1 类和实例
GObject实例用函数g_object_new创建。GObject不仅仅有实例,也有类。
- 一个GObject类在第一次访问g_object_new时候创建,只有有一个GObject类存在。
- GObject实例在任何时候访问g_object_new都会被创建,所以就会创建更多GObject实例。
从广义上讲,GObject意味着对象,这个对象包括它的类和实例。在狭义上将,GObject是一个C结构体的定义。
typedef struct _GObject GObject;
struct _GObject{
GTypeInstance g_type_instance;
/*< private >*/
guint ref_count; /* (atomic) */
GData *qdata;
};
struct _GObjectClass
{
GTypeClass g_type_class;
/*< private >*/
GSList *construct_properties;
/*< public >*/
/* seldom overridden */
GObject* (*constructor) (GType type,
guint n_construct_properties,
GObjectConstructParam *construct_properties);
/* overridable methods */
void (*set_property) (GObject *object,
guint property_id,
const GValue *value,
GParamSpec *pspec);
void (*get_property) (GObject *object,
guint property_id,
GValue *value,
GParamSpec *pspec);
void (*dispose) (GObject *object);
void (*finalize) (GObject *object);
/* seldom overridden */
void (*dispatch_properties_changed) (GObject *object,
guint n_pspecs,
GParamSpec **pspecs);
/* signals */
void (*notify) (GObject *object,
GParamSpec *pspec);
/* called when done constructing */
void (*constructed) (GObject *object);
/*< private >*/
gsize flags;
gsize n_construct_properties;
gpointer pspecs;
gsize n_pspecs;
/* padding */
gpointer pdummy[3];
};
这个GObject程序是在GLib源文件里面,可以从GNOME下载GLib源文件。
有个示例程序在src/misc目录里面,一个示例程序是example1.c,它的代码如下:
1 #include <glib-object.h>
2
3 int
4 main (int argc, char **argv) {
5 GObject *instance1, *instance2;
6 GObjectClass *class1, *class2;
7
8 instance1 = g_object_new (G_TYPE_OBJECT, NULL);
9 instance2 = g_object_new (G_TYPE_OBJECT, NULL);
10 g_print ("The address of instance1 is %p\n", instance1);
11 g_print ("The address of instance2 is %p\n", instance2);
12
13 class1 = G_OBJECT_GET_CLASS (instance1);
14 class2 = G_OBJECT_GET_CLASS (instance2);
15 g_print ("The address of the class of instance1 is %p\n", class1);
16 g_print ("The address of the class of instance2 is %p\n", class2);
17
18 g_object_unref (instance1);
19 g_object_unref (instance2);
20
21 return 0;
22 }
23
-
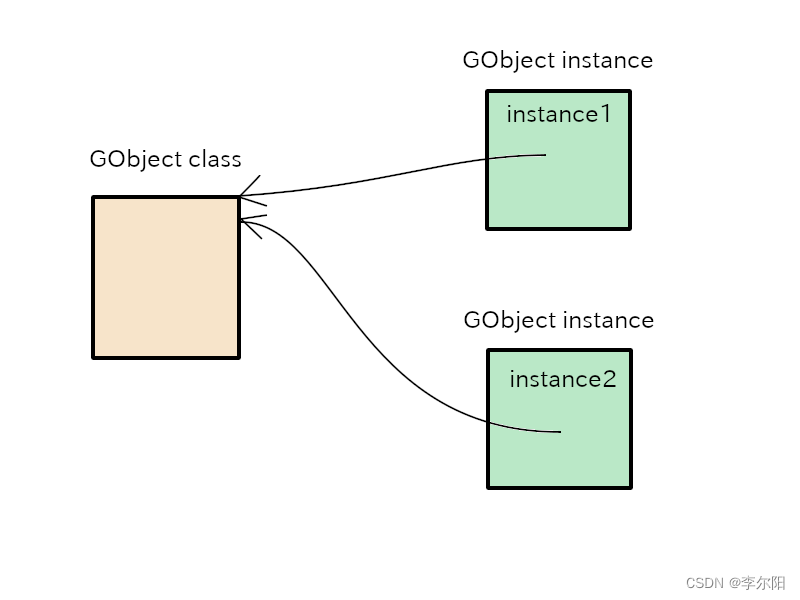
5-6:instance1和instance2是指向GObject实例的指针,class1和class2指向实例的一个类(同一个类)。
-
8-11:函数g_object_new创建一个GObject实例,GObject实例是一大块内存,这个内存里面有结构体(struct _GObject)。G_TYPE_OBJECT参数是一个GObject类型。这个类型是不同于C语言中的char或者int类型。Type系统是一GObject系统的基础。每个数据类型(比如GObject)都必须注册到类型系统。类型系统具有一系列用于注册的函数,这些函数的作用是为了注册。如果这些函数的某一个被访问,这时,这个类型系统会确定Gtype这个对象的类型值,然后返回它给函数访问者。在我的计算机上(主要依赖于计算机硬件,不同硬件可能long长度不一样),GType是一个无符号长整形(unsigned long)。g_object_new分配GObject-sized大小的内存,并返回指向内存顶部地址的指针。创建后,该程序显示实例的地址。
-
example代码运行结果:
The address of instance1 is 0x561ad5205a00
The address of instance2 is 0x561ad5205a20
The address of the class of instance1 is 0x561ad5205830
The address of the class of instance2 is 0x561ad5205830
两个实例instance1和instance2的位置是不同的,每个实例有它自己的内存。class1和class2的位置是相同的,两个实例共享同一个类。
2 引用计数(Reference Count)
GObject实例有自己的内存。它们是在创建时由系统分配的。如果它变得无用,就必须释放内存。然而,我们如何判断它是否无用呢? GObject系统提供引用计数去解决这个问题。实例由其他对象或主程序创建和使用。也就是说,实例被引用。如果实例被A和B引用,那么引用的编号为2。这个数字称为引用计数。让我们想象一个这样的场景:
- A调用g_object_new并拥有一个实例G。A引用G,因此G的引用计数为1。
- B也想使用G。B调用g_object_ref并将引用计数增加了1。现在引用计数是2。
- A不再使用G。A调用g_object_ref并将引用计数减少1。现在引用计数是1
- B不再使用G。B调用g_object_ref并将引用计数减少1。现在引用计数是0
- 因为引用计数为零,G知道没有人引用它。G开始自己完成这个过程。G消失,内存被释放。
程序example2.c是基于上述场景的:
1 #include <glib-object.h>
2
3 static void
4 show_ref_count (GObject *instance) {
5 if (G_IS_OBJECT (instance))
6 /* Users should not use ref_count member in their program. */
7 /* This is only for demonstration. */
8 g_print ("Reference count is %d.\n", instance->ref_count);
9 else
10 g_print ("Instance is not GObject.\n");
11 }
12
13 int
14 main (int argc, char **argv) {
15 GObject *instance;
16
17 instance = g_object_new (G_TYPE_OBJECT, NULL);
18 g_print ("Call g_object_new.\n");
19 show_ref_count (instance);
20 g_object_ref (instance);
21 g_print ("Call g_object_ref.\n");
22 show_ref_count (instance);
23 g_object_unref (instance);
24 g_print ("Call g_object_unref.\n");
25 show_ref_count (instance);
26 g_object_unref (instance);
27 g_print ("Call g_object_unref.\n");
28 show_ref_count (instance);
29
30 return 0;
31 }
32
代码执行结果如下:
Call g_object_new.
Reference count is 1.
Call g_object_ref.
Reference count is 2.
Call g_object_unref.
Reference count is 1.
Call g_object_unref.
Instance is not GObject.
- g_object_new创建一个新的GObject实例,并将其引用计数设置为1。
- g_object_ref将引用计数增加1。
- g_object_unref使引用计数减少1。如果引用计数降为零,实例将自行销毁。
3 初始化和销毁过程
GObject初始化和销毁的实际过程非常复杂。以下是不含细节的简单描述。
3.1 初始化
- 用类型系统注册GObject类型。这是在调用main函数之前在GLib初始化过程中完成的。(如果编译器是gcc,则使用__attribute__ (constructor) )来获得初始化函数。参考GCC手册)
- 为GObjectClass和GObject结构分配内存。
- 初始化GObjectClass结构内存。这个内存将是GObject的类。
- 初始化GObject结构内存。这个内存将是GObject的实例。
3.2 销毁
销毁GObject实例。实例的内存被释放。GObject类型是静态类型。静态类型从不破坏它的类。因此,即使被销毁的实例是最后一个实例,类仍然存在。
当您编写代码来定义GObject的子对象时,理解上面的过程很重要。后面的部分将解释详细的过程。
翻译自GObject tutorial