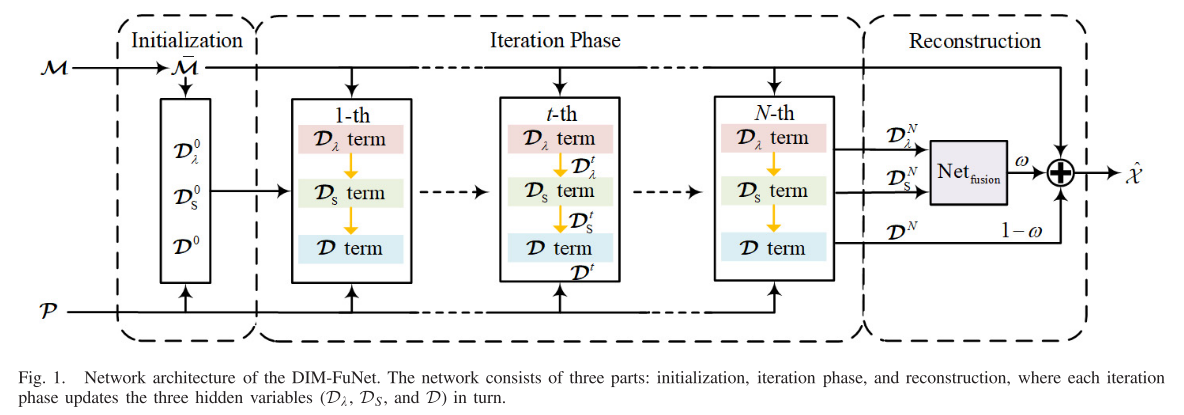
【 day3课前复习 】:
【AtomicInteger】:
原子性——都是用CAS机制来实现。
【 expected , update 】:
//有时候也会写三个值——你要修改的那个对象。
expected——期望值。(旧值)
update——更新值。(新值)
【 LongAdder 】:
//很多线程对一个数进行递增这件事,在实际工作中经常的会碰到。——《秒杀案例》
【三种方式效率比较】:
static long count2 = 0L;
static AtomicLong count1 = new AtomicLong(0L);
static LongAdder count3 = new LongAdder();
【比较代码】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no131;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
public class T02_AtomicVsSyncVsLongAdder {
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = 50;
private static final int LOOPS_COUNT = 100_0000;
static long count2 = 0L;
static AtomicLong count1 = new AtomicLong(0L);
static LongAdder count3 = new LongAdder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new Thread(() -> {
for (int k = 0; k < LOOPS_COUNT; k++) count1.incrementAndGet();
});
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Thread t : threads) t.start();
for (Thread t : threads) t.join();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println("Atomic: " + count1.get() + " time " + (end - start));
//-----------------------------------------------------------
Object lock = new Object();
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int k = 0; k < LOOPS_COUNT; k++)
synchronized (lock) {
count2++;
}
}
});
}
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Thread t : threads) t.start();
for (Thread t : threads) t.join();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Sync: " + count2 + " time " + (end - start));
//----------------------------------
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] =
new Thread(() -> {
for (int k = 0; k < LOOPS_COUNT; k++) count3.increment();
});
}
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Thread t : threads) t.start();
for (Thread t : threads) t.join();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println("LongAdder: " + count1.longValue() + " time " + (end - start));
}
static void microSleep(int m) {
try {
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(m);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
【最终输出】:
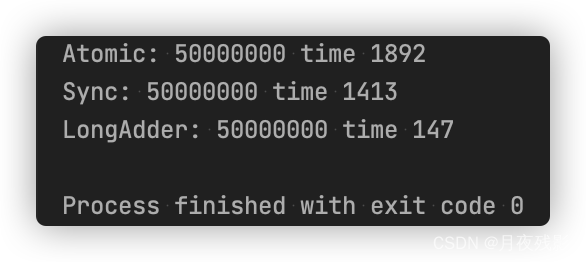
【LongAdder为何效率高呢?】:
其内部做了类似于分段锁的概念。
//在内部的时候会把这个值放到数组里。
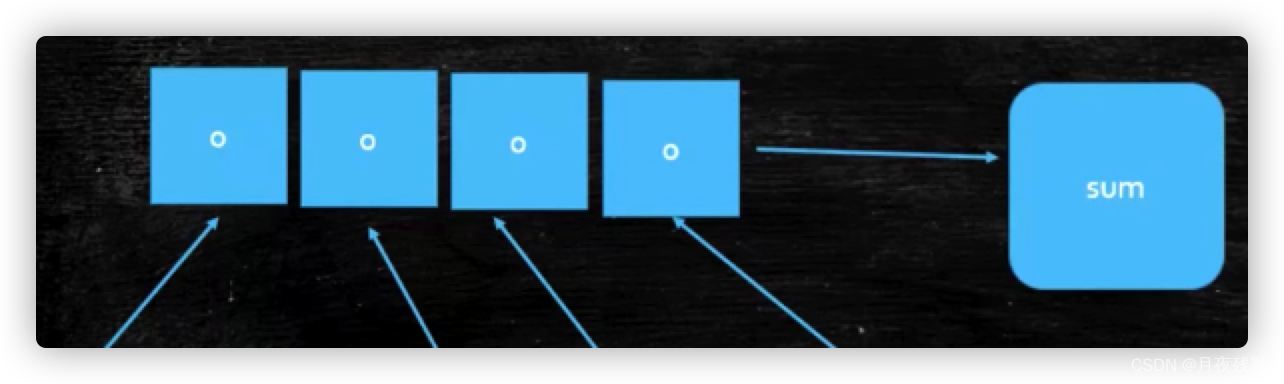
每250个线程锁在一个区域里 ,最后进行一个大汇总。线程数特别多的情况下LongAdder是有优势的。
【 间歇性复习 】:
【atomicXXX】:
CAS
【increment】:
- sync
- atomicXXX
- LongAdder
【 ReentrantLock 】:
//基于CAS操作的锁;
[ synchronized ]:
synchronized必须是可重入的,否则子类调用父类是无法实现的。
【test0】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no133;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class T00_ReentrantLock1 {
synchronized void m1() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
synchronized void m2() {
System.out.println("m2 ...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
T00_ReentrantLock1 rl = new T00_ReentrantLock1();
new Thread(rl::m1).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(rl::m2).start();
}
}
【最终输出】:

【test1】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no133;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class T01_ReentrantLock1 {
synchronized void m1() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(i);
if (i == 2) m2();
}
}
synchronized void m2() {
System.out.println("m2 ...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
T01_ReentrantLock1 rl = new T01_ReentrantLock1();
new Thread(rl::m1).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
【最终输出】:
【总结】:
上面的实验说明了sync锁是可重入的,sync是可以调sync方法的。
【替代sync】:
ReentrantLock是可以替代synchronized的。

synchronized是自动解锁的,只要sync后面的大括号执行完了这个锁就自动结束了。但是Lock必须得手动解锁。解锁语句一定要写在finally里面一定要保证最后解锁。
【 ReentrantLock的优点 】:
ReentrantLock有一些功能还是要比Synchronized要强大的。
使用synchronized如果锁不定,就会进入阻塞/等待状态,但是如果使用ReentrantLock我们自己就可以决定是否要去 wait 。
【实验测试】:
【没拿到】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no133;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class T03_ReentrantLock3_没拿到 {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
void m1() {
try {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(i);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 使用tryLock进行尝试锁定,不管锁定与否,方法都将继续执行;
* 可以根据tryLock的返回值来判定是否锁定;
* 也可以指定tryLock的时间 ,由于tryLock(time)抛出异常,所以要注意unclock�Ĵ�������ŵ�finally��
*/
void m2() {
/*
boolean locked = lock.tryLock();
System.out.println("m2 ..." + locked);
if(locked) lock.unlock();
*/
boolean locked = false;
try {
locked = lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("m2 ..." + locked);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (locked) lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
T03_ReentrantLock3_没拿到 rl = new T03_ReentrantLock3_没拿到();
new Thread(rl::m1).start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(rl::m2).start();
}
}
【拿到了】:
//只修改一处即可
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println(i);
}
【lockInterruptibly】:
/**
* 使用ReentrantLock还可以调用lockInterruptibly方法,可以对线程interrupt方法
* 在一个线程等待锁的过程中,可以被打断。
*/
package Ten_Class.t03.no133;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class T04_ReentrantLock4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
System.out.println("t1 start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println("t1 end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("interrupted!");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
//lock.lock(); //放开这个,注掉下面的,这样t2线程就无法被打断了。
lock.lockInterruptibly();
//可以对interrupt()方法做出响应。————我在lock的时候可以响应被别人打断( 你打断我,我是可以做出响应的 )。
//synchronized一旦 wait 了之后 , 你一定得让别人notify~~~ , 你才能够醒来 。
System.out.println("t2 start");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
System.out.println("t2 end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("interrupted!");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
t2.start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t2.interrupt(); //打断线程2的等待。
}
}
【公平锁的关键】:
//一个新线程过来抢锁,会不会先检查队列里的内容是公平锁的关键。
【代码中的公平锁】:
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //参数为true表示为公平锁,ReentrantLock默认其实是非公平锁。
//公平锁的意思就是谁等在前面就先让谁执行,而不是说谁后来了马上就执行。
package Ten_Class.t03.no133;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class T05_ReentrantLock5 extends Thread {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //参数为true表示为公平锁,
//公平锁的意思就是谁等在前面就先让谁执行,而不是说谁后来了马上就执行。
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得锁");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
T05_ReentrantLock5 rl = new T05_ReentrantLock5();
Thread th1 = new Thread(rl);
Thread th2 = new Thread(rl);
th1.start();
th2.start();
}
}
【 ReentrantLock VS synchronized 】:
- : RL是可以代替synchronized的;
2) :
cas VS sync
tryLock
lockinterupptibly
公平和非公平的切换
【 CountDownLatch 】:
//倒数的门栓,倒数的数字到了,54321,门栓就开了。
package Ten_Class.t03.no134;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class T06_TestCountDownLatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
usingJoin();
usingCountDownLatch();
}
private static void usingCountDownLatch() {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threads.length); //门栓上面记着数字————100。
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
int result = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) result += j;
latch.countDown(); //门栓上记录的数字减一。减到0的时候下面的栓才会往前走。
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i].start();
}
try {
latch.await(); //门栓在这里给我拴住门。————等待线程的结束。
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end latch");
}
private static void usingJoin() {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
int result = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) result += j;
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
try {
threads[i].join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("end join");
}
// @Test
public void testCountDown() {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
System.out.println(latch.getCount());
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(latch.getCount());
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(latch.getCount());
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(latch.getCount());
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(latch.getCount());
}
}
【 CyclicBarrier 】:
//循环栅栏 , 满了之后就推倒;
【构造器】:
【一参】:
数字——达到的数量。
【二参】:
new Runnable(){ }
【示例程序(只有一参) 】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no135;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
public class T07_FirstTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
barrier.await(); //这里等够20个线程了,就会开始发车。
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
【示例程序(两个参数)】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no135;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
public class T07_TestCyclicBarrier {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20, () -> System.out.println("满人"));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
barrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
【Phaser 】:
//用于遗传算法。
package Ten_Class.t03.no136;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Phaser;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class T09_TestPhaser2 {
static Random r = new Random();
static MarriagePhaser phaser = new MarriagePhaser();
static void milliSleep(int milli) {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(milli);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
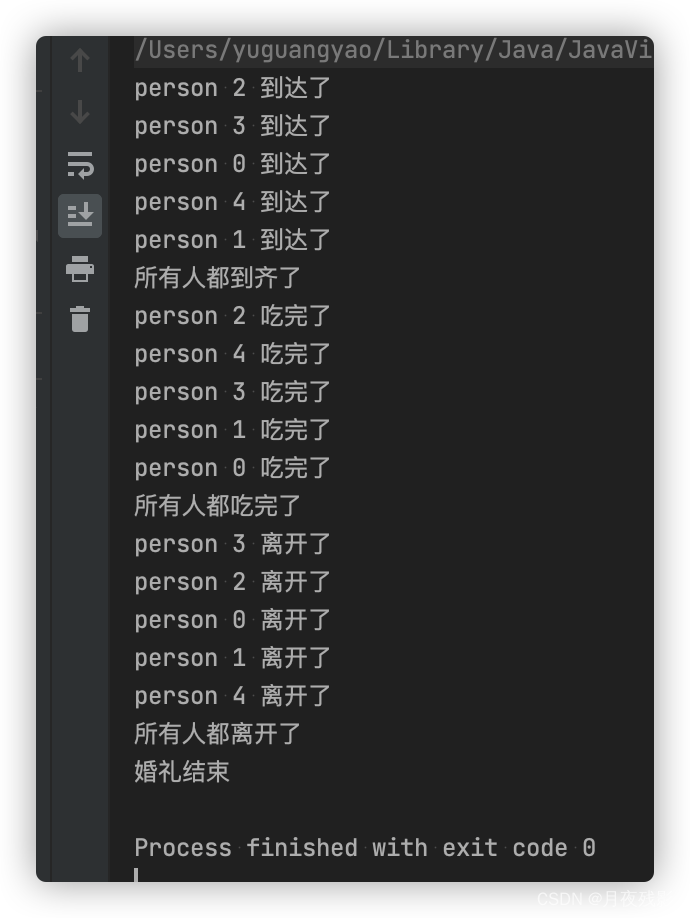
public static void main(String[] args) {
phaser.bulkRegister(7);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new Person("p" + i)).start();
}
new Thread(new Person("新郎")).start();
new Thread(new Person("新娘")).start();
}
static class MarriagePhaser extends Phaser {
@Override
protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {
switch (phase) {
case 0:
System.out.println("所有人都到齐了!" + registeredParties);
System.out.println();
return false;
case 1:
System.out.println("所有人都吃完了!" + registeredParties);
System.out.println();
return false;
case 2:
System.out.println("所有人都离开了!" + registeredParties);
System.out.println();
return false;
case 3:
System.out.println("婚礼结束!新郎新娘抱抱!" + registeredParties);
return true;
default:
return true;
}
}
}
static class Person implements Runnable {
String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void arrive() {
milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000));
System.out.printf("%s 到达现场!\n", name);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
}
public void eat() {
milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000));
System.out.printf("%s 吃完!\n", name);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
}
public void leave() {
milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000));
System.out.printf("%s 离开!\n", name);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
}
private void hug() {
if (name.equals("新郎") || name.equals("新娘")) {
milliSleep(r.nextInt(1000));
System.out.printf("%s 洞房!\n", name);
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
} else {
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();
//phaser.register()
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
arrive();
eat();
leave();
hug();
}
}
}
【 ReadWriteLock 】:
- 共享锁
- 排它锁
【 Semaphore 】:
//信号灯——信号灯亮的时候能够执行,不亮的话不能执行。

//构造器里写的是1 , 所以只能允许一个线程同时运行,acquire方法调用一次,最大允许数量就会减少一个。
【总结】:
我最多允许多少个线程同时运行 —— 限流。
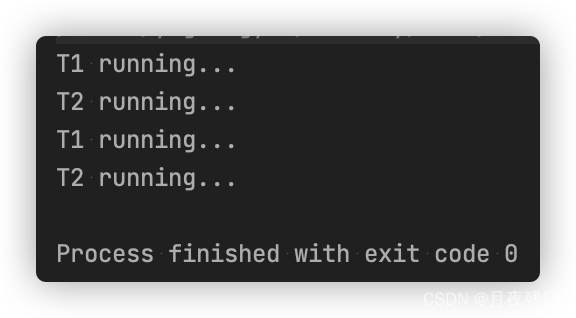
【程序测试】:
package Ten_Class.t03.no138;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class T11_TestSemaphore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Semaphore s = new Semaphore(2);
Semaphore s = new Semaphore(2, true); //默认非公平 , 传true代表公平 。
//允许一个线程同时执行
// Semaphore s = new Semaphore(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
s.acquire(); //阻塞方法。
System.out.println("T1 running...");
Thread.sleep(200);
System.out.println("T1 running...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
s.release();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
s.acquire();
System.out.println("T2 running...");
Thread.sleep(200);
System.out.println("T2 running...");
s.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}