1.原理
我们用这道题目 LCR 008. 长度最小的子数组 来讲解“滑动窗口”的解法。
1.1.暴力解法
遍历每一个子数组(都要大于等于 7),最统计出最小的数组。
这样做的话,划分左右区间(left 和 right)就需要
O
(
n
2
)
O(n^{2})
O(n2),然后每一个区间都要求和,所有求和又需要
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n),整体时间复杂度就是
O
(
n
3
)
O(n^{3})
O(n3)。
1.2.优化一次
如何将上述解法优化呢?首先在求和上就可以优化到 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
划分区间从 [left,left=right] 开始,先让 sum+arr[right],然后再 right++,这样子就不需要重复计算 sum 了,这样就可以优化为
O
(
n
2
)
O(n^{2})
O(n2)。
1.3.优化两次
全部都是正整数,也就是,加的数越多,得到的结果 sum 就越大(也就是具有单调性),因此当我们划分区间 [left,right] 后得到的 sum 只要比 target 大或等于就无需再 right++ 了,继续让其加加得到的数组肯定会比 target 大,但是数组长度也变大了,这是我们不需要的。
上述划分结束后,我们就得到了一个 [left,right] 窗口区间和对应的 sum,其中 [left,right-1] 的 sum 一定小于 [left,right] 的 sum 或者说 target。
后面让这个窗口区间挪动起来,找比这个区间长度要小,但是窗口的 sum 大于等于 target 的,并且实时更新 maxLength。
直接让 sum-arr[left],然后 left++ 即可得到 [left,right] 区间的新 sum。
查看这个 sum 是否大于 target,如果是继续加加,如果不是就整个窗口移动,直到 right 到结尾。
而这种 left 和 right 双指针同向移动的情况就称为“滑动窗口”。
class Solution
{
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector<int>& nums)
{
int sum = 0;
int maxLength = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
while (right < nums.size())
{
sum += nums[right];
if (sum >= target)
{
break;
}
right++;
}
maxLength = right - left + 1;
//得到窗口[left, right]
if(sum < target)
{
return 0;
}
while(right < nums.size())
{
sum -= nums[left];
left++;
if (sum >= target)
{
maxLength = right - left + 1;
}
else//sum < target
{
right++;
if (right >= nums.size())
{
break;
}
sum += nums[right];
}
}
return maxLength;
}
};
或者写得更加高明一些:
class Solution
{
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector<int>& nums)
{
int n = nums.size();
int sum = 0;
int len = INT_MAX;
for(int left = 0, right = 0; right < n; right++)
{
sum += nums[right];
while(sum >= target)
{
len = min(len, right - left + 1);
sum -= nums[left++];
}
}
return len == INT_MAX ? 0 : len;
}
};
时间复杂度:由于只操作两个指针,最坏情况下操作 n + n n+n n+n 次,也就是 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
因此可以看出,滑动窗口的题目基本都是:
- 设定窗口范围
- 让数据进窗口
- 判断是否符合要求,不符合则让数据出窗口
2.题目
2.1.LCR 016. 无重复字符的最长子串
2.1.1 暴力
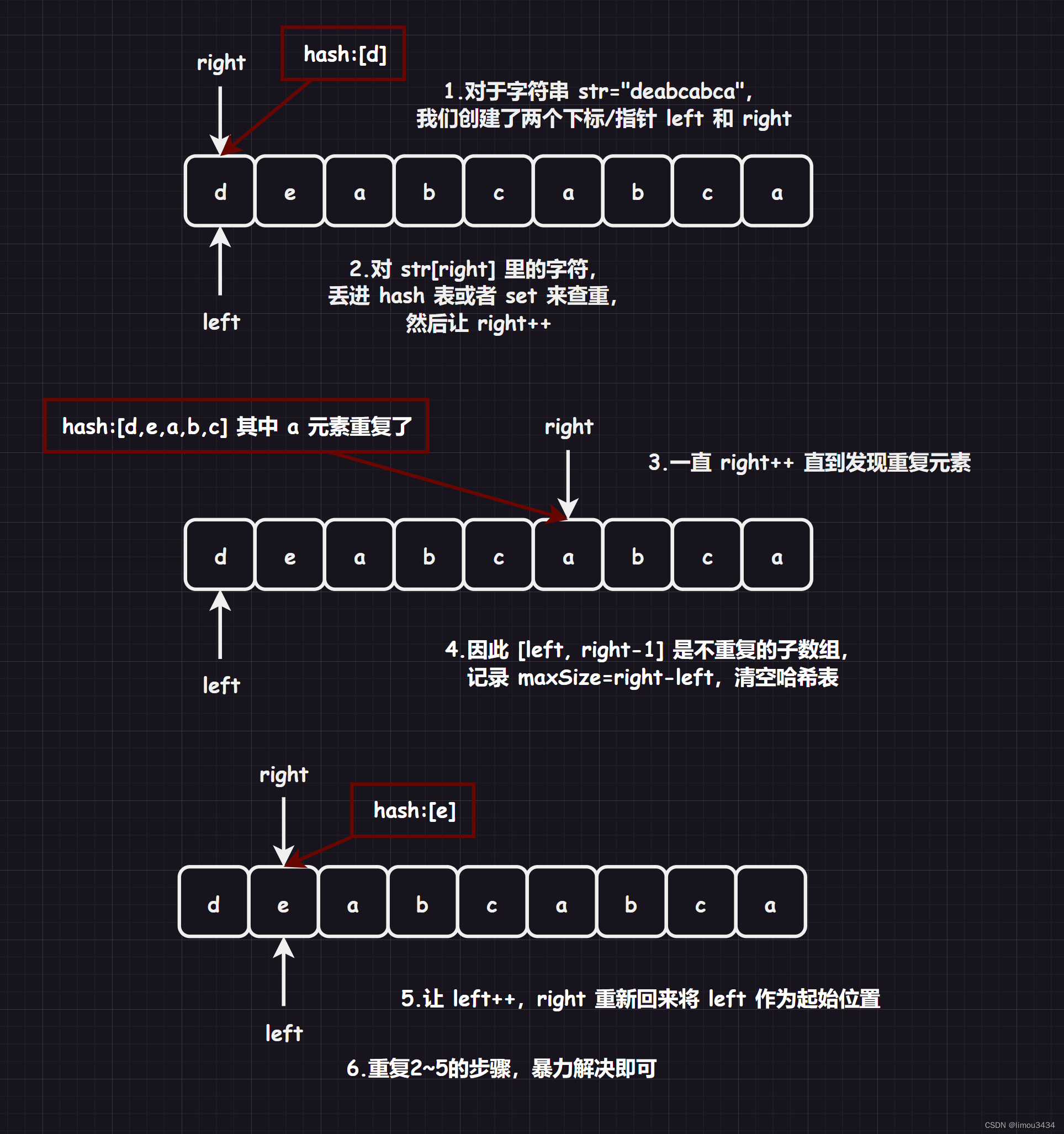
时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^{2}) O(n2)
2.1.2.优化
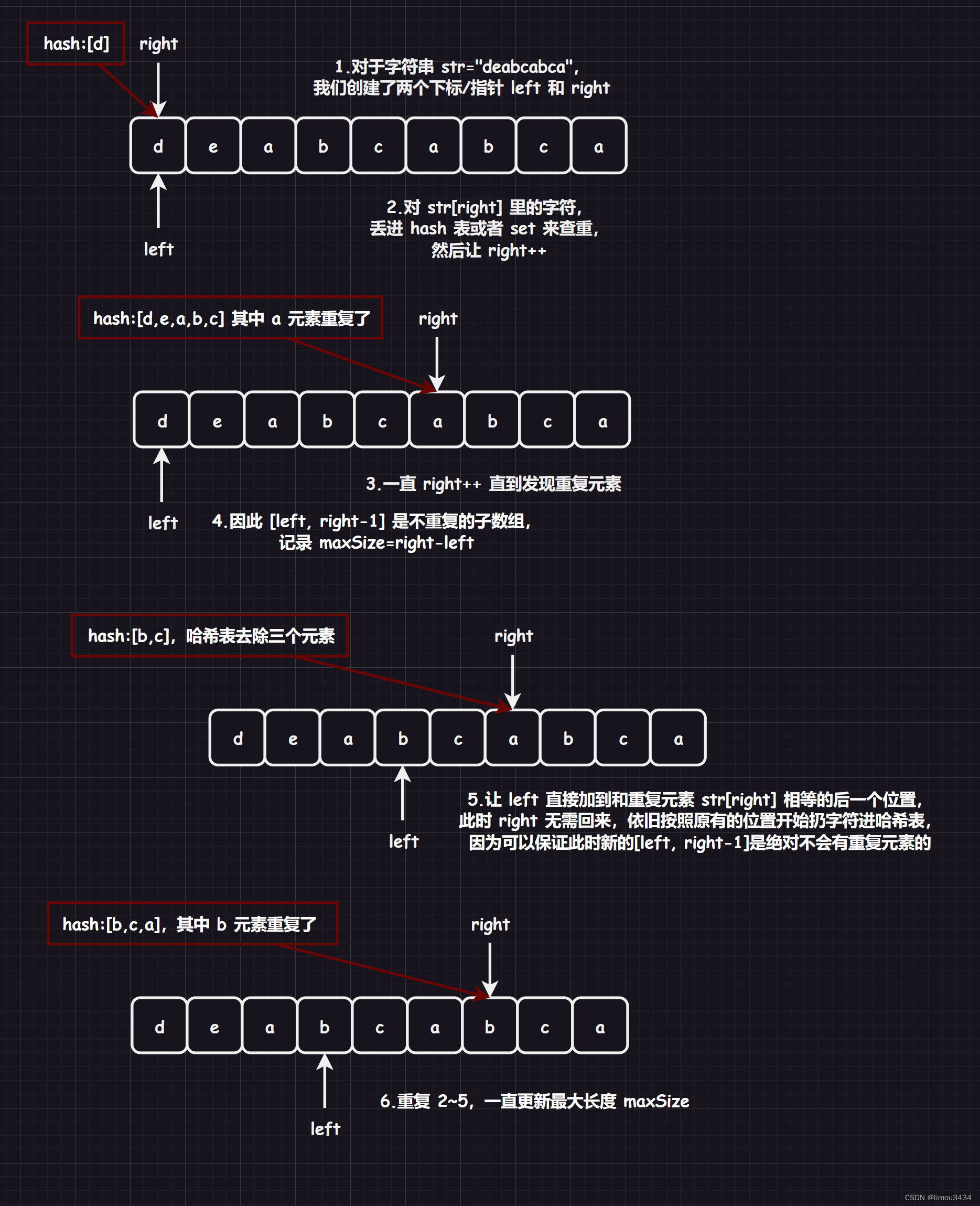
class Solution
{
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string str)
{
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int maxSize = 0;
int hash[128] = { 0 };
while (left < str.size())
{
while (right < str.size() && hash[str[right]] == 0)//不是重复的字符就放入哈希表之中
{
hash[str[right++]]++;
}
//走到这里说明出现了重复的字符,这个重复元素就是str[right]
maxSize = maxSize > right - left ? maxSize : right - left;//记录最大长度
while (str[left] != str[right])//让left直接跳到在和str[right]重复的元素后面
{
hash[str[left]]--;
left++;
}
hash[str[left]]--;
left++;//走到这里还要在加加一次
}
return maxSize;
}
};
还可以写得更加简洁:
class Solution
{
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string str)
{
int left = 0, right = 0, maxSize = 0, n = str.size(), hash[128] = { 0 };
while (right < n)
{
hash[str[right]]++;//进窗口
while (hash[str[right]] > 1)//判断
hash[str[left++]]--;//出窗口
maxSize = max(maxSize, right - left + 1);//记录最大长度
right++;
}
return maxSize;
}
};
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
2.2.1004. 最大连续 1 的个数 III
如果转变思路为:一个区间内包含的 0 的个数不超过 K,求这样的区间的最大值。
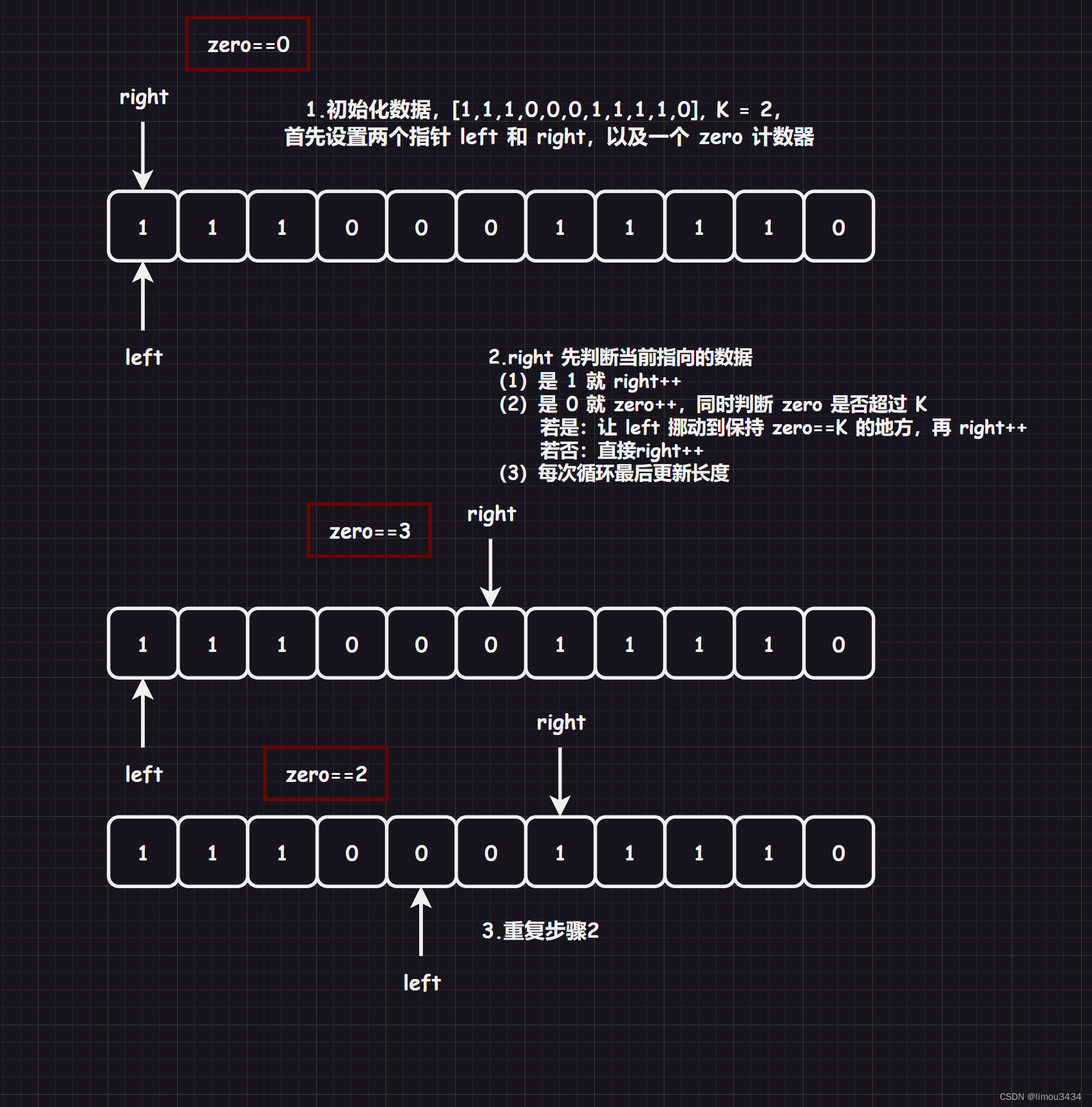
class Solution
{
public:
int longestOnes(vector<int> nums, int K)
{
int left = 0, right = 0;
int zero = 0;
int maxSize = 0;
int n = nums.size();
while (right < n)
{
if (nums[right] == 0) zero++;
while (zero > K)
{
if (nums[left] == 0) zero--;
left++;
}
right++;
maxSize = max(maxSize, right - left);
}
return maxSize;
}
};
2.3.1658. 将 x 减到 0 的最小操作数
这道题目正面做比较困难,可以反面做。
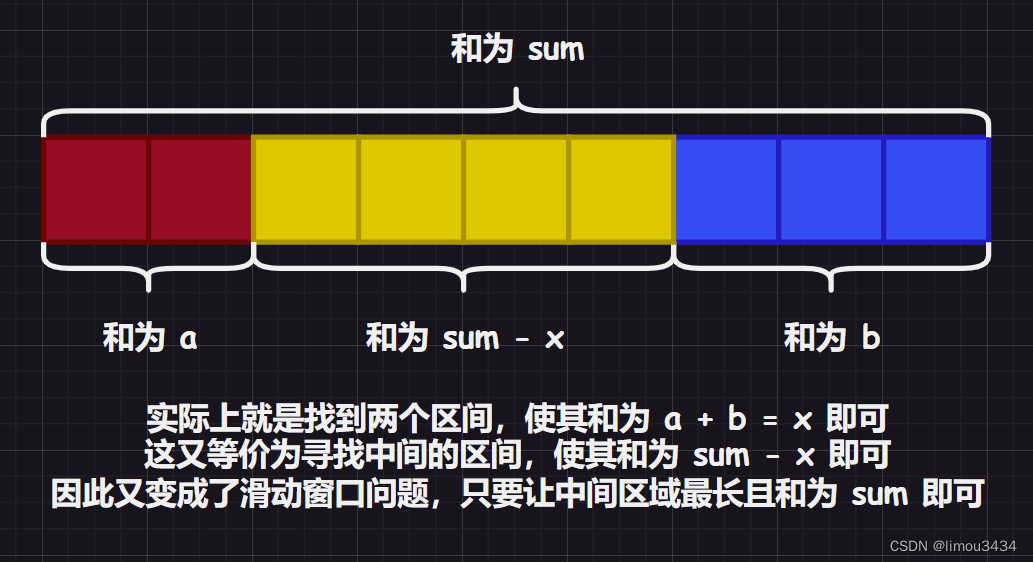
class Solution
{
public:
int minOperations(vector<int> nums, int x)
{
//1.设置 target
int sum = 0;//整个数组求和
for (auto e : nums) sum += e;
int target = sum - x;//求出 target
//2.处理特殊情况
if (target < 0)//target 不可能小于 0
return -1;
//3.下面开始找到中间区间和为 target 即可
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int ret = -1;//这里之所以设置为 -1 是因为有可能出现找不到的情况(例如:左右端的数字均大于 target)
int add = 0;
while (right < nums.size())
{
//1.进窗口
add += nums[right];
//2.判断出窗口
while (add > target)
{
add -= nums[left];
left++;
}
//3.更新结果
if (add == target)
{
ret = (int)max(ret, right - left + 1);
}
right++;
}
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
return nums.size() - ret;
}
};
2.4.904. 水果成篮
依旧是使用滑动窗口,这个题比较简单。
class Solution
{
public:
int totalFruit(vector<int>& fruits)
{
int left = 0, right = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> um;
int count = 0;
while (right < fruits.size())
{
//1.进窗口
um[fruits[right++]]++;
//2.出窗口
while (um.size() > 2)
{
um[fruits[left]]--;
if (um[fruits[left]] == 0)
um.erase(fruits[left]);
left++;
}
//3.更新
if (um.size() == 2)
{
count = max(count, right - left);
}
}
if (left == 0)
{
count = fruits.size();
}
return count;
}
};
或者修改一下,简化代码:
class Solution
{
public:
int totalFruit(vector<int>& fruits)
{
int left = 0, right = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> um;
int count = 0;
while (right < fruits.size())
{
//1.进窗口
um[fruits[right++]]++;
//2.出窗口
while (um.size() > 2)
{
um[fruits[left]]--;
if (um[fruits[left]] == 0)
{
um.erase(fruits[left]);
}
left++;
}
//3.更新
count = max(count, right - left);
}
return count;
}
};
但是这里的哈希删除效率比较低下,实际上我们可以根据题目特点(0 <= fruits[i] < fruits.length)来创建一个自己的哈希表,而不使用库内的哈希表,这也是一种做题技巧。
class Solution
{
public:
int totalFruit(vector<int>& fruits)
{
int left = 0, right = 0;
int um[100001] = { 0 };
int count = 0;
int kinds = 0;
while (right < fruits.size())
{
//1.进窗口
if(um[fruits[right]] == 0)
kinds++;
um[fruits[right++]]++;
//2.出窗口
while (kinds > 2)
{
um[fruits[left]]--;
if(um[fruits[left]] == 0)
kinds--;
left++;
}
//3.更新
count = max(count, right - left);
}
return count;
}
};
2.5.438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
这一题的解法比较好理解,如果直接使用库内的 unordered_map 哈希容器,写起来是很快的,因为这题的窗口是固定的,但是需要注意越界的问题。
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub)
{
//1.返回用的顺序表
vector<int> ret;
//2.匹配字符串的哈希表
unordered_map<char, int> um_sub;
for (auto ch : sub)
{
um_sub[ch]++;
}
//3.初始化对应匹配字符串长度的子串
unordered_map<char, int> um_str_sub;
for (int i = 0; i < sub.size(); i++)
{
um_str_sub[str[i]]++;
}
//4.判断子串和匹配字符串是否异位词
for (int i = 0; i + sub.size() - 1 < str.size(); i++)
{
if (um_sub == um_str_sub)
{
ret.push_back(i);
}
//5.更新固定窗口
um_str_sub[str[i]]--;
if (um_str_sub[str[i]] == 0)
{
um_str_sub.erase(str[i]);
}
um_str_sub[str[i + sub.size()]]++;
}
//6.返回索引结果
return ret;
}
};
当然,我们还可以优化一下,如果窗口的长度和匹配字符串不相等,那就无需判断是否异位了,直接更新窗口即可。
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub)
{
//1.返回用的顺序表
vector<int> ret;
if (sub.size() > str.size())//处理特殊情况
return ret;
//2.匹配字符串的哈希表
unordered_map<char, int> um_sub;
for (auto ch : sub)
{
um_sub[ch]++;
}
//3.初始化对应匹配字符串长度的子串
unordered_map<char, int> um_str_sub;
for (int i = 0; i < sub.size(); i++)
{
um_str_sub[str[i]]++;
}
//4.判断子串和匹配字符串是否异位词
for (int i = 0; i + sub.size() - 1 < str.size(); i++)
{
if (um_sub.size() == um_str_sub.size() && um_sub == um_str_sub)
{
ret.push_back(i);
}
//5.更新固定窗口
um_str_sub[str[i]]--;
if (um_str_sub[str[i]] == 0)
{
um_str_sub.erase(str[i]);
}
um_str_sub[str[i + sub.size()]]++;
}
//6.返回索引结果
return ret;
}
};
还可以不用库里的哈希表,直接用我们自己的用于映射的数组。
class Solution
{
public:
//判断两个 hash 是否相等
bool equality(int* hash_str_sub, int* hash_sub)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
if (hash_str_sub[i] != hash_sub[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub)
{
//1.防止匹配字符串长于主串
vector<int> ret;
if (sub.size() > str.size())
return ret;
//2.映射匹配字符串的 hash
int hash_sub[26] = { 0 };
int count1 = 0;
for (auto ch : sub)
{
if (++hash_sub[ch - 'a'] == 1)
count1++;//统计有效字符串
}
//3.设定好主串的 hash
int hash_str_sub[26] = { 0 };
int count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sub.size(); i++)
{
if (++hash_str_sub[str[i] - 'a'] == 1)
count2++;//统计有效字符串
}
for (int i = 0; i + sub.size() - 1 < str.size(); i++)
{
//4.只有在有效字符串匹配的情况下才需要比较 hash 是否相等
if (count2 == count1)
{
if (equality(hash_str_sub, hash_sub))
ret.push_back(i);
}
//5.保留之前的窗口,去除旧数据,新映射数据,让窗口走起来(注意避免越界)
if (i + sub.size() < str.size() && --hash_str_sub[str[i] - 'a'] == 0)
count2--;
if (i + sub.size() < str.size() && ++hash_str_sub[str[i + sub.size()] - 'a'] == 1)
count2++;
}
return ret;
}
};
还可以将数组优化使用 vector,可以让代码检查越界的情况,但其效能未必输过数组。
class Solution
{
public:
//判断两个 hash 是否相等
bool equality(const vector<int>& hash_str_sub, const vector<int>& hash_sub)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
if (hash_str_sub[i] != hash_sub[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub)
{
//1.防止匹配字符串长于主串
vector<int> ret;
if (sub.size() > str.size())
return ret;
//2.映射匹配字符串的 hash
vector<int> hash_sub(26, 0);
int count1 = 0;
for (auto ch : sub)
{
if (++hash_sub[ch - 'a'] == 1)
count1++;//统计有效字符串
}
//3.设定好主串的 hash
vector<int> hash_str_sub(26, 0);
int count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sub.size(); i++)
{
if (++hash_str_sub[str[i] - 'a'] == 1)
count2++;//统计有效字符串
}
for (int i = 0; i + sub.size() - 1 < str.size(); i++)
{
//4.只有在有效字符串匹配的情况下才需要比较 hash 是否相等
if (count2 == count1)
{
if (equality(hash_str_sub, hash_sub))
ret.push_back(i);
}
//5.保留之前的窗口,去除旧数据,新映射数据,让窗口走起来(注意避免越界)
if (i + sub.size() < str.size() && --hash_str_sub[str[i] - 'a'] == 0)
count2--;
if (i + sub.size() < str.size() && ++hash_str_sub[str[i + sub.size()] - 'a'] == 1)
count2++;
}
//6.返回索引结果
return ret;
}
};
当然也可以使用我们之前的滑动数组 进窗口-判断条件(出窗口)-更新结果 的模式来做。
class Solution
{
public:
//判断两个 hash 是否相等
bool equality(const vector<int>& hash_str_sub, const vector<int>& hash_sub)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
if (hash_str_sub[i] != hash_sub[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub)
{
//1.防止匹配字符串长于主串
vector<int> ret;
if (sub.size() > str.size())
return ret;
//2.映射匹配字符串的 hash
vector<int> hash_sub(26, 0);
int count1 = 0;
for (auto ch : sub)
{
if (++hash_sub[ch - 'a'] == 1)
count1++;//统计有效字符串
}
vector<int> hash_str_sub(26, 0);
int count2 = 0;
//3.初始化窗口
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
while (right < str.size())
{
//4.入窗口
while (right - left < sub.size())
{
if (++hash_str_sub[str[right] - 'a'] == 1)
count2++;//统计有效字符串
right++;
}
//5.判断条件,更新结果
if (count1 == count2 && equality(hash_str_sub, hash_sub))
ret.push_back(left);
//6.出窗口
if (--hash_str_sub[str[left++] - 'a'] == 0)
count2--;
if (right + 1 < str.size() && ++hash_str_sub[str[right++] - 'a'] == 1)
count2++;
}
//7.返回索引结果
return ret;
}
};
补充:但是我在力扣上测试,貌似使用数组会更快一些?不过这两者在实际中效率真的不会差太多,这里我也放入数组版本的。
class Solution { public: //判断两个 hash 是否相等 bool equality(int* hash_str_sub, int* hash_sub) { for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) { if (hash_str_sub[i] != hash_sub[i]) return false; } return true; } vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub) { //1.防止匹配字符串长于主串 vector<int> ret; if (sub.size() > str.size()) return ret; //2.映射匹配字符串的 hash int hash_sub[26] = { 0 }; int count1 = 0; for (auto ch : sub) { if (++hash_sub[ch - 'a'] == 1) count1++;//统计有效字符串 } int hash_str_sub[26] = { 0 }; int count2 = 0; //3.初始化窗口 int left = 0; int right = 0; while (right < str.size()) { //4.入窗口 while (right - left < sub.size()) { if (++hash_str_sub[str[right] - 'a'] == 1) count2++;//统计有效字符串 right++; } //5.判断条件,更新结果 if (count1 == count2 && equality(hash_str_sub, hash_sub)) ret.push_back(left); //6.出窗口 if (--hash_str_sub[str[left++] - 'a'] == 0) count2--; if (right + 1 < str.size() && ++hash_str_sub[str[right++] - 'a'] == 1) count2++; } //7.返回索引结果 return ret; } };
这里必须提一下,我们在写面试的笔试题目时,一定要先用库函数和库容器,保证自己的思路和解法清晰,在尝试能否进行优化(更换功能过重的库函数和库容器、排除特殊情况)
如果写得更加彻底一些,还可以直接根据有效字符判断两个哈希是否异位,而无需走固定的 26 次比较。
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> findAnagrams(const string& str, const string& sub)
{
vector<int> ret;
//1.映射匹配字符串的 hash1
int hash1[26] = { 0 };
for (auto ch : sub) hash1[ch - 'a']++;
//2.映射主串的 hash
int hash2[26] = { 0 };
int len = sub.size();
for (int left = 0, right = 0, count = 0; right < str.size(); right++)
{
//进窗口
char in = str[right];
hash2[in - 'a']++;
if (hash2[in - 'a'] <= hash1[in - 'a']) count++;//统计有效字符个数
//出窗口
if (right - left + 1 > len)//以前我们是用循环的,由于窗口固定不变,因此可以直接用 if
{
char out = str[left++];
if (hash2[out - 'a'] <= hash1[out - 'a']) count--;
hash2[out - 'a']--;
}
//更新结果
if (count == len) ret.push_back(left);
}
//3.返回索引结果
return ret;
}
};
从上面这种解法来看,两个动静态哈希判断相等未必需要遍历元素,在动态映射的过程中,可以使用变量记录映射后的值是否和另外一个静态映射后的值是否相等或者小于(然后统计这样的值的个数),插入完毕后,再查看这个个数和静态哈希的原数组是否相同。
这个结论很重要,可以提高我们比较两个动静态哈希的比较速度。
2.6.30. 串联所有单词的子串
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(const string& str, const vector<string>& subs)
{
vector<int> ret;
if(subs.size() * subs[0].size() > str.size()) //排除特殊情况,提高一点效率
return ret;
//1.映射匹配字符串的 hash1
//int hash1[26] = { 0 };
unordered_map<string, int> hash1;
//for (auto ch : sub) hash1[ch - 'a']++;
for (auto str : subs)
hash1[str]++;
//2.映射主串的 hash
//int hash2[26] = { 0 };
//hash2 转移到了循环内,局部的哈希表可以达到自动清理资源的目的
//如果 hash2 写在这里就需要在内循环执行一次后使用 hash2.clean()
//int len = sub.size();
int len = subs.size();
int n = subs[0].size();
for (int index = 0; index < n; index++)
{
unordered_map<string, int> hash2;
for (int left = index, right = index, count = 0; right + n <= str.size(); right += n)
{
//进窗口
//char in = str[right];
string in = str.substr(right, n);
//hash2[in - 'a']++;
hash2[in]++;
//if (hash2[in - 'a'] <= hash1[in - 'a'])
// count++;//统计有效字符个数
if (hash1.count(in) && hash2[in] <= hash1[in]) //这里的 hash1.cout(in) 是一个优化,不加也可以,但是可以避免哈希表进行无意义的插入,这个技巧值得学习
count++;//统计有效字符个数
//出窗口
//if (right - left + 1 > len) //滑动窗口本来是用循环的,由于窗口固定不变,因此可以直接用 if
if (right - left + 1 > len * n) //滑动窗口本来是用循环的,由于窗口固定不变,因此可以直接用 if
{
//char out = str[left++];
string out = str.substr(left, n);
left += n;
//if (hash2[out - 'a'] <= hash1[out - 'a'])
// count--;
if (hash1.count(out) && hash2[out] <= hash1[out]) //这里的 hash1.cout(in) 是一个优化,不加也可以,但是可以避免哈希表进行无意义的插入,这个技巧值得学习
count--;
//hash2[out - 'a']--;
hash2[out]--;
}
//更新结果
if (count == len)
ret.push_back(left);
}
}
//3.返回索引结果
return ret;
}
};
2.7.LCR 017. 最小覆盖子串
2.7.1.使用个数的 count
class Solution
{
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t)
{
string ret = s;
int flag = 0;
//1.设置哈希表
int hash1[128] = { 0 };
for (auto it : t)
hash1[it]++;
int hash2[128] = { 0 };
int count = 0;
int len = t.size();
for (int left = 0, right = 0; right < s.size(); right++)
{
//2.进窗口
hash2[s[right]]++;
if (hash2[s[right]] <= hash1[s[right]])
count++;
//3.判断(出窗口)
while (count == len)
{
//更新
if (ret.size() > s.substr(left, right - left + 1).size())
ret = s.substr(left, right - left + 1);
if (hash2[s[left]]-- <= hash1[s[left++]])
{
flag = 1;
count--;
}
}
}
if(flag == 1)
return ret;
return "";
}
};
这里有不少优化的地方,实际上我们可以不统计有效字符的个数,只需要统计子串中有效字符的种类,然后判断其种类是否和匹配字符串 t 中字符的种类一样多,一样多就代表是被最小覆盖的。
2.7.2.使用种类的 count
class Solution
{
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t)
{
string ret = s;
int flag = 0;
//1.设置哈希表
int kinds = 0;
int hash1[128] = { 0 };
for (auto it : t)
if(hash1[it]++ == 0)
kinds++;
int hash2[128] = { 0 };
int count = 0;
for (int left = 0, right = 0; right < s.size(); right++)
{
//2.进窗口
hash2[s[right]]++;
if (hash2[s[right]] == hash1[s[right]])
count++;
//3.判断(出窗口)
while (count == kinds)
{
//更新
if (ret.size() > s.substr(left, right - left + 1).size())
ret = s.substr(left, right - left + 1);
if (hash2[s[left]]-- <= hash1[s[left++]])
{
flag = 1;
count--;
}
}
}
if(flag == 1)
return ret;
return "";
}
};
2.7.3.去除字符串的冗余提取
生成子串其实只需要知道起始索引 begin 和长度 minlen 即可,因此我们可以在最后返回的时候提取字符串,而不是直接在更新条件中提取(这样会很慢,我们的滑动窗口思路本身效率很高,完全是被这个冗余的子串提取影响了效率),在更新的时候,只需要更新新子串的 begin 和 minlen 即可。
其中进出窗口的元素最好还是写明一下(in 和 cout),提高代码可读性,并且根据 begin 是否被更改来替代标记位 flag。
class Solution
{
public:
string minWindow(string s, string t)
{
string ret = s;
//1.设置哈希表
int kinds = 0;
int hash1[128] = { 0 };
for (auto it : t)
if(hash1[it]++ == 0)
kinds++;
int hash2[128] = { 0 };
int begin = -1, minlen = INT_MAX;
for (int left = 0, right = 0, count = 0; right < s.size(); right++)
{
//2.进窗口
char in = s[right];
if (++hash2[in] == hash1[in])
count++;
//3.判断(出窗口)
while (count == kinds)
{
//更新
if (right - left + 1 < minlen)
{
minlen = right - left + 1;
begin = left;
}
char out = s[left++];
if (hash2[out]-- == hash1[out])
count--;
}
}
if(begin == -1)
return "";
return ret.substr(begin, minlen);
}
};



![[DroneCAN]CAN-Convertor控制CAN电调电机](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e36b8708d49d40f5b6d48950a694f640.png)