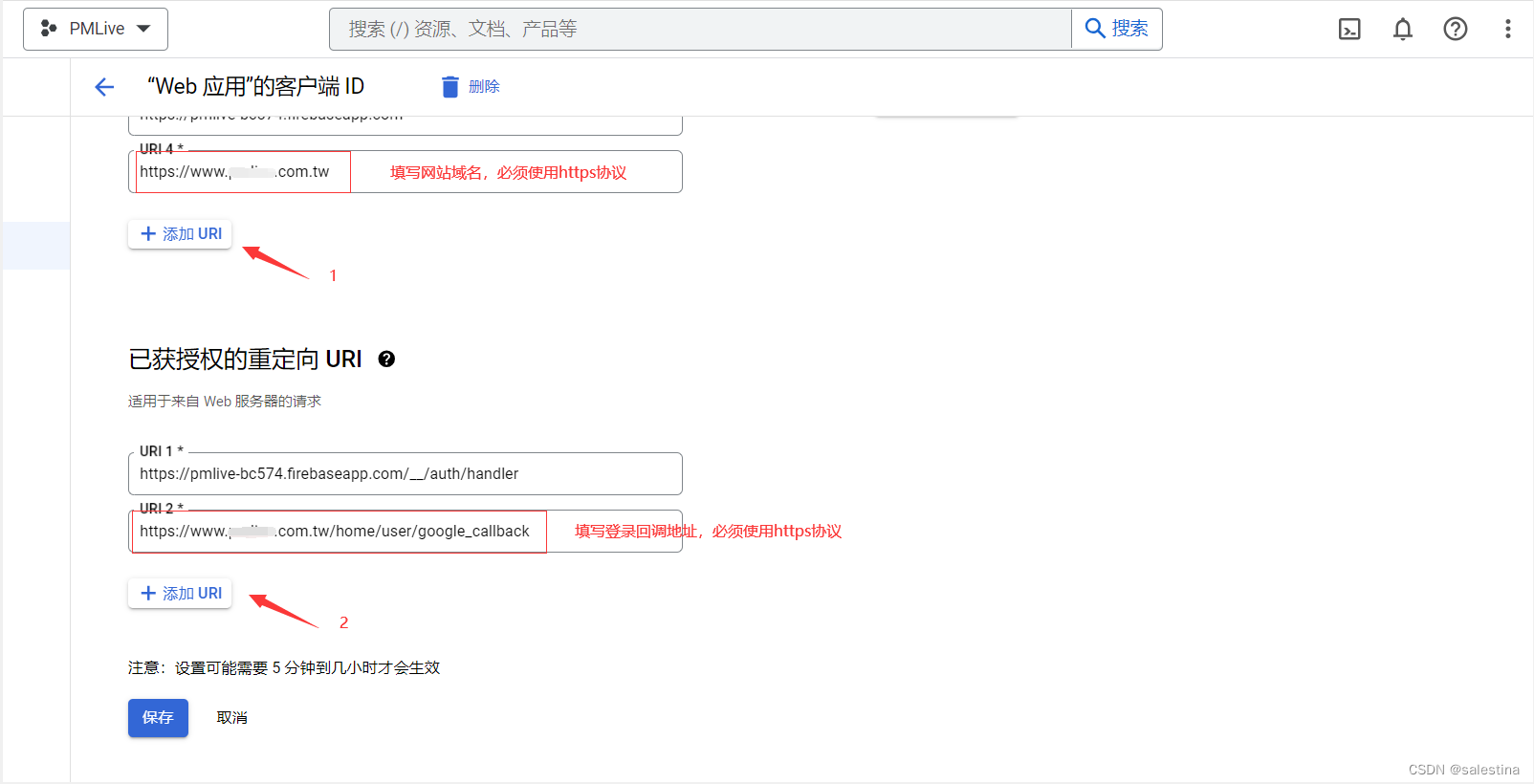
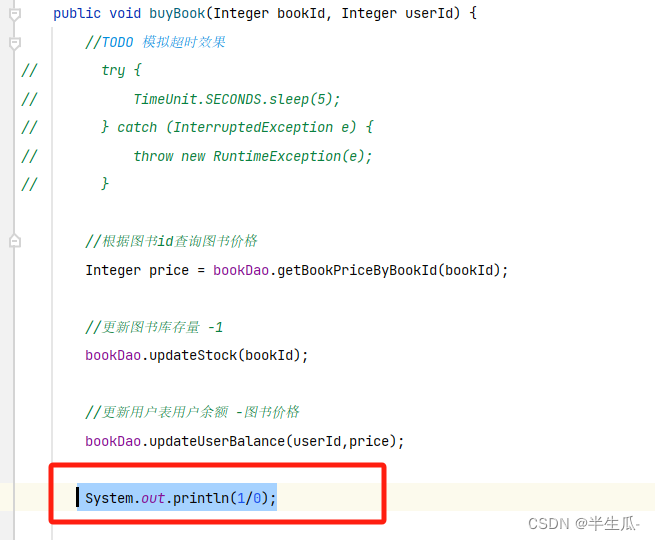
跳表
定义
在一个用有序链表描述的 n 个数对的字典中进行查找,至多需要 n 次关键字比较。如果在链表的中部节点加一个指针,则比较次数可以减少到 n/2+1。这时,为了查找一个数对,首先与中间的数对比较。如果查找的数对关键字比较小,则仅在链表的左半部分继续查找,否则,在链表右半部分继续查找。
在跳表结构中有一组等级链表。0 级链表包含所有数对,1 级链表的数对是 0 级链表数对的一个子集。i级链表的数对是i-1 级链表数对的子集。
在插入时级的分配
在规则的跳表结构中,i-1 级链表的数对个数与i级链表的数对个数之比是一个分数 p。因此,属于 i-1 级链表的数对同时属于 i 级链表的概率为 p。假设用一个统一的随机数生成器产生0和1间的实数,产生的随机数<=p的概率为p。若下一个随机数<=p,则新数对应在1级链表上。要确定该数对是否在 2 级链表上,要由下一个随机数来决定。若新的随机数<= p,则该元素也属于2级链表。重复这个过程,直到一随机数>p为止。
这种方法有潜在的缺点,某些数对被分配的级数可能特别大,远远超过 l o g 1 / p N log_{1/p}N log1/pN,其中N为字典数对的最大预期数目。为避免这种情况,可以设定一个级数的上限maxLevel,最大值为: ⌈ l o g 1 / p N ⌉ − 1 \lceil log_{1/p}N \rceil-1 ⌈log1/pN⌉−1
这种方法还有一个缺点,即使采用了级数的上限 maxLevel,还可能出现这样的情况:在插入一个新数对之前有 3 个链表,而在插入之后就有了 10 个链表。也就是说,尽管 3 ~8 级链表没有数对,新数对却被分配到9级链表。换句话说,在插入前后,没有3~8级链表。因为这些空级链表并没有什么好处,我们可以把新记录的链表等级调整为3。

练习题
【练习9】扩充类skipList,增加删除方法,删除关键字最小的节点,删除关键字最大的节点。计算每个方法的复杂度?
代码
每个node有值,还有一个数组,存储了该键值对每级的指针,键值对最高属于几级,那么该键值对也属于最高级一下的其他级;所以每个node的指针数组为最高级+1(还有0级)大小。
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "_24skipList.h"
int main() {
skipListTest();
return 0;
}
_24skipList.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月23日10点18分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 跳表类---随机决定是几级,插入的时候是几级,现在就是几级---头文件
查找时可以节省时间
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _SKIPLIST_H_
#define _SKIPLIST_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_23dictionary.h"
#include "_24skipNode.h"
using namespace std;
/*测试函数*/
void skipListTest();
template<class K, class E>
class skipList : public dictionary<K, E>
{
public:
skipList(K largeKey, int maxPairs = 10000, float prob = 0.5);
~skipList();
bool empty() const { return dSize == 0; }
int size() const { return dSize; }
pair<const K, E>* find(const K&) const;
void erase(const K&);
void insert(const pair<const K, E>&);
void deleteFront();
void deleteBack();
/*友元函数*/
/*输入字典*/
istream& input(istream& in);
// friend istream& operator>> <K, E>(istream& in, skipList<K, E>& m);
/*输出字典*/
ostream& output(ostream& out) const;
// friend ostream& operator<< <K, E>(ostream& out, const skipList<K, E>& m);
protected:
float cutOff; // used to decide level number--用于确定层数
int level() const; // generate a random level number
int levels; // max current nonempty chain
int dSize; // number of pairs in dictionary
int maxLevel; // max permissible chain level
K tailKey; // a large key
skipNode<K, E>* search(const K&) const;
// search saving last nodes seen
skipNode<K, E>* headerNode; // header node pointer
skipNode<K, E>* tailNode; // tail node pointer
skipNode<K, E>** last; // last[i] = last node seen on level i
};
/*输入字典*/
template<class K, class E>
istream& skipList<K, E>::input(istream& in)
//istream& operator>>(istream& in, skipList<K, E>& m)
{
int numberOfElement = 0;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
while (!(in >> numberOfElement))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the number of element:";
}
K first;
E second;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElement; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
while (!(in >> first >> second))
{
in.clear();//清空标志位
while (in.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the element " << i + 1 << ":";
}
const pair<const K, E> element(first, second);
insert(element);
}
return in;
}
template<class K, class E>
istream& operator>>(istream& in, skipList<K, E>& m){
m.input(in);
return in;
}
/*输出字典*/
template<class K, class E>
ostream& skipList<K, E>::output(ostream& out) const
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const skipList<K, E>& m)
{
skipNode<K, E>* currentNode = headerNode->next[0];
while (currentNode != tailNode)
{
out << *currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode->next[0];
}
cout << endl;
return out;
}
template<class K, class E>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const skipList<K, E>& m){
m.output(out);
return out;
}
/*构造函数*/
template<class K, class E>
skipList<K, E>::skipList(K largeKey, int maxPairs, float prob)
{
/*RAND_MAX这是一个宏定义,就是产生随机数的最大值,在stdlib头文件中*/
/*prob一般是0.5*/
cutOff = prob * RAND_MAX;
/*ceil()函数表示向下取整,logf()函数表示取对数,maxPairs表示数对个数的最大数*/
maxLevel = (int)ceil(logf((float)maxPairs) / logf(1 / prob)) - 1;//允许的最大层数
levels = 0; //初始非空层数为0
dSize = 0;//初始跳表大小为0
tailKey = largeKey;//表示最大键值
// create header & tail nodes and last array
pair<K, E> tailPair;
tailPair.first = tailKey;
headerNode = new skipNode<K, E>(tailPair, maxLevel + 1);//创建头节点
tailNode = new skipNode<K, E>(tailPair, 0);//创建尾节点
last = new skipNode<K, E> *[maxLevel + 1];//last[i]表示i层的最后结点
// 初始状态下所有的i级链表的头节点指向尾节点
for (int i = 0; i <= maxLevel; i++)
headerNode->next[i] = tailNode;
}
/*删除所有结点和 指针数组last*/
template<class K, class E>
skipList<K, E>::~skipList()
{// Delete all nodes and array last.
skipNode<K, E>* nextNode;
/*一定会让它执行一次,因为有头节点。*/
while (headerNode != tailNode)
{
nextNode = headerNode->next[0];
delete headerNode;
headerNode = nextNode;
}
delete tailNode;
delete[] last;
}
/*返回匹配的数对的指针;如果没有匹配的数对,则返回nullptr*/
template<class K, class E>
pair<const K, E>* skipList<K, E>::find(const K& theKey) const
{
if (theKey >= tailKey)
return nullptr; // no matching pair possible
// position beforeNode just before possible node with theKey
skipNode<K, E>* beforeNode = headerNode;
for (int i = levels; i >= 0; i--) // go down levels
// follow level i pointers
while (beforeNode->next[i]->element.first < theKey)
beforeNode = beforeNode->next[i];
// check if next node has theKey
if (beforeNode->next[0]->element.first == theKey)
return &beforeNode->next[0]->element;
return nullptr; // no matching pair
}
template<class K, class E>
int skipList<K, E>::level() const
{// Return a random level number <= maxLevel.
int lev = 0;
while (rand() <= cutOff)
lev++;
return (lev <= maxLevel) ? lev : maxLevel;
}
/*搜索关键字theKey,把每一级链表中要查看的最后一个结点存储在数组last中*/
/*返回包含关键字theKey的结点*/
/*位置beforeNode是关键字为theKey的结点之前最右边的位置*/
template<class K, class E>
skipNode<K, E>* skipList<K, E>::search(const K& theKey) const
{
skipNode<K, E>* beforeNode = headerNode;
for (int i = levels; i >= 0; i--)
{
while (beforeNode->next[i]->element.first < theKey)
beforeNode = beforeNode->next[i];
last[i] = beforeNode; //theKey关键字之前的结点
}
return beforeNode->next[0];//返回值是0级中 很有可能是theKey为关键字的结点,或比它的key值更大的结点
}
/*向链表中插入元素thePair,如果链表中不存在与thePair的关键字相同的元素则插入,否则更新该关键字相应的值*/
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::insert(const pair<const K, E>& thePair)
{
/*key值超过最大key值时*/
if (thePair.first >= tailKey) // key too large
{
ostringstream s("");
s << "Key = " << thePair.first << " Must be < " << tailKey;
throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());
}
/*thePair的key值已经存在时,更新该key对应的值*/
skipNode<K, E>* theNode = search(thePair.first);
if (theNode->element.first == thePair.first)
{
theNode->element.second = thePair.second;
return;
}
/*当不存在该key值时,决定等级i*/
int theLevel = level(); //随机计算新节点的等级
/*如果等级大于非空等级的个数,则修正*/
if (theLevel > levels)
{
theLevel = ++levels;
last[theLevel] = headerNode;
}
/*将新节点存储到theNode之后*/
skipNode<K, E>* newNode = new skipNode<K, E>(thePair, theLevel + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= theLevel; i++)
{// insert into level i chain
newNode->next[i] = last[i]->next[i];
last[i]->next[i] = newNode;
}
dSize++;
return;
}
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::erase(const K& theKey)
{// Delete the pair, if any, whose key equals theKey.
if (theKey >= tailKey) // too large
return;
// see if matching pair present
skipNode<K, E>* theNode = search(theKey);
if (theNode->element.first != theKey) // not present
return;
// delete node from skip list
for (int i = 0; i <= levels && last[i]->next[i] == theNode; i++)
last[i]->next[i] = theNode->next[i];
// update levels
while (levels > 0 && headerNode->next[levels] == tailNode)
levels--;
delete theNode;
dSize--;
}
/*练习9:删除关键字最小的结点*/
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::deleteFront()
{
if (dSize == 0)
return;
/*找到关键字最小的结点*/
skipNode<K, E>* frontNode = headerNode->next[0];
/*删除各个级的 该结点*/
for(int i = 0;i <= levels && headerNode->next[i] == frontNode;i++)
headerNode->next[i] = frontNode->next[i];
/*更新levels*/
while (levels > 0 && headerNode->next[levels] == tailNode)
levels--;
delete frontNode;
dSize--;
}
/*练习9:删除关键字最大的结点*/
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::deleteBack()
{
/*找到关键字最大的结点*/
skipNode<K, E>* deleteBack = headerNode;
for (int i = levels; i >= 0; i--)
{
while (deleteBack->next[i]->element.first < tailKey)
deleteBack = deleteBack->next[i];
}
/*找到各个级的 deleteBack 之前的元素地址*/
search(deleteBack->element.first);
/*删除各个级的 该结点*/
for (int i = 0; i <= levels && last[i]->next[i] == deleteBack; i++)
last[i]->next[i] = deleteBack->next[i];
/*更新levels*/
while (levels > 0 && headerNode->next[levels] == tailNode)
levels--;
delete deleteBack;
dSize--;
}
#endif
_24skipList.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月23日10点18分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 跳表类---随机决定是几级,插入的时候是几级,现在就是几级---cpp文件
*/
#include <iostream>
#include "_24skipList.h"
using namespace std;
void skipListTest()
{
cout << endl << "*********************************skipListTest()函数开始***************************************" << endl;
//测试输入和输出
cout << endl << "测试输入输出*******************************************" << endl;
cout << "输入输出************************" << endl;
skipList<int, int> a(20);
cin >> a;
cout << "The dictionary is " << a;
cout << endl << "测试成员函数*******************************************" << endl;
cout << "empty()*************************" << endl;
cout << "a.empty() = " << a.empty() << endl;
cout << "size()**************************" << endl;
cout << "a.size() = " << a.size() << endl;
cout << "find()**************************" << endl;
cout << "Element associated with 1 is " << a.find(1)->second << endl;
cout << "insert()************************" << endl;
pair<const int, int> insertData(4, 4);
a.insert(insertData);
cout << "The dictionary is " << a;
cout << "erase()*************************" << endl;
a.erase(1);
cout << "The dictionary is " << a;
cout << "deleteFront()*******************" << endl;
a.deleteFront();
cout << "The dictionary is " << a;
cout << "deleteBack()********************" << endl;
a.deleteBack();
cout << "The dictionary is " << a;
cout << "**********************************skipListTest()函数结束**************************************" << endl;
}
_23dictionary.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月22日09点17分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 字典的抽象类
*/
/*
pair:
介绍:是将2个数据组合成一组数据,是一个结构体,主要的两个成员变量first和second,分别存储两个数据.
使用:使用std命名空间引入对组std::pair
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _DICTIONARY_H_
#define _DICTIONARY_H_
using namespace std;
template<class K,class E>
class dictionary
{
public:
virtual ~dictionary() {}
/*返回为true,当且仅当字典为空*/
virtual bool empty() const = 0;
/*返回字典中数对的数目*/
virtual int size() const = 0;
/*返回匹配数对的指针*/
virtual pair<const K, E>* find(const K&) const = 0;
/*删除匹配的数对*/
virtual void erase(const K&) = 0;
/*往字典中插入一个数对*/
virtual void insert(const pair<const K, E>&) = 0;
};
#endif
_24skipNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月23日10点18分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 跳表结构
// node type used in skip lists
// node with a next and element field; element is a pair<const K, E>
// next is a 1D array of pointers
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _SKIPNODE_H_
#define _SKIPNODE_H_
template <class K, class E>
struct skipNode
{
typedef pair<const K, E> pairType;
pairType element;
skipNode<K, E>** next; // 1D array of pointers
skipNode(const pairType& thePair, int size)
:element(thePair) {
next = new skipNode<K, E>*[size];
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, skipNode<K, E>& m)
{
out << "(" << m.element.first << " ," << m.element.second << ")" << " ";
return out;
}
};
#endif
_1myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:
illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{
public:
illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{
public:
illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{
public:
matrixIndexOutOfBounds
(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{
public:
matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage =
"The size of the two matrics doesn't match")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{
public:
stackEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty stack")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{
public:
queueEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty queue")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{
public:
hashTableFull(string theMessage =
"The hash table is full")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{
public:
undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage =
"No edge weights defined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{
public:
undefinedMethod(string theMessage =
"This method is undefined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
#endif