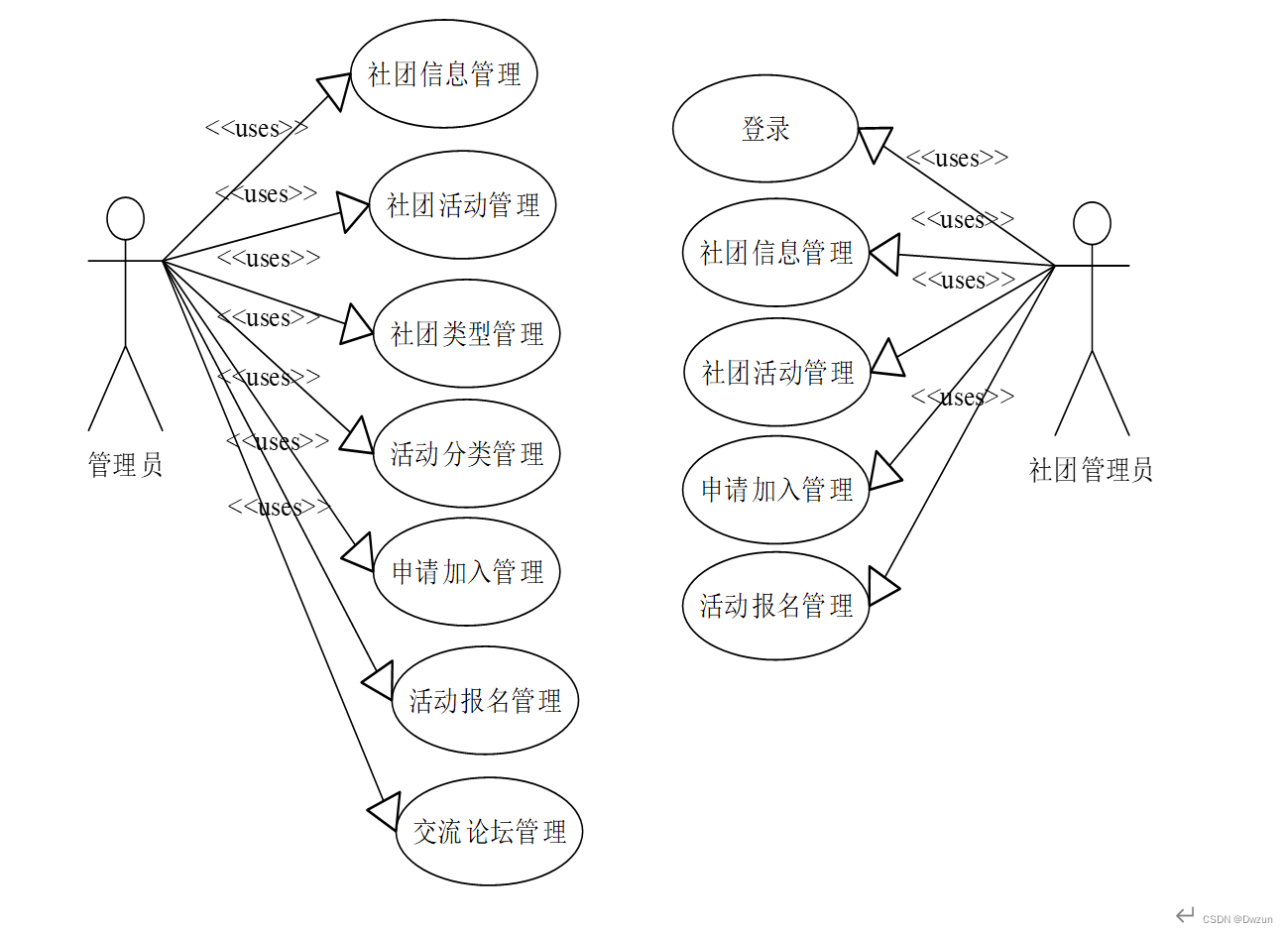
继上次实现文件从后往前数2k的数据进行复制,此次要求是文件的一半且是后半部分。
即复制源文件sour_file的后半部分到dest_file
除了数据上从后2K变化到后一半之外,其他的几乎没有什么变化。
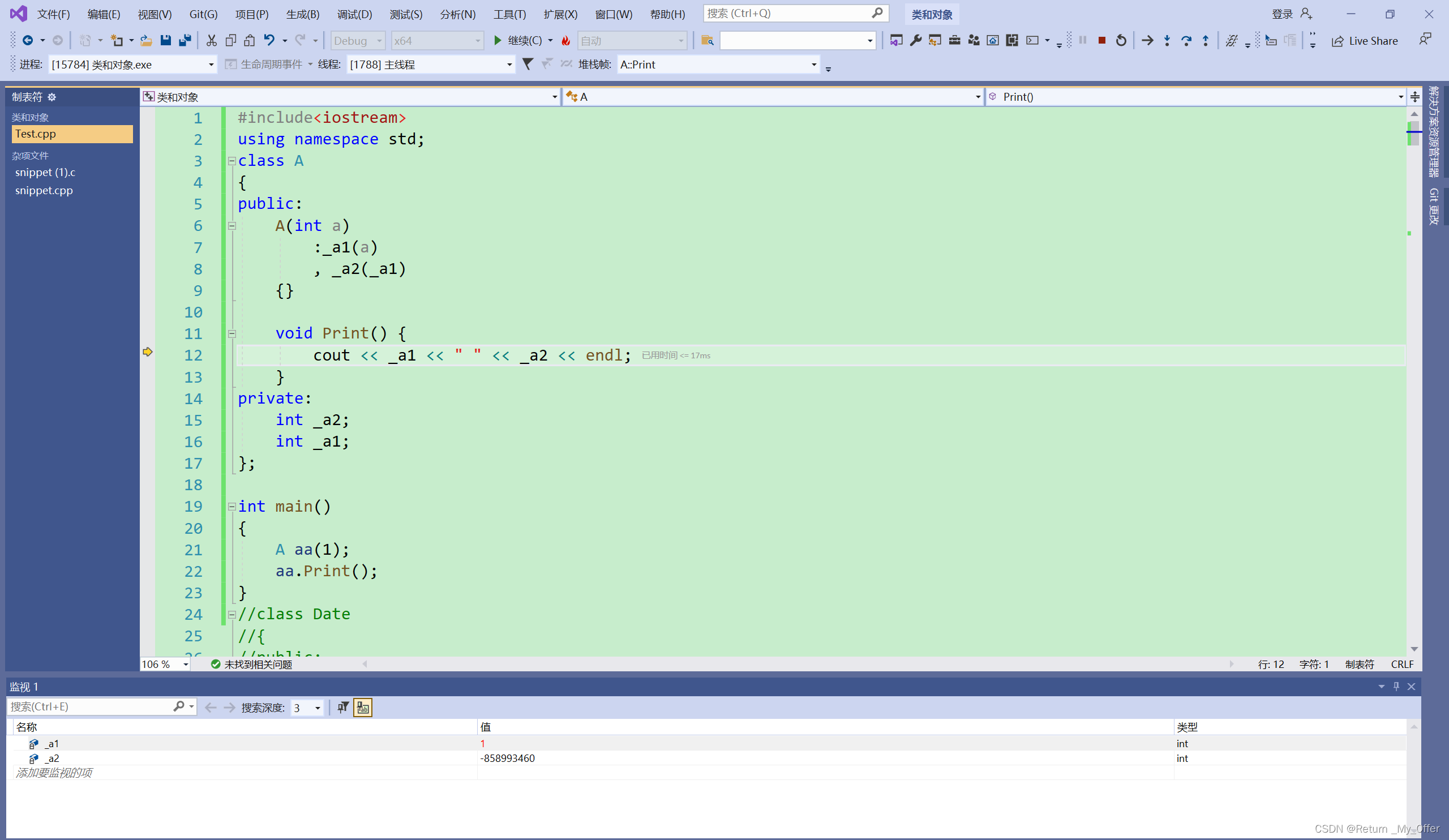
这道题的关键点就在于后一半怎么求,在经历了用 lseek(writed,0,SEEK_SET)求文件总长,用sizeof()函数求文件大小,strlen()函数求字符串长度等等等等N次尝试之后,意外发现了一种能达到效果且好用的方法:Struct stat 结构体。

如上图所示,struct stat 结构体内容是不需要自己写的,这算是自带属性。
这样一来就简单多了。
struct stat st;
//先把这个结构体拽出来
fstat(writed,&st);
//fstat函数的作用就是把得到的文件writed的属性给到结构体
int len=st.st_size;
//再调用得到其大小
如此就完整得到了源文件的大小。
我们只要后半部分,于是先取其一半
int filesize=len/2;
lseek(writed,filesize,SEEK_END);
//将光标从后往前移到文件二分之一处或者从前往后移动二分之一也可以
lseek(writed,filesize,SEEK_SET);然后从当前位置读取内容,写到目标文件就可以了
源码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int writed;
int readed;
int writed_len;
int readed_len;
int len_lseek;
struct stat st;
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("Input invaild\n");
return -1;
}
writed=open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);\\只读打开
if(writed<=0)
{
printf("Open Source File '%s' Failure",argv[1]);
return -1;
}
readed=open(argv[2],O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664);
if(readed<=0)
{
printf("Create Destination File '%s' Failure",argv[2]);
return -1;
}
fstat(writed,&st);//将writed文件属性全部复制到结构体
len_lseek=st.st_size; //利用stat结构体求得文件大小
char buf[1024];
lseek(writed,-len_lseek/2,SEEK_END);//将光标移动到文件1/2位置
int count=0;
while((readed_len=read(writed,buf,sizeof(buf)))!=0) //从源文件读取数据,直到全部读完
{
writed_len=write(readed,buf,readed_len);//将读取的内容写入到目标文件
if(writed_len>0)
{
printf("拷贝完成%d次\n",count+1);
}
if(writed_len<0)
{
printf("Write Destination File '%s' Failure",argv[2]);
}
count++;
}
printf("The File has been copied and Executed %d times\n", count);
close(writed);
close(readed);
}
网上随便复制了一段,放在了源文件里。
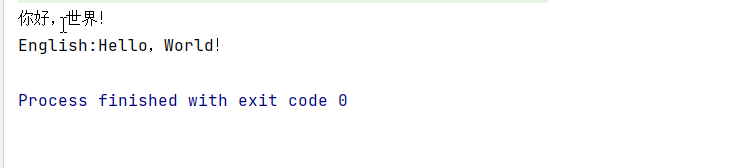
运行结果:
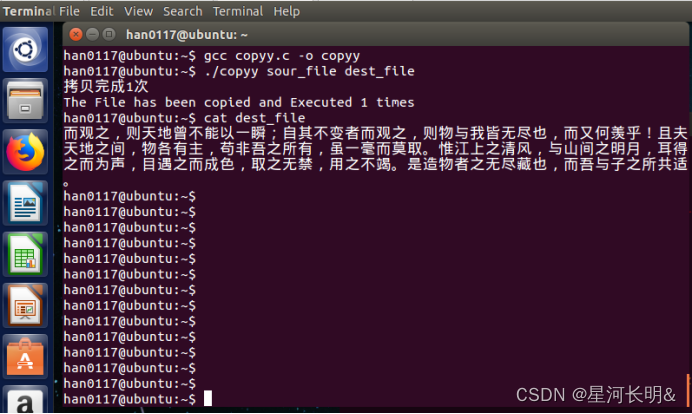
差不多是一半,我也没数,有强迫症可以数一数ヽ(゚∀゚)メ(゚∀゚)ノ ヾ(๑╹◡╹)ノ"ヾ(●´∀`●)