文章目录
- 简介
- 安装 BeautifulSoup 库
- BeautifulSoup 库的导入
- BeautifulSoup 库依赖的解析库
- 创建 BeautifulSoup 对象
- CSS选择器
- 1、通过标签名查找
- 2、通过 CSS 的类名查找
- 3、通过 Tag(标签) 的 id 查找
- 4、通过 是否存在某个属性来查找
- 5、通过 某个标签是否存在某个属性来查找
- 获取标签里面的文字内容
- 获取标签里面属性的内容
简介
BeautiSoup 库主要用来解析 HTML 格式的网络文件,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据。
安装 BeautifulSoup 库
对于BeautifulSoup ,目前 最新版本是 4.x 版本,已经移植到 BS4中,Soup 3已经停止开发。
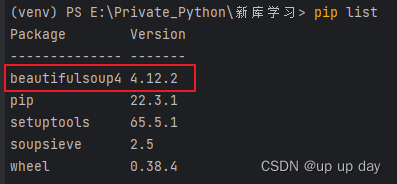
pip install beautifulsoup4 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
使用 pip list 查看是否安装成功
BeautifulSoup 库的导入
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup 库依赖的解析库
BeautifulSoup 在解析的时候实际上是需要依赖于解析器的,它除了支持 Python 标准库中的 HTML 解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器。
常见解析器比较:
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python 标准库 | BeautifulSoup (markup, "html.parser") | 1、Python 的内置标准库 2、执行速度适中 3、文档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3 或 3.2.2 前的版本中 文档容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup (markup, "lxml") | 1、速度快 2、文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup (markup, "xml") | 1、速度快 2、唯一支持 XML 的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup (markup, "html5lib") | 1、最好的容错性 2、以浏览器的方式解析文档 3、生成HTML5 格式的文档 | 速度慢,不依赖外部拓展 |
创建 BeautifulSoup 对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(markup, features)
markup:要解析的HTML格式的字符串features:要使用的解析器类型"html.parser""lxml""xml""html5lib"
CSS选择器
在CCS中,标签名不加任何修饰,类名前加点,ID名前加 # ,在这里我们也可以用类似的方法来筛选元素,用到的方法是 soup.select() , 返回类型是 list
示例 html 文件:
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>
The Dormouse's story
</b>
</p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<!--Elsie -->
</a>
,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">
<!--Lacie-->
</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">
Tillie
</a>
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">
...
</p>
</body>
</htm1>
1、通过标签名查找
通过标签名可以直接查找、逐层查找,也可以找到某个标记下的直接子标记和兄弟节点标签。
标签名不加任何修饰,类名前加点,ID名前加 #
# 直接查找 title 标记
print( soup.select( "title" ) )
output: [<titile>The Dormouse’ s story</title>]
# 逐层查找 title 标记
print( soup.select( "html head title" ) )
output: [<titile>The Dormouse’ s story</title>]
# 查找 直接子节点
# 查找 head 下的 title 标签
print( soup.select( "head title" ) )
output: [<titile>The Dormouse’ s story</title>]
# 查找 p 下的 id=“link1” 的标签
print( soup.select( "p #link1" ) )
output: [<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/elsie” id=“link1”>\ </a>]
# 查找 兄弟节点
# 查找 id=“link1” 之后 class=sister 的所有兄弟标签
print( soup.select( "#link1 ~ .sister " ) )
output: [<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/lacie” id=“link2”> <!–Lacie–> </a>,
<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/tillie” id=“link3”> Tillie </a>]
# 查找 紧跟着 id=“link1” 之后 class=sister 的所有子标签
print( soup.select( "#link1 + .sister " ) )
output: [<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/lacie” id=“link2”> <!–Lacie–> </a>]
2、通过 CSS 的类名查找
print( soup.select( ".sister" ) )
output: [<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/elsie” id=“link1”><!–Elsie --></a>,
<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/lacie” id=“link2”> <!–Lacie–> </a>,
<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/tillie” id=“link3”> Tillie </a>]
3、通过 Tag(标签) 的 id 查找
print( soup.select( "#link3" ) )
output: <a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/tillie” id=“link3”> Tillie </a>]
4、通过 是否存在某个属性来查找
# 查找 是标签a 并且有 href 属性的Tag
print( soup.select( "a[href]" ) )
output: [<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/elsie” id=“link1”><!–Elsie --></a>,
<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/lacie” id=“link2”> <!–Lacie–> </a>,
<a class=“sister” href=“http://example.com/tillie” id=“link3”> Tillie </a>]
5、通过 某个标签是否存在某个属性来查找
# 查找 是标签a 并且有 href 属性的Tag
print( soup.select( "a[href]" ) )
# 查找 是标签a 并且 id=‘link1’ 的Tag
print( soup.select( "a[ id='link1' ]" ) )
获取标签里面的文字内容
print( soup.title.string )
获取标签里面属性的内容
# 打印 标签p 的属性
# 返回的是一个字典
print( soup.p.attrs )
# 获取 标签p 的class 属性值
print( soup.p['class'] )