【图像分类】【深度学习】【Pytorch版本】 DenseNet模型算法详解
文章目录
- 【图像分类】【深度学习】【Pytorch版本】 DenseNet模型算法详解
- 前言
- DenseNet讲解
- Dense Block(稠密块)
- Dense Layer(稠密层)
- Transition Layer 过渡层
- DenseNet模型结构
- DenseNet Pytorch代码
- 完整代码
- 附加代码
- 总结
前言
DenseNet是康奈尔大学的Huang, Gao等人在《Densely Connected Convolutional Networks【CVPR-2017】》【论文地址】一文中提出的模型,受ResNet基本思路启发,将前面所有网络层输出特征与后面网络层输出特征进行密集连接(而非相加)从而实现特征重用,减少了参数量和计算成本并达到了显著的效果。
DenseNet讲解
随着卷积神经网络的网络层越来越深入,出现了新的研究问题:当输入(前向传播)或梯度(反向传播)的信息经过许多层时,信息可能会在到达网络末尾或起始时消失并“冲洗掉”,即网络退化问题。尽管不同的方法在网络拓扑和训练过程方面有所不同,但是都具有一个关键特点:这些方法创建了从浅层到深层的短路径。
从深度方向研究,ResNet【参考】解决了深层网络梯度消失问题;从宽度方向研究,GoogleNet【参考】解决了宽度增加时的计算和参数量的问题。DenseNet则是是从特征的角度入手,通过对特征的极致利用达到更好的效果和减少参数。
DenseNet架构将这种见解(关键特点)提炼为简单的连接模式:为了确保最大程度的信息在网络中各层之间流动,将所有层(相匹配的特征图大小)彼此直接连接。为了保留前馈特性,每个层都从所有先前的图层获取附加输入,并将其自身的特征图传递给所有后续层。
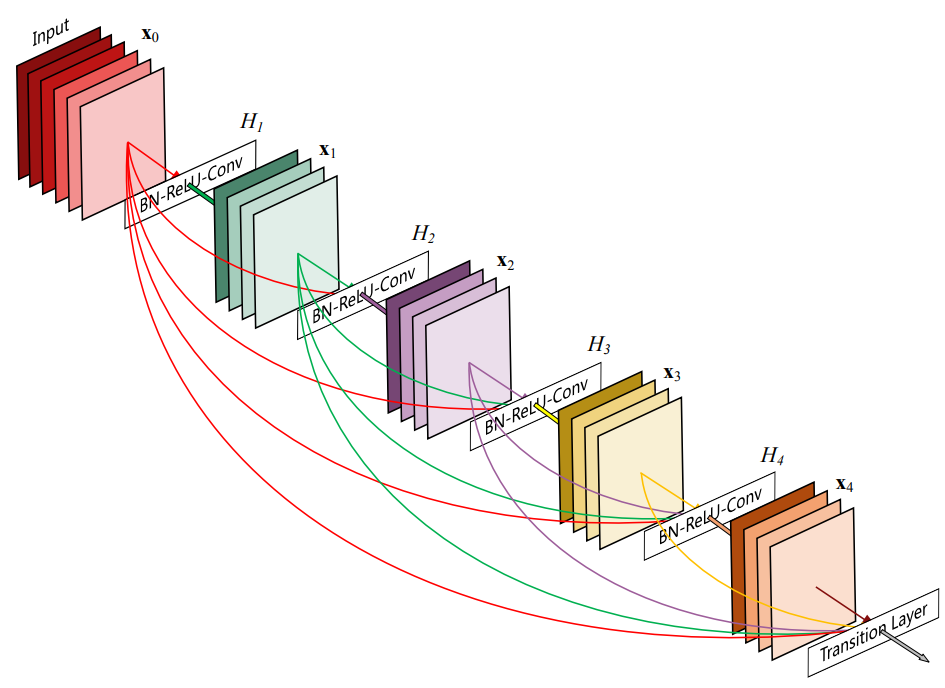
与ResNets将特征传递到图层之前通过求和来组合特征相比,DenseNet通过级联特征来组合它们。因此,第
L
L
L层具有
L
L
L个输入,由所有前面的卷积块的特征图组成。
Dense Block(稠密块)
DenseBlock包含很多互相连接的DenseLayer层,每个层的输出特征图大小相同,这样才可以在通道上进行连结,具体来说就是每一层的输入都来自于它前面所有层的特征,每一层的输出均会直接连接到它后面所有层的输入,层与层之间采用密集连接方式。

所以对于
L
L
L层的DenseBlock,采用密集连接方式共包含
L
(
L
+
1
)
2
\frac{{L\left( {L + 1} \right)}}{2}
2L(L+1)个连接(等差数列求和公式),相比
L
L
L层的ResNetBlock则只包含
(
L
−
1
)
×
2
+
1
\left( {L - 1} \right) \times 2 + 1
(L−1)×2+1个连接。DenseNet与ResNet最主要的区别在于DenseBlock是直接concat来自不同层的特征图实现特征重用,即对不同“级别”的不同表征进行总体性地再探索,提升效率;ResNetBlock是直接add上一层的特征图实现特征融合,将之前层次的信息直接传递给后续层次,解决梯度消失问题。
ResNet和DenseNet对比如下图所示:
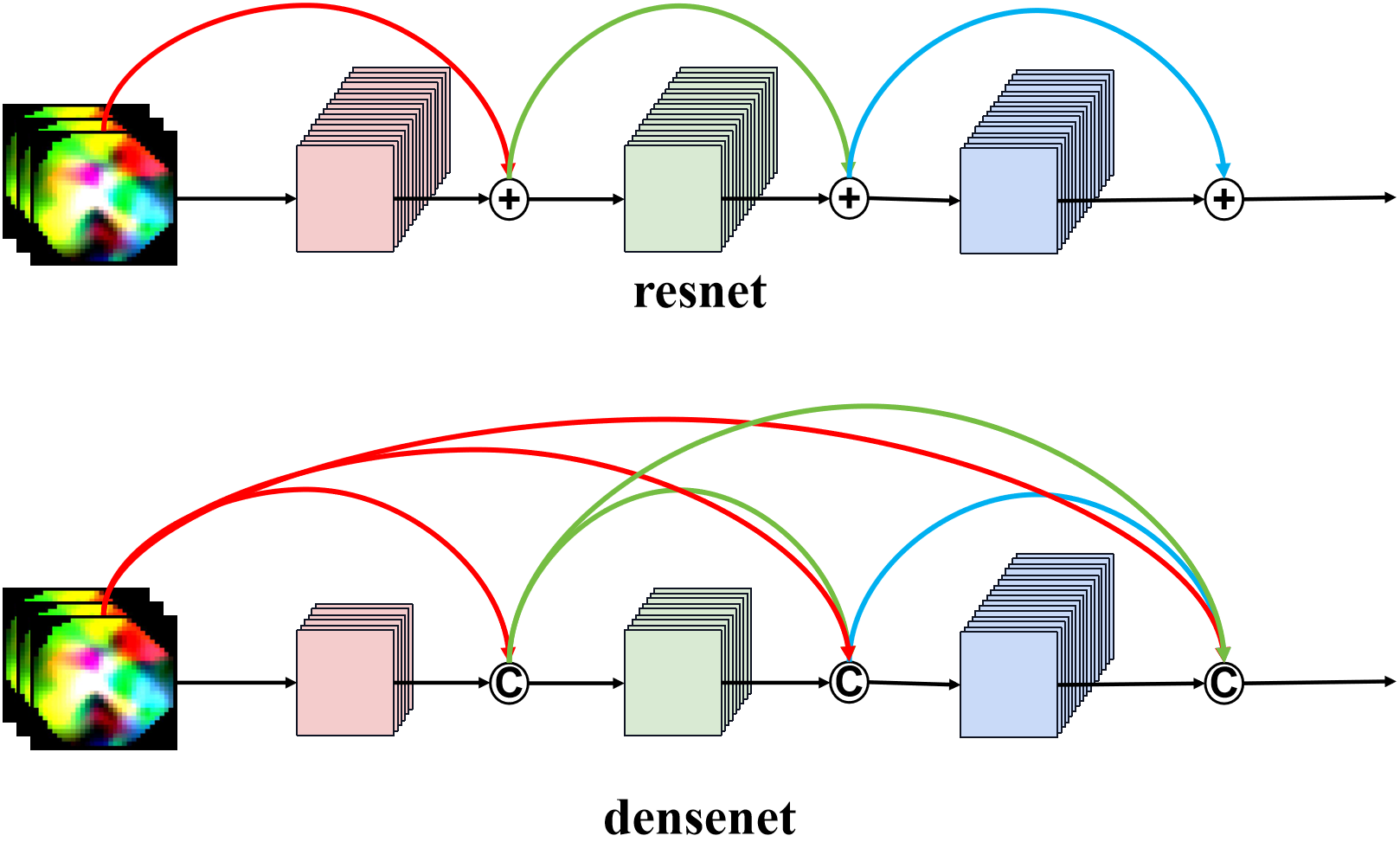
- ResNet: 传统的卷积前馈网络将第 ℓ t h {\ell ^{{\rm{th}}}} ℓth层的输出 x ℓ {x_\ell} xℓ作为输入连接到第 ( ℓ + 1 ) t h {(\ell + 1)^{{\rm{th}}}} (ℓ+1)th层得到输出 x ℓ + 1 = H ℓ + 1 ( x ℓ ) {x_{\ell + 1}} = {H_{\ell + 1}}({x_\ell}) xℓ+1=Hℓ+1(xℓ),ResNet增加了一个跳跃连接(通过一个恒等函数绕过非线性转换),得到输出 x ℓ + 1 = H ℓ + 1 ( x ℓ ) + x ℓ {x_{\ell + 1}} = {H_{\ell + 1}}({x_\ell }) + {x_\ell } xℓ+1=Hℓ+1(xℓ)+xℓ。
- DenseNet: 为了进一步改进层之间的信息流,将任何层直接连接到所有后续层,将第
1
t
h
{1^{{\rm{th}}}}
1th,
2
t
h
{2^{{\rm{th}}}}
2th,
3
t
h
{3 ^{{\rm{th}}}}
3th…
ℓ
t
h
{\ell ^{{\rm{th}}}}
ℓth层的输出
x
1
{x_1}
x1,
x
2
{x_2}
x2,
x
3
{x_3}
x3…
x
ℓ
{x_\ell}
xℓ作为输入连接到第${(\ell
- 1)^{{\rm{th}}}} 层得到输出 层得到输出 层得到输出{x_{\ell + 1}} = {H_{\ell + 1}}(\left[ {{x_1},{x_2},{x_3}…{x_\ell }} \right])$
H ℓ + 1 ( ∙ ) {H_{\ell +1}}( \bullet ) Hℓ+1(∙)定义为三个连续操作的复合函数:批量归一化层(BN)、激活函数(ReLU)[6]和卷积层(Conv)。
增长率 如果每一个DenseLayer H ℓ ( ∙ ) {H_\ell}( \bullet ) Hℓ(∙)生成 k k k个特征图,则第 ℓ \ell ℓ层具有 k 0 + k ( ℓ − 1 ) {k_0} + k\left( {\ell - 1} \right) k0+k(ℓ−1)个特征图,其中 k 0 k_0 k0是输入DenseBlock的特征图数量, k k k指的是网络的超参数增长率。每个DenseLayer都可以访问其块中的所有先前的特征图(即网络的“集体知识”),这些特征图被视为网络的全局状态,每个DenseLayer都将自己 k k k个特征图添加到全局状态,因此增长率控制着每一层为全局状态贡献多少新信息。写入后的全局状态可以在网络中的任何位置进行访问,并且与传统的网络体系结构不同,无需将其逐层复制。
DenseNet与现有网络体系结构之间的一个重要区别是DenseNet具有通道非常狭窄的DenseLayer,通常DenseBlock起始的DenseLayer就是通道就十分狭窄( k = 12 k=12 k=12),因为要考虑后续DenseLayer的增长。
Dense Layer(稠密层)
DenseLayer中采用的BN+ReLU+Conv的结构模式,不同于常见的是Conv+BN+ReLU,这是因为稠密层的输入包含了之前所有稠密层的输出特征,这些来自不同层的输出数值分布差异比较大,因此在输入到DenseLayer的Conv层之前,必须先经过BN层将其数值进行标准化,然后再进行卷积操作。
DenseLayer中采用BN+ReLU+1x1 Conv+BN+ReLU+3x3 Conv的结构:

瓶颈层 尽管每个DenseLayer仅产生
k
k
k个输出特征图,但由于密集连接模式,DenseLayer通常会有更多的输入。因此为了减少参数,DenseLayer在3×3卷积之前引入1×1卷积作为瓶颈层,以减少输入特征图的数量,从而提高计算效率。
Transition Layer 过渡层
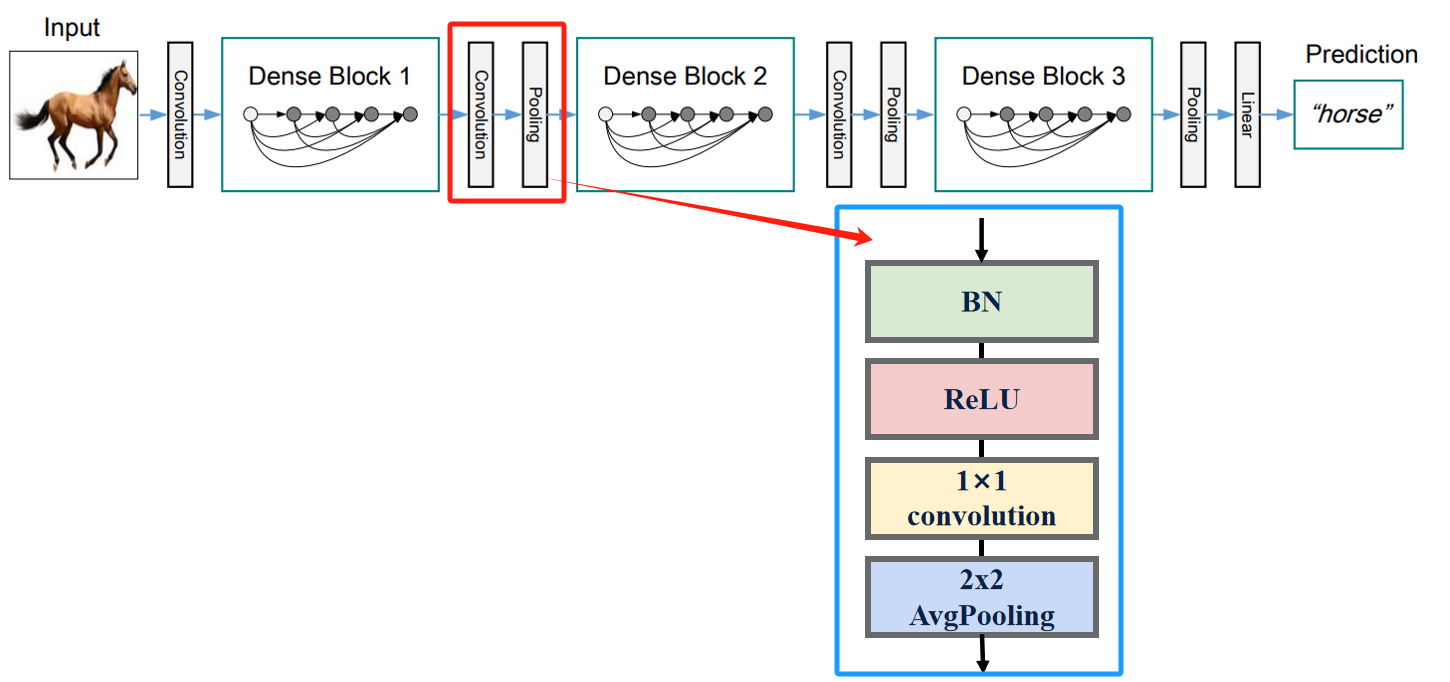
TransitionLayer进行卷积和池化以起到整合压缩的作用:卷积网络的重要组成部分是降低特征图尺寸的下采样层。为了便于DenseNet结构进行下采样,将DenseNet划分为为多个DenseBlock,TransitionLayer主要用于连接两个相邻的DenseBlock,整合前一个DenseBlock输出的特征,通过下采样缩小前一个DenseBlock的征图尺寸。
TransitionLayer中采用BN+ReLU+1x1 Conv+ 2x2 AvgPooling的结构:
压缩 为了进一步提高DenseNet的紧凑性,可以减少TransitionLayer的特征图数量。如果DenseBlock输出
m
m
m个特征图,则让之后的TransitionLayer输出
θ
m
{\theta _m}
θm个特征图。其中
0
<
θ
m
≤
1
0 < {\theta _m} \le 1
0<θm≤1称为压缩因子。当
θ
m
=
1
{\theta _m}=1
θm=1时,TransitionLayer的特征图数量与DenseBlock的保持不变。
DenseNet模型结构
下图是原论文给出的关于DenseNet模型结构的详细示意图:

Resnet在图像分类中分为两部分:backbone部分: 主要由卷积层、池化层(汇聚层)、稠密块和过渡层组成,分类器部分:由全局平均池化层和全连接层组成 。
DenseNet Pytorch代码
稠密层Dense Layer: BN+ReLU+1x1 Conv+BN+ReLU+3x3 Conv
class DenseLayer(nn.Module):
"""Basic unit of DenseBlock (DenseLayer) """
def __init__(self, input_c, growth_rate, bn_size, drop_rate):
super(DenseLayer, self).__init__()
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(input_c)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_c, bn_size * growth_rate,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(bn_size * growth_rate)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(bn_size * growth_rate, growth_rate,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
def forward(self, x):
# 1×1卷积 bottleneck瓶颈层
output = self.bn1(x)
output = self.relu1(output)
output = self.conv1(output)
# 3×3卷积
output = self.bn2(output)
output = self.relu2(output)
output = self.conv2(output)
if self.drop_rate > 0:
output = F.dropout(output, p=self.drop_rate)
return torch.cat([x, output], 1)
稠密块DenseBlock: 由多个稠密层组成
class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_layers, input_c, bn_size, growth_rate, drop_rate):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
for i in range(num_layers):
layer = DenseLayer(input_c + i * growth_rate,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
bn_size=bn_size,
drop_rate=drop_rate)
self.add_module("denselayer%d" % (i + 1), layer)
def forward(self, init_features):
features = [init_features]
for name, layer in self.items():
# 当前DenseLayer的输出特征
new_features = layer(features)
# 拼接所有DenseLayer的输出特征
features.append(new_features)
return torch.cat(features, 1)
过渡层TransitionLayer : BN+ReLU+1x1 Conv+ 2x2 AvgPooling
class Transition(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_c, output_c):
super(Transition, self).__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(input_c)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# 1×1卷积
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(input_c, output_c,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
# 2×2池化
self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(2, stride=2)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.bn(input)
output = self.relu(output)
output = self.conv(output)
output = self.pool(output)
return output
完整代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchsummary import summary
class DenseLayer(nn.Module):
"""Basic unit of DenseBlock (DenseLayer) """
def __init__(self, input_c, growth_rate, bn_size, drop_rate):
super(DenseLayer, self).__init__()
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(input_c)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_c, bn_size * growth_rate,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(bn_size * growth_rate)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(bn_size * growth_rate, growth_rate,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
def forward(self, inputs):
# 1×1卷积 bottleneck瓶颈层
output = self.bn1(inputs)
output = self.relu1(output)
output = self.conv1(output)
# 3×3卷积
output = self.bn2(output)
output = self.relu2(output)
output = self.conv2(output)
if self.drop_rate > 0:
output = F.dropout(output, p=self.drop_rate)
return output
class DenseBlock(nn.ModuleDict):
def __init__(self, num_layers, input_c, bn_size, growth_rate, drop_rate):
super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
for i in range(num_layers):
layer = DenseLayer(input_c + i * growth_rate,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
bn_size=bn_size,
drop_rate=drop_rate)
self.add_module("denselayer%d" % (i + 1), layer)
def forward(self, init_features):
features = [init_features]
for name, layer in self.items():
concat_features = torch.cat(features, 1)
# 当前DenseLayer的输出特征
new_features = layer(concat_features)
# 收集所有DenseLayer的输出特征
features.append(new_features)
return torch.cat(features, 1)
class Transition(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_c, output_c):
super(Transition, self).__init__()
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(input_c)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# 1×1卷积
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(input_c, output_c,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
# 2×2池化
self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(2, stride=2)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.bn(input)
output = self.relu(output)
output = self.conv(output)
output = self.pool(output)
return output
class DenseNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, growth_rate=32, block_config=(6, 12, 24, 16), num_init_features=64, bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5, drop_rate=0, num_classes=1000):
super(DenseNet, self).__init__()
# 前部 conv+bn+relu+pool
self.features = nn.Sequential(
# 第一层
nn.Conv2d(3, num_init_features, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_init_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 第二层
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, padding=1)
)
# 中部 DenseBlock
num_features = num_init_features
for i, num_layers in enumerate(block_config):
block = DenseBlock(num_layers=num_layers,
input_c=num_features,
bn_size=bn_size,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
drop_rate=drop_rate)
# 新增DenseBlock
self.features.add_module("denseblock%d" % (i + 1), block)
# 更新通道数
num_features = num_features + num_layers * growth_rate
# 除去最后一层DenseBlock不需要加Transition来连接两个相邻的DenseBlock
if i != len(block_config) - 1:
transition = Transition(input_c=num_features, output_c=int(num_features * compression_rate))
# 添加Transition
self.features.add_module("transition%d" % (i + 1), transition)
# 更新通道数
num_features = int(num_features * compression_rate)
# 后部 bn+ReLU
self.tail = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# 分类器 classification
self.classifier = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)
# 初始化权重
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
features = self.features(x)
tail_output = self.tail(features)
# 平均池化
out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(tail_output, (1, 1))
out = torch.flatten(out, 1)
out = self.classifier(out)
return out
def densenet121(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 25.35%
# 'densenet121': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet121-a639ec97.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 24, 16),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
def densenet169(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 24.00%
# 'densenet169': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet169-b2777c0a.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 32, 32),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
def densenet201(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 22.80%
# 'densenet201': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet201-c1103571.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 48, 32),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
def densenet161(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 22.35%
# 'densenet161': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet161-8d451a50.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=48,
block_config=(6, 12, 36, 24),
num_init_features=96,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = densenet121().to(device)
summary(model, input_size=(3, 224, 224))
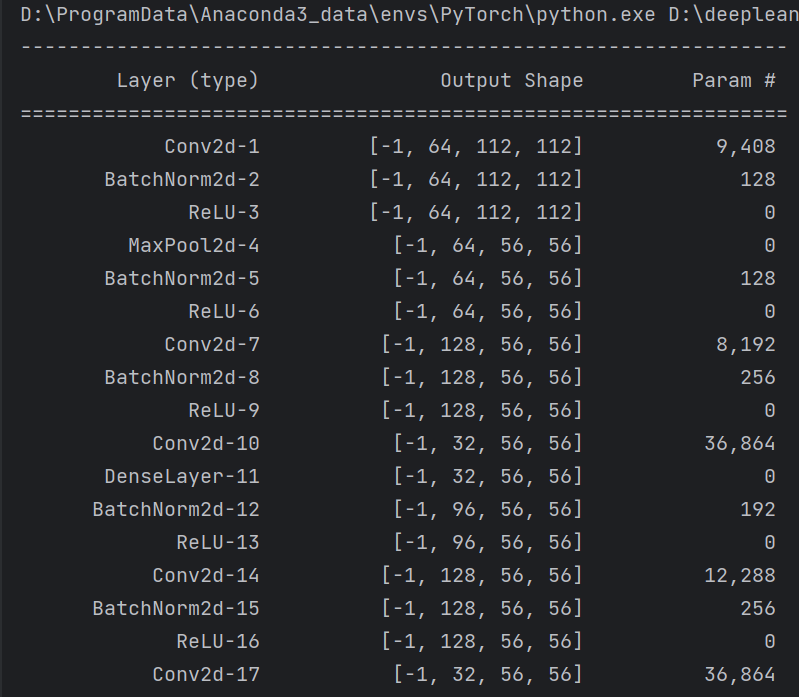
summary可以打印网络结构和参数,方便查看搭建好的网络结构。
附加代码
由于需要进行多次Concatnate操作,数据需要被复制多次,显存容易增加得很快,需要一定的显存优化技术。这里博主提供了优化后的代码。
import re
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.checkpoint as cp
from torchsummary import summary
class _DenseLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
input_c,
growth_rate,
bn_size,
drop_rate,
memory_efficient= False):
super(_DenseLayer, self).__init__()
self.add_module("norm1", nn.BatchNorm2d(input_c))
self.add_module("relu1", nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.add_module("conv1", nn.Conv2d(in_channels=input_c,
out_channels=bn_size * growth_rate,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
bias=False))
self.add_module("norm2", nn.BatchNorm2d(bn_size * growth_rate))
self.add_module("relu2", nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.add_module("conv2", nn.Conv2d(bn_size * growth_rate,
growth_rate,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
bias=False))
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.memory_efficient = memory_efficient
def bn_function(self, inputs):
# 1×1卷积
bottleneck_output = self.conv1(self.relu1(self.norm1(inputs)))
return bottleneck_output
# 所有连接都能保留梯度,否则不进行梯度更新
def any_requires_grad(inputs):
for tensor in inputs:
if tensor.requires_grad:
return True
return False
# 本函数主要是为了网络训练阶段高效内存管理
def call_checkpoint_bottleneck(self, inputs):
def closure(*inp):
return self.bn_function(inp)
return cp.checkpoint(closure, *inputs)
def forward(self, inputs):
if self.memory_efficient and self.any_requires_grad(inputs):
# 即非部署阶段
if torch.jit.is_scripting():
raise Exception("memory efficient not supported in JIT")
bottleneck_output = self.call_checkpoint_bottleneck(inputs)
else:
bottleneck_output = self.bn_function(inputs)
# 3×3卷积
new_features = self.conv2(self.relu2(self.norm2(bottleneck_output)))
# 随机失活
if self.drop_rate > 0:
new_features = F.dropout(new_features,
p=self.drop_rate,
training=self.training)
return new_features
class _DenseBlock(nn.ModuleDict):
_version = 2
def __init__(self,
num_layers,
input_c,
bn_size,
growth_rate,
drop_rate,
memory_efficient=False):
super(_DenseBlock, self).__init__()
for i in range(num_layers):
layer = _DenseLayer(input_c + i * growth_rate,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
bn_size=bn_size,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
memory_efficient=memory_efficient)
self.add_module("denselayer%d" % (i + 1), layer)
def forward(self, init_features):
features = [init_features]
for name, layer in self.items():
concat_features = torch.cat(features, 1)
new_features = layer(concat_features)
features.append(new_features)
return torch.cat(features, 1)
class _Transition(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self,
input_c,
output_c):
super(_Transition, self).__init__()
self.add_module("norm", nn.BatchNorm2d(input_c))
self.add_module("relu", nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
self.add_module("conv", nn.Conv2d(input_c,
output_c,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
bias=False))
self.add_module("pool", nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
class DenseNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 24, 16),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
drop_rate=0,
num_classes=1000,
memory_efficient= False):
super(DenseNet, self).__init__()
# 前部 conv+bn+relu+pool
self.features = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("conv0", nn.Conv2d(3, num_init_features, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)),
("norm0", nn.BatchNorm2d(num_init_features)),
("relu0", nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
("pool0", nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)),
]))
# 中部 DenseBlock
num_features = num_init_features
for i, num_layers in enumerate(block_config):
block = _DenseBlock(num_layers=num_layers,
input_c=num_features,
bn_size=bn_size,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
drop_rate=drop_rate,
memory_efficient=memory_efficient)
self.features.add_module("denseblock%d" % (i + 1), block)
# 更新通道数
num_features = num_features + num_layers * growth_rate
# 除去最后一层DenseBlock不需要加Transition来连接两个相邻的DenseBlock
if i != len(block_config) - 1:
trans = _Transition(input_c=num_features,
output_c=num_features // 2)
self.features.add_module("transition%d" % (i + 1), trans)
# 更新通道数
num_features = int(num_features * compression_rate)
# 后部 bn+ReLU
self.tail = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
# 分类器 classification
self.classifier = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)
# 初始化权重
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
features = self.features(x)
tail_output = self.tail(features)
# 平均池化
out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(tail_output, (1, 1))
out = torch.flatten(out, 1)
out = self.classifier(out)
return out
def densenet121(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 25.35%
# 'densenet121': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet121-a639ec97.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 24, 16),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
def densenet169(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 24.00%
# 'densenet169': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet169-b2777c0a.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 32, 32),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
def densenet201(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 22.80%
# 'densenet201': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet201-c1103571.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=32,
block_config=(6, 12, 48, 32),
num_init_features=64,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
def densenet161(**kwargs):
# Top-1 error: 22.35%
# 'densenet161': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet161-8d451a50.pth'
return DenseNet(growth_rate=48,
block_config=(6, 12, 36, 24),
num_init_features=96,
bn_size=4,
compression_rate=0.5,
**kwargs)
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = densenet121().to(device)
summary(model, input_size=(3, 224, 224))
总结
尽可能简单、详细的介绍了稠密结构的原理和在卷积神经网络中的作用,讲解了DenseNet模型的结构和pytorch代码。