本篇主要介绍mlr3包的基本使用。
一个简单的机器学习流程在mlr3中可被分解为以下几个部分:
- 创建任务
比如回归、分裂、生存分析、降维、密度任务等等 - 挑选学习器(算法/模型)
比如随机森林、决策树、SVM、KNN等等 - 训练和预测
创建任务
本次示例将使用mtcars数据集创建一个回归任务,结果变量(或者叫因变量等等)是mpg。
# 首先加载数据
data("mtcars",package = "datasets")
data <- mtcars[,1:3]
str(data)
## 'data.frame': 32 obs. of 3 variables:
## $ mpg : num 21 21 22.8 21.4 18.7 18.1 14.3 24.4 22.8 19.2 ...
## $ cyl : num 6 6 4 6 8 6 8 4 4 6 ...
## $ disp: num 160 160 108 258 360 ...
使用as_task_regr()创建回归任务,as_task_classif()可创建分类任务。
library(mlr3)
task_mtcars <- as_task_regr(data,target = "mpg",id="cars") # id是随便起一个名字
print(task_mtcars)
## <TaskRegr:cars> (32 x 3)
## * Target: mpg
## * Properties: -
## * Features (2):
## - dbl (2): cyl, disp
可以看到数据以供32行,3列,target是mpg,feature是cyl和disp,都是bdl类型。
在创建模型前先探索数据:
library("mlr3viz") # 使用此包可视化数据
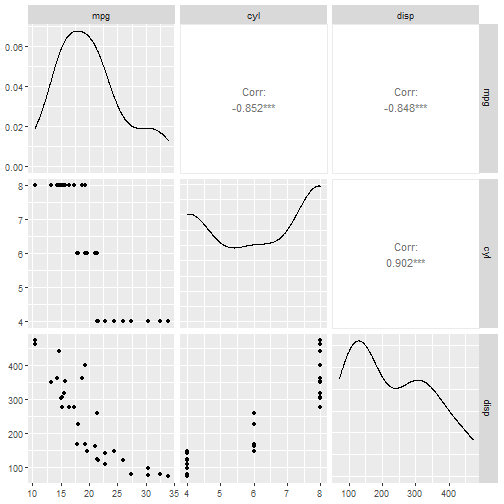
autoplot(task_mtcars, type = "pairs") # 基于GGally,我之前介绍过
## Registered S3 method overwritten by 'GGally':
## method from
## +.gg ggplot2
如果你觉得每次加载1个R包很烦,可以直接使用library(mlr3verse)加载所有基础包!
如果你想使用自带数据集进行学习,此包也自带了很多流行的机器学习数据集。
查看内置数据集:
as.data.table(mlr_tasks)
## key task_type nrow ncol properties lgl int dbl chr fct ord pxc
## 1: boston_housing regr 506 19 0 3 13 0 2 0 0
## 2: breast_cancer classif 683 10 twoclass 0 0 0 0 0 9 0
## 3: german_credit classif 1000 21 twoclass 0 3 0 0 14 3 0
## 4: iris classif 150 5 multiclass 0 0 4 0 0 0 0
## 5: mtcars regr 32 11 0 0 10 0 0 0 0
## 6: penguins classif 344 8 multiclass 0 3 2 0 2 0 0
## 7: pima classif 768 9 twoclass 0 0 8 0 0 0 0
## 8: sonar classif 208 61 twoclass 0 0 60 0 0 0 0
## 9: spam classif 4601 58 twoclass 0 0 57 0 0 0 0
## 10: wine classif 178 14 multiclass 0 2 11 0 0 0 0
## 11: zoo classif 101 17 multiclass 15 1 0 0 0 0 0
结果很详细,给出了任务类型,行列数,变量类型等。
如果想要使用内置数据集,可使用以下代码:
task_penguin <- tsk("penguins")
print(task_penguin)
## <TaskClassif:penguins> (344 x 8)
## * Target: species
## * Properties: multiclass
## * Features (7):
## - int (3): body_mass, flipper_length, year
## - dbl (2): bill_depth, bill_length
## - fct (2): island, sex
可以非常方便的取子集查看:
library("mlr3verse")
as.data.table(mlr_tasks)[, 1:4]
## key task_type nrow ncol
## 1: actg surv 1151 13
## 2: bike_sharing regr 17379 14
## 3: boston_housing regr 506 19
## 4: breast_cancer classif 683 10
## 5: faithful dens 272 1
## 6: gbcs surv 686 10
## 7: german_credit classif 1000 21
## 8: grace surv 1000 8
## 9: ilpd classif 583 11
## 10: iris classif 150 5
## 11: kc_housing regr 21613 20
## 12: lung surv 228 10
## 13: moneyball regr 1232 15
## 14: mtcars regr 32 11
## 15: optdigits classif 5620 65
## 16: penguins classif 344 8
## 17: pima classif 768 9
## 18: precip dens 70 1
## 19: rats surv 300 5
## 20: sonar classif 208 61
## 21: spam classif 4601 58
## 22: titanic classif 1309 11
## 23: unemployment surv 3343 6
## 24: usarrests clust 50 4
## 25: whas surv 481 11
## 26: wine classif 178 14
## 27: zoo classif 101 17
## key task_type nrow ncol
![]()
支持非常多探索数据的操作:
task_penguin$ncol
## [1] 8
task_penguin$nrow
## [1] 344
task_penguin$feature_names
## [1] "bill_depth" "bill_length" "body_mass" "flipper_length"
## [5] "island" "sex" "year"
task_penguin$feature_types
## id type
## 1: bill_depth numeric
## 2: bill_length numeric
## 3: body_mass integer
## 4: flipper_length integer
## 5: island factor
## 6: sex factor`在这里插入代码片`
## 7: year integer
task_penguin$target_names
## [1] "species"
task_penguin$task_type
## [1] "classif"
task_penguin$data()
## species bill_depth bill_length body_mass flipper_length island sex
## 1: Adelie 18.7 39.1 3750 181 Torgersen male
## 2: Adelie 17.4 39.5 3800 186 Torgersen female
## 3: Adelie 18.0 40.3 3250 195 Torgersen female
## 4: Adelie NA NA NA NA Torgersen <NA>
## 5: Adelie 19.3 36.7 3450 193 Torgersen female
## ---
## 340: Chinstrap 19.8 55.8 4000 207 Dream male
## 341: Chinstrap 18.1 43.5 3400 202 Dream female
## 342: Chinstrap 18.2 49.6 3775 193 Dream male
## 343: Chinstrap 19.0 50.8 4100 210 Dream male
## 344: Chinstrap 18.7 50.2 3775 198 Dream female
## year
## 1: 2007
## 2: 2007
## 3: 2007
## 4: 2007
## 5: 2007
## ---
## 340: 2009
## 341: 2009
## 342: 2009
## 343: 2009
## 344: 2009
task_penguin$head(3)
## species bill_depth bill_length body_mass flipper_length island sex
## 1: Adelie 18.7 39.1 3750 181 Torgersen male
## 2: Adelie 17.4 39.5 3800 186 Torgersen female
## 3: Adelie 18.0 40.3 3250 195 Torgersen female
## year
## 1: 2007
## 2: 2007
## 3: 2007
# 还有很多行列选择操作、改变变量的id(比如某个变量不参与模型训练)等多种操作
![]()
可视化数据:很多都是基于GGally包,可以看我之前的介绍
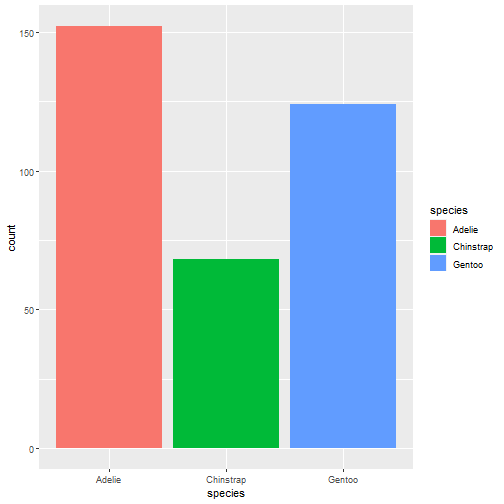
autoplot(task_penguin)
- 1
autoplot(task_penguin, type = "pairs")
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
## `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value with `binwidth`.
![]()

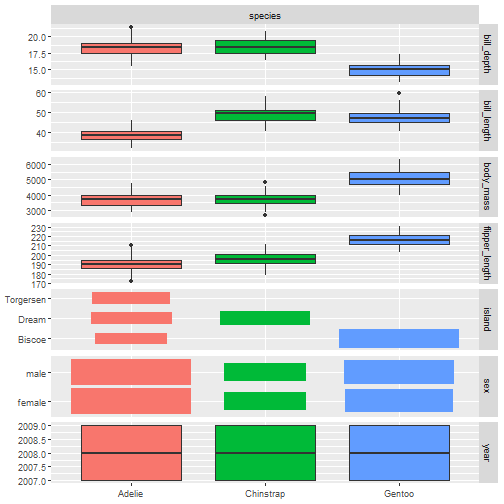
autoplot(task_penguin, type = "duo")
- 1
创建learner
所有的学习器都通过以下2个步骤工作: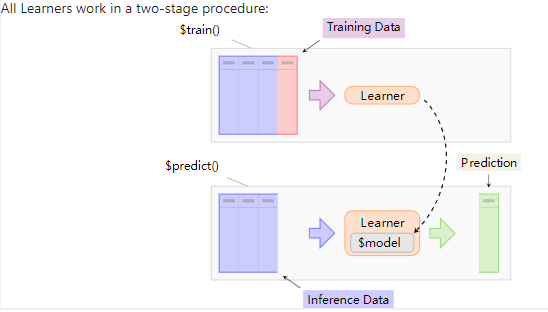
mlr3verse只支持常见的学习器,比如随机森林、决策树、SVM、KNN等,如果想要查看所有的学习器,可以安装mlr3extralearners。
查看所有的支持的learner:
All learners
# 加载R包,常见的算法
library("mlr3verse")
mlr_learners
## <DictionaryLearner> with 53 stored values
## Keys: classif.cv_glmnet, classif.debug, classif.featureless,
## classif.glmnet, classif.kknn, classif.lda, classif.log_reg,
## classif.multinom, classif.naive_bayes, classif.nnet, classif.qda,
## classif.ranger, classif.rpart, classif.svm, classif.xgboost,
## clust.agnes, clust.ap, clust.cmeans, clust.cobweb, clust.dbscan,
## clust.diana, clust.em, clust.fanny, clust.featureless, clust.ff,
## clust.hclust, clust.kkmeans, clust.kmeans, clust.MBatchKMeans,
## clust.meanshift, clust.pam, clust.SimpleKMeans, clust.xmeans,
## dens.hist, dens.kde, regr.cv_glmnet, regr.debug, regr.featureless,
## regr.glmnet, regr.kknn, regr.km, regr.lm, regr.ranger, regr.rpart,
## regr.svm, regr.xgboost, surv.coxph, surv.cv_glmnet, surv.glmnet,
## surv.kaplan, surv.ranger, surv.rpart, surv.xgboost
![]()
创建learner
# 决策树
learner = lrn("classif.rpart")
print(learner)
## <LearnerClassifRpart:classif.rpart>
## * Model: -
## * Parameters: xval=0
## * Packages: mlr3, rpart
## * Predict Type: response
## * Feature types: logical, integer, numeric, factor, ordered
## * Properties: importance, missings, multiclass, selected_features,
## twoclass, weights
查看支持的超参数
learner$param_set
## <ParamSet>
## id class lower upper nlevels default value
## 1: cp ParamDbl 0 1 Inf 0.01
## 2: keep_model ParamLgl NA NA 2 FALSE
## 3: maxcompete ParamInt 0 Inf Inf 4
## 4: maxdepth ParamInt 1 30 30 30
## 5: maxsurrogate ParamInt 0 Inf Inf 5
## 6: minbucket ParamInt 1 Inf Inf <NoDefault[3]>
## 7: minsplit ParamInt 1 Inf Inf 20
## 8: surrogatestyle ParamInt 0 1 2 0
## 9: usesurrogate ParamInt 0 2 3 2
## 10: xval ParamInt 0 Inf Inf 10 0
一目了然,方便使用,记不住了可以看看,毕竟太多了,这一点比tidymodels贴心。
设定超参数的值
learner$param_set$values = list(cp = 0.01, xval = 0)
learner
## <LearnerClassifRpart:classif.rpart>
## * Model: -
## * Parameters: cp=0.01, xval=0
## * Packages: mlr3, rpart
## * Predict Type: response
## * Feature types: logical, integer, numeric, factor, ordered
## * Properties: importance, missings, multiclass, selected_features,
## twoclass, weights
也可以在指定learner时设定
learner = lrn("classif.rpart", xval=0, cp = 0.001)
learner$param_set$values
## $xval
## [1] 0
##
## $cp
## [1] 0.001
训练、预测和性能评价
创建任务,选择模型
library("mlr3verse")
task = tsk("penguins") # 使用内置数据集
learner = lrn("classif.rpart") #决策树分类
划分训练集和测试集
spilt <- partition(task,ratio = 0.6, stratify = T)
spilt$train
## [1] 2 3 4 5 7 8 10 11 12 14 15 16 17 19 23 25 26 27
## [19] 28 30 31 33 34 36 37 40 42 45 46 48 50 51 53 56 59 60
## [37] 61 62 64 66 67 68 69 71 73 75 78 82 83 84 88 89 91 94
## [55] 96 97 99 100 101 102 104 107 108 113 114 115 118 120 121 123 125 126
## [73] 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 135 136 137 138 139 142 143 145 149 150 151
## [91] 152 154 156 157 159 160 163 169 170 171 172 173 175 176 179 180 181 182
## [109] 183 186 187 188 189 193 194 197 199 200 201 203 206 208 210 211 212 213
## [127] 214 215 216 218 219 220 222 223 224 225 226 228 229 230 233 236 237 239
## [145] 240 241 242 243 247 248 249 252 253 254 255 256 257 259 260 262 266 271
## [163] 272 273 274 277 279 280 285 288 290 291 293 294 295 296 297 299 300 301
## [181] 302 304 305 306 309 310 312 313 317 319 321 322 323 324 325 328 330 331
## [199] 332 334 337 338 339 340 341 342
训练模型
learner$train(task, row_ids = spilt$train)
print(learner$model)
## n= 206
##
## node), split, n, loss, yval, (yprob)
## * denotes terminal node
##
## 1) root 206 115 Adelie (0.44174757 0.19902913 0.35922330)
## 2) flipper_length< 207.5 128 39 Adelie (0.69531250 0.30468750 0.00000000)
## 4) bill_length< 42.35 86 0 Adelie (1.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000) *
## 5) bill_length>=42.35 42 3 Chinstrap (0.07142857 0.92857143 0.00000000) *
## 3) flipper_length>=207.5 78 4 Gentoo (0.02564103 0.02564103 0.94871795) *
预测
prediction <- learner$predict(task, row_ids = spilt$test)
print(prediction)
## <PredictionClassif> for 138 observations:
## row_ids truth response
## 1 Adelie Adelie
## 6 Adelie Adelie
## 9 Adelie Adelie
## ---
## 336 Chinstrap Chinstrap
## 343 Chinstrap Gentoo
## 344 Chinstrap Chinstrap
混淆矩阵
prediction$confusion
## truth
## response Adelie Chinstrap Gentoo
## Adelie 53 1 0
## Chinstrap 8 24 2
## Gentoo 0 2 48
可视化
autoplot(prediction)
- 1
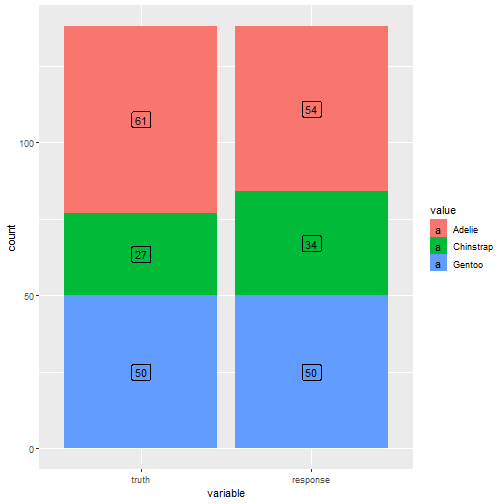
模型评价
先查看下支持的评价指标
mlr_measures
## <DictionaryMeasure> with 87 stored values
## Keys: aic, bic, classif.acc, classif.auc, classif.bacc, classif.bbrier,
## classif.ce, classif.costs, classif.dor, classif.fbeta, classif.fdr,
## classif.fn, classif.fnr, classif.fomr, classif.fp, classif.fpr,
## classif.logloss, classif.mbrier, classif.mcc, classif.npv,
## classif.ppv, classif.prauc, classif.precision, classif.recall,
## classif.sensitivity, classif.specificity, classif.tn, classif.tnr,
## classif.tp, classif.tpr, clust.ch, clust.db, clust.dunn,
## clust.silhouette, clust.wss, debug, dens.logloss, oob_error,
## regr.bias, regr.ktau, regr.mae, regr.mape, regr.maxae, regr.medae,
## regr.medse, regr.mse, regr.msle, regr.pbias, regr.rae, regr.rmse,
## regr.rmsle, regr.rrse, regr.rse, regr.rsq, regr.sae, regr.smape,
## regr.srho, regr.sse, selected_features, sim.jaccard, sim.phi,
## surv.brier, surv.calib_alpha, surv.calib_beta, surv.chambless_auc,
## surv.cindex, surv.dcalib, surv.graf, surv.hung_auc, surv.intlogloss,
## surv.logloss, surv.mae, surv.mse, surv.nagelk_r2, surv.oquigley_r2,
## surv.rmse, surv.schmid, surv.song_auc, surv.song_tnr, surv.song_tpr,
## surv.uno_auc, surv.uno_tnr, surv.uno_tpr, surv.xu_r2, time_both,
## time_predict, time_train
![]()
这里我们选择accuracy
measure <- msr("classif.acc")
prediction$score(measure)
## classif.acc
## 0.9057971
选择多个指标:
measures <- msrs(c("classif.acc","classif.auc","classif.ce"))
prediction$score(measures)
## classif.acc classif.auc classif.ce
## 0.9057971 NaN 0.0942029