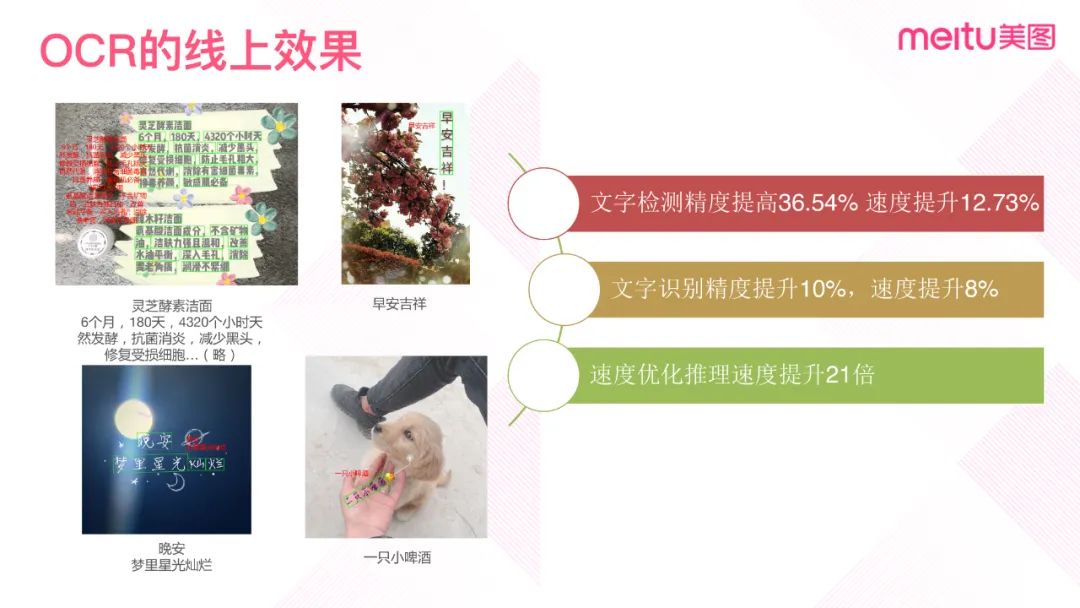
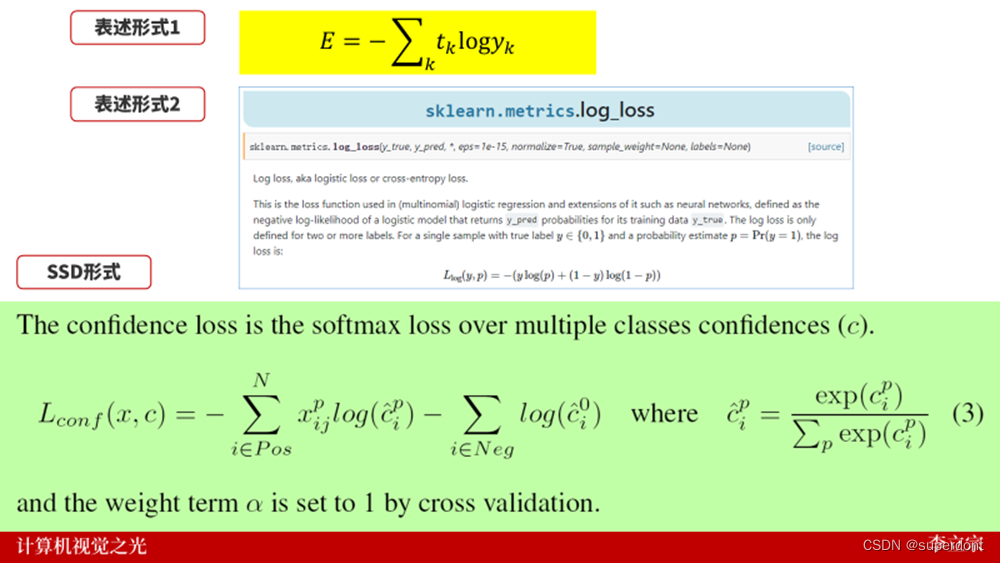
多分类交叉熵有多种不同的表示形式,如下图所示:
但是,有时候我们读论文会深陷其中不能自拔。
也有很多读者、观众会纠正其他作者的文章、视频的交叉熵形式。
实际上,上述三种形式都是没有问题的。
这里,我们就要了解交叉熵的本质。交叉熵,可以用一句话来形容:
正确标签的自然对数。

我们看个例子:
具体情况如下:
——三幅图像,其分别对应着数字3、数字6、数字8
如果将其标识位one-hot形式,则其对应的值为:

也就是对应位置上的值为1,其余位置为0.
——三幅图像的识别结果为y_pred如下图所示:

计算交叉熵,就是计算 【正确标签的自然对数】
具体来说,计算的是
-t*log(y_pred)
当然,根据需要后续需要计算和和均值。
所以,我们通常看到的表达式是:

或者:
![]()
都是可以的,因为代入数据,计算结果是一致的。
下面,我们分别通过三种不同的方式计算交叉熵损失函数
- 方式0:手动计算
- 方式1:调用sklearn函数计算
- 方式2:自定义函数计算
全部代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Nov 9 12:22:39 2022
@author: Administrator
"""
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
from math import log
# 三个样本对应的标签
# 这里指三幅图像分别对应着数值3、数字6、数字8
y_true = ['3', '6', '8']
# 预测值,这里使用softmax处理过了。所有概率和为0
# 例如:第一行对应着第一张图像的识别结果:0.1+0.3+0.6+一堆0=1
# 第2行:0.2+0.5+0.3+一堆0=1
# 第3行:0.3+0.5+0.2+一堆0=1
y_pred = [[0.1, 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0.2, 0, 0, 0, 0.5, 0, 0.3, 0],
[0, 0.3, 0, 0, 0.5, 0, 0, 0, 0.2, 0]
]
# 标签对应的值(识别数字)
labels = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
# =============================================================================
# 方法0:手算
# =============================================================================
# 真实值one-hot编码
t = [[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]]
y = np.array(y_pred) # 样本预测值
# 面临问题:log(0)为负无穷大,导致后续无法计算。
# 解决方案:将log(0)处理为一个log(接近零)
y[y < 1e-15] = 1e-15
Loss = 0
for i in range(3): # 逐个遍历样本
for k in range(10): # 逐个遍历标签
# 计算对应位置上的真实值*log(预测值)
Loss -= t[i][k] * log(y[i][k])
Loss /= 3
print("自定义的交叉熵:", Loss)
# =============================================================================
# 不用循环的可以改进计算:
# a = -np.multiply(t, np.log(y))
# print("自定义的交叉熵:",sum(map(sum, a))/3)
# =============================================================================
# =============================================================================
# 逐个处理也可以
#
# for i in range(3): # 逐个遍历样本
# for k in range(10): # 逐个遍历标签
# delta = 1e-15 # 控制值
# if y[i][k] < delta:
# y[i][k] = delta
# =============================================================================
# =============================================================================
# 方法1:使用sklearn计算
# =============================================================================
# 说明:
# 传递给sklearn的y_true = ['3', '6', '8']
# 会根据参数【labels】被识别为one-hot形式。
# [[0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
# [0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
# [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]]
sk_log_loss = log_loss(y_true, y_pred, labels=labels)
print("sklearn交叉熵:", sk_log_loss)
# =============================================================================
# 方法2:自定义函数形式
# =============================================================================
def lilizong():
# 将样本标签处理为one-hot形式
lb = LabelBinarizer()
lb.fit(labels)
transformed_labels = lb.transform(y_true)
# transformed_labels值为:
# [[0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0]
# [0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
# [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]]
# 计算样本个数、标签个数
sn = len(y_true) # 样本个数
ln = len(labels) # 标签个数
# 初始化值
# log(0)为无穷大,这样一来,后续无法计算
# 保护性对策:添加一个极小值δ,防止负无限大的发生
delta = 1e-15 # 控制值
Loss = 0 # 损失值初始化
# 循环遍历
for i in range(sn): # 逐个遍历样本
for k in range(ln): # 逐个遍历标签
if y_pred[i][k] < delta:
y_pred[i][k] = delta
if y_pred[i][k] > 1-delta:
y_pred[i][k] = 1-delta
# 计算对应位置上的真实值*log(预测值)
Loss -= transformed_labels[i][k]*log(y_pred[i][k])
Loss /= sn
return Loss
# 调用自定义函数
print("自定义的交叉熵:", lilizong())
# =============================================================================
# 参考资料1:sklearn官网说明
# =============================================================================
# https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/model_evaluation.html#log-loss
# =============================================================================
# 参考资料2:sklearn中log_loss源代码
# =============================================================================
# https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/ed5e127b/sklearn/metrics/classification.py#L1576
# def log_loss(y_true, y_pred, eps=1e-15, normalize=True, sample_weight=None,
# labels=None):
# """Log loss, aka logistic loss or cross-entropy loss.
# This is the loss function used in (multinomial) logistic regression
# and extensions of it such as neural networks, defined as the negative
# log-likelihood of the true labels given a probabilistic classifier's
# predictions. The log loss is only defined for two or more labels.
# For a single sample with true label yt in {0,1} and
# estimated probability yp that yt = 1, the log loss is
# -log P(yt|yp) = -(yt log(yp) + (1 - yt) log(1 - yp))
# Read more in the :ref:`User Guide <log_loss>`.
# Parameters
# ----------
# y_true : array-like or label indicator matrix
# Ground truth (correct) labels for n_samples samples.
# y_pred : array-like of float, shape = (n_samples, n_classes) or (n_samples,)
# Predicted probabilities, as returned by a classifier's
# predict_proba method. If ``y_pred.shape = (n_samples,)``
# the probabilities provided are assumed to be that of the
# positive class. The labels in ``y_pred`` are assumed to be
# ordered alphabetically, as done by
# :class:`preprocessing.LabelBinarizer`.
# eps : float
# Log loss is undefined for p=0 or p=1, so probabilities are
# clipped to max(eps, min(1 - eps, p)).
# normalize : bool, optional (default=True)
# If true, return the mean loss per sample.
# Otherwise, return the sum of the per-sample losses.
# sample_weight : array-like of shape = [n_samples], optional
# Sample weights.
# labels : array-like, optional (default=None)
# If not provided, labels will be inferred from y_true. If ``labels``
# is ``None`` and ``y_pred`` has shape (n_samples,) the labels are
# assumed to be binary and are inferred from ``y_true``.
# .. versionadded:: 0.18
# Returns
# -------
# loss : float
# Examples
# --------
# >>> log_loss(["spam", "ham", "ham", "spam"], # doctest: +ELLIPSIS
# ... [[.1, .9], [.9, .1], [.8, .2], [.35, .65]])
# 0.21616...
# References
# ----------
# C.M. Bishop (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer,
# p. 209.
# Notes
# -----
# The logarithm used is the natural logarithm (base-e).
# """
# y_pred = check_array(y_pred, ensure_2d=False)
# check_consistent_length(y_pred, y_true)
# lb = LabelBinarizer()
# if labels is not None:
# lb.fit(labels)
# else:
# lb.fit(y_true)
# if len(lb.classes_) == 1:
# if labels is None:
# raise ValueError('y_true contains only one label ({0}). Please '
# 'provide the true labels explicitly through the '
# 'labels argument.'.format(lb.classes_[0]))
# else:
# raise ValueError('The labels array needs to contain at least two '
# 'labels for log_loss, '
# 'got {0}.'.format(lb.classes_))
# transformed_labels = lb.transform(y_true)
# if transformed_labels.shape[1] == 1:
# transformed_labels = np.append(1 - transformed_labels,
# transformed_labels, axis=1)
# # Clipping
# y_pred = np.clip(y_pred, eps, 1 - eps)
# # If y_pred is of single dimension, assume y_true to be binary
# # and then check.
# if y_pred.ndim == 1:
# y_pred = y_pred[:, np.newaxis]
# if y_pred.shape[1] == 1:
# y_pred = np.append(1 - y_pred, y_pred, axis=1)
# # Check if dimensions are consistent.
# transformed_labels = check_array(transformed_labels)
# if len(lb.classes_) != y_pred.shape[1]:
# if labels is None:
# raise ValueError("y_true and y_pred contain different number of "
# "classes {0}, {1}. Please provide the true "
# "labels explicitly through the labels argument. "
# "Classes found in "
# "y_true: {2}".format(transformed_labels.shape[1],
# y_pred.shape[1],
# lb.classes_))
# else:
# raise ValueError('The number of classes in labels is different '
# 'from that in y_pred. Classes found in '
# 'labels: {0}'.format(lb.classes_))
# # Renormalize
# y_pred /= y_pred.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
# loss = -(transformed_labels * np.log(y_pred)).sum(axis=1)
# return _weighted_sum(loss, sample_weight, normalize)