一、synchronized实现
1.1、案例一(2个线程交替对变量执行+1、-1操作,来10轮)
1.1.1、资源类ShareDataOne
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 10:44
* @Description: 资源类
* 说明:2个线程使用if判断变量的值,没有问题,3个及3个以上线程会出现虚假唤醒的问题,需要注意!!!!!
*/
public class ShareDataOne {
private int number = 0;
/**
* 加1
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
// 1、判断
if (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 2、干活
++number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 3、通知
this.notifyAll();
}
/**
* 减1
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
// 1、判断
if (number == 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 2、干活
--number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 3、通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}1.1.2、线程类ShareDataOneMainApp
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 10:46
* @Description:
* 需求:两个线程,可以操作初始量为零的一个变量,实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量减1,交替来10轮
* Java里边如何进行工程级别的多线程编写?
* 1、多线程编程模板(套路上)
* 1.1、线程 操作 资源类
* 1.2、高内聚 低耦合
*
* 2、多线程编程模板(套路下)
* 2.1、判断
* 2.2、干活
* 2.3、通知
*
* 3、防止虚假唤醒用while
*/
public class ShareDataOneMainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataOne sd = new ShareDataOne();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sd.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sd.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "B").start();
}
}
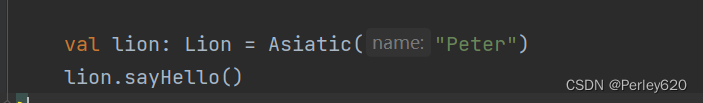
1.1.3、结果
1.2、案例二(4个线程交替对变量执行+1、-1操作,来10轮)
1.2.1、资源类ShareDataTwo
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 10:44
* @Description: 资源类
* 说明:2个线程使用if判断变量的值,没有问题,3个及3个以上线程会出现虚假唤醒的问题,需要注意!!!!!
* 解决方法:使用while做判断条件
* 原理:中断和虚假唤醒是由可能产生的,所以要用loob循环,if只判断一次,while是只要唤醒就要拉回来再判断一次,if换成while即可解决虚假唤醒的问题
*/
public class ShareDataTwo {
private int number = 0;
/**
* 加1
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
// 1、判断
while (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 2、干活
++number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 3、通知
this.notifyAll();
}
/**
* 减1
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
// 1、判断
while (number == 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 2、干活
--number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 3、通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
1.2.2、线程类
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 11:19
* @Description:
* 需求:四个线程,可以操作初始量为零的一个变量,实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量减1,交替来10轮
* Java里边如何进行工程级别的多线程编写?
* 1、多线程编程模板(套路上)
* 1.1、线程 操作 资源类
* 1.2、高内聚 低耦合
*
* 2、多线程编程模板(套路下)
* 2.1、判断
* 2.2、干活
* 2.3、通知
*
* 3、防止虚假唤醒用while
*/
public class ShareDataTwoMainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataTwo sdt = new ShareDataTwo();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "C").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "D").start();
}
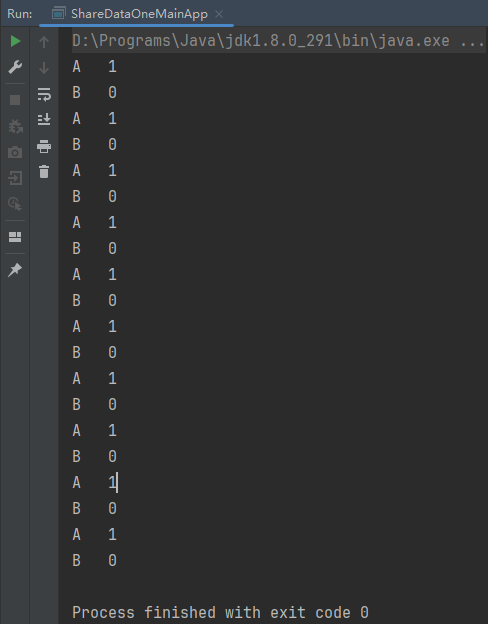
}1.2.3、结果

二、Condition实现
2.1、案例一(2个线程交替对变量执行+1、-1操作,来10轮)
2.1.1、资源类ShareDataThree
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 11:40
* @Description: 资源类
* 说明:2个线程使用if判断变量的值,没有问题,3个及3个以上线程会出现虚假唤醒的问题,需要注意!!!!!
* 解决方法:使用while做判断条件
* 原理:中断和虚假唤醒是由可能产生的,所以要用loob循环,if只判断一次,while是只要唤醒就要拉回来再判断一次,if换成while即可解决虚假唤醒的问题
*/
public class ShareDataThree {
private Integer number = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
/**
* 加1
*/
public void increment() {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断
while (number != 0) {
condition.await();
}
// 干活
++number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 通知
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 加1
*/
public void decrement() {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断
while (number == 0) {
condition.await();
}
// 干活
--number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);
// 通知
condition.signalAll();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}2.1.2、线程类ShareDataThreeMainApp
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 11:19
* @Description:
* 需求:两个线程,可以操作初始量为零的一个变量,实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量减1,交替来10轮
* Java里边如何进行工程级别的多线程编写?
* 1、多线程编程模板(套路上)
* 1.1、线程 操作 资源类
* 1.2、高内聚 低耦合
*
* 2、多线程编程模板(套路下)
* 2.1、判断
* 2.2、干活
* 2.3、通知
*
* 3、防止虚假唤醒用while
*/
public class ShareDataThreeMainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataThree sdt = new ShareDataThree();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "B").start();
}
}2.1.3、结果
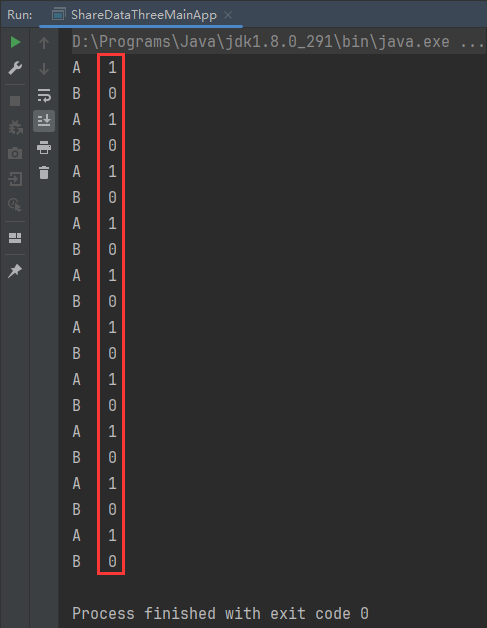
2.2、案例二(4个线程交替对变量执行+1、-1操作,来10轮)
2.2.1、资源类ShareDataThree
同2.1.1。
2.2.2、线程类
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 11:19
* @Description:
* 需求:四个线程,可以操作初始量为零的一个变量,实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量减1,交替来10轮
* Java里边如何进行工程级别的多线程编写?
* 1、多线程编程模板(套路上)
* 1.1、线程 操作 资源类
* 1.2、高内聚 低耦合
*
* 2、多线程编程模板(套路下)
* 2.1、判断
* 2.2、干活
* 2.3、通知
*
* 3、防止虚假唤醒用while
*/
public class ShareDataFourMainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataThree sdt = new ShareDataThree();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "C").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
try {
sdt.decrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "D").start();
}
}2.2.3、结果

三、线程间定制化通信
3.1、资源类ShareDataFive
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 12:12
* @Description: 资源类
* 说明:2个线程使用if判断变量的值,没有问题,3个及3个以上线程会出现虚假唤醒的问题,需要注意!!!!!
* 解决方法:使用while做判断条件
* 原理:中断和虚假唤醒是由可能产生的,所以要用loob循环,if只判断一次,while是只要唤醒就要拉回来再判断一次,if换成while即可解决虚假唤醒的问题
*/
public class ShareDataFive {
private Integer number = 1;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
public void print5(int totalLoopNumber) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断
while (number != 1) {
condition1.await();
}
// 干活
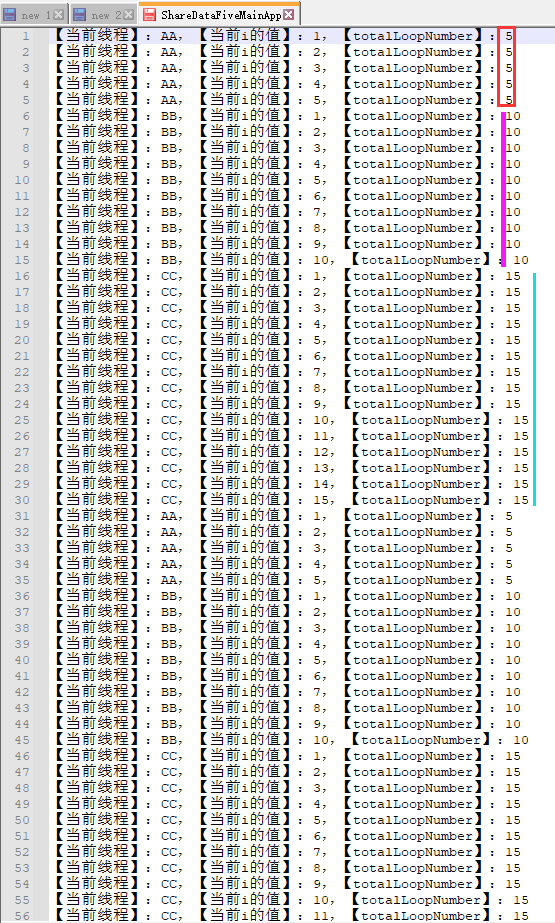
for (int i = 1; i <= totalLoopNumber; i++) {
System.out.println("【当前线程】:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",【当前i的值】:" + i + ",【totalLoopNumber】:" + totalLoopNumber);
}
// 通知
number = 2;
condition2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print10(int totalLoopNumber) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断
while (number != 2) {
condition2.await();
}
// 干活
for (int i = 1; i <= totalLoopNumber; i++) {
System.out.println("【当前线程】:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",【当前i的值】:" + i + ",【totalLoopNumber】:" + totalLoopNumber);
}
// 通知
number = 3;
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print15(int totalLoopNumber) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 判断
while (number != 3) {
condition3.await();
}
// 干活
for (int i = 1; i <= totalLoopNumber; i++) {
System.out.println("【当前线程】:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",【当前i的值】:" + i + ",【totalLoopNumber】:" + totalLoopNumber);
}
// 通知
number = 1;
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}3.2、线程类
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/11/20 12:22
* @Description: 需求:多个线程之间按顺序调用,实现AA>BB>CC,三个线程启动,
* 要求:
* AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
* 接着,AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
* ...
* 来10轮
*/
public class ShareDataFiveMainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataFive sdf = new ShareDataFive();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sdf.print5(5);
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sdf.print10(10);
}
}, "BB").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
sdf.print15(15);
}
}, "CC").start();
}
}3.3、结果


![2023年中国负极材料分类、产量及市场规模分析[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/d611948fb9ec855ae06a223d6a944cac.png)



![2023年中国中端连锁酒店分类、市场规模及主要企业市占率[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/b42814840a4a5db09e41cdde844cda44.png)

![2023年中国地产SaaS分类、产业链及市场规模分析[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/348ffe3aaf12c6229b617458217ab32a.png)