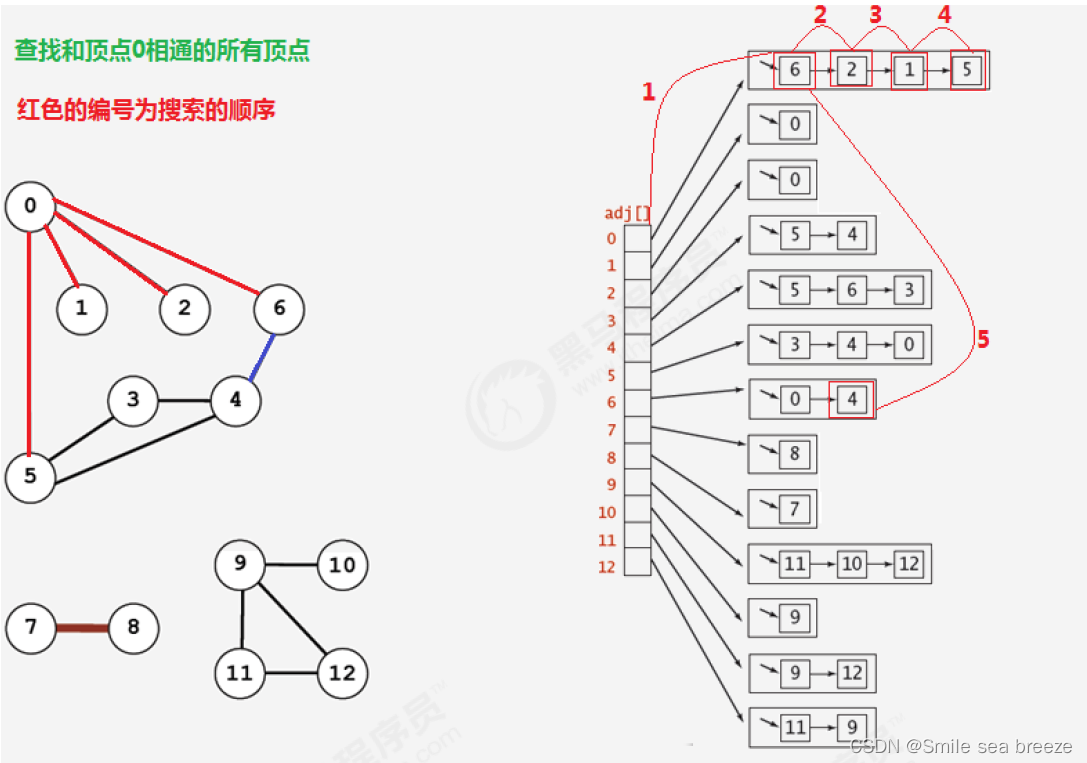
上文:AQS-Exchanger源码学习
源码下载:https://gitee.com/hong99/jdk8
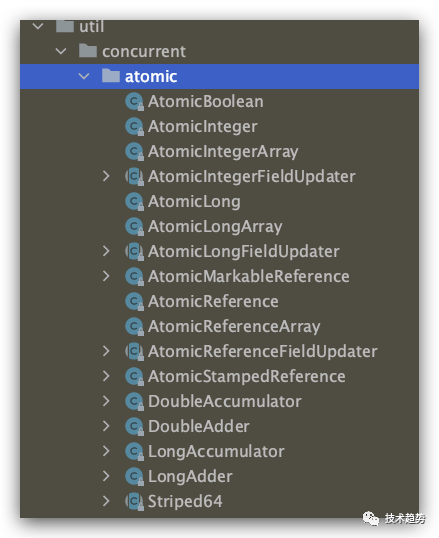
Atomic了解
atomic是并发框架中的一员,所属位置:java.util.concurrent.atomic 该类主要是用来解决内存可见性、有序、线程安全,当然底层也是通过cas来实现,所以性能相同步锁也是高不少。
Atomic解决了什么问题?
并发的三大特性:原子性、可见性、有序性
没错atomic就是解决以上三种特性而专门设计的一种在高并发下线程安全实现。主要的操作有三步,
首首:获取锁,这里是通过cas进行实现,并且是带版本的方式,解决了aba的问题;
其次:将所获取的值、版本号、新值进行更新,若成则进返回(同存可见通知其它处理器),若失败则直接返回结果;
最后:将结果返回给操作线程或让出线程,或中间让出线程。
Atomic相关基础学习
atomic相关类型如下:
基本类型:
AtomicLong | 长整型原子 |
AtomicInteger | 整型原子 |
AtomicBoolean | 布尔类型 |
引用类型:
AtomicReference | 引用类型(存在aba) |
AtomicStampedReference | 更新带版本号的引用类型 |
AtomicMarkableReference | 更新带标主的引用类型 |
数组类型:
AtomicLongArray | 更新长整型数组里的元素 |
AtomicIntegerArray | 更新整型数组里的元素 |
AtomicReferenceArray | 更新引用类型里面的元素 |
字段类型:
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater | 更新整型字段 |
AtomicLongFieldUpdater | 更新长整型字段 |
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater | 更新引用类型字段 |
类加器类型:
DoubleAccumulator | double累加器 |
DoubleAdder | double累加器 |
LongAccumulator | long类型累加器 |
LongAdder | long累加器 |
基础使用:
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
}
}).start();
}结果
1
3
2
4
0
5
6
7
8
9可以看出所有都是独立的,而不是重复。所以是线程安全跟内存可见的。
AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean();
while (!atomicBoolean.get()){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(atomicBoolean.getAndSet(true));
}
}).start();
}
System.out.println("结束了!");结果
false
结束了!
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true
true引用类型学习
AtomicReference<User> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<User>();
User user = new User("1","用户1");
User user2 = new User("2","用户2");
atomicReference.set(user);
boolean b = atomicReference.compareAndSet(user, user2);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(atomicReference.get().toString());结果
true
User{userName='2', userId='用户2'}其他的大至同上,所以不一一了解,需要了解的可以自行了解。
Atomic源码学习
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger 源码学习
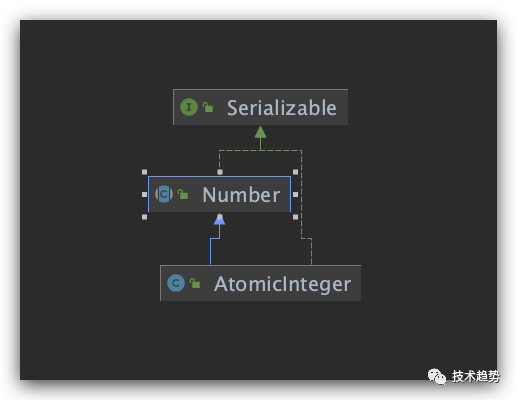
//整型原子类实现
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;
// 设置使用Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt进行更新
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
//存放变量value值的偏移量值
private static final long valueOffset;
//初始值
static {
try {
//初始化偏移量
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
private volatile int value;
//带参数的构造方法
public AtomicInteger(int initialValue) {
value = initialValue;
}
//空构造方法
public AtomicInteger() {
}
//获取当前值
public final int get() {
return value;
}
//设置新值
public final void set(int newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
//设置值(不带屏障会导致数据一致性问题)
public final void lazySet(int newValue) {
unsafe.putOrderedInt(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
//原子设置新值并返回旧值
public final int getAndSet(int newValue) {
return unsafe.getAndSetInt(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
//对比值并更新返回 true为成功 false为失败
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
//如果当前值等于期望则进行更新并返回 true 否则返回false
public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
//自增并返回旧值
public final int getAndIncrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1);
}
//自减并返回旧值
public final int getAndDecrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, -1);
}
//原子的添加指定的值并返回旧值
public final int getAndAdd(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta);
}
//自增1并返回新值
public final int incrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1) + 1;
}
//自减1并返回新值
public final int decrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, -1) - 1;
}
//新增指定的值并返回新值
public final int addAndGet(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta) + delta;
}
//通过函数方式进行更新值并返回旧值
public final int getAndUpdate(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return prev;
}
//同上类型,返回新值
public final int updateAndGet(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return next;
}
//x为新值及函数进行更新返回之前的值
public final int getAndAccumulate(int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return prev;
}
//同上类似,返回更新的新值
public final int accumulateAndGet(int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return next;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(get());
}
//获取当前值
public int intValue() {
return get();
}
//获取长整型的当前值
public long longValue() {
return (long)get();
}
//获取浮点数的当前值
public float floatValue() {
return (float)get();
}
//获取double类型当前值
public double doubleValue() {
return (double)get();
}
}可以看到这个AtomicInteger非常简单,主要是利用Unsafe进行实现,不过Unsafe大部分都是c++代码,这里Java层面看不了,需要去深入c++,这里不再细究。
当然AtomicBoolean与AtomicLong都差不多这里不深入。
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference 源码学习
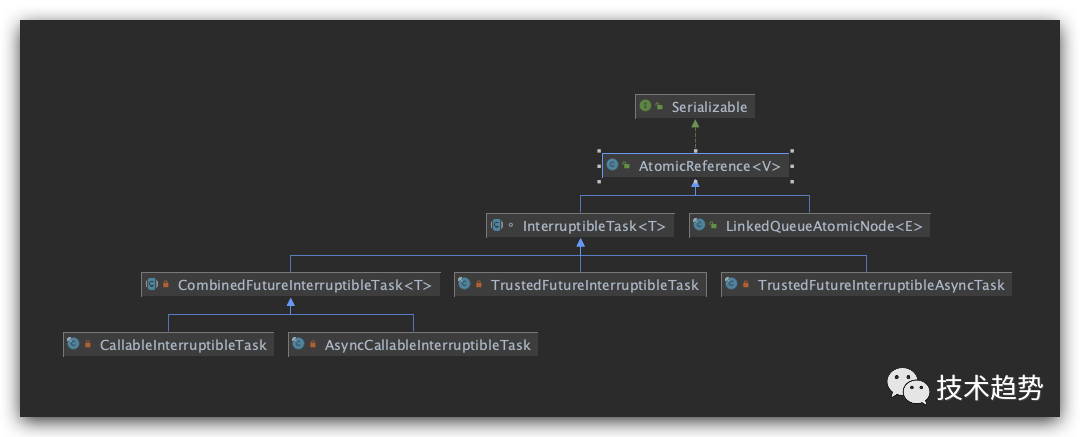
package java.util.concurrent.atomic;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
import java.util.function.BinaryOperator;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
//原子引用(存在aba问题)
public class AtomicReference<V> implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1848883965231344442L;
//使用Unsafe做为更新的实现
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
//存放变量value值的偏移量值
private static final long valueOffset;
//初始化
static {
try {
//初始化偏移量
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicReference.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
//可见的值
private volatile V value;
//构造方法,带初始参
public AtomicReference(V initialValue) {
value = initialValue;
}
//构造方法
public AtomicReference() {
}
//获取当前值
public final V get() {
return value;
}
//设置新值方法
public final void set(V newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
//延迟的值设置方法
public final void lazySet(V newValue) {
unsafe.putOrderedObject(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
//当前值等于期望则更新成功,否则失败
public final boolean compareAndSet(V expect, V update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
//不保证排序,当前值等于期望则更新成功,否则失败
public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(V expect, V update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
//原子的设置值,并返回旧值
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public final V getAndSet(V newValue) {
return (V)unsafe.getAndSetObject(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
//通过函数进行更新,并返回旧值
public final V getAndUpdate(UnaryOperator<V> updateFunction) {
V prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = updateFunction.apply(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return prev;
}
//同上类似,返回新值
public final V updateAndGet(UnaryOperator<V> updateFunction) {
V prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = updateFunction.apply(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return next;
}
//通过函数更新新值并返回旧值
public final V getAndAccumulate(V x,
BinaryOperator<V> accumulatorFunction) {
V prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = accumulatorFunction.apply(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return prev;
}
//同上类似,返回新值
public final V accumulateAndGet(V x,
BinaryOperator<V> accumulatorFunction) {
V prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = accumulatorFunction.apply(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return next;
}
/**
* Returns the String representation of the current value.
* @return the String representation of the current value
*/
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(get());
}
}注意当前这个引用类型的是存在aba的问题,如果需要使用尽量还是用AtomicStampedReference详细,请看看这个的源码实现,也挺简单的。
java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 源码学习
package java.util.concurrent.atomic;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedActionException;
import java.security.PrivilegedExceptionAction;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.function.IntBinaryOperator;
import java.util.function.IntUnaryOperator;
import sun.reflect.CallerSensitive;
import sun.reflect.Reflection;
//对象整型类型的
public abstract class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<T> {
//返回一个初始化对象
@CallerSensitive
public static <U> AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<U> newUpdater(Class<U> tclass,
String fieldName) {
return new AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl<U>
(tclass, fieldName, Reflection.getCallerClass());
}
//无参构造方法
protected AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater() {
}
//当前值等于期望值进行更新并返回true
public abstract boolean compareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update);
//不保证排序 当前值等于期望值进行更新
public abstract boolean weakCompareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update);
//设置新值
public abstract void set(T obj, int newValue);
//延迟设置新值
public abstract void lazySet(T obj, int newValue);
//获取当前值方法
public abstract int get(T obj);
//设置新值并返回旧值
public int getAndSet(T obj, int newValue) {
int prev;
do {
prev = get(obj);
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, newValue));
return prev;
}
//自增1并返回旧值
public int getAndIncrement(T obj) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = prev + 1;
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return prev;
}
//自减1并返回旧值
public int getAndDecrement(T obj) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = prev - 1;
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return prev;
}
//原子的将delta的值加上并返回旧值
public int getAndAdd(T obj, int delta) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = prev + delta;
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return prev;
}
//自增1并返回新值
public int incrementAndGet(T obj) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = prev + 1;
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return next;
}
//自减1并返回新值
public int decrementAndGet(T obj) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = prev - 1;
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return next;
}
//新增当前值加上delta并返回新值
public int addAndGet(T obj, int delta) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = prev + delta;
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return next;
}
//更新并返回旧值
public final int getAndUpdate(T obj, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return prev;
}
//更新并返回新值
public final int updateAndGet(T obj, IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return next;
}
//通过函数的方法进行更新并返回旧值
public final int getAndAccumulate(T obj, int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return prev;
}
//同上类似返回新值
public final int accumulateAndGet(T obj, int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get(obj);
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(obj, prev, next));
return next;
}
//具体实现的方法
private static final class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl<T>
extends AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<T> {
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private final long offset;
//
private final Class<?> cclass;
/** class holding the field */
private final Class<T> tclass;
//构造实现方法
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterImpl(final Class<T> tclass,
final String fieldName,
final Class<?> caller) {
final Field field;
final int modifiers;
try {
//反射获取到的属值信息
field = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Field>() {
public Field run() throws NoSuchFieldException {
return tclass.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
}
});
//用于判断是不是public
modifiers = field.getModifiers();
sun.reflect.misc.ReflectUtil.ensureMemberAccess(
caller, tclass, null, modifiers);
ClassLoader cl = tclass.getClassLoader();
ClassLoader ccl = caller.getClassLoader();
if ((ccl != null) && (ccl != cl) &&
((cl == null) || !isAncestor(cl, ccl))) {
sun.reflect.misc.ReflectUtil.checkPackageAccess(tclass);
}
} catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw new RuntimeException(pae.getException());
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
//类型判断是不是int
if (field.getType() != int.class)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be integer type");
//必须被volatile修饰
if (!Modifier.isVolatile(modifiers))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must be volatile type");
//判断获取caller或tclass 通过判断是否在同包或private或者为超类
this.cclass = (Modifier.isProtected(modifiers) &&
tclass.isAssignableFrom(caller) &&
!isSamePackage(tclass, caller))
? caller : tclass;
//目标类
this.tclass = tclass;
//偏移量
this.offset = U.objectFieldOffset(field);
}
//判断第二个类加载器被第一个已加载,如果是返回true(多亲委派)
private static boolean isAncestor(ClassLoader first, ClassLoader second) {
ClassLoader acl = first;
do {
acl = acl.getParent();
if (second == acl) {
return true;
}
} while (acl != null);
return false;
}
//两个是否在同一个包和修饰符一样
private static boolean isSamePackage(Class<?> class1, Class<?> class2) {
return class1.getClassLoader() == class2.getClassLoader()
&& Objects.equals(getPackageName(class1), getPackageName(class2));
}
//获取包名称
private static String getPackageName(Class<?> cls) {
String cn = cls.getName();
int dot = cn.lastIndexOf('.');
return (dot != -1) ? cn.substring(0, dot) : "";
}
//判断是cclass的实例,如果不是抛出异常
private final void accessCheck(T obj) {
if (!cclass.isInstance(obj))
throwAccessCheckException(obj);
}
//若受保护异常则跑出异常
private final void throwAccessCheckException(T obj) {
if (cclass == tclass)
throw new ClassCastException();
else
throw new RuntimeException(
new IllegalAccessException(
"Class " +
cclass.getName() +
" can not access a protected member of class " +
tclass.getName() +
" using an instance of " +
obj.getClass().getName()));
}
//对比值并更新返回 true为成功 false为失败
public final boolean compareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update) {
accessCheck(obj);
return U.compareAndSwapInt(obj, offset, expect, update);
}
//不带排序 如果当前值等于期望则进行更新并返回 true 否则返回false
public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(T obj, int expect, int update) {
accessCheck(obj);
return U.compareAndSwapInt(obj, offset, expect, update);
}
//设置新值
public final void set(T obj, int newValue) {
accessCheck(obj);
U.putIntVolatile(obj, offset, newValue);
}
//延迟设置新值
public final void lazySet(T obj, int newValue) {
accessCheck(obj);
U.putOrderedInt(obj, offset, newValue);
}
//获取当前对象的值
public final int get(T obj) {
accessCheck(obj);
return U.getIntVolatile(obj, offset);
}
//设置并返回旧值
public final int getAndSet(T obj, int newValue) {
accessCheck(obj);
return U.getAndSetInt(obj, offset, newValue);
}
//旧值加delta并返回旧值
public final int getAndAdd(T obj, int delta) {
accessCheck(obj);
return U.getAndAddInt(obj, offset, delta);
}
//自增1返回旧值
public final int getAndIncrement(T obj) {
return getAndAdd(obj, 1);
}
//自减1返回旧值
public final int getAndDecrement(T obj) {
return getAndAdd(obj, -1);
}
//自增1返回新值
public final int incrementAndGet(T obj) {
return getAndAdd(obj, 1) + 1;
}
//自减1返回旧值
public final int decrementAndGet(T obj) {
return getAndAdd(obj, -1) - 1;
}
//当前值+delta并返回新值
public final int addAndGet(T obj, int delta) {
return getAndAdd(obj, delta) + delta;
}
}
}可以看到上面的的更新和实现大至都是类似,主要是这个AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater是带各种限制的,比如 必须是interger属性必须是public且被volatile修饰。
java.util.concurrent.atomic.DoubleAdder 源码学习
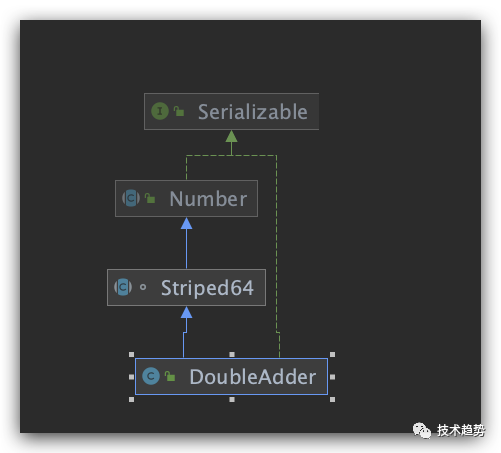
package java.util.concurrent.atomic;
import java.io.Serializable;
//累加器
public class DoubleAdder extends Striped64 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246863182397L;
//无参构造方法
public DoubleAdder() {
}
//新增方法
public void add(double x) {
Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a;
//先判断是cells为空,如果是进行初始化;
//casBase对base的偏移量进行操作(没有竟争下)
if ((as = cells) != null ||
!casBase(b = base,
Double.doubleToRawLongBits
(Double.longBitsToDouble(b) + x))) {
boolean uncontended = true;
//as为空则进行初始化
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value,
Double.doubleToRawLongBits
(Double.longBitsToDouble(v) + x))))
doubleAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);
}
}
//求合方法
public double sum() {
Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;
double sum = Double.longBitsToDouble(base);
//循环累加计算
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += Double.longBitsToDouble(a.value);
}
}
return sum;
}
//重置(清空初始值)
public void reset() {
Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;
base = 0L; // relies on fact that double 0 must have same rep as long
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
a.value = 0L;
}
}
}
//返回该值为累加和(可能为旧值)
public double sumThenReset() {
Cell[] as = cells; Cell a;
double sum = Double.longBitsToDouble(base);
base = 0L;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null) {
long v = a.value;
a.value = 0L;
sum += Double.longBitsToDouble(v);
}
}
}
return sum;
}
/**
* Returns the String representation of the {@link #sum}.
* @return the String representation of the {@link #sum}
*/
public String toString() {
return Double.toString(sum());
}
//返回当前的累加合
public double doubleValue() {
return sum();
}
//long类型的累加合
public long longValue() {
return (long)sum();
}
//整型的累加合
public int intValue() {
return (int)sum();
}
//浮点型的累加合
public float floatValue() {
return (float)sum();
}
//序列化
private static class SerializationProxy implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246863182397L;
/**
* The current value returned by sum().
* @serial
*/
private final double value;
SerializationProxy(DoubleAdder a) {
value = a.sum();
}
/**
* Returns a {@code DoubleAdder} object with initial state
* held by this proxy.
*
* @return a {@code DoubleAdder} object with initial state
* held by this proxy.
*/
private Object readResolve() {
DoubleAdder a = new DoubleAdder();
a.base = Double.doubleToRawLongBits(value);
return a;
}
}
//序列化
private Object writeReplace() {
return new SerializationProxy(this);
}
//读取字符流
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.InvalidObjectException {
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Proxy required");
}
}最后
其它的子类有兴趣的同学可以去深入了解,但是这里有一个特别要注意的,每个atomic类里面的实现大同小异的情况下,有些是特定版本解决特定问题而新建的比如aba问题我们一般要用AtomicStampedReference而不是直接用AtomicReference,所以在使用上,建议多看看别人踩过的坑。
参考文章:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/494321482
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12Y411b7vL/?vd_source=7d0e42b081e08cb3cefaea55cc1fa8b7