set和map
- 前言
- 一、使用
- 1. set
- (1)、模板参数列表
- (2)、常见构造
- (3)、find和count
- (4)、insert和erase
- (5)、iterator
- (6)、lower_bound和upper_bound
- 2. multiset
- 3. map
- (1)、模板参数列表
- (2)、构造
- (3)、modifiers和operations
- (4)、operator[]
- 4. multimap
- 二、封装
- RBTree
- 迭代器原理
- RBTree实现代码
- map
- set
- 三、总结
前言
本文介绍的是树型关联式容器。
关联式容器:用来存储数据,存储的是<key, value>结构的键值对,在检索时效率更高。主要有这四种:map,set,multimap,multiset。
键值对:用来标识具有一一对应关系的结构,该结构一般包含两个成员变量key和value,key表示键值,value表示与key对应的信息。
SGI—STL中关于键值对的定义:
//pair底层
template<class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{
typedef T1 first_type;
typedef T2 second_type;
T1 first;
T2 second;
pair()
:first(T1())
, second(T2())
{}
pair(const T1& a, const T2& b)
:first(a)
, second(b)
{}
};
一、使用
1. set
(1)、模板参数列表
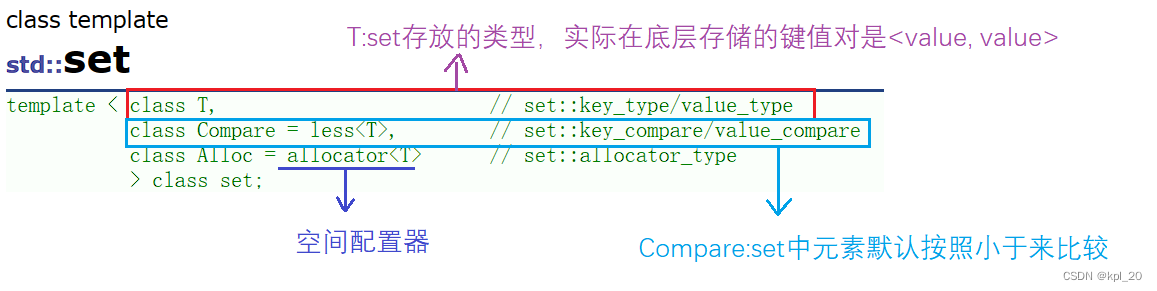
(2)、常见构造
void test_constructor()
{
set<int> s1; //无参构造
int arr[] = { 10,20,30,40,50 };
set<int> s2(arr, arr + 5); //数组范围构造
set<int> s3(s2.begin(), s2.end()); //迭代器区间构造
set<int> s4(s3); //拷贝构造
}
(3)、find和count
void test_find()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(5);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(8);
s.insert(2);
//find return value: iterator(val is found)
//otherwise set::end
if (s.find(5) != s.end())
{
cout << "find:找到了" << endl;
}
//count return value:1 (val is found),or 0 otherwise
if (s.count(5))
{
cout << "count:找到了" << endl;
}
}
(4)、insert和erase
void test_modify()
{
//insert
//去重+排序
set<int> s;
s.insert(10);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(6);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(2);
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " "; //2 5 6 7 10
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器
set<int>::iterator sit;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret; //接收插入返回值
//pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type & val); insert参数列表
ret = s.insert(1);
if (ret.second == true)
sit = ret.first;
cout << *sit << endl; //1
ret = s.insert(1);
if (ret.second == false)
sit = ret.first;
cout << *sit << endl; //1
//iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type & val); insert参数列表
sit = s.insert(sit, 20);
cout << *sit << endl; //20
// template <class InputIterator>
//void insert(InputIterator first, InputIterator last); insert参数列表
int arr[] = { 0,10,15 }; // 10 already in set, not inserted
s.insert(arr, arr + 3);
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " "; //0 1 2 5 6 7 10 15 20
}
cout << endl;
///
//erase
//void erase(iterator position); erase参数列表
s.erase(sit); //*sit = 20
//size_type erase(const value_type & val); erase参数列表
int e_ret = s.erase(0);
cout << e_ret << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " "; //1 2 5 6 7 10 15
}
cout << endl;
//void erase(iterator first, iterator last); erase参数列表
s.erase(s.begin(), s.end());
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " "; //empty
}
cout << endl;
}
(5)、iterator
void test_iteator()
{
int arr[] = { 10,20,30,40,50 };
set<int> s(arr, arr + 5);
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
set<int>::const_iterator cit = s.cbegin();
set<int>::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
set<int>::const_reverse_iterator crit = s.crbegin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " "; //10 20 30 40 50
it++;
}
cout << endl;
while (cit != s.cend())
{
cout << *cit << " "; //10 20 30 40 50
cit++;
}
cout << endl;
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " "; //50 40 30 20 10
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
while (crit != s.crend())
{
cout << *crit << " "; //50 40 30 20 10
crit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
(6)、lower_bound和upper_bound
//iterator lower_bound(const value_type & val) const; lower_bound的声明
//iterator upper_bound(const value_type & val) const; upper_bound的声明
//pair<iterator, iterator> equal_range(const value_type& val) const; equal_range的声明
void test_bound()
{
set<int> s;
set<int>::iterator itlow, itup;
for (size_t i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
s.insert(i * 10); //10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
}
//左闭右开[30,70)
itlow = s.lower_bound(30);
itup = s.upper_bound(60);
cout << *itlow << endl; //30
cout << *itup << endl; //70
set<int>::iterator it = s.lower_bound(35);
// s > 35
cout << *it << endl; //40
//*it = 50; //不能修改,保护键值
s.erase(itlow, itup);
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " "; //10 20 70 80 90
}
cout << endl;
//
//equal_range - most_use multiset
//pair<set<int>::const_iterator, set<int>::const_iterator>
auto ret1 = s.equal_range(15);
itlow = ret1.first;
itup = ret1.second;
//因为不存在15,所以itlow和itup是一段不存在的区间
cout << *itlow << endl; //20
cout << *itup << endl; //20 左开右闭
auto ret2 = s.equal_range(80);
itlow = ret2.first;
itup = ret2.second;
//[80,90)
cout << *itlow << endl; //80
cout << *itup << endl; //90
auto ret = s.equal_range(90);
itlow = ret.first;
itup = ret.second;
//程序直接崩溃,到最后了
cout << *itlow << endl; //90
cout << *itup << endl; //end()
}
2. multiset
这里的演示就不和set一样分开表示了,主要是multiset不去重
void test_multiset()
{
//排序
int arr[] = { 7, 7, 7, 3, 6, 5, 2, 3, 3, 3 };
multiset<int> s(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
//不去重
for (auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
multiset<int>::iterator pos = s.find(3); //返回中序遍历的第一个3
while (pos != s.end()) //find失败返回end()
{
//*pos = 10; //err 不能修改,保护键值
cout << *pos << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
cout << s.count(3) << endl; //4个3
pair<multiset<int>::iterator, multiset<int>::iterator> ret = s.equal_range(7);
multiset<int>::iterator itlow = ret.first;
multiset<int>::iterator itup = ret.second;
// [itlow, itup)
// [7,end()) s.equal_range(7);
//cout << *itlow << endl;
//cout << *itup << endl; //error *itup没有值
// [itlow, itup)
// [5,5) s.equal_range(4);
ret = s.equal_range(4);
itlow = ret.first;
itup = ret.second;
cout << *itlow << endl;
cout << *itup << endl; //ok
s.erase(itlow, itup); //没有进行删除 [5, 5)
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
3. map
(1)、模板参数列表
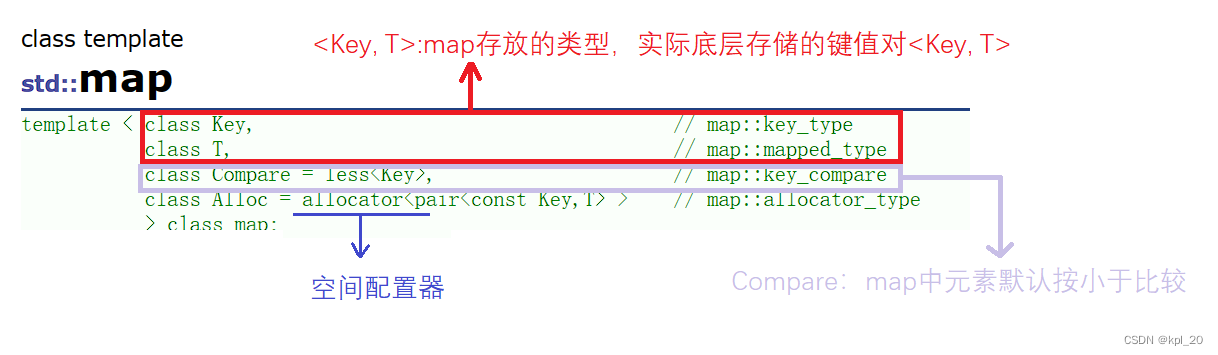
(2)、构造
void test_constructor()
{
map<string, string> dict;
//"insert"和"插入"都分别有隐式类型转换,const char* 转成const string&
//不能直接进行隐式类型转换,原因:多参数
pair<string, string> kv1("insert", "插入");
dict.insert(kv1);
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("sort", "排序")); //匿名对象
//常用
// C++98
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
// C++11 多参数的构造函数隐式类型转换
dict.insert({ "string", "字符串" }); //{}会自动调用pair的构造
// 隐式类型的转换 构造+拷贝构造(优化)
string str1 = "hello";
pair<string, string> kv2 = { "string", "字符串" };
//const pair<string, string>& kv2 = { "string", "字符串" }; 引用一个临时变量
}
(3)、modifiers和operations
void test_modifiers()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
dict.insert(make_pair("success", "成功"));
//key已经有了就不会插入 //pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val); 插入的参数列表
pair<map<string, string>::iterator, bool> ret = dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "xxx"));
if (ret.second == false) {
cout << "element already existed:";
cout << ret.first->first << ":" << ret.first->second << endl;
}
//iterator insert (iterator position, const value_type& val); 插入的参数列表
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
it = dict.insert(it, make_pair("begin", "开始")); // max efficiency inserting
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
/*template <class InputIterator>
void insert(InputIterator first, InputIterator last);*/ //插入的参数列表
map<string, string> copymap;
//iterator find (const key_type& k); //查找的参数列表,返回值是查找这个位置的迭代器,如果没查找到,返回end()
copymap.insert(dict.begin(), dict.find("success"));
it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
//it->first = "xxx"; //error
//it->second = "sss"; //ok
//cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
int number = dict.erase("sucess");
cout << number << endl;
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
}
(4)、operator[]
注意key不存在,operator[]是插入,at是抛异常
void test_operator()
{
string arr[] = { "西瓜", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& e : arr)
{
auto it = countMap.find(e);
if (it == countMap.end())
{
countMap.insert(make_pair(e, 1)); //首次插入
}
else
{
it->second++; //统计次数
}
}
//pair<map<char, int>::iterator, bool>::iterator it = this->insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type()))
//(*(it.first)).second
for (const auto& e : arr)
{
//查找e是否存在,如果不存在进行插入,如果存在,返回value
countMap[e]++;
}
for (const auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
4. multimap
multimap和map的唯一不同,前者的key可以重复
二、封装
set和map的封装的底层结构使用的都是红黑树(这篇博客介绍了红黑树的旋转),在STL中set底层实际存储的数据是键值对< value, value >,这样就可以调用同个红黑树。
RBTree
迭代器原理
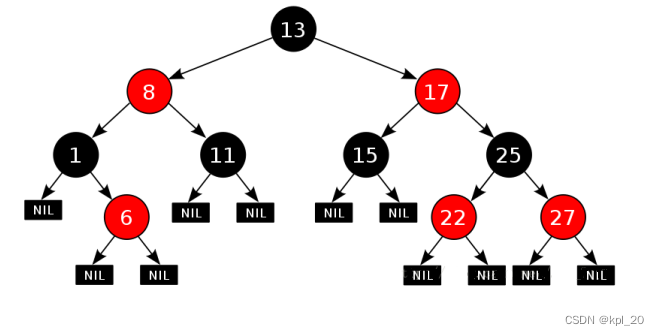
双向迭代器 -> 根据红黑树的特征:
- 迭代器++,只需要判断当前位置的右侧节点的情况
- 迭代器- -,只需要判断当前位置的左侧节点的情况
- 迭代器++
- 右孩子不为空,访问右子树的最左节点(最小节点)。
- 右孩子为空,下一个访问的是孩子是父亲左的祖先节点。
代码实现:
Self& operator++()
{
//右不为空
if (_node->_right)
{
//右子树的最左节点(右子树最小节点)
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
else //右为空
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//父节点为空,或者当前节点不是父节点的左孩子,循环继续
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
//parent为空的情况和找到下一个节点的情况
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
- 迭代器–
- 左孩子不为空,访问左子树的最右节点(最大节点)。
- 左孩子为空,下一个访问的是孩子是父亲右的祖先节点。
Self& operator--()
{
//左孩子不为空
if (_node->_left)
{
Node* subRight = _node->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_node = subRight;
}
else //左孩子为空
{
//孩子是父亲右的那个节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
//parent为空的情况和找到下一个节点的情况
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
RBTree实现代码
//节点的颜色
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
//这里一个模板参数T就可以,这个T既是set的key,也是map的value
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data;
Color _color;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _color(RED)
{}
};
//迭代器
template<class T, class Ptr, class Ref>
struct __TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ptr, Ref> Self;
//无论被实例化成什么,都是普通迭代器
typedef __TreeIterator<T, T*, T&> Iterator;
//这个类被实列化成const迭代器时,这个函数是一个构造,支持普通迭代器构造const迭代器
//这个类被实列化成普通迭代器时,这个函数是一个拷贝构造
__TreeIterator(const Iterator& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}
Node* _node;
//节点初始化
__TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left)
{
Node* subRight = _node->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_node = subRight;
}
else
{
//孩子是父亲右的那个节点
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
//parent为空的情况和找到下一个节点的情况
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator++()
{
//右不为空
if (_node->_right)
{
//右子树的最左节点(右子树最小节点)
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
else //右为空
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
//parent为空的情况和找到下一个节点的情况
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
};
//set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
//map->RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
//KeyOfT是上层传下来的仿函数
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef __TreeIterator<T, T*, T&> iterator;
typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T*, const T&> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* leftMin = _root;
while (leftMin && leftMin->_left)
{
leftMin = leftMin->_left;
}
return iterator(leftMin);
}
iterator end()
{
//区分,这里和STL源码中的结束方式不同,
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
Node* leftMin = _root;
while (leftMin && leftMin->_left)
{
leftMin = leftMin->_left;
}
return iterator(leftMin);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
//传K的作用
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
//没找到,返回nullptr
return nullptr;
}
//注意insert的返回值是一个键值对
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_color = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
//寻找要链接新节点的位置
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
//插入节点 + 链接
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_color = RED;
//保存节点,用于返回
Node* newnode = cur;
if (kot(parent->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//调整 这里parent是否为空,是为了下一次循环判断
// 如果parent->_color == BLACK也不用玩了
while (parent && parent->_color == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//u为红
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED)
{
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
//继续向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //u不存在 或 存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p
//c
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
//调整完之后,就不需要继续改变了
break;
}
}
else //grandfather->_right == parent
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//u为红
if (uncle && uncle->_color == RED)
{
parent->_color = uncle->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
//继续向上调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else //u不存在 或 存在且为黑
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
//g
// p
// c
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
else
{
//g
// p
//c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_color = BLACK;
grandfather->_color = RED;
}
//调整完之后,就不需要继续改变了
break;
}
}
}
//根节点的颜色改成黑色
_root->_color = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
//判断该树是不是红黑树
bool IsBalance()
{
return _IsBalance(_root);
}
//计算红黑树的高度
int Height()
{
return Height(_root);
}
private:
int Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
bool CheckColor(Node* root, int blacknum, int benchmark)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (blacknum != benchmark)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//计算每条路径的黑色节点
if (root->_color == BLACK)
{
++blacknum;
}
if (root->_color == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_color == RED)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "出现连续红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return CheckColor(root->_left, blacknum, benchmark)
&& CheckColor(root->_right, blacknum, benchmark);
}
bool _IsBalance(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (root->_color != BLACK)
{
return false;
}
//基准值 --> 用于比较别的路径黑色节点个数
int benchmark = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_color == BLACK)
benchmark++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return CheckColor(root, 0, benchmark);
}
//旋转
//都是二叉树的旋转,所以和AVLTree的旋转一样,只不过这里没有平衡因子
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_left;
Node* curright = cur->_right;
parent->_left = curright;
if (curright)
curright->_parent = parent;
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
cur->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* cur = parent->_right;
Node* curleft = cur->_left;
//重新链接
parent->_right = curleft;
if (curleft)
curleft->_parent = parent;
cur->_left = parent;
//提前保存parent->_parent,可能是根节点,也可能是子树的根节点
Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
if (ppnode == nullptr)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppnode->_left == parent)
{
ppnode->_left = cur;
}
else
{
ppnode->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = ppnode;
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
map
namespace kpl
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
//RBTree仿函数的主要作用在这里,set的封装只是跟跑
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
set
namespace kpl
{
template<class K>
class set
{
//仿函数
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
//set只保留一个const即可
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
//这里返回值的first的迭代器是普通迭代器,用普通迭代器接收
pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(key);
//使用普通迭代器构造一个const的迭代器,这里就体现出迭代器实现中的那个拷贝构造
return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
三、总结
set
- 插入的元素只需要value,不用键值对
- set中的元素不能重复(set可以去重)
- 单个元素的访问速度比unordered_set慢
- 中序遍历有序,使用其迭代器访问也是有序
- 不允许修改,破坏结构
map
- map中的元素是键值对
- map中的key是唯一的,不能修改,但是value可以修改
- 中序遍历有序,使用其迭代器访问也是有序
- 支持operator[]
- 单个元素的访问速度比unordered_set慢
multiset和multimap(区分set和map)
multiset的value可以重复,multimap的key也可以重复