C++基础语法
此语法笔记面向算法竞赛考研,可供参考,本人的一些笔记的记录~
失踪人口回归,将近半个月没有更新,那么接下来也会逐步开始更新分享知识内容~
本篇将分享cpp基础语法中的变量、输出输入语句、表达式、顺序语句、条件判断、循环
接下来将会保持定时定量的更新~敬请期待
文章目录
- C++基础语法
- 失踪人口回归,将近半个月没有更新,那么接下来也会逐步开始更新分享知识内容~
- 01 变量、输入输出、表达式、顺序语句
- 主体结构
- 常用头文件
- 变量
- 输入输出
- 字符的读入
- 字符的输出
- a+b问题
- 表达式
- abs 函数
- 变量的强制类型转换
- 笔记
- 浮点数的比较运算
- 02 判断语句
- 从未注意到的点
- 笔记
- 03 循环语句
- 斐波那契
- do while
- for循环
- break和continue
- 判断质数
- 输出1-100的偶数和
- 多层循环
- 曼哈顿距离
- 练习
- 偶数
- 奇数
- 正数
- 连续奇数的和①
- 递增序列
- 完全数
01 变量、输入输出、表达式、顺序语句
主体结构
// 框架
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*
结构
*/
return 0;
}
最简单的C++程序:
//头文件
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//命名空间
//主函数
int main()
{
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
//cout 输出
//cin 输入
return 0;
}
常用头文件
iostream包括cin、cout、scanf、printf
cstdin包括scanf、printf、cmath
万能头文件bits/stdc++.h
变量
变量先定义才能使用。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
1 byte = 8 bit
bool false/true 1 byte
char 'a', 'c', ' ', '\n' 1 byte
int -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 4 byte
float 1.23, 2.5, 1.235e2, 单精度浮点数,6-7位有效数字 4 byte
double 15-16位有效数字 8 byte
long long -2^63 ~2^63-1 8 byte
long double 18-19位有效数字 16 byte
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b = 2, c =b;
float d = 1.5, e = 1, f = 1.235e2;
bool g = true, h = false;
char j = 'a';
long long l = 121212132323232LL;
long dounle m = 121321.232;
return 0;
}
输入输出
字符的读入
scanf("%c%c", &a, &b); // 会把空格读入
cin >> a >> b; // 会忽略中间的空格(1个或多个)
字符的输出
printf();
cout << << endl;
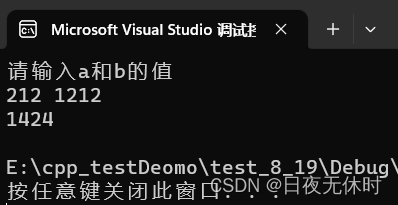
a+b问题
#include<iostream>
#include<cstido>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b; //定义两个变量
cout << "请输入a和b的值" << endl;
cin >> a >> b; // 输入
cout << a + b << endl; // 输出 endl --> 回车
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
printf("两数的和为:%d", a + b);
return 0;
}
在算法中,在所有能用cin cout,都可以使用scanf printf ,但是反之就不一定可以了,前者的效率会低于后者。所以建议使用后者。
注意:使用printf时最好添加头文件#include <cstdio>。
/*
int %d
float %f
char %c
double %lf
long long %lld
*/
这里有个点:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a, b;
scanf("%c%c", &a, &b); //---->这里的%c%c会读入空格,但是cin就不会,这也是cin与scanf的一个区别
cin >> a >> b;
printf("%c %c\n", a,b);
return 0;
}
scanf 和 cin 的区别
注意:scanf 是不会自动过滤掉空格 和回车的 \n 的。
表达式
+ - * / %
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 6 + 3 * 4 / 2 - 1;
cout << a << endl;
int b = a * 10 + 5 / 2;
cout << b << endl;
cout << 23 + 232 - 998 << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 6;
int c = a++;
cout << a << c << endl;
int b = 6;
int d = ++b;
cout << b << d << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
输出结果:
76
77
*/
-= += /= *= %=
abs 函数
求两数的最大值,公式:
m a x ( a , b ) = [ a + b + a b s ( a − b ) 2 ] max(a,b)= [\frac{a+b+abs(a-b)}{2}] max(a,b)=[2a+b+abs(a−b)]
也就是:
m a x = [ a + b + ∣ a − b ∣ 2 ] max = [\frac {a + b + |a - b|}{2}] max=[2a+b+∣a−b∣]
因为 “ 短 + 二者之差 = 长 ”
所以有 “ 长 + ( 短 + 二者之差 )= 长 + 长 = 2 * 长 ”
变量的强制类型转换
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float x = 123.12;
int y = (int)x;
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
return 0;
}
//输出结果
//123.12 123
笔记
浮点数的比较运算
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namspace std;
const double eps = 1e-6;
int main()
{
double x = 1.23456789;
double a = x * x;
double b = sqrt(a);
printf("%.10f\n", b);
if(fabs(x-b) <= eps) puts("相等");
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 3;
if(fbs(sqrt(3) * sqrt(3) < 3))
puts("相等");
return 0;
}
02 判断语句
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score;
cin >> score;
if (score >= 60)
{
cout << "及格";
}
else
{
cout << "不及格";
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int grade;
cin >> grade;
/*if (grade >= 85) cout << 'A' << endl;
else
{
if (grade >= 70) cout << 'B' << endl;
else
{
if (grade >= 60) cout << 'C' << endl;
else
cout << 'D' << endl;
}
}*/
//简化版本
if (grade >= 85) cout << 'A' << endl;
else if (grade >= 70) cout << 'B' << endl;
else if (grade >= 60) cout << 'C' << endl;
o
else cout << 'D' << endl;
return 0;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
char c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (c == '+') cout << a + b << endl;
else if (c == '-') cout << a - b << endl;
else if (c == '*') cout << a * b << endl;
else if (c == '/')
{
if (b == 0)cout << "Divied by zero!" << endl;
else cout << a / b << endl;
}
else cout << "Invaild operator" << endl;
return 0;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
/*
判断闰年。闰年有两种情况
(1)能被100整除时,必须能被400整除;
(2)不能被100整除时,被4整除即可。
输入一个年份,如果是闰年输出yes,否则输出no。
*/
int main()
{
int year;
cin >> year;
if (year % 100 == 0) {
if (year % 400 == 0)cout << "yes" << endl;
else cout << "no" << endl;
}
else
{
if (year % 4 == 0) cout << "yes" << endl;
else cout << "no" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if (a >= b && a >= c)cout << a << endl;
if (b >= b && b >= c)cout << b << endl;
if (c >= b && c >= a)cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
从未注意到的点
672. 税 - AcWing题库
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double salary;
scanf("%lf", &salary);
if(salary > 0 && salary <= 2000) printf("Isento");
else if(salary > 2000 && salary <= 3000) printf("R$ %.2lf", (salary - 2000) * 0.08);
else if(salary > 3000 && salary <= 4500) printf("R$ %.2lf", 80 + (salary - 3000) * 0.18);
else printf("R$ %.2lf", 350 + (salary - 4500) * 0.28);
return 0 ;
}
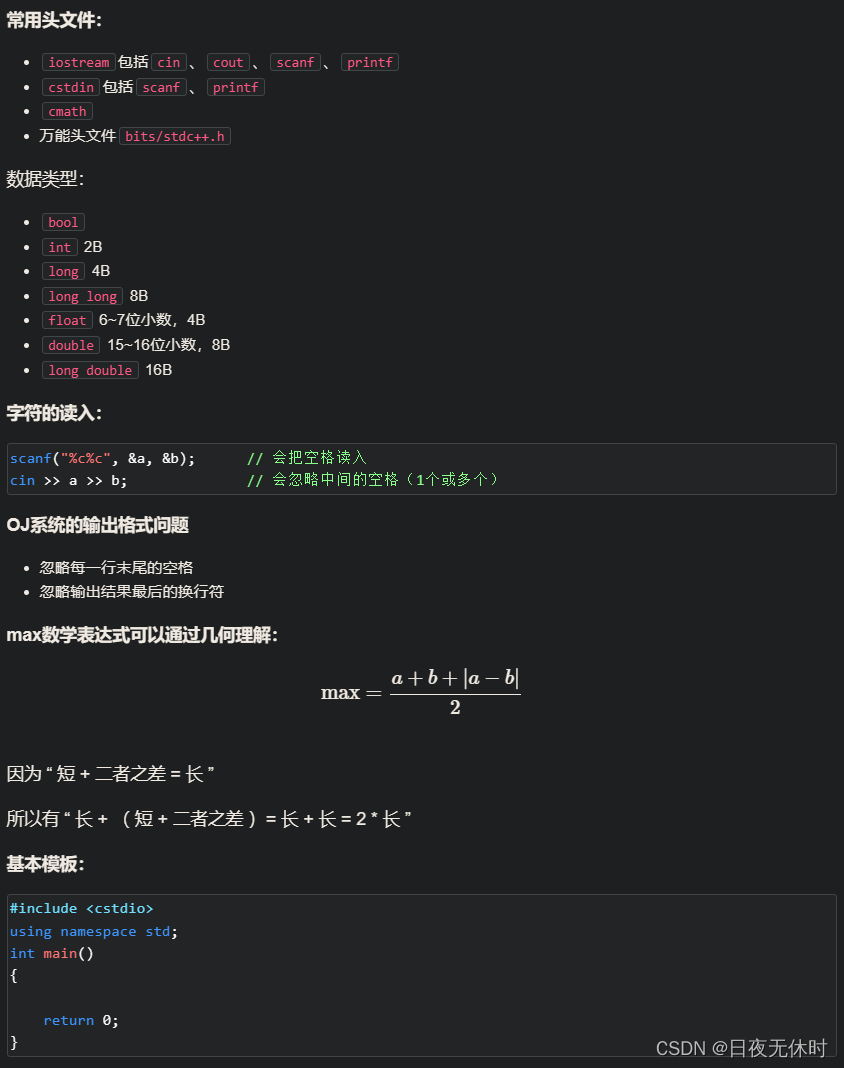
最开始我是
scanf("%.2lf", &salary);
然后在调试阶段就发现问题了
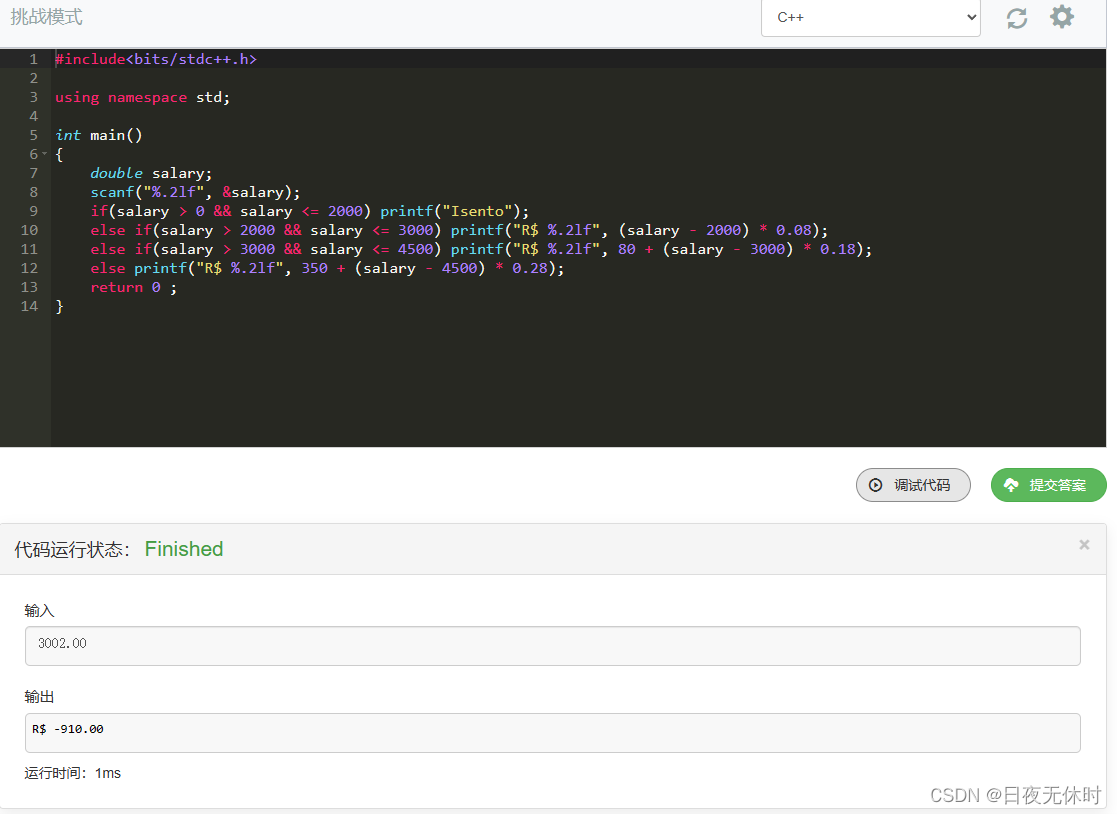
我就开始意识到是.2f的问题,于是翻了一下资料
果然~
-
scanf("%lf", &salary)用于读取一个带有任意小数位数的浮点数。这意味着用户可以输入类似3000.2、3000.25或3000.254等值。因此,当输入3000.2时,程序会执行else if(salary > 2000 && salary <= 3000)这个条件分支。 -
scanf("%.2lf", &salary)的格式化字符串%.2lf会截断输入的小数位数为两位。所以,不论用户输入的小数位数是多少,都会截断为两位小数。当输入3000.2时,实际上salary的值被截断为3000.00,而不是期望的3000.20。因此,程序会执行else if(salary > 3000 && salary <= 4500)这个分支。
这就是两个代码示例输出结果不同的原因。
总结起来,使用 scanf("%lf", &salary) 可以读取任意位数的小数值,而使用 scanf("%.2lf", &salary) 则只读取两位小数的值,并截断输入的其他小数位。
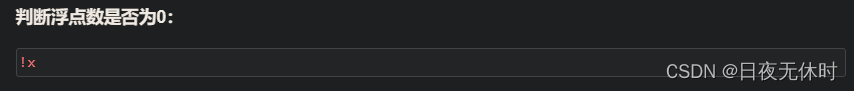
笔记
03 循环语句
斐波那契
f(1) = 1 f(2) = 1
n>=3 f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
a = 1;
b = 1;
int n;
cin >> n;
int i = 0;
while(i < n - 1)
{
int c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
i++;
}
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
注意死循环!循环永久进行,无法结束
do while
使用很少,无论条件的值是什么,至少执行一次
先上车,再买票的feel~
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int s = 0;
int i = 1;
do
{
s += i;
i++;
}while( i <= 10);
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
for循环
for(int 语句; 条件语句; 表达式)
{
}
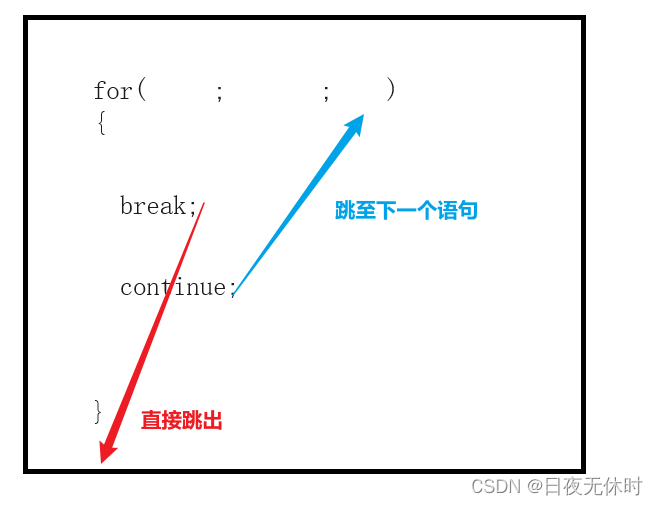
break和continue
判断质数
条件:n>=2,因数只有它本身和1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
bool is_Prime = true;
for(int = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
// 看他的因子
cout << i << endl;
is_Prime = false;
break;
}
}
if(is_Prime) cout << "yes" << endl;
else cout << "no" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出1-100的偶数和
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i % 2) continue;
sum += i;
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
多层循环
曼哈顿距离
d i s t = ∣ x 1 − x 2 ∣ + ∣ y 1 − y 2 ∣ dist = |x1 - x2|+|y1-y2| dist=∣x1−x2∣+∣y1−y2∣
用曼哈顿距离解决菱形输出问题:
曼哈顿距离指的是两个点在标准坐标系上的绝对轴距离之和
输出 n = 5 n=5 n=5 的菱形矩阵,分析如下:
(
4
3
2
3
4
3
2
1
2
3
2
1
0
1
2
3
2
1
2
3
4
3
2
3
4
)
\left(\begin {array}{c} 4 &3 &2 &3 & 4 \\ 3 &2 &1 &2 &3 \\ 2 &1 &0 &1 &2 \\ 3 &2 &1 &2 &3 \\ 4 &3 &2 &3 & 4 \\ \end{array}\right)
4323432123210123212343234
若在元素值 <=代码:
n
2
\frac{n}{2}
2n输出*, >
n
2
\frac{n}{2}
2n输出空格即可
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int cx = n / 2, cy = n / 2;
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(abs(i - cx) + abs(j - cy) <= n / 2)
cout << '*';
else
cout << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
想要空心的效果就将if(abs(i - cx) + abs(j - cy) <= n / 2)判断条件换成==就好了。
练习
偶数
编写一个程序,输出 11 到 100100 之间(包括 11 和 100100)的全部偶数。
输入格式
无输入。
输出格式
输出全部偶数,每个偶数占一行。
输入样例
No input
输出样例
2
4
6
...
100
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
奇数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for(int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
正数
输入 66 个实数,它们要么是正数,要么是负数。
请你统计并输出正数的个数。
输入格式
六个数字,每个占一行。
输出格式
输出格式为 x positive numbers,其中 x为正数的个数。
数据范围
输入数字的绝对值不超过 100100。
输入样例:
7
-5
6
-3.4
4.6
12
输出样例:
4 positive numbers
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int cnt = 0;
for(int i =0; i < 6; i++)
{
double x;
cin >> x;
if(x > 0) cnt++;
}
cout << cnt << " positive numbers" << endl;
return 0;
}
连续奇数的和①
给定两个整数 X和 Y,输出在他们之间(不包括 X和 Y)的所有奇数的和。
输入格式
第一行输入 X,第二行输入 Y。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示所有满足条件的奇数的和。
数据范围
−100≤X,Y≤100−100≤x,Y≤100
输入样例1:
6
-5
输出样例1:
5
输入样例2:
15
12
输出样例2:
13
输入样例3:
12
12
输出样例3:
0
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if(x > y) swap(x, y);
int sum = 0;
int i = x + 1;
while(i < y)
{
if(i % 2) sum += i;
i++;
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
递增序列
//第一种输入方式
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
while (true)
{
cin >> x;
if (!x) break;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++ ) cout << i << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
//第二种输入方式
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
while (cin >> x && x)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++ ) cout << i << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
//第三种输入方式
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x;
while (cin >> x, x)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++ ) cout << i << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
完全数
一个整数,除了本身以外的其他所有约数的和如果等于该数,那么我们就称这个整数为完全数。
例如,66 就是一个完全数,因为它的除了本身以外的其他约数的和为 1+2+3=61+2+3=6。
现在,给定你 N个整数,请你依次判断这些数是否是完全数。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 N,表示共有 N 个测试用例。
接下来 N行,每行包含一个需要你进行判断的整数 X。
输出格式
每个测试用例输出一个结果,每个结果占一行。
如果测试数据是完全数,则输出 X is perfect,其中 X 是测试数据。
如果测试数据不是完全数,则输出 X is not perfect,其中 X是测试数据。
输入样例:
3
6
5
28
输出样例:
6 is perfect
5 is not perfect
28 is perfect
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
int s = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < x; i++)
{
if(x % i == 0) s += i;
}
if(s == x) printf("%d is perfect\n",x);
else printf("%d is not perfect\n",x);
}
return 0;
}
不幸的是,这样超时了,有时间限制。

为了提高效率,可以对算法进行一些优化,减少不必要的因子计算。一个常见的优化是只计算 x 的一半(包括1),然后将因子对应地相加。这可以减少循环次数,提高效率。
以下是优化后的代码示例:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int x;
cin >> x;
int s = 1; // 初始值设为1,包括1本身
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(x); i++) {
if (x % i == 0) {
s += i;
if (i != x / i) {
s += x / i;
}
}
}
if (s == x) {
printf("%d is perfect\n", x);
} else {
printf("%d is not perfect\n", x);
}
}
return 0;
}
这个优化后的代码应该更加高效,减少了因子的计算次数。它先计算 x 的平方根以下的因子,再根据对称性计算其它因子。这种优化应该能够显著减少运行时间,避免超时。
726. 质数 - AcWing题库
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while(n--)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
bool is_prime = true;
for(int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++)
{
if(x % i == 0)
{
is_prime = false;
break;
}
}
if(is_prime) printf("%d is prime\n", x);
else printf("%d is not prime\n", x);
}
return 0;
}