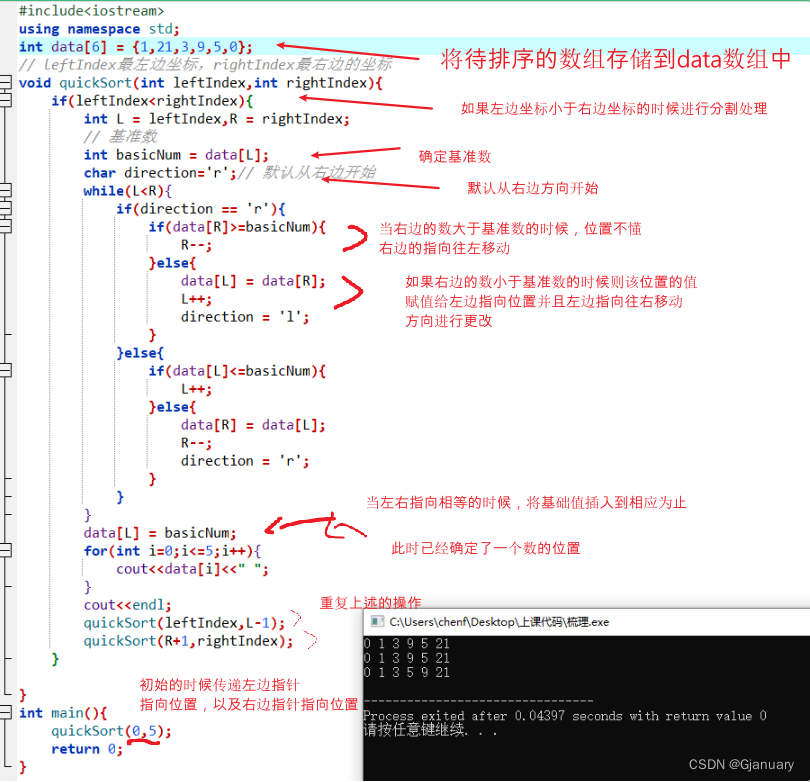
声明:所有代码都可以运行,可以直接粘贴运行(只有库函数没有声明)
线性表的定义和基本操作
基本操作
- 定义
静态:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MaxSize 10
//静态
typedef struct{
int data[MaxSize];
int length;
}SqList;
void InitList(SqList &L)//初始化
{
for(int i=0;i<MaxSize;i++){
L.data[i]=0;
}
L.length=0;
}
int main(void)
{
SqList L;
InitList(L);
for(int i=0;i<L.length;i++){
printf("the data %d is %d",i,L.data[i]);
}
return 0;
}
动态:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define InitSize 10
typedef struct{
int *data;
int MaxSize;//最大容量
int length;//当前长度
}SeqList;
void Init(SeqList &L)
{
L.data=(int *)malloc(InitSize*sizeof(int));
L.length=0;
L.MaxSize=InitSize;
}
int main(void){
return 0;
}
- 插入
静态:
//插入操作,bool用于判断操作是否成功 (处理异常情况)
bool ListInsert(SqList &L,int i,int e){
if(i<1 || i>L.length+1) return false;//条件判断
if(L.length >= MaxSize) return false;
for(int j=L.length;j>=i;i--){
L.data[j]=L.data[j-1];
}
L.data[i-1]=e;
L.length++;
}

动态:
- 删除
静态:
bool ListDelete(SqList &L,int i,int &e){
if(i<1||i>L.length) return false;
e=L.data[i-1];
for(int j=i;j<L.length;j++)
{
L.data[j-1]=L.data[j];
}
L.length--;
return true;
}
动态顺序表以及各个操作
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define InitSize 10
typedef struct{
int *data;
int MaxSize;
int length;
}SqList;
void debug(SqList L){
printf("当前顺序表的数据为length=%d maxsize=%d\n",L.length,L.MaxSize);
}
//初始化
void InitList(SqList &L){
L.data=(int *)malloc(InitSize*sizeof(int));
L.length=0;
L.MaxSize=InitSize;
}
//增加动态数组的长度
void IncreaseSize(SqList &L,int len){
int *p=L.data;
L.data=(int *)malloc((L.MaxSize+len)*sizeof(int));
for(int i=0;i<L.length;i++){
L.data[i]=p[i];//将数据复制到新区域
}
L.MaxSize=L.MaxSize+len;//顺序表最大长度增加len
free(p);//释放空间
}
//插入操作
bool ListInsert(SqList &L,int i,int e){
//范围判断
if(i<1 || i>L.length+1)
return false;
if(L.length>L.MaxSize)
return false;
for(int j=L.length;j>=i;j--)
{
L.data[j]=L.data[j-1];
}
L.data[i-1]=e;
L.length++;
return true;
}
删除操作,删除第i个数据并且返回被删除的数据
bool ListDelete(SqList &L,int i,int &e)
{
//范围判断
if(i<1 || i>L.length+1) return false;
else{
//保存删除元素
e=L.data[i];
for(int j=i;j<L.length;j++)
{
L.data[j]=L.data[j+1];
}
L.length--;
}
return true;
}
//按位查找
int getElemBybit(SqList L,int i){
//Check if the line has been crossed
if(i<1 || i>L.length){
printf("Cross the border!");
return 0;
}
return L.data[i-1];
}
//按值查找
int getElemByValue(SqList L,int value){
for(int i=0;i<L.length;i++)
{
if(L.data[i] == value)
{
return i-1;
}
}
printf("Can`t find the elem!");
return 0;
}
//打印操作
void print(SqList L){
for(int i=0;i<L.length;i++)
{
printf("%d ",L.data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//测试函数
int main(void){
SqList L;debug(L);
InitList(L);debug(L);
for(int i=0;i<L.MaxSize;i++)
{
L.data[i]=i;
L.length++;
}
IncreaseSize(L,5);debug(L);
print(L);
if(ListInsert(L,2,5)){
printf("插入成功,插入后数值");
print(L);
}else printf("插入失败");
int e=0;
if(ListDelete(L,3,e))
{
print(L);
printf("被删除元素为:%d",e);
}
int value,position;
printf("\nPlease input the value and the position:");
scanf("%d %d", &value, &position);
printf("\nget the emlem by value :the elem position is%d\n",getElemByValue(L,value));
printf("\nget the emlem by positon:the value is%d\n",getElemBybit(L,position));
return 0;
}
链表基本
链表结构:
单链表:
//定义单链表
typedef struct LNode {
int data; // 数据域
struct LNode* next; // 指针域
} LNode, * LinkList;
双链表:
//定义结构
typedef struct DNode{
int data;//数据域
struct DNode *prior,*next;//指针域
}DNode,*DLinkList;
单链表
操作:
// 初始化一个链表,带头结点
bool InitList(LinkList* L);
// 按照位序插入
bool ListInsert(LinkList* L, int i, int e);
// 指定结点的后插操作
bool InsertNextNode(LNode* p, int e);
// 指定结点的前插操作
bool InsertPriorNode(LNode* p, int e);
// 按位序删除结点
bool ListDelete(LinkList* L, int i, int* e);
// 创建方式 - 头插法创建
LinkList List_HeadInsert(LinkList* L);
//创建方法 - 尾插法创建
LinkList List_TailInsert(LinkList* L);
//指定结点的删除
bool DeleteNode(LNode *p);
//按位查找
LNode *GetElem(LinkList L,int i);
//按值查找
LNode *LocateElem(LinkeList L,int e);
//求单链表的长度
int length(LinkList L);
//链表逆置
LNode *Inverse(LNode *L);
// 打印链表
void print(LinkList L);
操作实现:
// 打印链表
void print(LinkList L) {
LinkList E = L->next;
while (E != NULL) {
printf("%d ", E->data);
E = E->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 初始化一个链表,带头结点
bool InitList(LinkList* L) {
*L = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if (*L == NULL) return false;
(*L)->next = NULL;
printf("Initialization of the linked list succeeded!\n");
return true;
}
// 按照位序插入
bool ListInsert(LinkList* L, int i, int e) {
if (i < 1) return false; // 判断操作合法
LNode* p = *L;
int j = 0;
while (p != NULL && j < i - 1) {
p = p->next;
j++;
}
int choice =0;
printf("Prior or next?(1/2)");
scanf("%d",&choice);
if(choice == 2)
return InsertNextNode(p, e);
if(choice == 1)
return InsertPriorNode(p,e);
else
return false;
}
// 指定结点的后插操作
bool InsertNextNode(LNode* p, int e) {
if (p == NULL) return false; // 判断合法
LNode* s = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if (s == NULL) return false; // 内存分配失败
s->data = e;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
return true;
}
// 指定结点的前插操作
bool InsertPriorNode(LNode* p, int e) {
if (p == NULL) return false;
LNode* s = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if (s == NULL) return false;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
s->data = p->data; // 交换数值从而实现前插操作,方法还是后插的方法
p->data = e;
return true;
}
// 按位序删除结点并返回删除数据
bool ListDelete(LinkList* L, int i, int* e) {
if (i < 1) return false; // 判断操作合法
LNode* p = *L;
int j = 0;
while (p != NULL && j < i - 1) {
p = p->next;
j++;
} // 定位到删除结点
if (p == NULL) return false;
if (p->next == NULL) return false;
LNode* q = p->next;
*e = q->data;
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
return true;
}
// 创建方式
// 1. 头插法创建 O(n)
LinkList List_HeadInsert(LinkList* L) {
*L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode)); // 建立头结点
(*L)->next = NULL; // 初始为空链表,这步不能少!
int x;
LNode* s;
printf("input the x:");
scanf("%d", &x);
while (x != 9999) {
s = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = (*L)->next;
(*L)->next = s;
printf("Continue input the x:");
scanf("%d", &x);
}
return *L;
}
//指定结点的删除(重点理解)
bool DeleteNode(LNode *p){
if(p == NULL) return false;
LNode *q=p->next;
p->data=p->next->data;
p->next=q->next;
free(q);
return true;
}
//按位查找
LNode *GetElem(LinkList L,int i){
if(i<1) return false;
LNode *p=L->next;
int j;
while(p!=NULL && j<i-1){
p=p->next;
j++;
}
return p;
}
//按值查找
LNode *LocateElem(LinkList L,int e){
if(L == NULL) return false;
LNode *p=L->next;
while(p != NULL && p->data!=e){
p=p->next;
}
return p;
}
//求单链表的长度
int length(LinkList L){
int len=0;
LNode *p=L;
while(p->next!=NULL)
{
p=p->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//创建方法 - 尾插法创建
//创建方法 - 尾插法创建
LinkList List_TailInsert(LinkList* L){
int x;
*L=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
LNode *s,*r=*L;
printf("输入插入的结点的值:");
scanf("%d",&x);
while(x != 9999){
s=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=x;
r->next=s;
r=s;
scanf("%d",&x);
}
r->next=NULL;
return *L;
}
//链表逆置(重点理解)
LNode *Inverse(LNode *L){
LNode *p,*q;
p=L->next;
L->next=NULL;
while(p!=NULL){
q=p;
p=p->next;
q->next=L->next;
L->next=q;
}
return L;
}
测试代码
int main(void) {
LinkList L = NULL;
LNode *elem = NULL;
int e=0;
List_HeadInsert(&L);print(L);
printf("Insert:\n");
ListInsert(&L,2,3); print(L);
ListDelete(&L,3,&e);print(L);
printf("Deleted elem:%d\n",e);
printf("Delete the elem by Node\n");
DeleteNode(L->next->next);print(L);
printf("Search by position\n");
elem=GetElem(L,3);printf("the elem is:%d\n",elem->data);
printf("Inverse the Link\n");
L=Inverse(L);print(L);
return 0;
}
双链表
操作:
//打印
void print(DLinkList L);
//链表的初始化 ,
bool InitLinkList(DLinkList *L);
//判空
bool isEmpty(DLinkList L);
//后插操作,将s插入p之后
bool InsertNextNode(DNode *p,DNode *s);
//前插操作
bool InsertPriorNode(DNode *p,DNode *s);
定义:
bool InitLinkList(DLinkList *L){
*L = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
if(L == NULL) return false;
(*L)->next=NULL;
(*L)->prior=NULL;
return true;
}
bool isEmpty(DLinkList L){
if(L->next==NULL) return true;
else
return false;
}
bool InsertNextNode(DNode *p,DNode *s){
if(p==NULL || s==NULL){
printf("非法\n");return false;
}
s->next=p->next;
s->prior=p;
p->next=s;
printf("Insert next node success!\n");
return true;
}
bool InsertPriorNode(DNode *p,DNode *s){
if(p==NULL || s==NULL || p->prior==NULL){
printf("非法\n");return false;
}
s->prior=p->prior;
s->next=p;
p->prior=s;
printf("Insert prior node success!\n");
return true;
}
void print(DLinkList L){
L=L->next;//因为有头结点
while(L!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",L->data);
L=L->next;
}
}
测试:
//测试
int main(void){
DLinkList L;
DNode *node;
int data,x;
if(InitLinkList(&L)){
printf("初始化成功!");
}
printf("开始插入(9999停止)\n");
scanf("%d",&x);
while(x !=9999){
node=(DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
node->data=x;
InsertNextNode(L,node);
scanf(" %d",&x);
}
print(L);
return 0;
}
单循环链表.
//循环链表
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//循环单链表
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}DNode,*LinkList;
//打印
void print(LinkList L);
//初始化一个循环单链表
bool InitList(LinkList *L);
//判空
bool isEmpty(LinkList L);
//判断结点是否为表尾指针
bool ifTail(LinkList L,LNode *p);
//插入结点
bool InsertNextNode(LNode *p,LNode *q);
int main(void)
{
LinkList L;
LNode *node;
int x;
if(InitList(&L)) printf("初始化成功!\n");
printf("输入9999结束!\n");
scanf("%d",&x);
while(x != 9999){
node=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
node->data=x;
InsertNextNode(L,node);
scanf(" %d",&x);
}
print(L);
return 0;
}
bool InitList(LinkList *L){
*L=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(*L==NULL) return false;
(*L)->next = *L;
return true;
}
bool isEmpty(LinkList L){
if(L->next == L)return true;
else
return false;
}
void print(LinkList L){
LinkList head=L->next;
while(head != L){
printf("%d ",head->data);
head=head->next;
}
}
bool ifTail(LinkList L,LNode *p){
if(p->next == L)return true;
else
return false;
}
bool InsertNextNode(LNode *p,LNode *q){
if(p==NULL || q==NULL) return false;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
return true;
}