移动语义(Move Semantics)是C++11引入的一个重要特性,它允许在不复制数据的情况下将资源(如内存、指针等)从一个对象转移到另一个对象,从而可以提高程序的性能。
在C++11添加了右值引用,并且不能使用左值初始化右值引用,如果想要使用左值初始化一个右值引用需要借助std::move()函数,使用std::move方法可以将左值转换为右值。使用这个函数并不能移动任何东西,而是和移动构造函数一样都具有移动语义,将对象的状态或者所有权从一个对象转移到另一个对象,只是转移,没有内存拷贝。
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test() {}
};
int main()
{
list<string> ls;
ls.push_back("hello");
ls.push_back("world");
list<string> ls1 = ls; // 需要拷贝, 效率低
list<string> ls2 = move(ls);
cout << "************_ls_**************" << endl;
for (auto& it : ls)
{
cout << it << endl;
}
cout << "*************_ls1_*************" << endl;
for (auto& it : ls1)
{
cout << it << endl;
}
cout << "*************_ls2_*************" << endl;
for (auto& it : ls2)
{
cout << it << endl;
}
return 0;
}
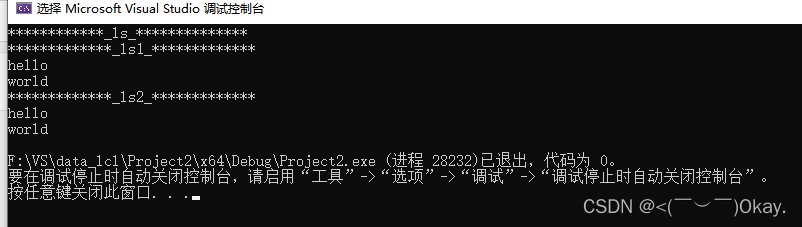
list ls1 = ls; // 需要拷贝, 效率低
list ls2 = move(ls); //效率高,但是执行完成后,ls将为空