今日内容
零、 复习昨日
一、MySQL
一、约束
1.1 约束
是什么? 约束,即限制,就是通过设置约束,可以限制对数据表数据的插入,删除,更新
怎么做?
约束设置的语法,大部分是
create table 表名( 字段 数据类型(长度) 约束, 字段 数据类型(长度) 约束 );
1.1 数据类型
其实数据类型也是一种约束,例如设置id列为int类型,那就不能乱给id设置字符串或者日期等数据
1.2 主键约束[重要]
主键(
primary key)约束非常重要,以后开发中基本上每张表都要有主键约束,作用是设置了主键约束的列,有以下效果
- 不能为空
- 不能重复
一般主键是给id设置的
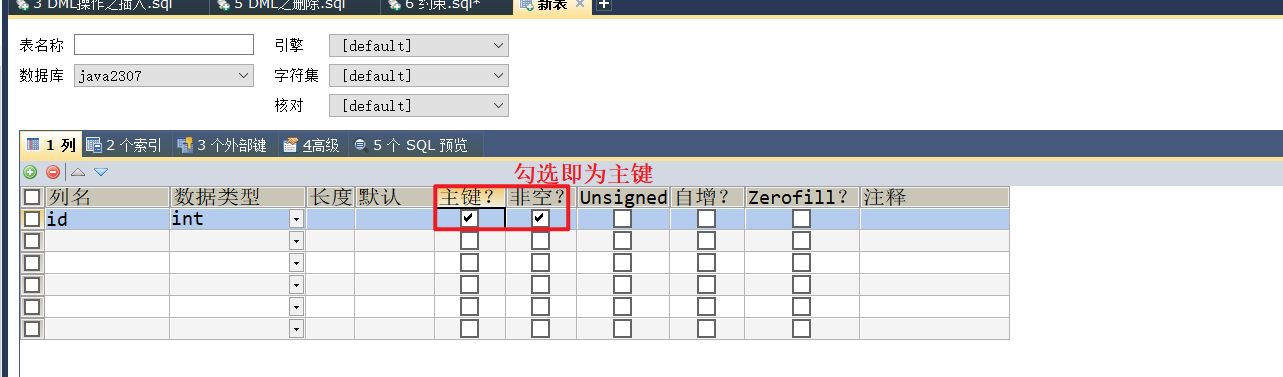
设置主键方式有四种:
- 在建表时给列直接指定
- 在建表语句的最后指定某一列是主键
- 给以建好的表修改设置主键
- 图形化操作
-- =============== 主键约束 ===============
-- 主键约束: 该列数据不能为空,不能重复
-- 方案1: 建表时给定主键
create table tb_1(
id int primary key, -- 建表时设置id为主键
age int
);
insert into tb_1 (age) value (18); -- 报错,主键不能为空
insert into tb_1 (id) value (1);
insert into tb_1 (id) value (1); -- 报错,主键不能重复
-- 方案2: 建表时,在最后设置主键
create table tb_2(
id int,
age int,
primary key(id)
);
insert into tb_2 (age) value (18); -- 报错,主键不能为空
insert into tb_2 (id) value (1);
insert into tb_2 (id) value (1); -- 报错,主键不能重复
-- 这种设置主键的方式,一般适合用于设置联合主键
create table tb_3(
id int,
age int,
primary key(id,age) -- id和age是联合主键
);
insert into tb_3 (age) value (18); -- 报错,主键id不能为空
insert into tb_3 (id) value (1); -- 报错,主键age不能为空
insert into tb_3 (id,age) value (1,18); -- 可以
insert into tb_3 (id,age) value (2,18); -- 可以
insert into tb_3 (id,age) value (2,11); -- 可以
insert into tb_3 (id,age) value (1,18); -- 报错,联合主键重复
-- 方案3: 建表后再修改添加主键
create table tb_4(
id int,
age int
);
insert into tb_4 (age) value (18);
insert into tb_4 (id) value (1);
-- 修改表,添加主键
alter table tb_4 add primary key(id);
-- 方案4:图形操作
insert into tb_5 (age) value (18);
insert into tb_5 (id) value (1);
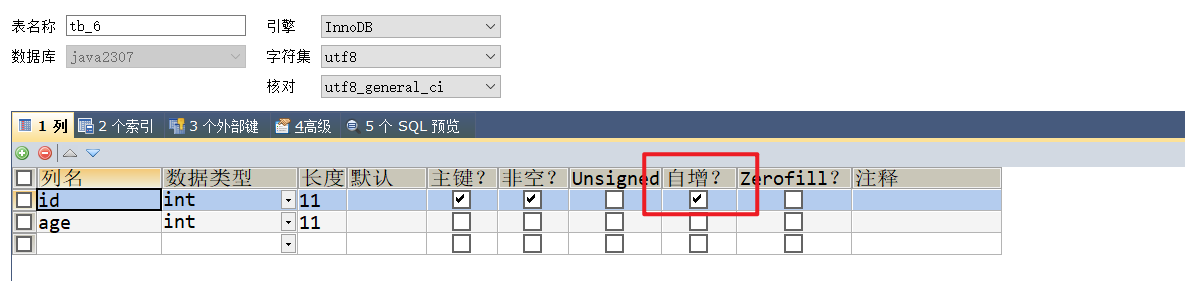
1.3 自增约束
自增(
auto_increment)约束,主要是配合主键使用,防止主键为空,重复
-- =============== 主键自增约束 ===============
create table tb_6(
id int primary key auto_increment,
age int
);
insert into tb_6 (age) value (18);-- 没有给主键赋值,会从1开始递增
insert into tb_6 (age) value (18);-- 每次递增1
insert into tb_6 (id,age) value (4,18);-- 虽然有递增,也可以自己指定
insert into tb_6 (age) value (18);-- 在上一行数据基础上递增1
delete from tb_6 where id = 5; -- 删除数据不影响递增
insert into tb_6 (age) value (18);
1…4 唯一约束
唯一(
unique)约束,设置了唯一约束的列,的值不能重复
-- ================= 唯一约束 ================
create table t5(
id int,
name varchar(20) unique -- 唯一约束
);
insert into t5(name) values('aa');
-- 报错,name列的值重复, Duplicate entry 'aa' for key 'name'
insert into t5(name) values('aa');
1.5 非空约束
非空(
not null)约束,设置了非空约束的列的值不能为空
-- ================= 非空约束 ================
create table t6(
id int,
name varchar(20) not null -- 非空约束
);
-- name不能没有值
insert into t6 (id) values (1);
-- 给name赋值
insert into t6 (id,name) values (1,'aaa');
-- 只是不能为空,可以重复
insert into t6 (id,name) values (2,'aaa');
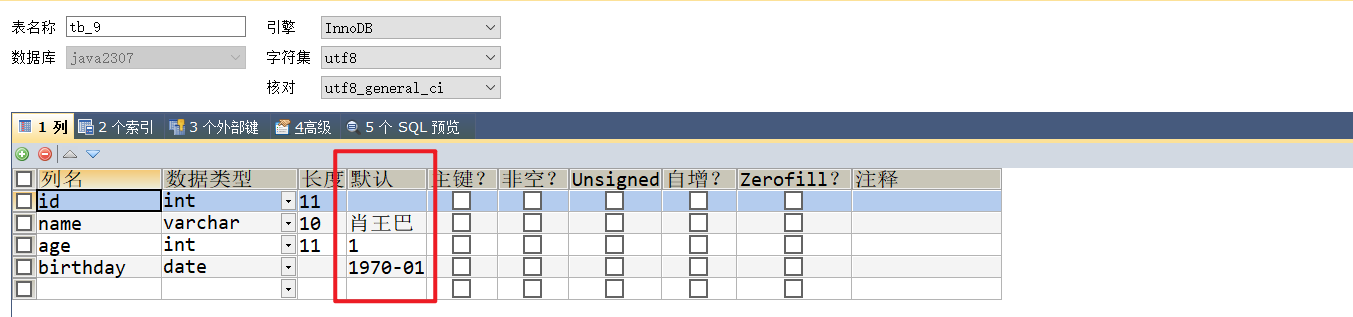
1.6 默认值
默认值(
default),给列设置默认值约束后,如果该列在插入数据时没有给值,就自动赋值默认值
-- =============== 默认值约束 ===============
-- 默认的默认值是null
-- 也可以主动设置默认值
create table tb_1. (
id int,
name varchar(10) default '肖王巴',
age int default 1,
birthday date default '11.70-01-01'
)
insert into tb_1. (id) values (1);-- 其他列没设置值,就会用默认值替代
insert into tb_1. (id,name,age,birthday)
values (2,'小李',18,'2020-01-01');-- 给定有值,就不使用默认值
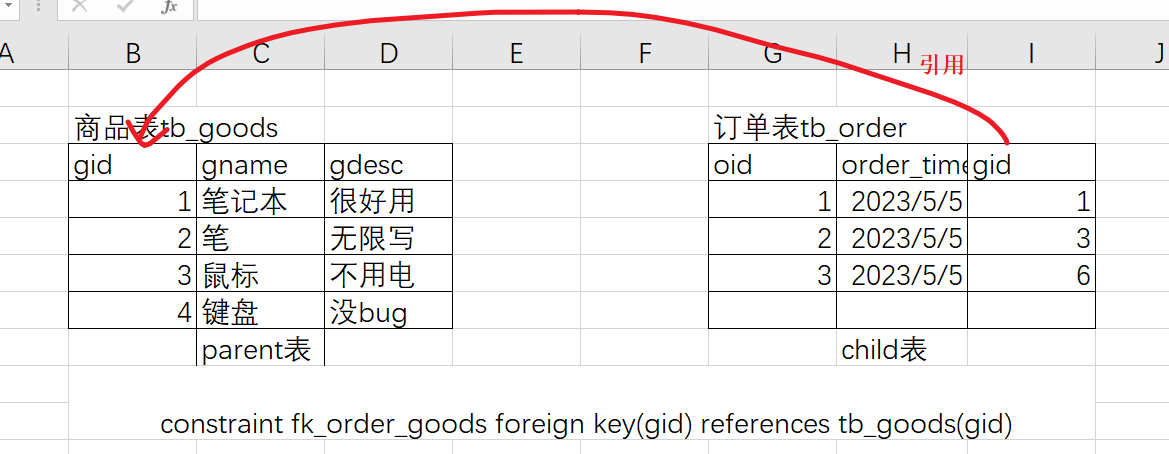
1.7 外键约束[了解]
外键,是多表之间接的一种关联关系的一种限制.
语法
constraint 外键名 foreign key (当前表中的列名) references 表(主键);
设计订单表和商品表,订单表的数据要关联商品表数据
-- 商品表
create table tb_goods(
gid int primary key,
gname varchar(20),
descr varchar(20)
);
-- 订单表 (订单表关联了商品表)
create table tb_order(
oid int primary key,
order_time datetime,
gid int,
-- 设置外键
constraint fk_order_goods foreign key(gid) references tb_goods(gid)
);
/*
被引用的表称为父表 parent , tb_goods
引用别人的表称为子表 child , tb_order
*/
-- 给父表随便插入数据
insert into tb_goods values (2,'键盘','敲代码没有bug');
-- 给子表随便插入数据不行!! 这个数据得是父表中有的才行
insert into tb_order values (1,'2022-11-11',1);
-- 子表可以删除数据
delete from tb_order where oid = 1;
-- 父表被引用的数据不能删除
delete from tb_goods where gid = 2;
delete from tb_goods where gid = 1;
1.8 练习
自己创建表,设计字段,把所有约束都试一遍
宠物(pet)表
id 整型 主键自增
昵称 字符串 唯一
体重 浮点型 不能为空
性别 默认值 公
create table pet(
id int primary key auto_increment,
nick varchar(10) unique,
weight double(10,2) not null,
sex char(1) default '公'
);
插入,更新测试
insert into pet (nick,weight) values ('小黑',5.2);
二、DQL[非常重要]
DQL 主要指查询语句,有查询单表数据,也有查多表数据表,今天主要学习
单表查询
- 基本查询
- 条件查询
- 模糊查询
- 排序查询
- 聚合查询
- 去重查询
- 分组查询
- 限制查询
2.1 数据准备
将发的stu.sql导入到MySql中

2.2 基本查询
select 字段1,字段2,… from 表名;
查询返回的是一张
虚拟表,查询对原表数据没有任何影响,默认查询的全表数据
-- 基本查询
-- 查询所有列
select sid,sname,age,sex,score,cid groupLeaderId from stu;
-- 查询所有列,在测试,练习时可以使用*代替
select * from stu;
-- 查询指定 列
select sid,sname,sex from stu;
-- 查询的列名可以取别名,使用as,但是一般as不写
select sid as 学号,sname as 姓名,score 成绩 from stu
-- 年龄+1
select age+1 from stu;
| 算数运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| + | 两列做加法运算 |
| - | 两列做减法运算 |
| * | 两列做乘法运算 |
| / | 两列做除法运算 |
注意:%是占位符,而非模运算符。
2.3 条件查询
条件查询就是在基础查询基础上,再给sql设置条件,只查询
部分符合条件的数据
条件语句 : select 字段1,字段2,… from 表名
where 字段 条件 值;
条件运算符
- = ,在这里是相等,不是赋值
>- <
>=- <=
- !=
- and 条件并列
- or 条件选择
- in 范围
- not in
- between…and 条件范围
-- ============== 条件查询 ==============
-- 查询学号为1001的学生信息
select * from stu where sid = 1001;
-- 查询学生成绩大于60的学生id 姓名,成绩
select sid,sname,score from stu where score > 60;
-- 查询学生性别为女,并且年龄小于50的记录
select * from stu where sex = '女' and age < 50;
-- 查询学生学号为1001,或者姓名为李四的记录
select * from stu where sid = 1001 or sname = '李四';
-- 查询学号为1001,1002,1003的记录
select * from stu where sid = 1001 or sid = 1002 or sid = 1003;
select * from stu where sid in (1001,1002,1003);
select * from stu where sid >= 1001 and sid <= 1003;
-- 查询学号不是1001,1002,1003的记录
select * from stu where sid not in (1001,1002,1003);
select * from stu where sid != 1001 and sid != 1002 and sid != 1003;
-- 查询学生年龄在20到40之间的学生记录
select * from stu where age >= 20 and age <= 40;
select * from stu where age between 20 and 40;
-- 查询性别非男的学生记录
select * from stu where sex != '男';
select * from stu where sex = '女';
-- 查询性别为null的学生记录
update stu set sex = null where sid = 1001.;
-- 查询是不能=null运算
-- select * from stu where sex = null;
select * from stu where sex is null;
-- 查询性别不为null的学生记录
select * from stu where sex is not null;
2.4 模糊查询
模糊查询其实也是条件查询
语法: select 字段1,字段2,… from 表名 where
字段 like '_值%';
- % 匹配任意多个字符
-- ============== 模糊查询 ==============
-- 查询姓名以“张”开头的学生记录
select * from stu where sname like '张%';
-- 查询姓名中包含“三”的学生记录
select * from stu where sname like '%三%';
2.5 排序查询
对查询后的数据按照指定字段以及指定规则排序
语法: select 字段1,字段2,… from 表名
order by 字段 [desc|asc];
- desc 降序
- asc 升序,默认是升序
排序查询写在最后
-- ============== 排序查询 ==============
-- 查询所有学生记录,按年龄升序排序
select * from stu order by age asc;
select * from stu order by age;
-- 查询所有学生记录,按年龄降序排序
select * from stu order by age desc;
-- 查询所有学生记录,按年龄升序排序,如果年龄相同时,按编号降序排序
select * from stu order by age asc , sid desc;
-- 查询成绩大于60的学生id,姓名,成绩,并根据成绩降序
select sid,sname,score from stu where score > 60 order by score desc;
2.6 聚合函数
将查询的结果,聚合运算得到
一个结果值,语法特点
聚合运算完,结果只有一行数据其他字段不能和聚合函数同时查询,除非有分组查询
聚合函数分类
- count(expr) 计算指定列的不为null的行数
- max(expr) 计算指定列的最大值
- min(expr) 计算指定列的最小值
- avg(expr) 计算指定列的平均数,除以不为null的条数
- sum(expr) 计算指定列的和 ,计算不为null的数据
- 函数中的expr,可以写列名,也可以写函数表达式
语法: select 聚合函数(字段) from 表名;
-- ================== 聚合函数 ==================
/*
聚合函数:
把多行数据聚合在一起运算得到一个结果
注意:
聚合函数执行完,返回的结果只有一行记录
与聚合函数一同出现的列必须出现在group by后
函数:
count(字段) : 对该列不为null的行计数
sum(字段): 对该列不为null的数据求和
avg(字段): 对该列不为null的数据求和再求平均值
min(字段): 对该列不为null的数据求最小值
max(字段): 对该列不为null的数据求最大值
语法:
放在select后from前,对查询的结果列进行运算
放在having后使用
*/
-- 查询stu表中记录数
select count(sid) from stu;
select count(sid),sname from stu; -- 报错,语法不对
-- 查询stu表中有成绩的人数
select count(score) from stu;
select count(sex) from stu;
-- 查询stu表中成绩大于60的人数
-- 先执行from获得全部数据,再通过where过滤数据,再计算select后
select count(sid) from stu where score > 60;
-- 查询所有学生成绩和
select sum(score) from stu;
-- 统计所有学生平均成绩(所有有成绩的人的平均分)
select avg(score) from stu;
-- 统计所有学生平均成绩(所有人包括成绩为空的)
select sum(score) / count(sid) from stu;
select sname,age from stu;
-- 扩展: 使用as取别名,as可以省略
select sum(score) / count(sid) as 平均数 from stu;-- 可以
select sum(score) / count(sid) as '平均数' from stu;-- 可以
select sum(score) / count(sid) '平均数' from stu;-- 可以
-- 查询最高成绩和最低成绩
select max(score),min(score) from stu;
select max(score) 'max',min(score) 'min' from stu;
2.7 去重函数[了解]
可以将某列数据去重查询,
distinct,一般不单独使用,配合聚合函数使用
-- ============== 去重查询 ==============
-- 查询年龄不重复的共有多少人
select count(distinct age) from stu;
2.8 分组查询
分组查询,就是按照一定条件(列)将查询的数据分为几组.
语法: select 字段1,字段2,… from 表名 [where 字段 条件 值]
group by 字段 having 字段 条件值;
- group by 字段,根据指定字段分组
- having 字段 值, 分组后再过滤
有个非常重要特点: SQL只要有分组,分成几组,查询结果就只有几行,所以一般配合聚合函数来使用,是组内数据的聚合
与聚合函数同时出现的列,必须出现在group by语句中
或者说group by后面的字段可以出现在select后
having和where都是过滤
- where是分组前过滤,having是分组后过滤
- where后不能使用聚合函数,having可以聚合函数
-- ================== 分组查询 ==================
/*
分组查询:
按照一定条件将数据分成若干组,然后对每个组内单独操作
主要事项:
分组查询的结果,有几组结果就几行
与聚合函数一同出现的列必须出现在group by后
或者说,group by后出现的列可以与聚合函数同时出现
语法:
select * from tb_name where ... group by 字段 having 条件
having 和where区别:
- having是分组后过滤数据,where是分组前过滤数据
- having后可以跟聚合函数的,where后不行
*/
-- 查询男生多少人,女生多少人
select count(sid) from stu group by sex;
-- 查询男生多少人,女生多少人
select sex,count(sid) from stu group by sex;-- 可以,3行(男,女,空)
-- 查询男生多少人,女生多少人,以及名字
select sex,sname,count(sid) from stu group by sex; -- 报错!!!
-- 在性别分组的基础上,再按照姓名分组
select sex,sname,count(sid) from stu group by sex,sname; -- 可以,(10行)
-- 查询每个班级的班级编号和每个班级的成绩和:
select cid,sum(score) from stu group by cid;
-- 查询每个班级的班级编号以及每个班级的人数:
select cid,count(sid) from stu group by cid;
-- 查询每个班级的班级编号以及每班内男生女生各多少人
select cid,sex,count(sid) from stu group by cid,sex;
-- 查询成绩总和大于200的班级编号以及成绩和:
select cid,sum(score) from stu group by cid having sum(score) > 200
-- 查询所有人成绩都大于50的班级的班级编号和人数
select cid,count(sid) from stu group by cid having min(score) > 50
-- 查询每个班成绩大于60的人数
select cid,count(sid) from stu where score > 60 group by cid; -- 这个有逻辑问题,有的班会直接被过滤掉
select cid,count(if(score > 60,score,null)) from stu group by cid;-- 这个可行
-- 基本查询,条件查询,分组,排序
-- 查询成绩总和大于200的班级编号以及成绩和并根据成绩总和升序
select cid,sum(score) from stu
group by cid having sum(score) > 200
order by sum(score) asc
--
select cid,sum(score) s from stu
group by cid having s > 200
order by s asc
2.9 限制查询
就是将查询完的数据,可以限制展现条数
语法: limit n – 限制输出指定n条,从第一条开始
limit x,y – 限制输出,从x下标处输出y条,第一条的下标是0
常用于分页操作
-- ================== 分页(limit)查询 ==================
-- 在最后写limit x[,y]
-- limit x,限制输出结果的条数为x
select * from stu limit 5;
select * from stu where score > 40 limit 5;
-- limit x,y 限制从x行处输出y条,x从0开始
select * from stu limit 0,4;
-- 分页中有些已知条件
-- 当前面 pageNo = 1
-- 每页数据量pageSize = 3
-- 数据总量 total = count(sid)
-- 页数 pageCount = total%pageSize==0?total/pageSize:(total/pageSize)+1
-- 第一页
select * from stu limit 0,3
-- 第二页
select * from stu limit 3,3
-- 第三页
select * from stu limit 6,3
-- 第pageNo页
select * from stu limit (pageNo-1)*pageSize,pageSize
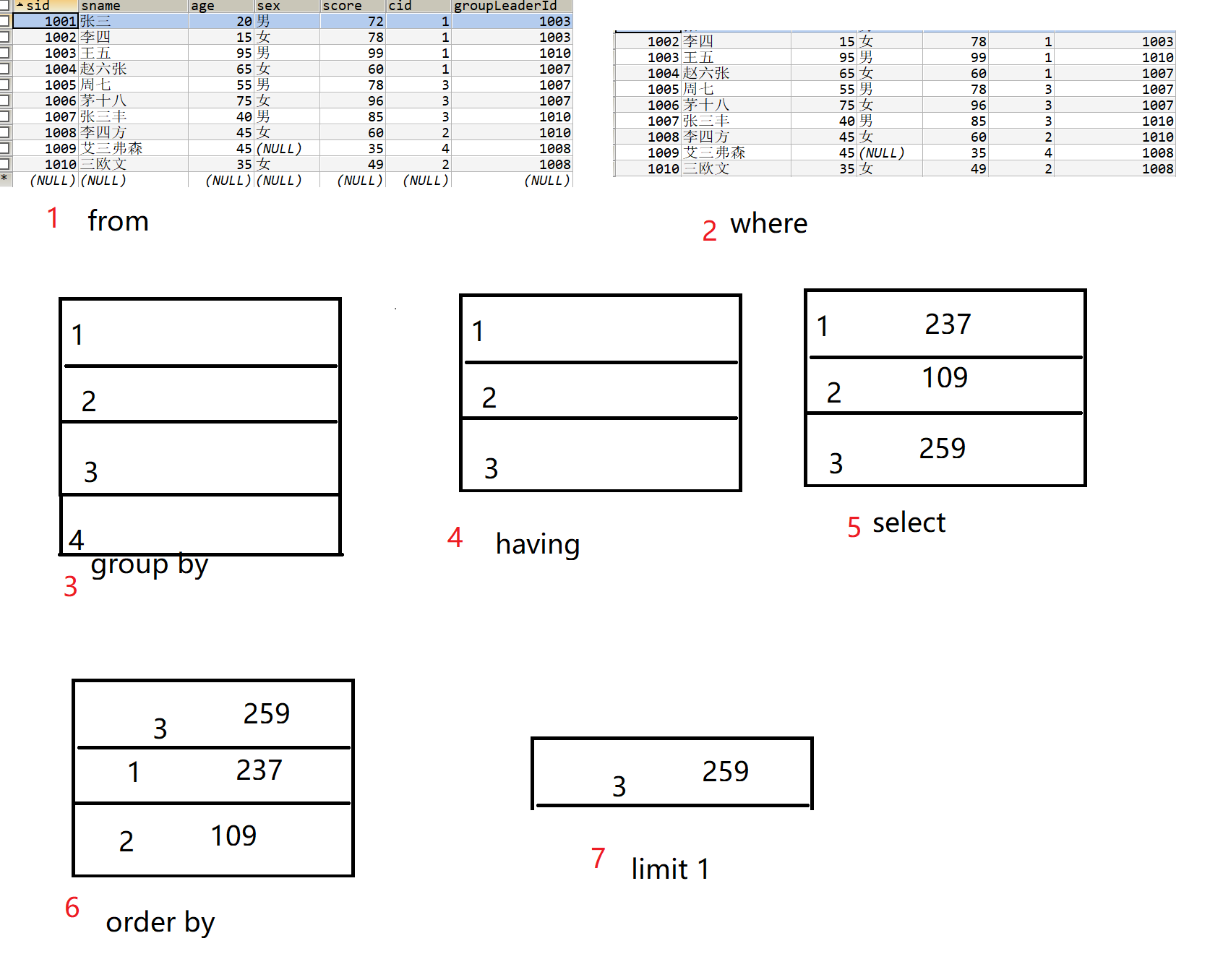
三、SQL顺序
3.1 书写顺序
select *
from 表名
where 条件
group by 字段
having 条件
order by
limit x,y
------
select cid,sum(score)
from stu
where sid >= 1002
group by cid
having sum(score) > 100
order by sum(score) desc
limit 1
3.2 执行顺序
from 获得全部数据10条件
where 过滤一部分数据,剩下9条
group by 分组,4组
having 过滤分组后的数据,剩下3组
select 查询展现数据,这里有聚合的话在此时聚合
order 排序
limit 限制
四、多表联查[重要]
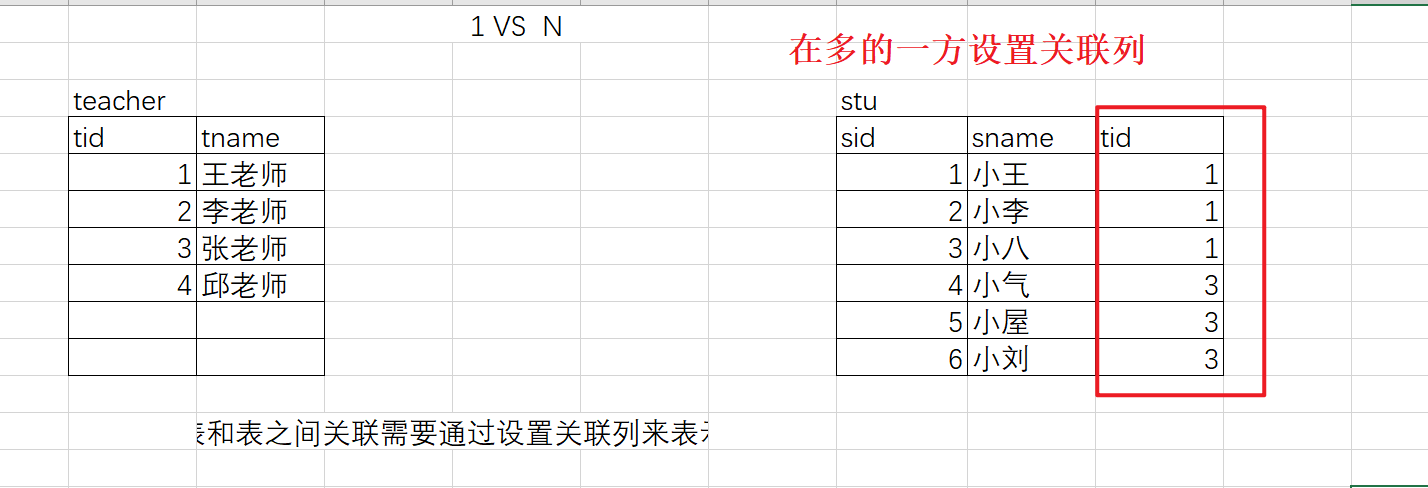
4.1 表之间的关系
表和表的关系有:
- 一对一 老公 --> 老婆 , 人 —> 身份证/户口本
- 一对多 皇帝 --> 妻妾 , 人 —> 房/车
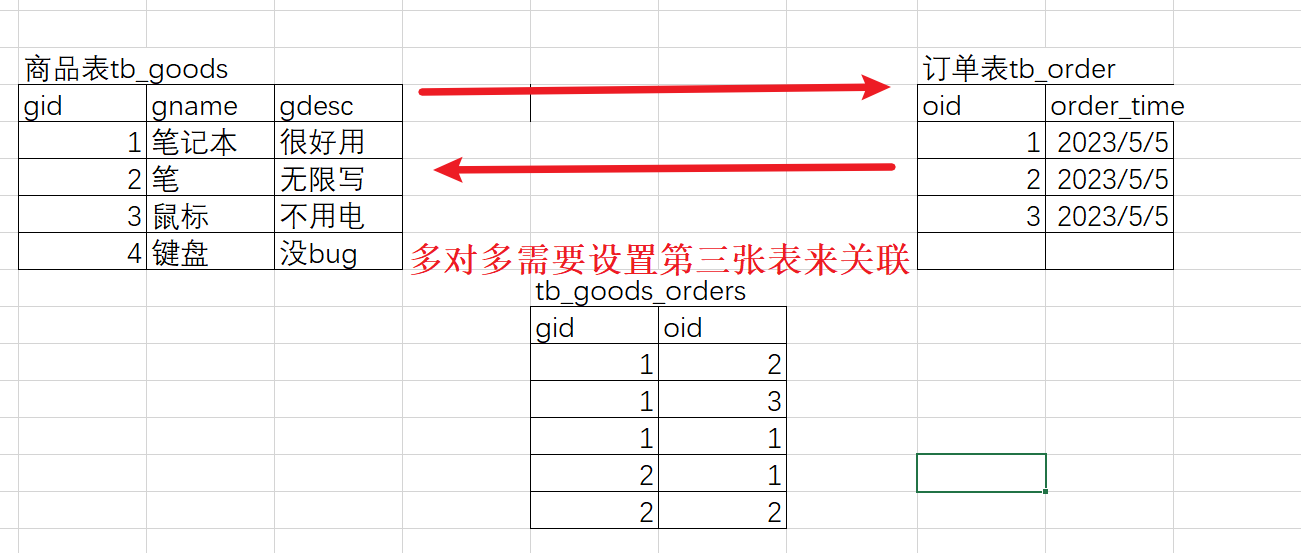
- 多对多 订单 --> 商品
一对一: 表关联的列,设计在哪个表都行
一对多图
多对多图
4.2 合并结果集(了解)
合并结果集,是将多表查询的结果纵向合并
语法:
select field1,field2 from t1 union -- 合并结果集 select field1,field2 from t2
create table tb_a(
id int,
name char(10),
age int
);
create table tb_b(
id int,
name char(10)
);
/*
合并结果集的两个表的字段
数量,类型要一致
-----------
union 联合数据,将数据纵向拼接,如果有重复数据会去重
union all 如果有重复数据会全部保留
--------------
场景:
当表很大时,可以拆分成多个表
就可以使用联合查询
*/
select id,name from tb_a
union all
select id,name from tb_b
4.3 连接查询【重要】
连接查询是将多张表数据连接在一起(横向)查询返回,
这个连接是多表的乘积,t1 * t2 , 这就是笛卡尔积
连接查询需要使用表之间的关联关系来过滤数据
连接查询分为以下几种
- 内连接
- 外连接
4.3.1 内连接
数据准备, class表是班级表,stu是学生表, 一个班级对应多个学生
两表的关联列是 学生表(stu)中的cid,引用了班级表(class)中的主键cid
语法:
select 字段列表 from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段
/*
内连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段
*/
-- 查询学生信息以及学生关联的班级信息
select * from stu inner join class on stu.cid = class.cid;
-- 查询学生的学号,姓名,分数,班号,班名
select stu.sid,stu.sname,stu.score,stu.cid,class.cname
from stu
inner join class
on stu.cid = class.cid;
-- 也可以给表设置别名
select s.sid,s.sname,s.score,s.cid,c.cname
from stu s
inner join class c
on s.cid = c.cid;
-- 内连接特点:只会查询满足关联条件的数据
-- 内连接标准写法
select * from stu inner join class on stu.cid = class.cid;
-- 内连接可以简写成(推荐)
select * from stu s,class c where s.cid = c.cid;
练习
-- 查询1班信息,以及对应学生信息
select * from class c,stu s where c.cid = s.cid and c.cid = 1;
-- 查询成绩大于60的学生信息,以及对应的专业
select * from stu s,class c where s.cid = c.cid and score > 60;
-- 查询班级编号,班级名称,和每班人数
select c.cid,c.cname,count(sid) from class c,stu s
where c.cid = s.cid
group by c.cid,c.cname
4.3.2 外连接
外连接又分为左外连接,右外连接
法:
select 字段列表 from 表1 left|right outer join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段
内外连接有什么区别?
- 内连接只查询符合关联条件的数据
- 外连接会保留不符合条件的数据
-- 1) 外连接会保留不符合条件的数据
-- 2) 左外是以左表为主,左表中有不符合条件的数据也会保留
-- 右外相反...
-- 查询学生信息以及对应的班级信息
-- 左外
select * from stu s left outer join class c on s.cid = c.cid
-- 右外
select * from stu s right outer join class c on s.cid = c.cid
-- outer可以省略
select * from stu s left join class c on s.cid = c.cid
4.4 子查询【重要】
子查询(subquery)也叫嵌套查询
- 将sql语句当表,写在from后面
- 将sql语句当条件,写在where后面
-- 子查询就是嵌套查询
-- 查询的结果是一张虚拟表
select sid,sname,age from stu where sex = '男'
-- 子查询当表
select * from
(select sid,sname,age from stu where sex = '男') t
where t.age > 50
-- 子查询当条件,但是要注意条件的值的个数(列数和行数)
select age from stu where sid = 1001
-- 年龄大于学号为1001这个人的年龄
select * from stu
where age > (select age from stu where sid = 1001)
-- 查询与张三同一个班级的学生。
select * from stu
where cid = (select cid from stu where sname = '张三');
-- 成绩高于3号班级所有人的学生信息
select * from stu
where score > (select max(score) from stu where cid = 3)
-- 有2个以上直接组员的学生信息
select * from stu where sid in(
select groupLeaderId from stu
group by groupLeaderId
having count(sid) > 2)
-- 求1008学生编号、姓名、组长编号和组长姓名
SELECT
t1.sid,
t1.sname,
t1.groupLeaderId,
t2.sname
FROM
stu t1,(
SELECT
*
FROM
stu
WHERE
sid = ( SELECT groupLeaderId FROM stu WHERE sid = 1008 )
) t2
WHERE
t1.sid = 1008
-- 上面这题可以改造成自连接
select s.sid,s.sname,s.groupLeaderId,z.sname from stu s,stu z where s.groupLeaderId = z.sid and s.sid = 1008