invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors的理解
Spring中有两个非常重要的扩展点:
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- BeanPostProcessor
其中第一个是可以对BeanDefinition注册时进行扩展,而第二个是对spring中IOC容器中的对象进行实例化的时候进行扩展。
今天主要谈一下对BeanFactoryPostProcessor的几点理解:
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 这是个重要的接口,其还有一个子接口:BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor:
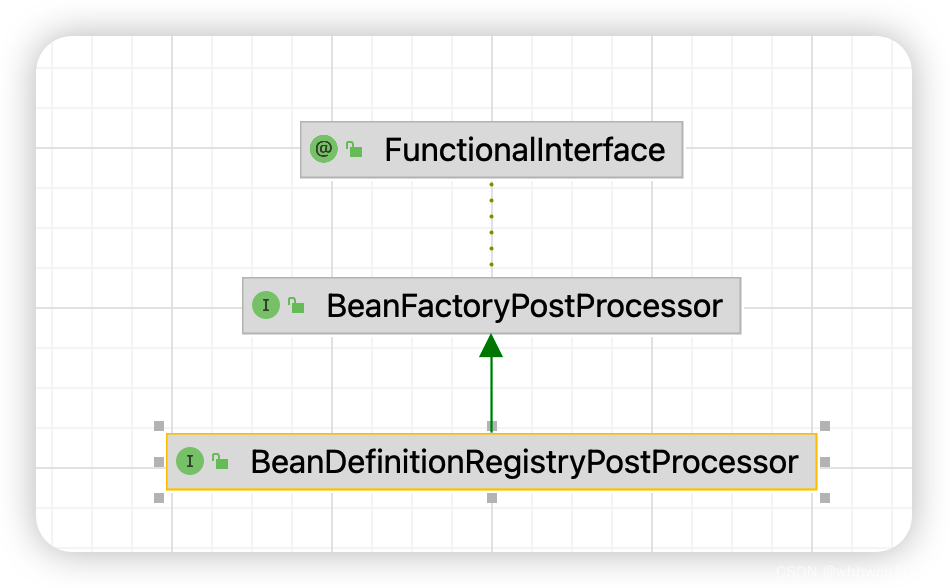
- 在spring容器的启动过程,对所有组件的注册主要就是通过对这两个接口的处理来完成的。
- spring启动时,最主要的方法就是refresh方法:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
- 其中,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors这个方法,就是处理容器中所有bean的注册过程
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors这个方法具体如下:
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
- 这个方法,其实只有第一条语句中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,是重要且对容器bean注册有效
- 这个方法传入的参数第一个是工厂,第二个参数是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的list
- 正常启动的时候,如果我们不做处理,那么第二个参数就是一个空的list
- 我们也可以在代码中进行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的注入
- spring容器启动到这里时,会自动注册5个bean:

上述图片中:
- 第一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,实现的是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,是最主要的扫描和注册
- 第三个EventListenerMethodProcessor,实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,与事件相关的处理组件
- 第四个和第五个实现BeanPostProcessor接口,参与对象创建过程中的注入等处理
- 在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中,spring会通过所有BeanFactoryPostProcessor的功能,来扫描并注册所有的bean,从方法名称来看,其作用就是调用所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,
其主要处理流程如下:
- 对传入的BeanFactoryPostProcessor进行处理,添加进等待运行的列表中
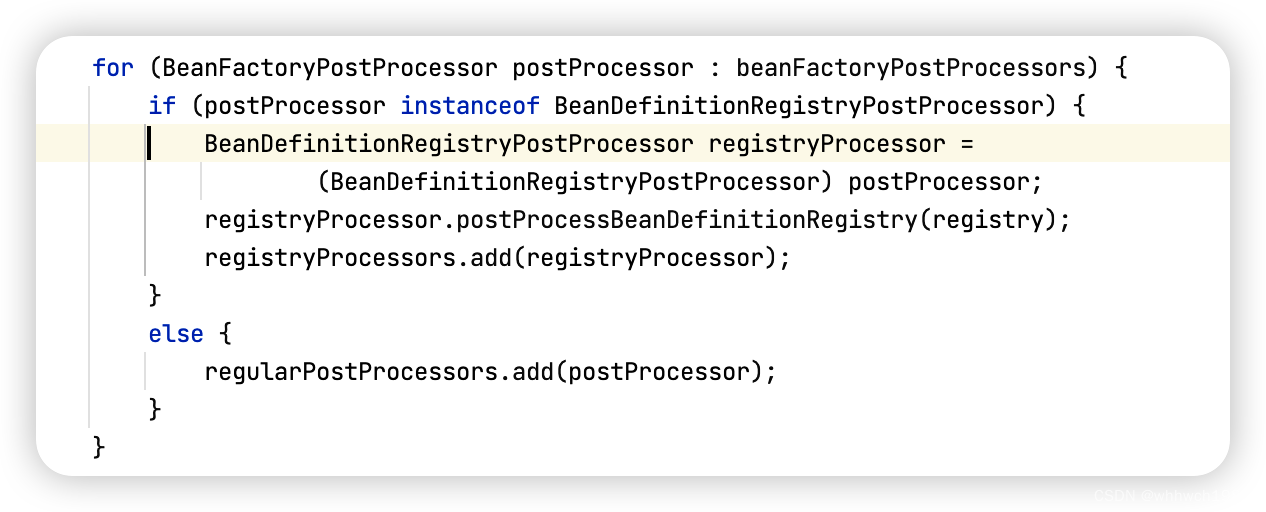
- 对实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor以及PriorityOrdered接口的组件进行实例化,并调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口方法,此时,就是调用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个组件,来进行容器中bean的注册,具体的注册过程此处略过不表
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
- 对实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor以及Ordered接口的组件进行实例化,并调用相应接口方法
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
- 对只实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的组件进行实例化,并调用相应接口方法
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
- 对实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的组件,调用其父接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
- 对实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor以及PriorityOrdered接口的组件,调用相应接口中的方法
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
- 对实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor以及Ordered接口的组件进行实例化,并调用相应接口方法
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
- 对只实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的组件进行实例化,并调用相应接口方法
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
总结:
- 此方法主要作用,就是按照顺序分别调用实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的组件以及实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的组件;其中最主要的组件就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,其实现的是子接口,实现的方法功能,就是对容器中进行beanDefinition的注册。