Leetcode刷题之用队列实现栈(C语言版)
- 一、题目描述
- 二、题目要求
- 三、题目示例
- 四、题目解析
- Ⅰ、MyStack* myStackCreate
- Ⅱ、void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
- Ⅲ、int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
- Ⅳ、int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
- Ⅴ、bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
- Ⅵ、void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
- 五、完整代码
225、用队列实现栈
一、题目描述
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
①、void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
②、nt pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
③、int top() 返回栈顶元素。
④、boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二、题目要求
Ⅰ、你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
Ⅱ、你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
三、题目示例
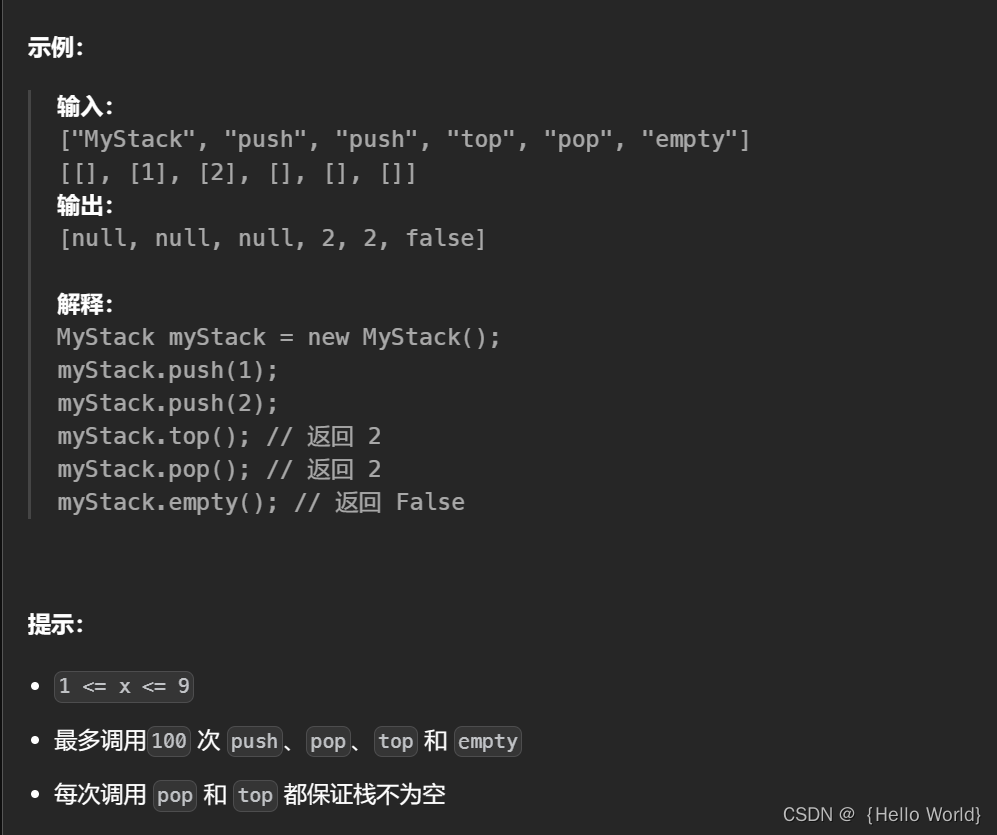
四、题目解析
首先我们看到本题是用队列实现栈。那么我们便要对栈和队列的相关特性有一定的了解,例如栈是先进后出的,而队列是先进先出的。如果有伙伴对这两种数据结构有些遗忘的话,建议看一下博主之前的两篇文章,分别是《数据结构——栈的详细介绍》和《数据结构——看完这篇保证你学会队列》。
我们想要解决这道题,首先便要实现一个完整的队列,其中的接口包括初始化队列,销毁队列,入队,出队等,其代码如下:

//定义数据类型
typedef int QueueDataType;
//定义队列结构
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QueueDataType Data;
}Qnode;
//定义头、尾指针
typedef struct Queue
{
Qnode* phead;
Qnode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化
void InitQueue(Queue* pq);
//销毁
void DestoryQueue(Queue* pq);
//入队
void PushQueue(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x);
//出队
void PopQueue(Queue* pq);
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//获取SIze
int SizeQueue(Queue* pq);
//获取队头元素
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队尾元素
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
void InitQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void DestoryQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
Qnode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
Qnode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入队
void PushQueue(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
Qnode* newnode = (Qnode*)malloc(sizeof(Qnode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
//赋值
newnode->Data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//分情况讨论
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出队
void PopQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//一个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
//多个节点
else
{
//头删
Qnode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
//获取SIze
int SizeQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//获取队头元素
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->Data;
}
//获取队尾元素
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->Data;
}
构建好队列的各种接口之后,我们需要在Mystack的结构体中创建两个队列变量。代码如下:
typedef struct
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
Ⅰ、MyStack* myStackCreate
该接口,需要我们在内存中开辟空间,利用malloc函数,并且将q1和q2进行初始化。
MyStack* myStackCreate()
{
MyStack*obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
InitQueue(&obj->q1);
InitQueue(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
Ⅱ、void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
如果两个队列都为空,那么任选一个进行入队操作即可,后续入队往有数据的队列进行入队操作即可。
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
PushQueue(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
PushQueue(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
Ⅲ、int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
最为复杂的便是出栈了,我们的大体思路便是假定q1为空,q2不为空:如果结果相反,则调换一下二者的顺序,我们将不为空的队列进行出队操作,并将其数据压入为空的队列,直到为空的队列中只剩下一个数据,我们将这个数据定义为top,并对其进行出队操作,最后将其进行返回。
Queue*EmptyQ=&obj->q1;
Queue*NonEmptyq=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
EmptyQ=&obj->q2;
NonEmptyq=&obj->q1;
}
while(SizeQueue(NonEmptyq)>1)
{
PushQueue(EmptyQ,QueueFront(NonEmptyq));
PopQueue(NonEmptyq);
}
int top=QueueFront(NonEmptyq);
PopQueue(NonEmptyq);
return top;
Ⅳ、int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
解决这个接口,我们首先需要找到不为空的那个队列,然后调用其获取队尾数据的函数,最后将这个函数返回的结果返回即可。
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
Ⅴ、bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
我们需要保证我们的两个队列都为空,这样才能够保证我们创建的队列为空。
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
Ⅵ、void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
需要先对我们所创建的q1和q2队列进行销毁,然后再对ob进行free操作,以防止内存的泄漏。
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
DestoryQueue(&obj->q1);
DestoryQueue(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
五、完整代码
//定义数据类型
typedef int QueueDataType;
//定义队列结构
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QueueDataType Data;
}Qnode;
//定义头、尾指针
typedef struct Queue
{
Qnode* phead;
Qnode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化
void InitQueue(Queue* pq);
//销毁
void DestoryQueue(Queue* pq);
//入队
void PushQueue(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x);
//出队
void PopQueue(Queue* pq);
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//获取SIze
int SizeQueue(Queue* pq);
//获取队头元素
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队尾元素
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
void InitQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//销毁
void DestoryQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
Qnode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
Qnode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入队
void PushQueue(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
Qnode* newnode = (Qnode*)malloc(sizeof(Qnode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
//赋值
newnode->Data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//分情况讨论
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出队
void PopQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
//一个节点
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
//多个节点
else
{
//头删
Qnode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size == 0;
}
//获取SIze
int SizeQueue(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//获取队头元素
QueueDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->Data;
}
//获取队尾元素
QueueDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->Data;
}
typedef struct
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate()
{
MyStack*obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
if(obj==NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
InitQueue(&obj->q1);
InitQueue(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
PushQueue(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
PushQueue(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{
Queue*EmptyQ=&obj->q1;
Queue*NonEmptyq=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
EmptyQ=&obj->q2;
NonEmptyq=&obj->q1;
}
while(SizeQueue(NonEmptyq)>1)
{
PushQueue(EmptyQ,QueueFront(NonEmptyq));
PopQueue(NonEmptyq);
}
int top=QueueFront(NonEmptyq);
PopQueue(NonEmptyq);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
DestoryQueue(&obj->q1);
DestoryQueue(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();
* myStackPush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);
* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);
* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);
* myStackFree(obj);
*/