db_config)
type_md = """
| requester_id | int |
| accepter_id | int |
| accept_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
+--------------+-------------+-------------+
| requester_id | accepter_id | accept_date |
+--------------+-------------+-------------+
| 1 | 2 | 2016/06/03 |
| 1 | 3 | 2016/06/08 |
| 2 | 3 | 2016/06/08 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016/06/09 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016/06/10 |
+--------------+-------------+-------------+
"""
md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "RequestAccepted", db_config)
FriendRequest表包含发送请求的用户的 ID ,接受请求的用户的 ID 以及请求的日期。
RequestAccepted表包含发送请求的用户的 ID ,接受请求的用户的 ID 以及请求通过的日期。
求出好友申请的通过率,用 2 位小数表示。通过率由接受好友申请的数目除以申请总数。
提示:
- 通过的好友申请不一定都在表
friend_request中。你只需要统计总的被通过的申请数(不管它们在不在表FriendRequest中),并将它除以申请总数,得到通过率 - 一个好友申请发送者有可能会给接受者发几条好友申请,也有可能一个好友申请会被通过好几次。这种情况下,重复的好友申请只统计一次。
- 如果一个好友申请都没有,应该返回
accept_rate为 0.00 。
首先获取总通过数:
select count(distinct requester_id,accepter_id) from requestaccepted;
再查询申请总数:
select count(distinct sender_id,send_to_id) from friendrequest;
只需两者相除即可:
select
round(
ifnull(
(select count(distinct requester_id,accepter_id) from requestaccepted)/
(select count(distinct sender_id,send_to_id) from friendrequest)
,0)
,2) accept_rate;
好友申请:谁有最多的好友
示例:II :谁有最多的好友
数据:
type_md = """
| requester_id | int |
| accepter_id | int |
| accept_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
+--------------+-------------+-------------+
| requester_id | accepter_id | accept_date |
+--------------+-------------+-------------+
| 1 | 2 | 2016/06/03 |
| 1 | 3 | 2016/06/08 |
| 2 | 3 | 2016/06/08 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016/06/09 |
+--------------+-------------+-------------+
"""
md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "RequestAccepted", db_config)
(requester_id, accepter_id) 是这张表的主键。
这张表包含发送好友请求的人的 ID ,接收好友请求的人的 ID ,以及好友请求通过的日期。
现在要求找出拥有最多的好友的人和他拥有的好友数目。
要统计每个用户的好友数,只需:
select
id,count(distinct id2) num
from(
select requester_id id,accepter_id id2 from RequestAccepted
union all
select accepter_id,requester_id from RequestAccepted
) a
group by id
order by num desc limit 1;
id num
------ --------
3 3
产品销售分析1
示例:1068. 产品销售分析 I
数据:
type_md = """
| sale_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| year | int |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| sale_id | product_id | year | quantity | price |
+---------+------------+------+----------+-------+
| 1 | 100 | 2008 | 10 | 5000 |
| 2 | 100 | 2009 | 12 | 5000 |
| 7 | 200 | 2011 | 15 | 9000 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Sales", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar(20) |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | product_name |
+------------+--------------+
| 100 | Nokia |
| 200 | Apple |
| 300 | Samsung |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Product", db_config)
print(df)
获取 Sales 表中所有产品对应的 产品名称 product_name 以及该产品的所有 售卖年份 year 和 价格 price 。
select
p.product_name,s.year,s.price
from sales s join product p on s.product_id=p.product_id;
product_name year price
------------ ------ --------
Nokia 2009 5000
Nokia 2008 5000
Apple 2011 9000
示例:1069. 产品销售分析 II
按产品 id product_id 来统计每个产品的销售总量。
select
product_id,sum(quantity) total_quantity
from sales
group by product_id;
product_id total_quantity
---------- ----------------
100 22
200 15
示例:1070. 产品销售分析 III
选出每个销售产品 第一年 销售的 产品 id、年份、数量 和 价格。
select
product_id,year first_year,quantity,price
from(
select
product_id,year,quantity,price,
rank() over(partition by product_id order by year) rn
from sales
) a
where rn=1;
product_id first_year quantity price
---------- ---------- -------- --------
100 2008 10 5000
200 2011 15 9000
产品销售分析4
示例:2324. 产品销售分析 IV
数据:
type_md = """
| sale_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| user_id | int |
| quantity | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| sale_id | product_id | user_id | quantity |
+---------+------------+---------+----------+
| 1 | 1 | 101 | 10 |
| 2 | 3 | 101 | 7 |
| 3 | 1 | 102 | 9 |
| 4 | 2 | 102 | 6 |
| 5 | 3 | 102 | 10 |
| 6 | 1 | 102 | 6 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Sales", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| product_id | int |
| price | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| product_id | price |
+------------+-------+
| 1 | 10 |
| 2 | 25 |
| 3 | 15 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Product", db_config)
print(df)
查询每个用户消费最多的产品 id。如果同一用户在两个或多个产品上花费了最多的钱,获取所有花费了最多的钱的产品。
select
user_id,product_id
from(
select
user_id,a.product_id,
rank() over(partition by user_id order by sum(quantity*price) desc) rk
from sales a join product b using(product_id)
group by user_id,a.product_id
) a
where rk=1;
user_id product_id
------- ------------
101 3
102 1
102 2
102 3
示例:2329. 产品销售分析Ⅴ
查询每个用户的消费额,按用户消费额 spending 递减的顺序返回。在消费额相等的情况下,以 user_id 递增的顺序将其排序。
select
user_id,sum(quantity*ifnull(price,0)) spending
from sales a left join product using(product_id)
group by user_id
order by 2 desc,1;
user_id spending
------- ----------
102 450
101 205
Hopper 公司查询1
示例:1635. Hopper 公司查询 I
数据:
type_md = """
| driver_id | int |
| join_date | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| driver_id | join_date |
| --------- | ---------- |
| 10 | 2019-12-10 |
| 8 | 2020-1-13 |
| 5 | 2020-2-16 |
| 7 | 2020-3-8 |
| 4 | 2020-5-17 |
| 1 | 2020-10-24 |
| 6 | 2021-1-5 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Drivers", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| ride_id | int |
| user_id | int |
| requested_at | date |
"""
sql_text = """
| ride_id | user_id | requested_at |
| ------- | ------- | ------------ |
| 6 | 75 | 2019-12-9 |
| 1 | 54 | 2020-2-9 |
| 10 | 63 | 2020-3-4 |
| 19 | 39 | 2020-4-6 |
| 3 | 41 | 2020-6-3 |
| 13 | 52 | 2020-6-22 |
| 7 | 69 | 2020-7-16 |
| 17 | 70 | 2020-8-25 |
| 20 | 81 | 2020-11-2 |
| 5 | 57 | 2020-11-9 |
| 2 | 42 | 2020-12-9 |
| 11 | 68 | 2021-1-11 |
| 15 | 32 | 2021-1-17 |
| 12 | 11 | 2021-1-19 |
| 14 | 18 | 2021-1-27 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "Rides", db_config)
print(df)
type_md = """
| ride_id | int |
| driver_id | int |
| ride_distance | int |
| ride_duration | int |
"""
sql_text = """
| ride_id | driver_id | ride_distance | ride_duration |
| ------- | --------- | ------------- | ------------- |
| 10 | 10 | 63 | 38 |
| 13 | 10 | 73 | 96 |
| 7 | 8 | 100 | 28 |
| 17 | 7 | 119 | 68 |
| 20 | 1 | 121 | 92 |
| 5 | 7 | 42 | 101 |
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 38 |
| 11 | 8 | 37 | 43 |
| 15 | 8 | 108 | 82 |
| 12 | 8 | 38 | 34 |
| 14 | 1 | 90 | 74 |
"""
df = md2sql(sql_text, type_md, "AcceptedRides", db_config)
print(df)
表 Drivers每一行表示司机入职Hopper公司的日期。driver_id是该表的主键。
表Rides每一行表示乘客发起的一个乘车请求。ride_id是该表的主键。
表 AcceptedRides每一行表示被接受的行程信息。ride_id是该表的主键。
编写SQL查询2020年每个月的以下统计信息:
- 截至某月底,当前在Hopper公司工作的司机数量(
active_drivers)。 - 该月接受的乘车次数(
accepted_rides)。
返回按month 升序排列的结果表,其中month 是月份的数字(一月是1,二月是2,依此类推)。
要计算2020年每个月当前工作的司机数量,首先需要计算2020年每个月入职的司机数量和2020年之前入职的司机数量。2020年1月工作的司机为2020年1月入职的司机数量和2020年之前入职的司机数量,那么可以将2020年之前入职的司机都视为2020年1月入职。最终查询每月入职的驾驶员数量:
select
if(year(join_date)<2020,1,month(join_date)) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Drivers
where year(join_date)<=2020
group by 1;
month cnt
------ --------
1 2
2 1
3 1
5 1
10 1
为了计算每个月的累积数量,需要先生成12个月的序列再连接:
with recursive nums(month) as(
select 1 month
union all
select month+1 from nums
where month<12
)
select
month,
sum(ifnull(cnt,0)) over(order by a.month) active_drivers
from nums a left join(
select
if(year(join_date)<2020,1,month(join_date)) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Drivers
where year(join_date)<=2020
group by 1
) b using(month);
month active_drivers
------ ----------------
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 4
5 5
6 5
7 5
8 5
9 5
10 6
11 6
12 6
这样顺利得到2020年每个月当前工作的司机数量。
然后计算2020年每个月被接受的乘车次数:
select
month(requested_at) month,
count(distinct ride_id) cnt
from Rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month;
month cnt
------ --------
3 1
6 1
7 1
8 1
11 2
12 1
最后合并即可:
with recursive nums(month) as(
select 1 month
union all
select month+1 from nums
where month<12
)
select
month,
sum(ifnull(b.cnt,0)) over(order by a.month) active_drivers,
ifnull(c.cnt,0) accepted_rides
from nums a left join(
select
if(year(join_date)<2020,1,month(join_date)) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Drivers
where year(join_date)<=2020
group by 1
) b using(month)
left join(
select
month(requested_at) month,
count(distinct ride_id) cnt
from Rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month
) c using(month);
month active_drivers accepted_rides
------ -------------- ----------------
1 2 0
2 3 0
3 4 1
4 4 0
5 5 0
6 5 1
7 5 1
8 5 1
9 5 0
10 6 0
11 6 2
12 6 1
Hopper 公司查询2
示例:1645.Hopper 公司查询 II
数据依然使用上一题的数据,现在要求查询以报告2020年每个月的工作驱动因素百分比(working_percentage),即每月被接受至少一个行程的司机数量/该月工作的司机数量
注意:如果一个月内可用司机的数量为零,认为working_percentage为0。
返回按month升序排列的结果表,其中month是月份的编号(一月是1,二月是2,等等)。将working_percentage四舍五入至小数点后两位。
首先查询2020年每个月被接受至少一个行程的司机数量:
select
month(requested_at) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month;
month cnt
------ --------
3 1
6 1
7 1
8 1
11 2
12 1
按照上一题的思路可以计算每个月工作的司机数量:
with recursive nums(month) as(
select 1 month
union all
select month+1 from nums
where month<12
)
select
month,
sum(ifnull(cnt,0)) over(order by a.month) active_drivers
from nums a left join(
select
if(year(join_date)<2020,1,month(join_date)) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Drivers
where year(join_date)<=2020
group by 1
) b using(month);
连接后相除,即可得到要求的结果:
with recursive nums(month) as(
select 1 month
union all
select month+1 from nums
where month<12
)
select
month,
ifnull(round(b.cnt*100/
sum(ifnull(c.cnt,0)) over(order by a.month),2),0) working_percentage
from nums a left join(
select
month(requested_at) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month
) b using(month)
left join(
select
if(year(join_date)<2020,1,month(join_date)) month,
count(distinct driver_id) cnt
from Drivers
where year(join_date)<=2020
group by 1
) c using(month)
month working_percentage
------ --------------------
1 0.00
2 0.00
3 25.00
4 0.00
5 0.00
6 20.00
7 20.00
8 20.00
9 0.00
10 0.00
11 33.33
12 16.67
Hopper 公司查询3
示例:1651. Hopper 公司查询 III
依然是上题的数据。
查询从 2020年1月至3月 至 2020年10月至12月 的每三个月窗口的 average_ride_distance 和 average_ride_duration 。
将 average_ride_distance 和 average_ride_duration 四舍五入至 小数点后两位 。
通过将三个月的总 ride_distance 相加并除以 3 来计算 average_ride_distance 。average_ride_duration 的计算方法与此类似。
返回按 month 升序排列的结果表。
首先计算每月的 ride_distance 和 ride_duration:
select
month(requested_at) month,
sum(ride_distance) ride_distance,
sum(ride_duration) ride_duration
from rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month;
month ride_distance ride_duration
------ ------------- ---------------
3 63 38
6 73 96
7 100 28
8 119 68
11 163 193
12 6 38
然后生成月份序列,按照三个月的时间窗口求平均值:
with recursive nums(month) as(
select 1 month
union all
select month+1 from nums
where month<12
)
select
nums.month,
avg(ifnull(ride_distance,0)) over(order by nums.month rows 2 PRECEDING) average_ride_distance,
avg(ifnull(ride_duration,0)) over(order by nums.month rows 2 PRECEDING) average_ride_duration
from nums left join(
select
month(requested_at) month,
sum(ride_distance) ride_distance,
sum(ride_duration) ride_duration
from rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month
) a using(month);
month average_ride_distance average_ride_duration
------ --------------------- -----------------------
1 0.0000 0.0000
2 0.0000 0.0000
3 21.0000 12.6667
4 21.0000 12.6667
5 21.0000 12.6667
6 24.3333 32.0000
7 57.6667 41.3333
8 97.3333 64.0000
9 73.0000 32.0000
10 39.6667 22.6667
11 54.3333 64.3333
12 56.3333 77.0000
最后调整一下月份并过滤即可:
with recursive nums(month) as(
select 1 month
union all
select month+1 from nums
where month<12
)
select
month-2 month,
round(average_ride_distance,2) average_ride_distance,
round(average_ride_duration,2) average_ride_duration
from(
select
nums.month,
avg(ifnull(ride_distance,0)) over(order by nums.month rows 2 PRECEDING) average_ride_distance,
avg(ifnull(ride_duration,0)) over(order by nums.month rows 2 PRECEDING) average_ride_duration
from nums left join(
select
month(requested_at) month,
sum(ride_distance) ride_distance,
sum(ride_duration) ride_duration
from rides join AcceptedRides using(ride_id)
where year(requested_at)=2020
group by month
) a using(month)
) b
where month>=3;
month average_ride_distance average_ride_duration
------ --------------------- -----------------------
1 21.00 12.67
2 21.00 12.67
3 21.00 12.67
4 24.33 32.00
5 57.67 41.33
6 97.33 64.00
7 73.00 32.00
8 39.67 22.67
9 54.33 64.33
10 56.33 77.00