文章目录
- 主要完成任务
- 代码结构
- 1.action space
- 2.default_config
- 3.reward
- _agent_rewards
- _agent_reward
- _reward
- _rewards
- 小结
- 4.terminated & truncated
- 5.reset
- _make_road
- _make_vehicles
- _spawn_vehicle
- 6.step
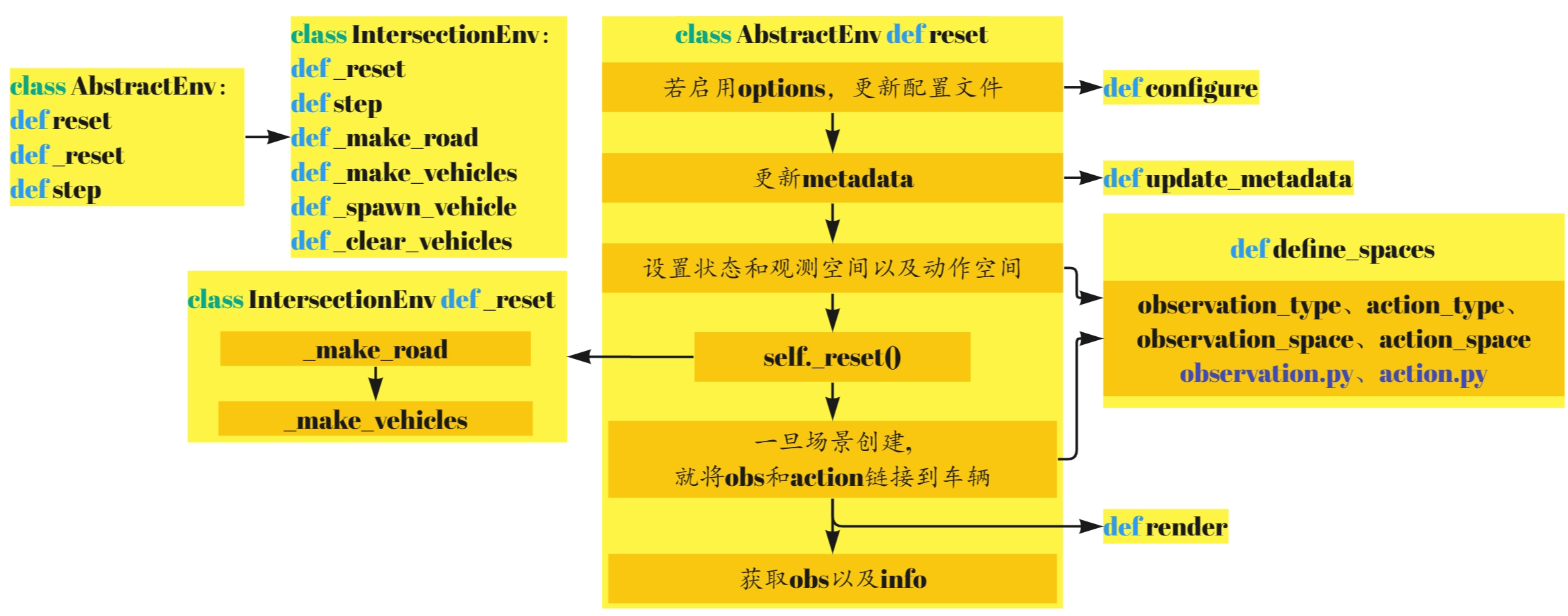
主要完成任务
IntersectionEnv继承自AbstractEnv,主要完成以下4个任务
default_config环境默认的配置define_spaces设置相应的动作空间和观测空间step以一定的频率(policy frequency)执行策略并以一定的频率(simulation frequency)模拟环境render用于显示
代码结构
这部分的代码大致可以分为以下几个部分,我也将从以下几个方面进行分析。

另附上AbstractEnv部分的代码结构。

1.action space
在IntersectionEnv类中首先定义了action space,如下所示:分为SLOWER、IDLE和FASTER。默认设置期望速度设置为[0, 4.5, 9]

2.default_config
default_config设置了环境的默认配置,如下所示:
@classmethod
def default_config(cls) -> dict:
config = super().default_config()
config.update({
"observation": {
"type": "Kinematics",
"vehicles_count": 15,
"features": ["presence", "x", "y", "vx", "vy", "cos_h", "sin_h"],
"features_range": {
"x": [-100, 100],
"y": [-100, 100],
"vx": [-20, 20],
"vy": [-20, 20],
},
"absolute": True,
"flatten": False,
"observe_intentions": False
},
"action": {
"type": "DiscreteMetaAction",
"longitudinal": True,
"lateral": False,
"target_speeds": [0, 4.5, 9]
},
"duration": 13, # [s]
"destination": "o1",
"controlled_vehicles": 1,
"initial_vehicle_count": 10,
"spawn_probability": 0.6,
"screen_width": 600,
"screen_height": 600,
"centering_position": [0.5, 0.6],
"scaling": 5.5 * 1.3,
"collision_reward": -5,
"high_speed_reward": 1,
"arrived_reward": 1,
"reward_speed_range": [7.0, 9.0],
"normalize_reward": False,
"offroad_terminal": False
})
return config
默认配置文件还有AbstractEnv中所定义的部分。
@classmethod
def default_config(cls) -> dict:
"""
Default environment configuration.
Can be overloaded in environment implementations, or by calling configure().
:return: a configuration dict
"""
return {
"observation": {
"type": "Kinematics"
},
"action": {
"type": "DiscreteMetaAction"
},
"simulation_frequency": 15, # [Hz]
"policy_frequency": 1, # [Hz]
"other_vehicles_type": "highway_env.vehicle.behavior.IDMVehicle",
"screen_width": 600, # [px]
"screen_height": 150, # [px]
"centering_position": [0.3, 0.5],
"scaling": 5.5,
"show_trajectories": False,
"render_agent": True,
"offscreen_rendering": os.environ.get("OFFSCREEN_RENDERING", "0") == "1",
"manual_control": False,
"real_time_rendering": False
}
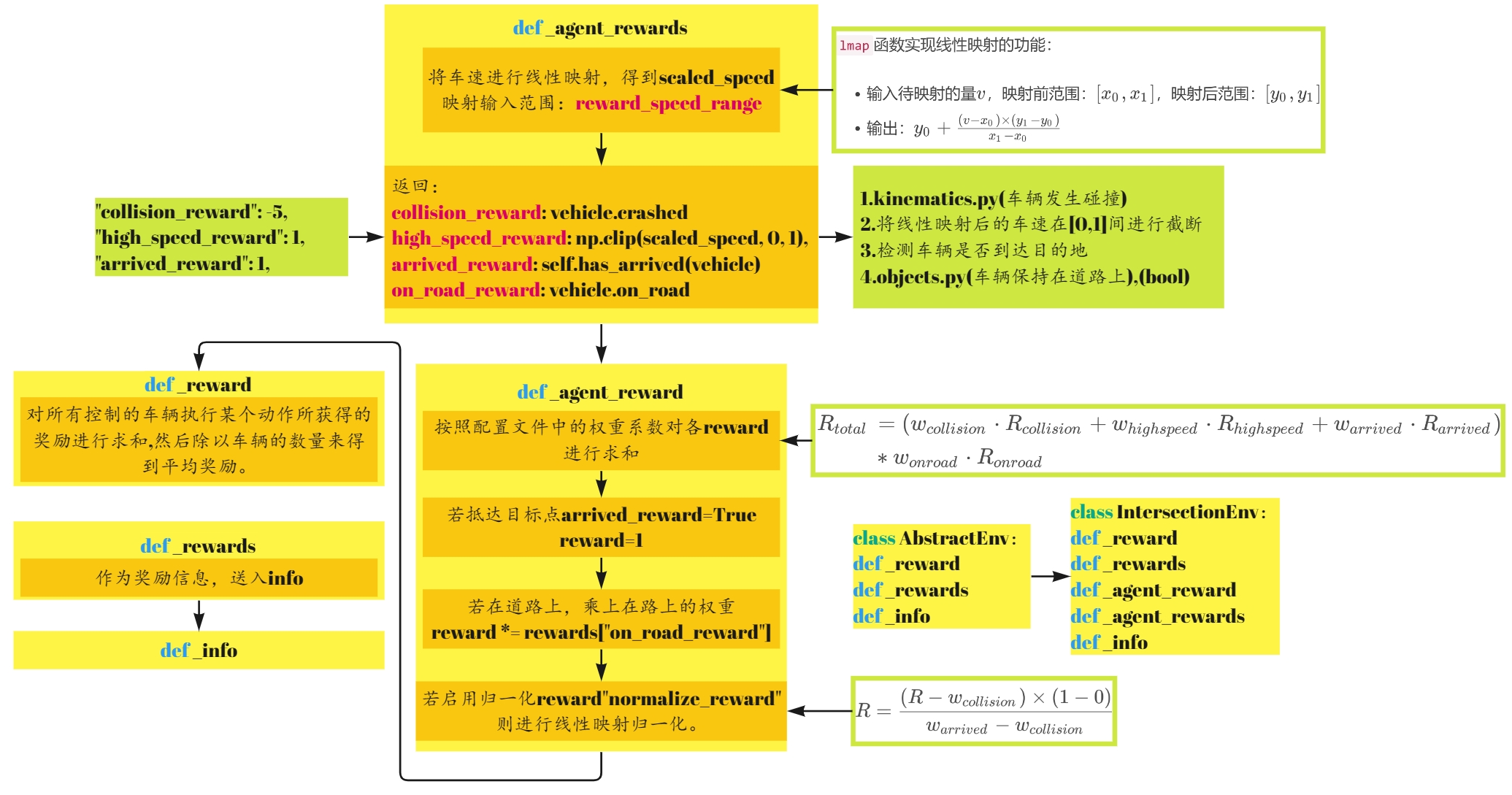
3.reward
接着来介绍奖励函数部分,在AbstractEnv中定义了_reward和_rewards函数,其中_rewards只在info中进行使用。
def _reward(self, action: Action) -> float:
"""
Return the reward associated with performing a given action and ending up in the current state.
:param action: the last action performed
:return: the reward
"""
raise NotImplementedError
def _rewards(self, action: Action) -> Dict[Text, float]:
"""
Returns a multi-objective vector of rewards.
If implemented, this reward vector should be aggregated into a scalar in _reward().
This vector value should only be returned inside the info dict.
:param action: the last action performed
:return: a dict of {'reward_name': reward_value}
"""
raise NotImplementedError
在IntersectionEnv类中,实现了_reward、_rewards、_agent_reward以及_agent_rewards四个函数,我们首先从第四个函数开始看起:
_agent_rewards
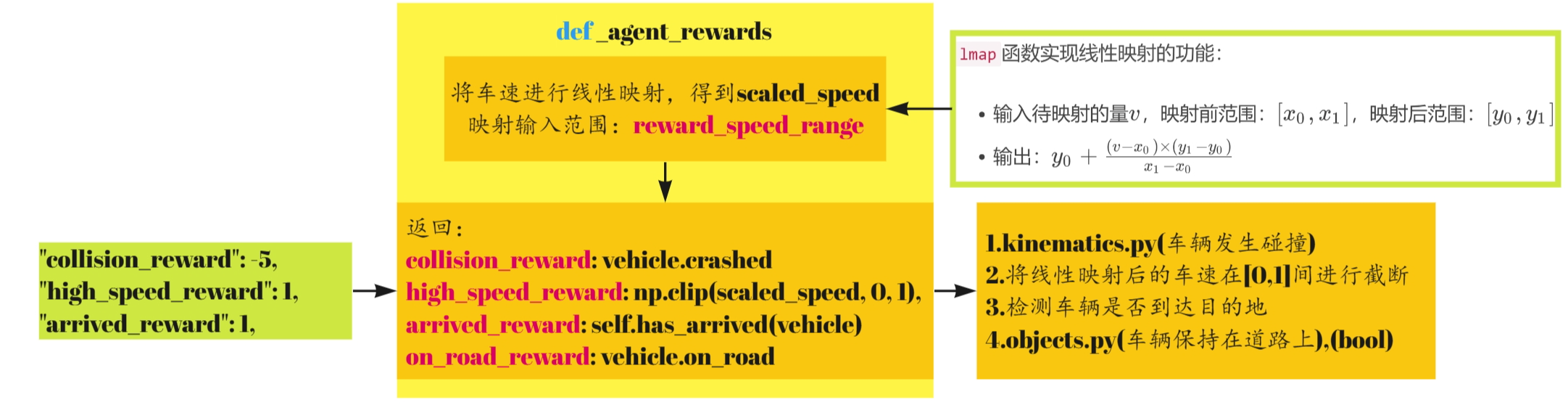
def _agent_rewards(self, action: int, vehicle: Vehicle) -> Dict[Text, float]:
"""Per-agent per-objective reward signal."""
scaled_speed = utils.lmap(vehicle.speed, self.config["reward_speed_range"], [0, 1])
return {
"collision_reward": vehicle.crashed,
"high_speed_reward": np.clip(scaled_speed, 0, 1),
"arrived_reward": self.has_arrived(vehicle),
"on_road_reward": vehicle.on_road
}
首先将车速进行线性映射,得到scaled_speed。
lmap函数实现线性映射的功能:
- 输入待映射的量 v v v,映射前范围: [ x 0 , x 1 ] [x_0,x_1] [x0,x1],映射后范围: [ y 0 , y 1 ] [y_0,y_1] [y0,y1]
- 输出: y 0 + ( v − x 0 ) × ( y 1 − y 0 ) x 1 − x 0 y_0 + \frac{{(v-x_0)}\times{(y_1-y_0)}}{x_1-x_0} y0+x1−x0(v−x0)×(y1−y0)
如:scaled_speed = utils.lmap(5, [7, 9], [0, 1])输出为-1.
utils.py
def lmap(v: float, x: Interval, y: Interval) -> float:
"""Linear map of value v with range x to desired range y."""
return y[0] + (v - x[0]) * (y[1] - y[0]) / (x[1] - x[0])
has_arrived根据如下条件进行判断,lane_index是一个三元组(例,(‘il1’,‘o1’,0)),判断车辆是否在车道上,是否抵达目的地,且是否在车道坐标系中的纵向坐标大于exit_distance。
def has_arrived(self, vehicle: Vehicle, exit_distance: float = 25) -> bool:
return "il" in vehicle.lane_index[0] \
and "o" in vehicle.lane_index[1] \
and vehicle.lane.local_coordinates(vehicle.position)[0] >= exit_distance
_agent_reward
_agent_reward接受来自_agent_rewards的字典,进行reward求和并判断是否启用奖励归一化。
R
t
o
t
a
l
=
(
w
c
o
l
l
i
s
i
o
n
⋅
R
c
o
l
l
i
s
i
o
n
+
w
h
i
g
h
s
p
e
e
d
⋅
R
h
i
g
h
s
p
e
e
d
+
w
a
r
r
i
v
e
d
⋅
R
a
r
r
i
v
e
d
)
∗
w
o
n
r
o
a
d
⋅
R
o
n
r
o
a
d
\begin{aligned}R_{total}&=(w_{collision}\cdot R_{collision}+w_{highspeed}\cdot R_{highspeed}+w_{arrived}\cdot R_{arrived})\\ &*w_{onroad}\cdot R_{onroad}\end{aligned}
Rtotal=(wcollision⋅Rcollision+whighspeed⋅Rhighspeed+warrived⋅Rarrived)∗wonroad⋅Ronroad
启用归一化:
R
=
(
R
−
w
c
o
l
l
i
s
i
o
n
)
×
(
1
−
0
)
w
a
r
r
i
v
e
d
−
w
c
o
l
l
i
s
i
o
n
R= \frac{{(R-w_{collision})}\times{(1-0)}}{w_{arrived}-w_{collision}}
R=warrived−wcollision(R−wcollision)×(1−0)
def _agent_reward(self, action: int, vehicle: Vehicle) -> float:
"""Per-agent reward signal."""
rewards = self._agent_rewards(action, vehicle)
reward = sum(self.config.get(name, 0) * reward for name, reward in rewards.items())
reward = self.config["arrived_reward"] if rewards["arrived_reward"] else reward
reward *= rewards["on_road_reward"]
if self.config["normalize_reward"]:
reward = utils.lmap(reward, [self.config["collision_reward"], self.config["arrived_reward"]], [0, 1])
return reward
_reward
_reward通过对所有控制的车辆执行某个动作所获得的奖励进行求和,然后除以车辆的数量来得到平均奖励。
def _reward(self, action: int) -> float:
"""Aggregated reward, for cooperative agents."""
return sum(self._agent_reward(action, vehicle) for vehicle in self.controlled_vehicles
) / len(self.controlled_vehicles)
_rewards
_rewards 方法计算的是合作智能体的多目标奖励。对于每个动作,它计算所有控制车辆的奖励,并将这些奖励按名称聚合起来,然后除以车辆的数量得到平均奖励。这个方法返回的是一个字典,其中每个键都是一个奖励的名称,每个值都是对应的平均奖励。最后将信息送人info.
def _rewards(self, action: int) -> Dict[Text, float]:
"""Multi-objective rewards, for cooperative agents."""
agents_rewards = [self._agent_rewards(action, vehicle) for vehicle in self.controlled_vehicles]
return {
name: sum(agent_rewards[name] for agent_rewards in agents_rewards) / len(agents_rewards)
for name in agents_rewards[0].keys()
}
AbstractEnv
def _info(self, obs: Observation, action: Optional[Action] = None) -> dict:
"""
Return a dictionary of additional information
:param obs: current observation
:param action: current action
:return: info dict
"""
info = {
"speed": self.vehicle.speed,
"crashed": self.vehicle.crashed,
"action": action,
}
try:
info["rewards"] = self._rewards(action)
except NotImplementedError:
pass
return info
IntersectionEnv
def _info(self, obs: np.ndarray, action: int) -> dict:
info = super()._info(obs, action)
info["agents_rewards"] = tuple(self._agent_reward(action, vehicle) for vehicle in self.controlled_vehicles)
info["agents_dones"] = tuple(self._agent_is_terminal(vehicle) for vehicle in self.controlled_vehicles)
return info
小结
4.terminated & truncated
- 当车辆发生碰撞或者抵达终点或者偏离道路,则视为
_is_terminated - 当车辆所经历的时间大于预定的时间
duration,则truncated _agent_is_terminal方法在info中使用。
def _is_terminated(self) -> bool:
return any(vehicle.crashed for vehicle in self.controlled_vehicles) \
or all(self.has_arrived(vehicle) for vehicle in self.controlled_vehicles) \
or (self.config["offroad_terminal"] and not self.vehicle.on_road)
def _agent_is_terminal(self, vehicle: Vehicle) -> bool:
"""The episode is over when a collision occurs or when the access ramp has been passed."""
return (vehicle.crashed or
self.has_arrived(vehicle))
def _is_truncated(self) -> bool:
"""The episode is truncated if the time limit is reached."""
return self.time >= self.config["duration"]
5.reset
_make_road
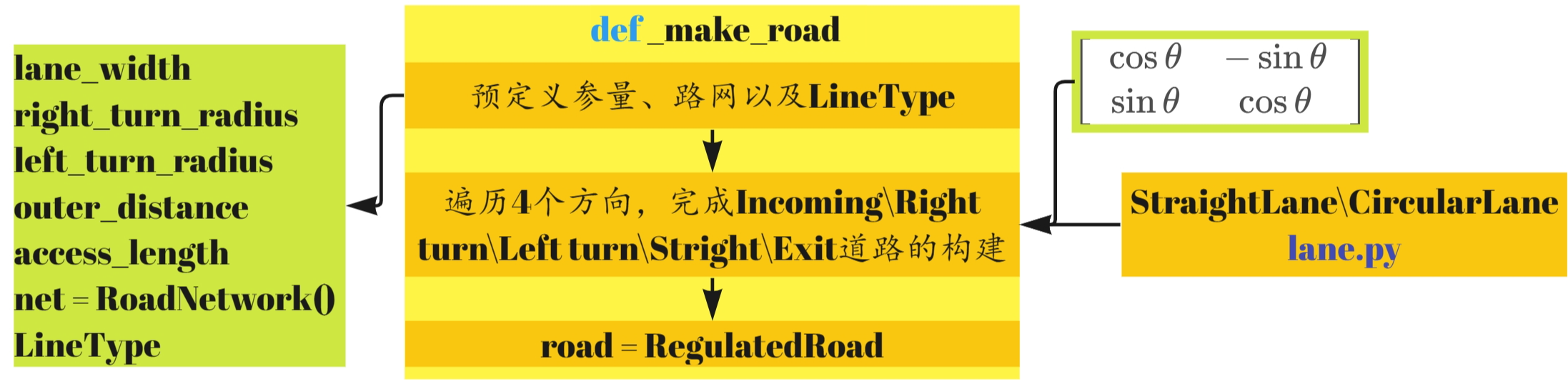
_make_road实现了一个4-way的路口场景,共有以下四种优先级:
| 驾驶行为 | 优先级 | 图示 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | horizontal straight lanes and right-turns |  |
| 2 | horizontal left-turns | 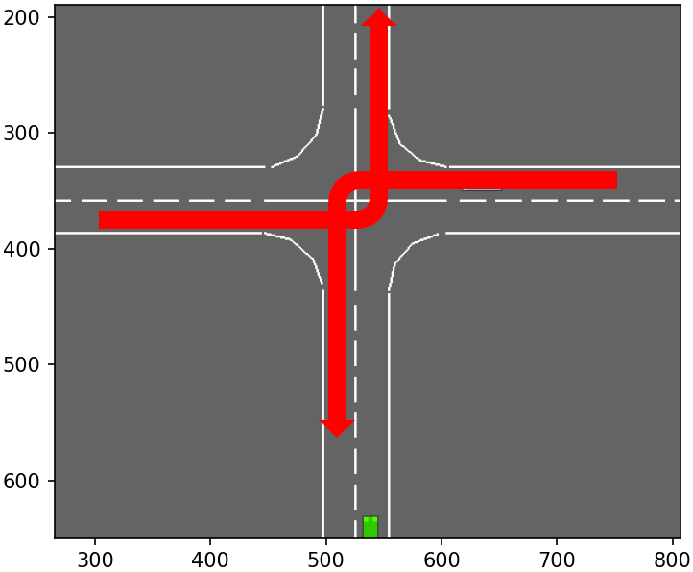 |
| 1 | vertical straight lanes and right-turns | 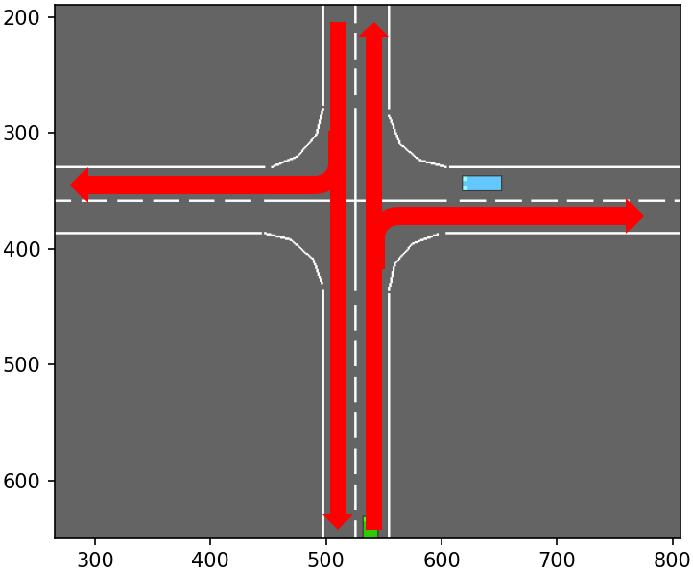 |
| 0 | vertical left-turns | 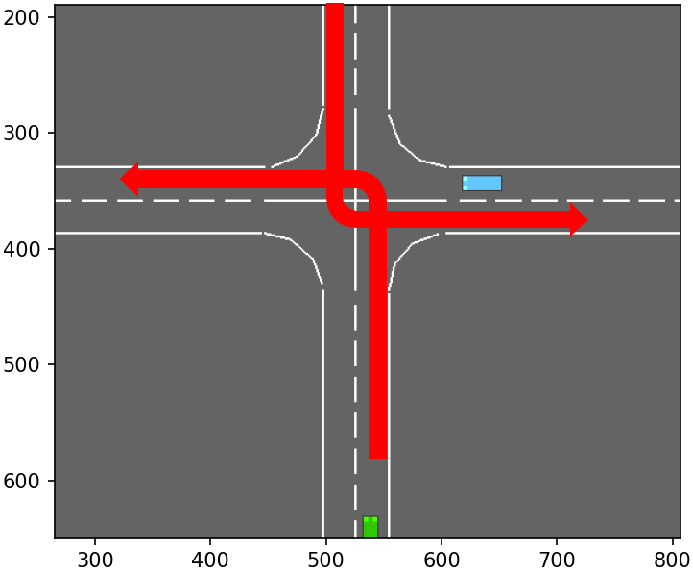 |
路网中的节点按如下规则进行标识:
(o:outer | i:inner + [r:right, l:left]) + (0:south | 1:west | 2:north | 3:east)
def _make_road(self) -> None:
"""
Make an 4-way intersection.
The horizontal road has the right of way. More precisely, the levels of priority are:
- 3 for horizontal straight lanes and right-turns
- 1 for vertical straight lanes and right-turns
- 2 for horizontal left-turns
- 0 for vertical left-turns
The code for nodes in the road network is:
(o:outer | i:inner + [r:right, l:left]) + (0:south | 1:west | 2:north | 3:east)
:return: the intersection road
"""
lane_width = AbstractLane.DEFAULT_WIDTH
right_turn_radius = lane_width + 5 # [m}
left_turn_radius = right_turn_radius + lane_width # [m}
outer_distance = right_turn_radius + lane_width / 2
access_length = 50 + 50 # [m]
net = RoadNetwork()
n, c, s = LineType.NONE, LineType.CONTINUOUS, LineType.STRIPED
for corner in range(4):
angle = np.radians(90 * corner)
is_horizontal = corner % 2
priority = 3 if is_horizontal else 1
rotation = np.array([[np.cos(angle), -np.sin(angle)], [np.sin(angle), np.cos(angle)]])
# Incoming
start = rotation @ np.array([lane_width / 2, access_length + outer_distance])
end = rotation @ np.array([lane_width / 2, outer_distance])
net.add_lane("o" + str(corner), "ir" + str(corner),
StraightLane(start, end, line_types=[s, c], priority=priority, speed_limit=10))
# Right turn
r_center = rotation @ (np.array([outer_distance, outer_distance]))
net.add_lane("ir" + str(corner), "il" + str((corner - 1) % 4),
CircularLane(r_center, right_turn_radius, angle + np.radians(180), angle + np.radians(270),
line_types=[n, c], priority=priority, speed_limit=10))
# Left turn
l_center = rotation @ (np.array([-left_turn_radius + lane_width / 2, left_turn_radius - lane_width / 2]))
net.add_lane("ir" + str(corner), "il" + str((corner + 1) % 4),
CircularLane(l_center, left_turn_radius, angle + np.radians(0), angle + np.radians(-90),
clockwise=False, line_types=[n, n], priority=priority - 1, speed_limit=10))
# Straight
start = rotation @ np.array([lane_width / 2, outer_distance])
end = rotation @ np.array([lane_width / 2, -outer_distance])
net.add_lane("ir" + str(corner), "il" + str((corner + 2) % 4),
StraightLane(start, end, line_types=[s, n], priority=priority, speed_limit=10))
# Exit
start = rotation @ np.flip([lane_width / 2, access_length + outer_distance], axis=0)
end = rotation @ np.flip([lane_width / 2, outer_distance], axis=0)
net.add_lane("il" + str((corner - 1) % 4), "o" + str((corner - 1) % 4),
StraightLane(end, start, line_types=[n, c], priority=priority, speed_limit=10))
road = RegulatedRoad(network=net, np_random=self.np_random, record_history=self.config["show_trajectories"])
self.road = road
首先是lane_width、right_turn_radius、left_turn_radius、outer_distance、access_length等参数的设置,图示如下:


旋转矩阵: [ cos θ − sin θ sin θ cos θ ] \left[ {\begin{array}{ccccccccccccccc}{\cos \theta }&{ - \sin \theta }\\{\sin \theta }&{\cos \theta }\end{array}} \right] [cosθsinθ−sinθcosθ]
代码遍历4个方向,构建相应的路网,图示如下:



_make_vehicles
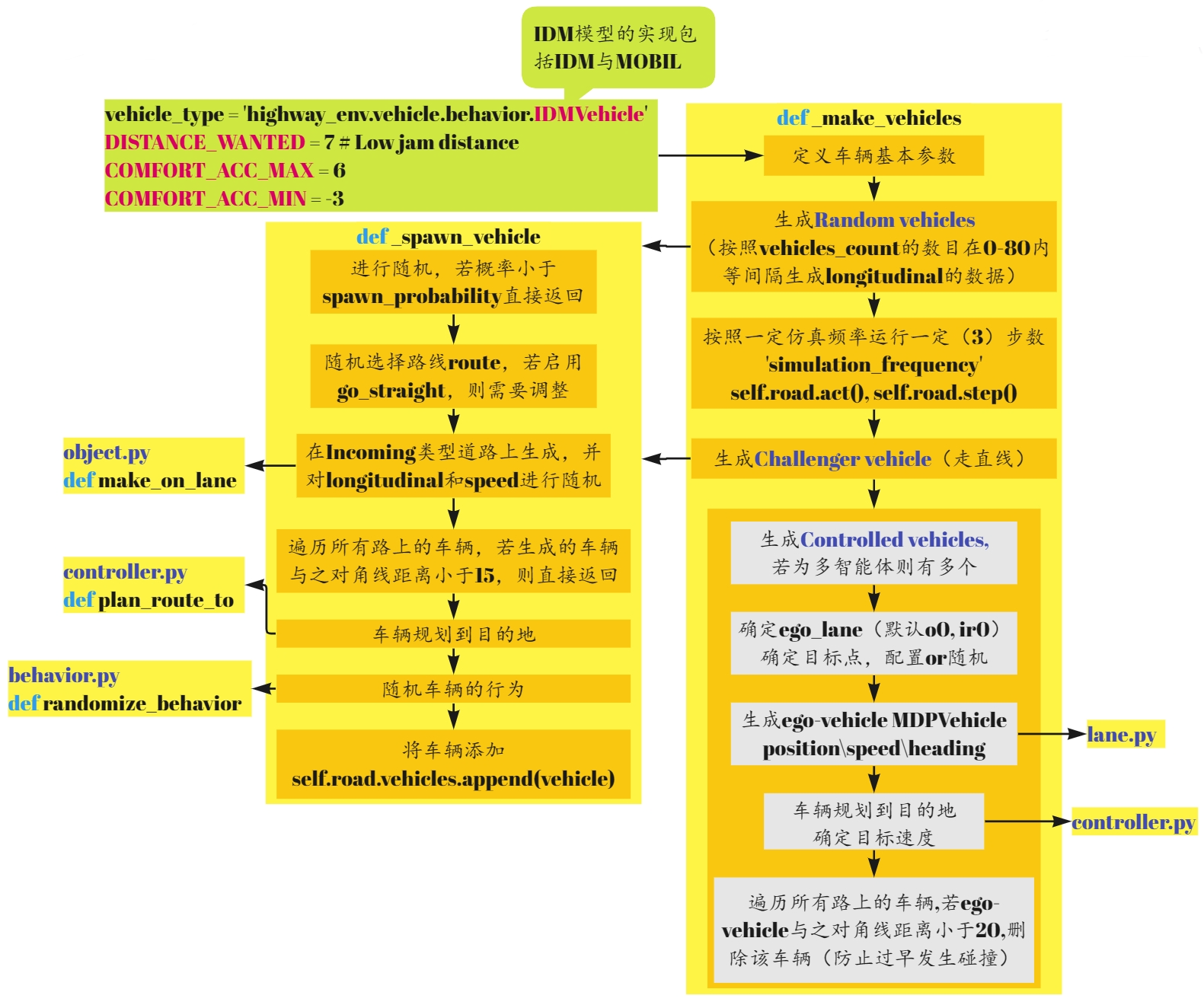
def _make_vehicles(self, n_vehicles: int = 10) -> None:
"""
Populate a road with several vehicles on the highway and on the merging lane
:return: the ego-vehicle
"""
# Configure vehicles
vehicle_type = utils.class_from_path(self.config["other_vehicles_type"])
vehicle_type.DISTANCE_WANTED = 7 # Low jam distance
vehicle_type.COMFORT_ACC_MAX = 6
vehicle_type.COMFORT_ACC_MIN = -3
# Random vehicles
simulation_steps = 3
for t in range(n_vehicles - 1):
self._spawn_vehicle(np.linspace(0, 80, n_vehicles)[t])
for _ in range(simulation_steps):
[(self.road.act(), self.road.step(1 / self.config["simulation_frequency"])) for _ in range(self.config["simulation_frequency"])]
# Challenger vehicle
self._spawn_vehicle(60, spawn_probability=1, go_straight=True, position_deviation=0.1, speed_deviation=0)
# Controlled vehicles
self.controlled_vehicles = []
for ego_id in range(0, self.config["controlled_vehicles"]):
ego_lane = self.road.network.get_lane(("o{}".format(ego_id % 4), "ir{}".format(ego_id % 4), 0))
destination = self.config["destination"] or "o" + str(self.np_random.randint(1, 4))
ego_vehicle = self.action_type.vehicle_class(
self.road,
ego_lane.position(60 + 5*self.np_random.normal(1), 0),
speed=ego_lane.speed_limit,
heading=ego_lane.heading_at(60))
try:
ego_vehicle.plan_route_to(destination)
ego_vehicle.speed_index = ego_vehicle.speed_to_index(ego_lane.speed_limit)
ego_vehicle.target_speed = ego_vehicle.index_to_speed(ego_vehicle.speed_index)
except AttributeError:
pass
self.road.vehicles.append(ego_vehicle)
self.controlled_vehicles.append(ego_vehicle)
for v in self.road.vehicles: # Prevent early collisions
if v is not ego_vehicle and np.linalg.norm(v.position - ego_vehicle.position) < 20:
self.road.vehicles.remove(v)
_spawn_vehicle
def _spawn_vehicle(self,
longitudinal: float = 0,
position_deviation: float = 1.,
speed_deviation: float = 1.,
spawn_probability: float = 0.6,
go_straight: bool = False) -> None:
if self.np_random.uniform() > spawn_probability:
return
route = self.np_random.choice(range(4), size=2, replace=False)
route[1] = (route[0] + 2) % 4 if go_straight else route[1]
vehicle_type = utils.class_from_path(self.config["other_vehicles_type"])
vehicle = vehicle_type.make_on_lane(self.road, ("o" + str(route[0]), "ir" + str(route[0]), 0),
longitudinal=(longitudinal + 5
+ self.np_random.normal() * position_deviation),
speed=8 + self.np_random.normal() * speed_deviation)
for v in self.road.vehicles:
if np.linalg.norm(v.position - vehicle.position) < 15:
return
vehicle.plan_route_to("o" + str(route[1]))
vehicle.randomize_behavior()
self.road.vehicles.append(vehicle)
return vehicle
6.step
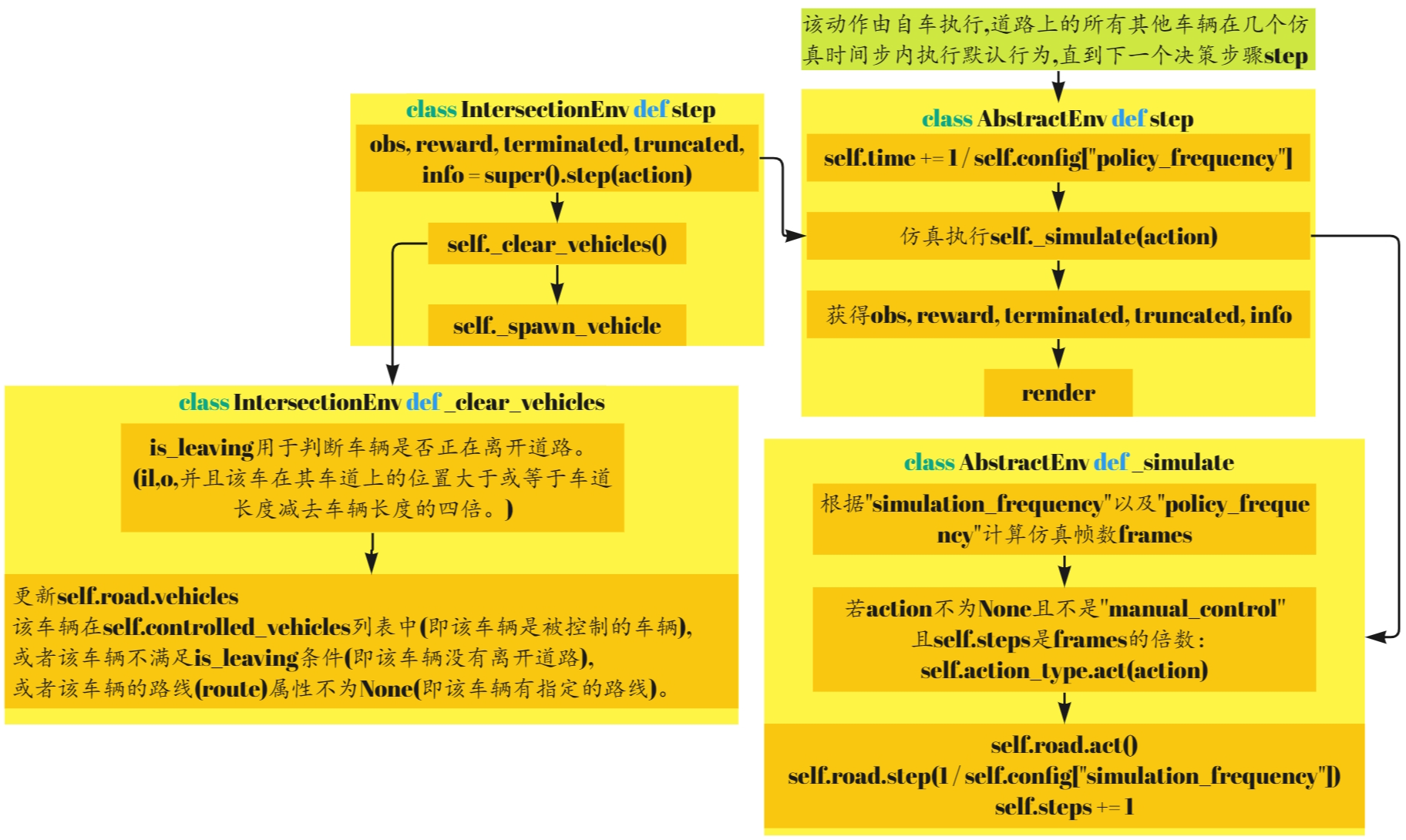
abstract.py
def step(self, action: Action) -> Tuple[Observation, float, bool, bool, dict]:
"""
Perform an action and step the environment dynamics.
The action is executed by the ego-vehicle, and all other vehicles on the road performs their default behaviour
for several simulation timesteps until the next decision making step.
:param action: the action performed by the ego-vehicle
:return: a tuple (observation, reward, terminated, truncated, info)
"""
if self.road is None or self.vehicle is None:
raise NotImplementedError("The road and vehicle must be initialized in the environment implementation")
self.time += 1 / self.config["policy_frequency"]
self._simulate(action)
obs = self.observation_type.observe()
reward = self._reward(action)
terminated = self._is_terminated()
truncated = self._is_truncated()
info = self._info(obs, action)
if self.render_mode == 'human':
self.render()
return obs, reward, terminated, truncated, info
intersection_env.py
def step(self, action: int) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, float, bool, bool, dict]:
obs, reward, terminated, truncated, info = super().step(action)
self._clear_vehicles()
self._spawn_vehicle(spawn_probability=self.config["spawn_probability"])
return obs, reward, terminated, truncated, info
def _simulate(self, action: Optional[Action] = None) -> None:
"""Perform several steps of simulation with constant action."""
frames = int(self.config["simulation_frequency"] // self.config["policy_frequency"])
for frame in range(frames):
# Forward action to the vehicle
if action is not None \
and not self.config["manual_control"] \
and self.steps % int(self.config["simulation_frequency"] // self.config["policy_frequency"]) == 0:
self.action_type.act(action)
self.road.act()
self.road.step(1 / self.config["simulation_frequency"])
self.steps += 1
# Automatically render intermediate simulation steps if a viewer has been launched
# Ignored if the rendering is done offscreen
if frame < frames - 1: # Last frame will be rendered through env.render() as usual
self._automatic_rendering()
self.enable_auto_render = False