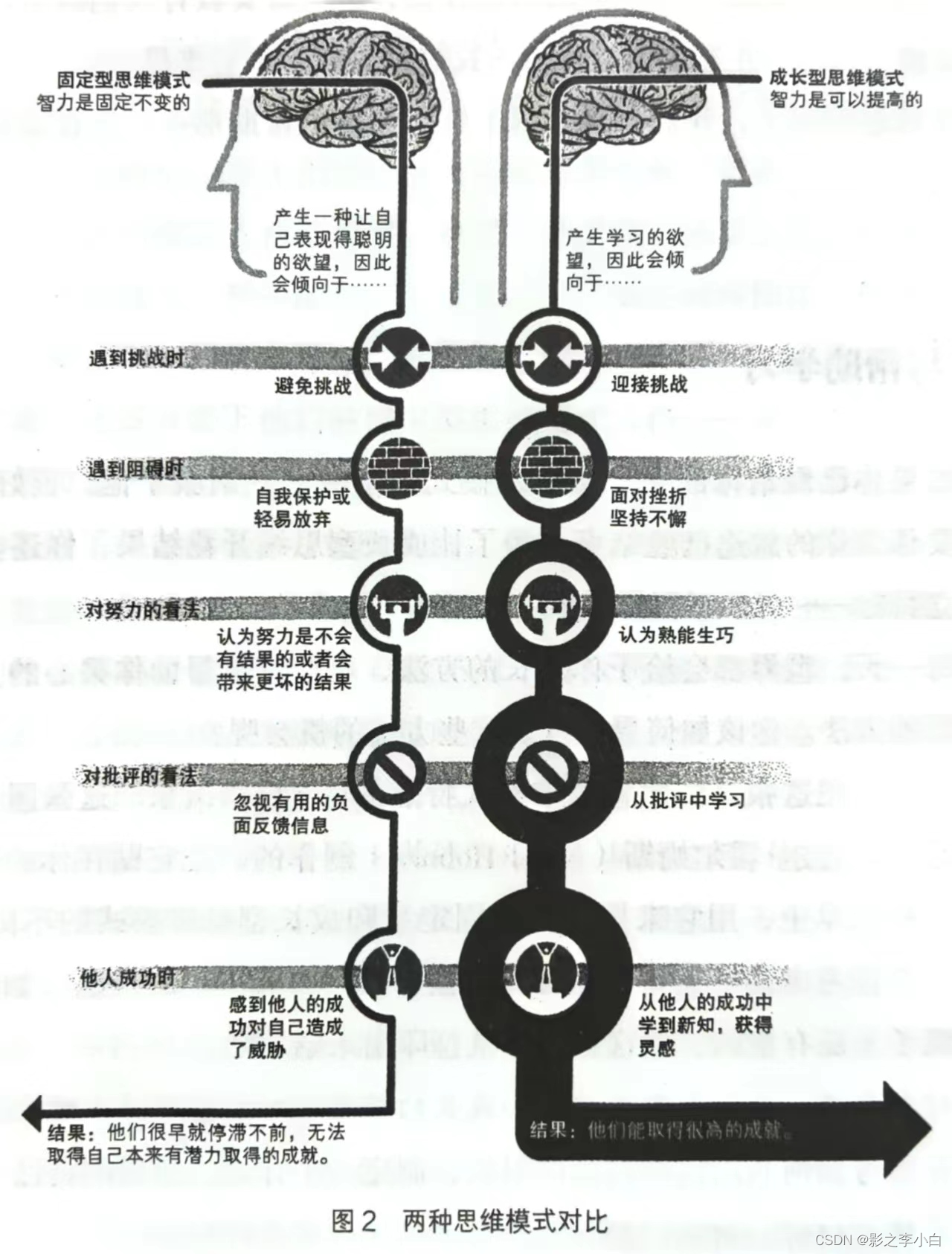
yolov3的整体网络结构
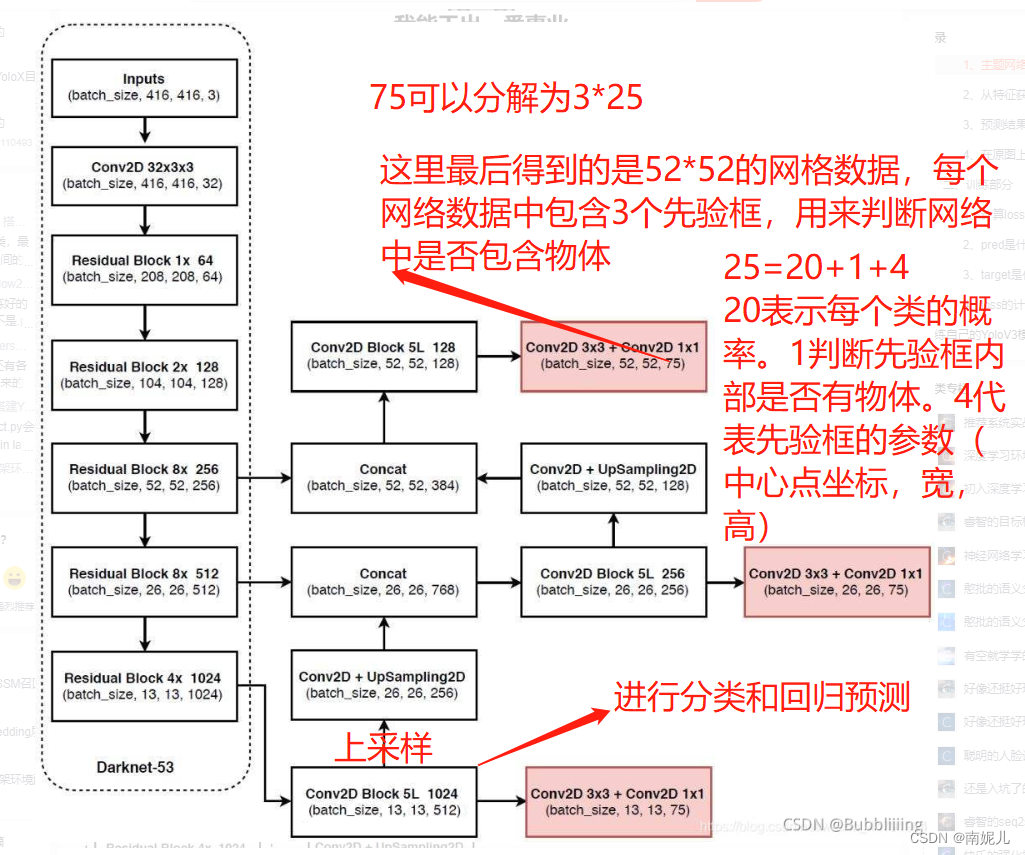
主要包含了两个部分。左边的Darknet-53主干特征提取网络主要用于提取特征。右边是一个FPN金字塔结构。
主干特征提取网络(提取特征)
import math
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch.nn as nn
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 残差结构
# 利用一个1x1卷积下降通道数,然后利用一个3x3卷积提取特征并且上升通道数
# 最后接上一个残差边
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes[0], kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes[0])
self.relu1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes[0], planes[1], kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes[1])
self.relu2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu1(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu2(out)
out += residual
return out
class DarkNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layers):
super(DarkNet, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 32
# 416,416,3 -> 416,416,32
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.inplanes)
self.relu1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
# 416,416,32 -> 208,208,64
self.layer1 = self._make_layer([32, 64], layers[0])
# 208,208,64 -> 104,104,128
self.layer2 = self._make_layer([64, 128], layers[1])
# 104,104,128 -> 52,52,256
self.layer3 = self._make_layer([128, 256], layers[2])
# 52,52,256 -> 26,26,512
self.layer4 = self._make_layer([256, 512], layers[3])
# 26,26,512 -> 13,13,1024
self.layer5 = self._make_layer([512, 1024], layers[4])
self.layers_out_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]
# 进行权值初始化
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 在每一个layer里面,首先利用一个步长为2的3x3卷积进行下采样
# 然后进行残差结构的堆叠
#---------------------------------------------------------------------#
def _make_layer(self, planes, blocks):
layers = []
# 下采样,步长为2,卷积核大小为3
layers.append(("ds_conv", nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes[1], kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)))
layers.append(("ds_bn", nn.BatchNorm2d(planes[1])))
layers.append(("ds_relu", nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)))
# 加入残差结构
self.inplanes = planes[1]
for i in range(0, blocks):
layers.append(("residual_{}".format(i), BasicBlock(self.inplanes, planes)))
return nn.Sequential(OrderedDict(layers))
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu1(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
out3 = self.layer3(x)
out4 = self.layer4(out3)
out5 = self.layer5(out4)
return out3, out4, out5
def darknet53():
model = DarkNet([1, 2, 8, 8, 4])
return model
if __name__=='__main__':
import torch
from torchinfo import summary
input=torch.randn(1,3,416,416)
model=darknet53()
summary(model,input.shape)
output=model(input)
print(output[0].shape,output[1].shape,output[2].shape)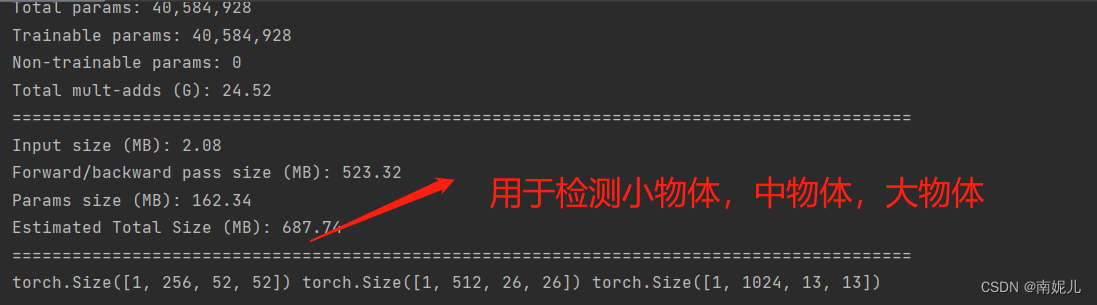
FPN特征金子塔加强特征提取和利用yolo head预测结果
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from nets.darknet import darknet53
def conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size):
pad = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 if kernel_size else 0
return nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("conv", nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=pad, bias=False)),
("bn", nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out)),
("relu", nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)),
]))
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# make_last_layers里面一共有七个卷积,前五个用于提取特征。
# 后两个用于获得yolo网络的预测结果
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
def make_last_layers(filters_list, in_filters, out_filter): #in_filters 表示输入通道,out_filter表示输出通道
m = nn.Sequential(
conv2d(in_filters, filters_list[0], 1),
conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 3),
conv2d(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 3),
conv2d(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 3),
nn.Conv2d(filters_list[1], out_filter, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
)
return m
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors_mask, num_classes, pretrained = False):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 生成darknet53的主干模型
# 获得三个有效特征层,他们的shape分别是:
# 52,52,256
# 26,26,512
# 13,13,1024
#---------------------------------------------------#
self.backbone = darknet53()
if pretrained:
self.backbone.load_state_dict(torch.load("model_data/darknet53_backbone_weights.pth"))
#---------------------------------------------------#
# out_filters : [64, 128, 256, 512, 1024] 自己定义的属性,表示darknet五个残差模块中输出的特征通道数
#---------------------------------------------------#
out_filters = self.backbone.layers_out_filters
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算yolo_head的输出通道数,对于voc数据集而言
# final_out_filter0 = final_out_filter1 = final_out_filter2 = 75
#------------------------------------------------------------------------#
self.last_layer0 = make_last_layers([512, 1024], out_filters[-1], len(anchors_mask[0]) * (num_classes + 5))
self.last_layer1_conv = conv2d(512, 256, 1)
self.last_layer1_upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
self.last_layer1 = make_last_layers([256, 512], out_filters[-2] + 256, len(anchors_mask[1]) * (num_classes + 5))
self.last_layer2_conv = conv2d(256, 128, 1)
self.last_layer2_upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
self.last_layer2 = make_last_layers([128, 256], out_filters[-3] + 128, len(anchors_mask[2]) * (num_classes + 5))
def forward(self, x):
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得三个有效特征层,他们的shape分别是:
# 52,52,256;26,26,512;13,13,1024
#---------------------------------------------------#
x2, x1, x0 = self.backbone(x)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第一个特征层
# out0 = (batch_size,255,13,13)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512
out0_branch = self.last_layer0[:5](x0) ###得到特征增强的特征
out0 = self.last_layer0[5:](out0_branch) ##进行回归预测
# 13,13,512 -> 13,13,256 -> 26,26,256
x1_in = self.last_layer1_conv(out0_branch)
x1_in = self.last_layer1_upsample(x1_in)
# 26,26,256 + 26,26,512 -> 26,26,768
x1_in = torch.cat([x1_in, x1], 1)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第二个特征层
# out1 = (batch_size,255,26,26)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 26,26,768 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256
out1_branch = self.last_layer1[:5](x1_in)
out1 = self.last_layer1[5:](out1_branch)
# 26,26,256 -> 26,26,128 -> 52,52,128
x2_in = self.last_layer2_conv(out1_branch)
x2_in = self.last_layer2_upsample(x2_in)
# 52,52,128 + 52,52,256 -> 52,52,384
x2_in = torch.cat([x2_in, x2], 1)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 第一个特征层
# out3 = (batch_size,255,52,52)
#---------------------------------------------------#
# 52,52,384 -> 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128
out2 = self.last_layer2(x2_in)
return out0, out1, out2
if __name__=='__main__':
import torch
from torchinfo import summary
input=torch.randn(1,3,416,416)
model=YoloBody(anchors_mask=[[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],num_classes=20)
summary(model,input.shape)
output=model(input)
print(output[0].shape,output[1].shape,output[2].shape)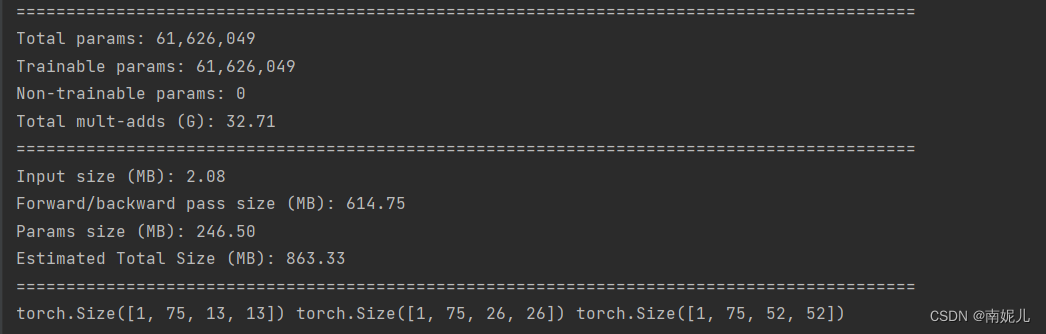
预测结果进行解码
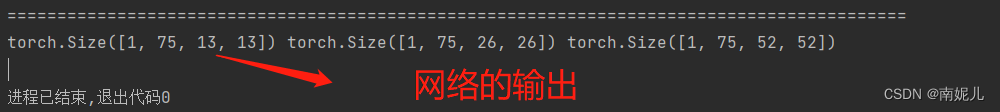
最后网络的输出格式就像上图一样。其中13表示特征图的大小,表示将整个图像分为了13*13的网格。每个网络点具有3个先验框。所以75可以分解为3*25,其中3表示这个网络点具有三个先验框。25可以分解为20+1+4,其中20表示该先验框的分类结果,这里使用的是VOC数据集,VOC数据集共有20个类别。1表示置信度,表示该先验框包含物体的概率。4用来表示先验框的位置信息。
YoloV3的解码过程分为两步:
- 先将每个网格点加上它对应的x_offset和y_offset,加完后的结果就是预测框的中心。
- 然后再利用 先验框和h、w结合 计算出预测框的宽高。这样就能得到整个预测框的位置了。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision.ops import nms
import numpy as np
class DecodeBox():
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, anchors_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]]):
super(DecodeBox, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.input_shape = input_shape
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
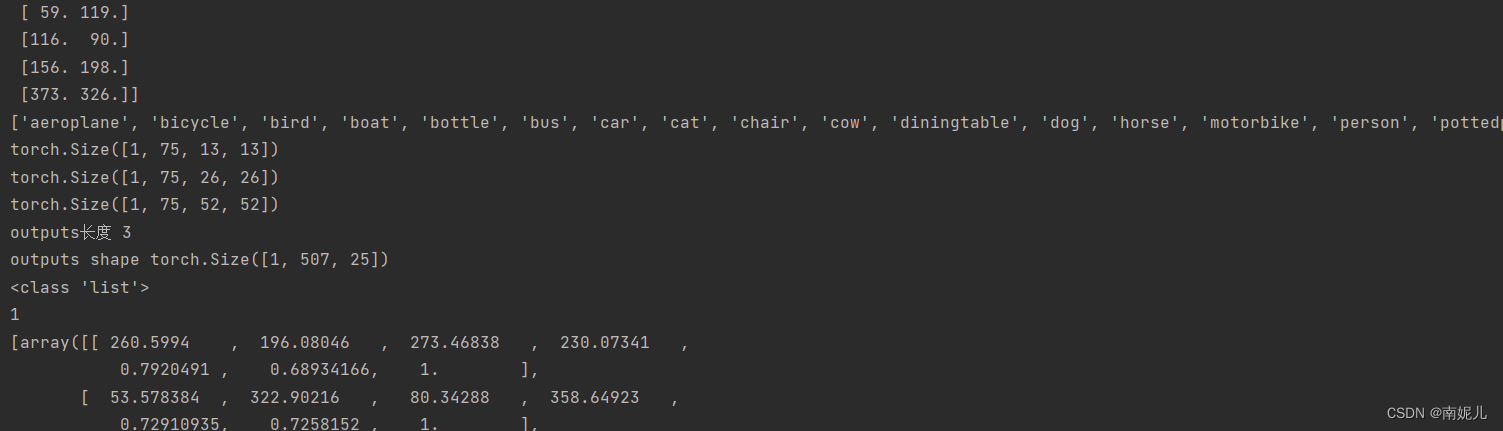
# 13x13的特征层对应的anchor是[116,90],[156,198],[373,326]
# 26x26的特征层对应的anchor是[30,61],[62,45],[59,119]
# 52x52的特征层对应的anchor是[10,13],[16,30],[33,23]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
self.anchors_mask = anchors_mask
def decode_box(self, inputs):
outputs = []
for i, input in enumerate(inputs):
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# batch_size, 255, 13, 13
# batch_size, 255, 26, 26
# batch_size, 255, 52, 52
#-----------------------------------------------#
batch_size = input.size(0)
input_height = input.size(2)
input_width = input.size(3)
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入为416x416时
# stride_h = stride_w = 32、16、8
#-----------------------------------------------#
stride_h = self.input_shape[0] / input_height
stride_w = self.input_shape[1] / input_width
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 此时获得的scaled_anchors大小是相对于特征层的
#-------------------------------------------------#
scaled_anchors = [(anchor_width / stride_w, anchor_height / stride_h) for anchor_width, anchor_height in self.anchors[self.anchors_mask[i]]]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 85
# batch_size, 3, 26, 26, 85
# batch_size, 3, 52, 52, 85
#-----------------------------------------------#
prediction = input.view(batch_size, len(self.anchors_mask[i]),
self.bbox_attrs, input_height, input_width).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
w = prediction[..., 2]
h = prediction[..., 3]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得置信度,是否有物体
#-----------------------------------------------#
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 种类置信度
#-----------------------------------------------#
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:])
FloatTensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
LongTensor = torch.cuda.LongTensor if x.is_cuda else torch.LongTensor
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角
# batch_size,3,13,13
#----------------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, input_width - 1, input_width).repeat(input_height, 1).repeat(
batch_size * len(self.anchors_mask[i]), 1, 1).view(x.shape).type(FloatTensor)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, input_height - 1, input_height).repeat(input_width, 1).t().repeat(
batch_size * len(self.anchors_mask[i]), 1, 1).view(y.shape).type(FloatTensor)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 按照网格格式生成先验框的宽高
# batch_size,3,13,13
#----------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_w = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([0]))
anchor_h = FloatTensor(scaled_anchors).index_select(1, LongTensor([1]))
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(batch_size, 1).repeat(1, 1, input_height * input_width).view(h.shape)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用预测结果对先验框进行调整
# 首先调整先验框的中心,从先验框中心向右下角偏移
# 再调整先验框的宽高。
#----------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes = FloatTensor(prediction[..., :4].shape)
pred_boxes[..., 0] = x.data + grid_x
pred_boxes[..., 1] = y.data + grid_y
pred_boxes[..., 2] = torch.exp(w.data) * anchor_w
pred_boxes[..., 3] = torch.exp(h.data) * anchor_h
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将输出结果归一化成小数的形式
#----------------------------------------------------------#
_scale = torch.Tensor([input_width, input_height, input_width, input_height]).type(FloatTensor)
output = torch.cat((pred_boxes.view(batch_size, -1, 4) / _scale,
conf.view(batch_size, -1, 1), pred_cls.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_classes)), -1)
outputs.append(output.data)
return outputs
def yolo_correct_boxes(self, box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image):
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 把y轴放前面是因为方便预测框和图像的宽高进行相乘
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
box_yx = box_xy[..., ::-1]
box_hw = box_wh[..., ::-1]
input_shape = np.array(input_shape)
image_shape = np.array(image_shape)
if letterbox_image:
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
# 这里求出来的offset是图像有效区域相对于图像左上角的偏移情况
# new_shape指的是宽高缩放情况
#-----------------------------------------------------------------#
new_shape = np.round(image_shape * np.min(input_shape/image_shape))
offset = (input_shape - new_shape)/2./input_shape
scale = input_shape/new_shape
box_yx = (box_yx - offset) * scale
box_hw *= scale
box_mins = box_yx - (box_hw / 2.)
box_maxes = box_yx + (box_hw / 2.)
boxes = np.concatenate([box_mins[..., 0:1], box_mins[..., 1:2], box_maxes[..., 0:1], box_maxes[..., 1:2]], axis=-1)
boxes *= np.concatenate([image_shape, image_shape], axis=-1)
return boxes
def non_max_suppression(self, prediction, num_classes, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果的格式转换成左上角右下角的格式。
# prediction [batch_size, num_anchors, 85]
#----------------------------------------------------------#
box_corner = prediction.new(prediction.shape)
box_corner[:, :, 0] = prediction[:, :, 0] - prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 1] = prediction[:, :, 1] - prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 2] = prediction[:, :, 0] + prediction[:, :, 2] / 2
box_corner[:, :, 3] = prediction[:, :, 1] + prediction[:, :, 3] / 2
prediction[:, :, :4] = box_corner[:, :, :4]
output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))]
for i, image_pred in enumerate(prediction):
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 对种类预测部分取max。
# class_conf [num_anchors, 1] 种类置信度
# class_pred [num_anchors, 1] 种类
#----------------------------------------------------------#
class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(image_pred[:, 5:5 + num_classes], 1, keepdim=True)
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 利用置信度进行第一轮筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
conf_mask = (image_pred[:, 4] * class_conf[:, 0] >= conf_thres).squeeze()
#----------------------------------------------------------#
# 根据置信度进行预测结果的筛选
#----------------------------------------------------------#
image_pred = image_pred[conf_mask]
class_conf = class_conf[conf_mask]
class_pred = class_pred[conf_mask]
if not image_pred.size(0):
continue
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# detections [num_anchors, 7]
# 7的内容为:x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------#
detections = torch.cat((image_pred[:, :5], class_conf.float(), class_pred.float()), 1)
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得预测结果中包含的所有种类
#------------------------------------------#
unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique()
if prediction.is_cuda:
unique_labels = unique_labels.cuda()
detections = detections.cuda()
for c in unique_labels:
#------------------------------------------#
# 获得某一类得分筛选后全部的预测结果
#------------------------------------------#
detections_class = detections[detections[:, -1] == c]
#------------------------------------------#
# 使用官方自带的非极大抑制会速度更快一些!
#------------------------------------------#
keep = nms(
detections_class[:, :4],
detections_class[:, 4] * detections_class[:, 5],
nms_thres
)
max_detections = detections_class[keep]
# # 按照存在物体的置信度排序
# _, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(detections_class[:, 4]*detections_class[:, 5], descending=True)
# detections_class = detections_class[conf_sort_index]
# # 进行非极大抑制
# max_detections = []
# while detections_class.size(0):
# # 取出这一类置信度最高的,一步一步往下判断,判断重合程度是否大于nms_thres,如果是则去除掉
# max_detections.append(detections_class[0].unsqueeze(0))
# if len(detections_class) == 1:
# break
# ious = bbox_iou(max_detections[-1], detections_class[1:])
# detections_class = detections_class[1:][ious < nms_thres]
# # 堆叠
# max_detections = torch.cat(max_detections).data
# Add max detections to outputs
output[i] = max_detections if output[i] is None else torch.cat((output[i], max_detections))
if output[i] is not None:
output[i] = output[i].cpu().numpy()
box_xy, box_wh = (output[i][:, 0:2] + output[i][:, 2:4])/2, output[i][:, 2:4] - output[i][:, 0:2]
output[i][:, :4] = self.yolo_correct_boxes(box_xy, box_wh, input_shape, image_shape, letterbox_image)
return output
if __name__=='__main__':
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得先验框
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def get_anchors(anchors_path):
'''loads the anchors from a file'''
with open(anchors_path, encoding='utf-8') as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
anchors = np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
return anchors, len(anchors)
# ---------------------------------------------------#
# 获得类
# ---------------------------------------------------#
def get_classes(classes_path):
with open(classes_path, encoding='utf-8') as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names, len(class_names)
anchors,anchors_num=get_anchors('../model_data/yolo_anchors.txt')
##anchcors表示的是先验框
print(anchors)
anchors_mask= [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
#class_name 表示类别的名称
class_name,class_num=get_classes('../model_data/voc_classes.txt')
print(class_name)
#输入图片的大小
input_shape=[416,416]
decode_box=DecodeBox(anchors=anchors,num_classes=class_num,input_shape=(input_shape[0],input_shape[1]),anchors_mask=anchors_mask)
from nets.yolo import YoloBody
#定义模型
model=YoloBody(anchors_mask=anchors_mask,num_classes=20)
input=torch.randn(1,3,416,416)
outputs=model(input)
print(outputs[0].shape)
print(outputs[1].shape)
print(outputs[2].shape)
outputs=decode_box.decode_box(outputs)
print('outputs长度',len(outputs))
print('outputs shape',outputs[0].shape)
result=decode_box.non_max_suppression(prediction=torch.cat(outputs, 1),
num_classes=class_num,
input_shape=input_shape,
image_shape=np.array([416,416]),
letterbox_image=False,
conf_thres=0.5,
nms_thres=0.3)
print(type(result))
print(len(result))
print(result)
# print('非极大抑制',result)loss的计算
判断真实框在图片中的位置,判断其属于哪一个网格点去检测。判断真实框和这个特征点的哪个先验框重合程度最高。计算该网格点应该有怎么样的预测结果才能获得真实框,与真实框重合度最高的先验框被用于作为正样本。
根据网络的预测结果获得预测框,计算预测框和所有真实框的重合程度,如果重合程度大于一定门限,则将该预测框对应的先验框忽略。其余作为负样本。
最终损失由三个部分组成:a、正样本,编码后的长宽与xy轴偏移量与预测值的差距。b、正样本,预测结果中置信度的值与1对比;负样本,预测结果中置信度的值与0对比。c、实际存在的框,种类预测结果与实际结果的对比。
import math
from functools import partial
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class YOLOLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors, num_classes, input_shape, cuda, anchors_mask = [[6,7,8], [3,4,5], [0,1,2]]):
super(YOLOLoss, self).__init__()
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 13x13的特征层对应的anchor是[116,90],[156,198],[373,326]
# 26x26的特征层对应的anchor是[30,61],[62,45],[59,119]
# 52x52的特征层对应的anchor是[10,13],[16,30],[33,23]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
self.anchors = anchors
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.bbox_attrs = 5 + num_classes
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.anchors_mask = anchors_mask
self.giou = True
self.balance = [0.4, 1.0, 4]
self.box_ratio = 0.05
self.obj_ratio = 5 * (input_shape[0] * input_shape[1]) / (416 ** 2)
self.cls_ratio = 1 * (num_classes / 80)
self.ignore_threshold = 0.5
self.cuda = cuda
def clip_by_tensor(self, t, t_min, t_max):
t = t.float()
result = (t >= t_min).float() * t + (t < t_min).float() * t_min
result = (result <= t_max).float() * result + (result > t_max).float() * t_max
return result
def MSELoss(self, pred, target):
return torch.pow(pred - target, 2)
def BCELoss(self, pred, target):
epsilon = 1e-7
pred = self.clip_by_tensor(pred, epsilon, 1.0 - epsilon)
output = - target * torch.log(pred) - (1.0 - target) * torch.log(1.0 - pred)
return output
def box_giou(self, b1, b2):
"""
输入为:
----------
b1: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
b2: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 4), xywh
返回为:
-------
giou: tensor, shape=(batch, feat_w, feat_h, anchor_num, 1)
"""
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求出预测框左上角右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
b1_xy = b1[..., :2]
b1_wh = b1[..., 2:4]
b1_wh_half = b1_wh/2.
b1_mins = b1_xy - b1_wh_half
b1_maxes = b1_xy + b1_wh_half
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求出真实框左上角右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
b2_xy = b2[..., :2]
b2_wh = b2[..., 2:4]
b2_wh_half = b2_wh/2.
b2_mins = b2_xy - b2_wh_half
b2_maxes = b2_xy + b2_wh_half
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 求真实框和预测框所有的iou
#----------------------------------------------------#
intersect_mins = torch.max(b1_mins, b2_mins)
intersect_maxes = torch.min(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
intersect_wh = torch.max(intersect_maxes - intersect_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
intersect_area = intersect_wh[..., 0] * intersect_wh[..., 1]
b1_area = b1_wh[..., 0] * b1_wh[..., 1]
b2_area = b2_wh[..., 0] * b2_wh[..., 1]
union_area = b1_area + b2_area - intersect_area
iou = intersect_area / union_area
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 找到包裹两个框的最小框的左上角和右下角
#----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_mins = torch.min(b1_mins, b2_mins)
enclose_maxes = torch.max(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_wh = torch.max(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes))
#----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
#----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_area = enclose_wh[..., 0] * enclose_wh[..., 1]
giou = iou - (enclose_area - union_area) / enclose_area
return giou
def forward(self, l, input, targets=None):
#----------------------------------------------------#
# l代表的是,当前输入进来的有效特征层,是第几个有效特征层
# input的shape为 bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 13, 13
# bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 26, 26
# bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 52, 52
# targets代表的是真实框。
#----------------------------------------------------#
#--------------------------------#
# 获得图片数量,特征层的高和宽
# 13和13
#--------------------------------#
bs = input.size(0)
in_h = input.size(2)
in_w = input.size(3)
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算步长
# 每一个特征点对应原来的图片上多少个像素点
# 如果特征层为13x13的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的32个像素点
# 如果特征层为26x26的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的16个像素点
# 如果特征层为52x52的话,一个特征点就对应原来的图片上的8个像素点
# stride_h = stride_w = 32、16、8
# stride_h和stride_w都是32。
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------#
stride_h = self.input_shape[0] / in_h
stride_w = self.input_shape[1] / in_w
#-------------------------------------------------#
# 此时获得的scaled_anchors大小是相对于特征层的
#-------------------------------------------------#
scaled_anchors = [(a_w / stride_w, a_h / stride_h) for a_w, a_h in self.anchors]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 输入的input一共有三个,他们的shape分别是
# bs, 3*(5+num_classes), 13, 13 => batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 5 + num_classes
# batch_size, 3, 26, 26, 5 + num_classes
# batch_size, 3, 52, 52, 5 + num_classes
#-----------------------------------------------#
prediction = input.view(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), self.bbox_attrs, in_h, in_w).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous()
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的中心位置的调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
x = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 0])
y = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 1])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 先验框的宽高调整参数
#-----------------------------------------------#
w = prediction[..., 2]
h = prediction[..., 3]
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得置信度,是否有物体
#-----------------------------------------------#
conf = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 4])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 种类置信度
#-----------------------------------------------#
pred_cls = torch.sigmoid(prediction[..., 5:])
#-----------------------------------------------#
# 获得网络应该有的预测结果
#-----------------------------------------------#
y_true, noobj_mask, box_loss_scale = self.get_target(l, targets, scaled_anchors, in_h, in_w)
#---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果进行解码,判断预测结果和真实值的重合程度
# 如果重合程度过大则忽略,因为这些特征点属于预测比较准确的特征点
# 作为负样本不合适
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
noobj_mask, pred_boxes = self.get_ignore(l, x, y, h, w, targets, scaled_anchors, in_h, in_w, noobj_mask)
if self.cuda:
y_true = y_true.type_as(x)
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.type_as(x)
box_loss_scale = box_loss_scale.type_as(x)
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# box_loss_scale是真实框宽高的乘积,宽高均在0-1之间,因此乘积也在0-1之间。
# 2-宽高的乘积代表真实框越大,比重越小,小框的比重更大。
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale = 2 - box_loss_scale
loss = 0
obj_mask = y_true[..., 4] == 1
n = torch.sum(obj_mask)
if n != 0:
if self.giou:
#---------------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算预测结果和真实结果的giou
#----------------------------------------------------------------#
giou = self.box_giou(pred_boxes, y_true[..., :4]).type_as(x)
loss_loc = torch.mean((1 - giou)[obj_mask])
else:
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心偏移情况的loss,使用BCELoss效果好一些
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
loss_x = torch.mean(self.BCELoss(x[obj_mask], y_true[..., 0][obj_mask]) * box_loss_scale[obj_mask])
loss_y = torch.mean(self.BCELoss(y[obj_mask], y_true[..., 1][obj_mask]) * box_loss_scale[obj_mask])
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算宽高调整值的loss
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
loss_w = torch.mean(self.MSELoss(w[obj_mask], y_true[..., 2][obj_mask]) * box_loss_scale[obj_mask])
loss_h = torch.mean(self.MSELoss(h[obj_mask], y_true[..., 3][obj_mask]) * box_loss_scale[obj_mask])
loss_loc = (loss_x + loss_y + loss_h + loss_w) * 0.1
loss_cls = torch.mean(self.BCELoss(pred_cls[obj_mask], y_true[..., 5:][obj_mask]))
loss += loss_loc * self.box_ratio + loss_cls * self.cls_ratio
loss_conf = torch.mean(self.BCELoss(conf, obj_mask.type_as(conf))[noobj_mask.bool() | obj_mask])
loss += loss_conf * self.balance[l] * self.obj_ratio
# if n != 0:
# print(loss_loc * self.box_ratio, loss_cls * self.cls_ratio, loss_conf * self.balance[l] * self.obj_ratio)
return loss
def calculate_iou(self, _box_a, _box_b):
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算真实框的左上角和右下角
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b1_x1, b1_x2 = _box_a[:, 0] - _box_a[:, 2] / 2, _box_a[:, 0] + _box_a[:, 2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = _box_a[:, 1] - _box_a[:, 3] / 2, _box_a[:, 1] + _box_a[:, 3] / 2
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算先验框获得的预测框的左上角和右下角
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
b2_x1, b2_x2 = _box_b[:, 0] - _box_b[:, 2] / 2, _box_b[:, 0] + _box_b[:, 2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = _box_b[:, 1] - _box_b[:, 3] / 2, _box_b[:, 1] + _box_b[:, 3] / 2
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 将真实框和预测框都转化成左上角右下角的形式
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
box_a = torch.zeros_like(_box_a)
box_b = torch.zeros_like(_box_b)
box_a[:, 0], box_a[:, 1], box_a[:, 2], box_a[:, 3] = b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2
box_b[:, 0], box_b[:, 1], box_b[:, 2], box_b[:, 3] = b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# A为真实框的数量,B为先验框的数量
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
A = box_a.size(0)
B = box_b.size(0)
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算交的面积
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
max_xy = torch.min(box_a[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(A, B, 2), box_b[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(A, B, 2))
min_xy = torch.max(box_a[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(A, B, 2), box_b[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(A, B, 2))
inter = torch.clamp((max_xy - min_xy), min=0)
inter = inter[:, :, 0] * inter[:, :, 1]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算预测框和真实框各自的面积
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
area_a = ((box_a[:, 2]-box_a[:, 0]) * (box_a[:, 3]-box_a[:, 1])).unsqueeze(1).expand_as(inter) # [A,B]
area_b = ((box_b[:, 2]-box_b[:, 0]) * (box_b[:, 3]-box_b[:, 1])).unsqueeze(0).expand_as(inter) # [A,B]
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
# 求IOU
#-----------------------------------------------------------#
union = area_a + area_b - inter
return inter / union # [A,B]
def get_target(self, l, targets, anchors, in_h, in_w):
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算一共有多少张图片
#-----------------------------------------------------#
bs = len(targets)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 用于选取哪些先验框不包含物体
#-----------------------------------------------------#
noobj_mask = torch.ones(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), in_h, in_w, requires_grad = False)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 让网络更加去关注小目标
#-----------------------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale = torch.zeros(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), in_h, in_w, requires_grad = False)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# batch_size, 3, 13, 13, 5 + num_classes
#-----------------------------------------------------#
y_true = torch.zeros(bs, len(self.anchors_mask[l]), in_h, in_w, self.bbox_attrs, requires_grad = False)
for b in range(bs):
if len(targets[b])==0:
continue
batch_target = torch.zeros_like(targets[b])
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算出正样本在特征层上的中心点
#-------------------------------------------------------#
batch_target[:, [0,2]] = targets[b][:, [0,2]] * in_w
batch_target[:, [1,3]] = targets[b][:, [1,3]] * in_h
batch_target[:, 4] = targets[b][:, 4]
batch_target = batch_target.cpu()
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 将真实框转换一个形式
# num_true_box, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
gt_box = torch.FloatTensor(torch.cat((torch.zeros((batch_target.size(0), 2)), batch_target[:, 2:4]), 1))
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 将先验框转换一个形式
# 9, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
anchor_shapes = torch.FloatTensor(torch.cat((torch.zeros((len(anchors), 2)), torch.FloatTensor(anchors)), 1))
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算交并比
# self.calculate_iou(gt_box, anchor_shapes) = [num_true_box, 9]每一个真实框和9个先验框的重合情况
# best_ns:
# [每个真实框最大的重合度max_iou, 每一个真实框最重合的先验框的序号]
#-------------------------------------------------------#
best_ns = torch.argmax(self.calculate_iou(gt_box, anchor_shapes), dim=-1)
for t, best_n in enumerate(best_ns):
if best_n not in self.anchors_mask[l]:
continue
#----------------------------------------#
# 判断这个先验框是当前特征点的哪一个先验框
#----------------------------------------#
k = self.anchors_mask[l].index(best_n)
#----------------------------------------#
# 获得真实框属于哪个网格点
#----------------------------------------#
i = torch.floor(batch_target[t, 0]).long()
j = torch.floor(batch_target[t, 1]).long()
#----------------------------------------#
# 取出真实框的种类
#----------------------------------------#
c = batch_target[t, 4].long()
#----------------------------------------#
# noobj_mask代表无目标的特征点
#----------------------------------------#
noobj_mask[b, k, j, i] = 0
#----------------------------------------#
# tx、ty代表中心调整参数的真实值
#----------------------------------------#
if not self.giou:
#----------------------------------------#
# tx、ty代表中心调整参数的真实值
#----------------------------------------#
y_true[b, k, j, i, 0] = batch_target[t, 0] - i.float()
y_true[b, k, j, i, 1] = batch_target[t, 1] - j.float()
y_true[b, k, j, i, 2] = math.log(batch_target[t, 2] / anchors[best_n][0])
y_true[b, k, j, i, 3] = math.log(batch_target[t, 3] / anchors[best_n][1])
y_true[b, k, j, i, 4] = 1
y_true[b, k, j, i, c + 5] = 1
else:
#----------------------------------------#
# tx、ty代表中心调整参数的真实值
#----------------------------------------#
y_true[b, k, j, i, 0] = batch_target[t, 0]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 1] = batch_target[t, 1]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 2] = batch_target[t, 2]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 3] = batch_target[t, 3]
y_true[b, k, j, i, 4] = 1
y_true[b, k, j, i, c + 5] = 1
#----------------------------------------#
# 用于获得xywh的比例
# 大目标loss权重小,小目标loss权重大
#----------------------------------------#
box_loss_scale[b, k, j, i] = batch_target[t, 2] * batch_target[t, 3] / in_w / in_h
return y_true, noobj_mask, box_loss_scale
def get_ignore(self, l, x, y, h, w, targets, scaled_anchors, in_h, in_w, noobj_mask):
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算一共有多少张图片
#-----------------------------------------------------#
bs = len(targets)
#-----------------------------------------------------#
# 生成网格,先验框中心,网格左上角
#-----------------------------------------------------#
grid_x = torch.linspace(0, in_w - 1, in_w).repeat(in_h, 1).repeat(
int(bs * len(self.anchors_mask[l])), 1, 1).view(x.shape).type_as(x)
grid_y = torch.linspace(0, in_h - 1, in_h).repeat(in_w, 1).t().repeat(
int(bs * len(self.anchors_mask[l])), 1, 1).view(y.shape).type_as(x)
# 生成先验框的宽高
scaled_anchors_l = np.array(scaled_anchors)[self.anchors_mask[l]]
anchor_w = torch.Tensor(scaled_anchors_l).index_select(1, torch.LongTensor([0])).type_as(x)
anchor_h = torch.Tensor(scaled_anchors_l).index_select(1, torch.LongTensor([1])).type_as(x)
anchor_w = anchor_w.repeat(bs, 1).repeat(1, 1, in_h * in_w).view(w.shape)
anchor_h = anchor_h.repeat(bs, 1).repeat(1, 1, in_h * in_w).view(h.shape)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算调整后的先验框中心与宽高
#-------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes_x = torch.unsqueeze(x + grid_x, -1)
pred_boxes_y = torch.unsqueeze(y + grid_y, -1)
pred_boxes_w = torch.unsqueeze(torch.exp(w) * anchor_w, -1)
pred_boxes_h = torch.unsqueeze(torch.exp(h) * anchor_h, -1)
pred_boxes = torch.cat([pred_boxes_x, pred_boxes_y, pred_boxes_w, pred_boxes_h], dim = -1)
for b in range(bs):
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 将预测结果转换一个形式
# pred_boxes_for_ignore num_anchors, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
pred_boxes_for_ignore = pred_boxes[b].view(-1, 4)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算真实框,并把真实框转换成相对于特征层的大小
# gt_box num_true_box, 4
#-------------------------------------------------------#
if len(targets[b]) > 0:
batch_target = torch.zeros_like(targets[b])
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算出正样本在特征层上的中心点
#-------------------------------------------------------#
batch_target[:, [0,2]] = targets[b][:, [0,2]] * in_w
batch_target[:, [1,3]] = targets[b][:, [1,3]] * in_h
batch_target = batch_target[:, :4].type_as(x)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 计算交并比
# anch_ious num_true_box, num_anchors
#-------------------------------------------------------#
anch_ious = self.calculate_iou(batch_target, pred_boxes_for_ignore)
#-------------------------------------------------------#
# 每个先验框对应真实框的最大重合度
# anch_ious_max num_anchors
#-------------------------------------------------------#
anch_ious_max, _ = torch.max(anch_ious, dim = 0)
anch_ious_max = anch_ious_max.view(pred_boxes[b].size()[:3])
noobj_mask[b][anch_ious_max > self.ignore_threshold] = 0
return noobj_mask, pred_boxes
def weights_init(net, init_type='normal', init_gain = 0.02):
def init_func(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if hasattr(m, 'weight') and classname.find('Conv') != -1:
if init_type == 'normal':
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, init_gain)
elif init_type == 'xavier':
torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)
elif init_type == 'kaiming':
torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data, a=0, mode='fan_in')
elif init_type == 'orthogonal':
torch.nn.init.orthogonal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)
else:
raise NotImplementedError('initialization method [%s] is not implemented' % init_type)
elif classname.find('BatchNorm2d') != -1:
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
print('initialize network with %s type' % init_type)
net.apply(init_func)
def get_lr_scheduler(lr_decay_type, lr, min_lr, total_iters, warmup_iters_ratio = 0.05, warmup_lr_ratio = 0.1, no_aug_iter_ratio = 0.05, step_num = 10):
def yolox_warm_cos_lr(lr, min_lr, total_iters, warmup_total_iters, warmup_lr_start, no_aug_iter, iters):
if iters <= warmup_total_iters:
# lr = (lr - warmup_lr_start) * iters / float(warmup_total_iters) + warmup_lr_start
lr = (lr - warmup_lr_start) * pow(iters / float(warmup_total_iters), 2) + warmup_lr_start
elif iters >= total_iters - no_aug_iter:
lr = min_lr
else:
lr = min_lr + 0.5 * (lr - min_lr) * (
1.0 + math.cos(math.pi* (iters - warmup_total_iters) / (total_iters - warmup_total_iters - no_aug_iter))
)
return lr
def step_lr(lr, decay_rate, step_size, iters):
if step_size < 1:
raise ValueError("step_size must above 1.")
n = iters // step_size
out_lr = lr * decay_rate ** n
return out_lr
if lr_decay_type == "cos":
warmup_total_iters = min(max(warmup_iters_ratio * total_iters, 1), 3)
warmup_lr_start = max(warmup_lr_ratio * lr, 1e-6)
no_aug_iter = min(max(no_aug_iter_ratio * total_iters, 1), 15)
func = partial(yolox_warm_cos_lr ,lr, min_lr, total_iters, warmup_total_iters, warmup_lr_start, no_aug_iter)
else:
decay_rate = (min_lr / lr) ** (1 / (step_num - 1))
step_size = total_iters / step_num
func = partial(step_lr, lr, decay_rate, step_size)
return func
def set_optimizer_lr(optimizer, lr_scheduler_func, epoch):
lr = lr_scheduler_func(epoch)
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr第一次看yolov3的代码,感觉代码好多啊,里面的原理很多都不太清楚。慢慢学吧
参考文献:
YOLOv3详解 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
睿智的目标检测26——Pytorch搭建yolo3目标检测平台_Bubbliiiing的博客-CSDN博客_睿智的目标检测