目录
引入
一、Matplotlib模块(常用)
1、绘图流程&常用图
编辑
2、绘制子图&添加标注
编辑
3、面向对象画图
4、Pylab模块应用
二、Seaborn模块(常用)
1、常用图
2、代码示例
编辑
编辑
编辑
编辑
三、Artist模块
四、Pandas绘图
1、数据框(dataframe)&系列(series)
2、pandas常用绘图函数
引入
Python中数据可视化有多种实现方式,下面以实战项目需求为导向介绍几种比较流行的数据可视化模块:Pyplot模块、Seaborn模块、Artist模块、Pandas模块。(个人经常用到pyplot和seaborn)
一、Matplotlib模块(常用)
Matplotlib提供了一整套和Matlab类似的命令API,适合交互式制图。可方便地作为绘图控件,嵌入GUI应用程序。文档完备https://matplotlib.org/3.1.1/gallery/index.html各种图打开都有源程序。
1、绘图流程&常用图
①分别导入Matplotlib.pyplot和numpy
②定义横轴标度并以横轴标度为自变量,定义纵轴功能函数
③figure()函数指定图像长宽比
④plot()函数绘制功能函数
⑤plt的属性函数设置图像属性
⑥show()函数显示图像格式:
plt.plot(x,y,其他参数)其他参数label、color、linewidth、b--(同时指定颜色和线型,点(.)实线(-)虚点线(-.)点线(:)虚线(--)无线条(‘"‘))
常用图类型:

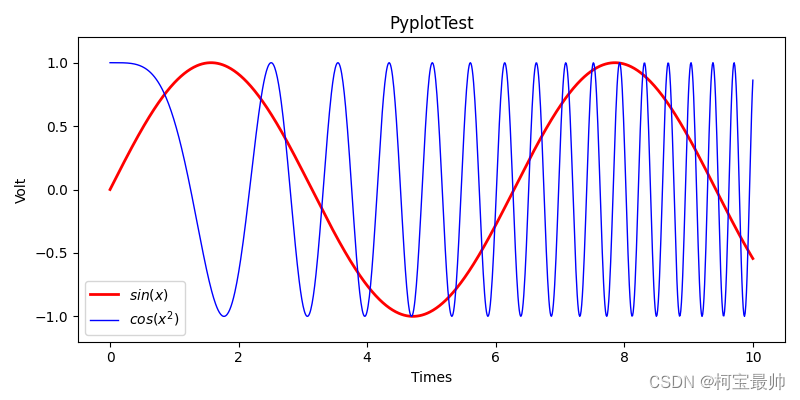
折线图plt.plot演示:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0,10,1000)
y = np.sin(x)
z = np.cos(x**2)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
plt.plot(x,y,label = "$sin(x)$",color = "red",linewidth = 2) #绘图并指定了线的标签,颜色,粗细
plt.plot(x,z,label = "$cos(x^2)$",color = "blue",linewidth = 1)
plt.xlabel("Times")
plt.ylabel("Volt")
plt.title("PyplotTest")
plt.ylim(-1.2,1.2) #y轴显示范围
plt.legend() #显示图中左下角的提示信息,即提示标签(哪个线是哪个函数)
2、绘制子图&添加标注
Matplotlib中用轴表示一个绘图区域,一个绘图对象(figure)可包含多个轴(axis),可理解为子图。可用subplot函数快速绘制有多个轴的图表(子图):
subplot(numRows,numCols,plotNum)将绘图区域分为numRows x numCols个子区域,从左到右从上到下依次编号,从编号1开始。三个参数都小于10时可省略之间逗号
标注即为图的注释:
①text()函数可将文本放置在轴域的任意位置,用来标注绘图的某些特征
②annotate()方法提供辅助函数进行定位,使标注变得准确方便
文本位置及标注点位置均由元组(x,y)描述,参数x,y表示标注点位置,参数xytext表示文本位置
③...
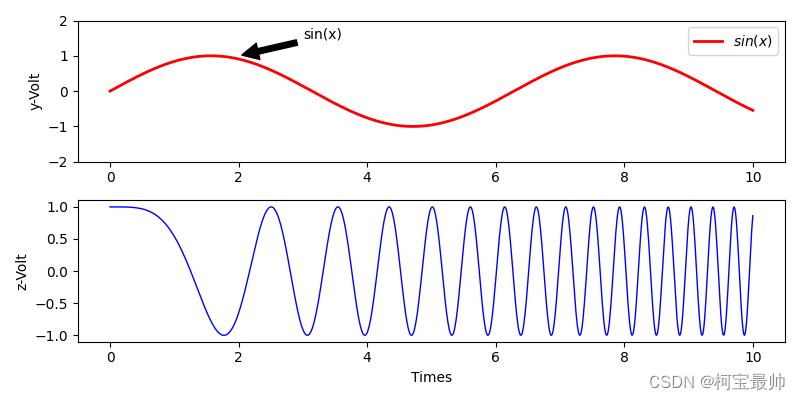
#子图绘制演示(接着上面示例的构建的函数)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,4))
ax = fig.add_subplot(211) #创建Axes对象
plt.subplot(2,1,1) #两行一列个子区域,编号1位置
plt.plot(x,y,label = "$sin(x)$",color = "red",linewidth = 2)
plt.ylabel("y-Volt")
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(2,1,2) #两行一列个子区域,编号2位置
plt.plot(x,z,label = "$cos(x^2)$",color = "blue",linewidth = 1)
plt.ylabel("z-Volt")
plt.xlabel("Times")
ax.annotate("sin(x)",xy=(2,1),xytext=(3,1.5),arrowprops = dict(facecolor='black',shrink = 0.05)) #添加文字和黑色箭头(Artist模块的简单类型Artist)
ax.set_ylim(-2,2)
plt.show()3、面向对象画图
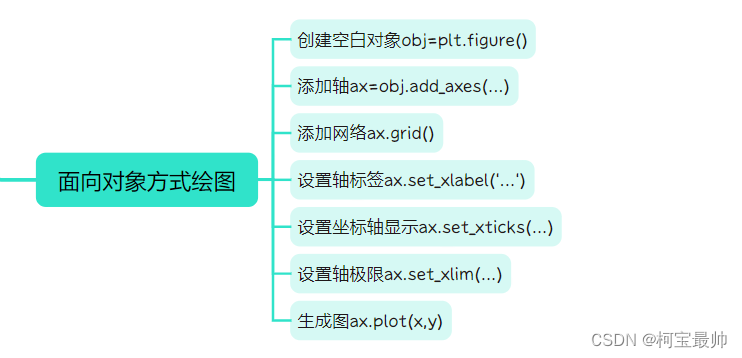
4、Pylab模块应用
也是matplotlib里面的一个模块,提供可绘制二维、三维数据的工具模块,包含numpy和pyplot模块中的常见函数,方便快速计算和绘图。
二、Seaborn模块(常用)
它基于matplotlib,但提供了更高级的统计图形方法!
1、常用图

2、代码示例
下面选取逻辑回归算法(一种分类算法,titannic数据集)中特征工程(数据预处理)中的一段代码演示:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn
import sklearn
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn import preprocessing
titanic_data = pd.read_csv("titanic_data.csv") #泰坦尼克号幸存或遇难者信息
titanic_data = titanic_data[['Survived', 'Pclass', 'Sex', 'Age', 'SibSp', 'Parch', 'Embarked', 'Fare']] #选取需要的8列
#1.特征工程
titanic_data['Age'].fillna((titanic_data['Age'].mean()), inplace=True) #Age有177个空值,这里用平均值替代
titanic_data.dropna(inplace=True) #Embarked只有2个空值,可放弃这两个值
titanic_data_X = titanic_data[['Pclass', 'Sex', 'Age', 'SibSp', 'Parch', 'Embarked', 'Fare']]
titanic_data_Y = titanic_data[['Survived']] #分离自变量X和因变量Y(最后的分类结果为2个1或0,是否存活)
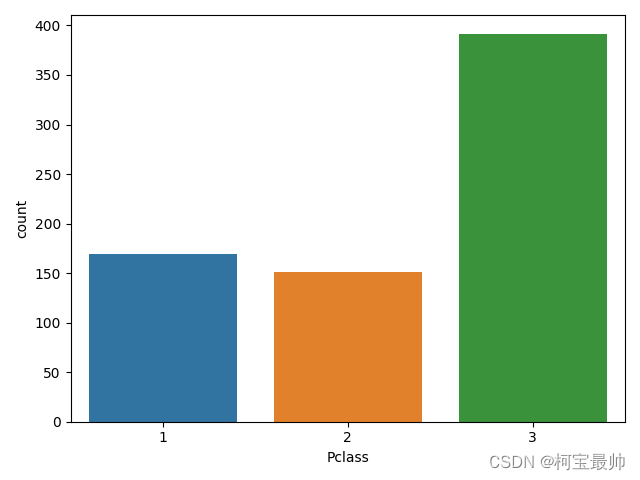
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(titanic_data_X, titanic_data_Y,test_size=0.20) #将数据分成训练集和测试集seaborn.countplot(x='Pclass', data = X_train) #检查Pclass(舱位等级)柱状图
plt.show()seaborn.displot(X_train['Age']) #检查Age分布图(柱状图+核密度估计)
plt.show()seaborn.displot(X_train['Fare']) #检查Fare(票价)分布图(柱状图+核密度估计)
plt.show()age_scaler = StandardScaler() #创建Z-Score标准化对象,对Age进行分类特征标准化
age_scaler.fit(pd.DataFrame(X_train['Age']))
X_train.loc[:, 'Age'] = age_scaler.transform(X_train[['Age']]) #双[]
fare_scaler = StandardScaler() #创建Z-Score标准化对象,对Fare(票价)进行分类特征标准化
fare_scaler.fit(pd.DataFrame(X_train['Fare']))
X_train.loc[:, 'Fare'] = fare_scaler.transform(X_train[['Fare']]) #双[]
X_train.loc[:, 'Sex'] = X_train['Sex'].map({'female': 0, 'male': 1}) #将Sex映射为0,1
embarked_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder() #创建编码对象,对Embarked(登船口3个)编码
embarked_encoder.fit(pd.DataFrame(X_train['Embarked']))
X_train.loc[:, 'Embarked'] = embarked_encoder.transform(X_train[['Embarked']])
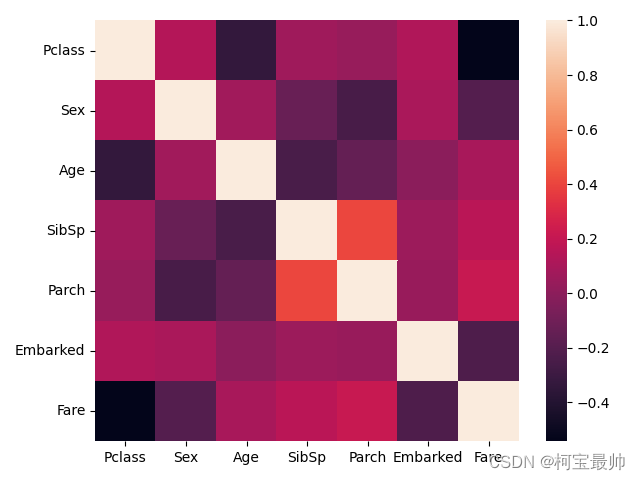
#截至此,将所有数据的格式转换完成,用heatmap检查下特征之间的关联性
seaborn.heatmap(X_train.corr())
plt.show()三、Artist模块
Matplotlib绘图库的API包含3个图层——画板、渲染、artist.Artist(如何渲染)。相比Pyplot和Pylab两个API,Artist用于处理所有的高级结构,如处理图表、文字、曲线等的绘制和布局,不需要关注底层的绘制细节。
Artist分简单类型、容器类型两种。简单类型的Artist为标准的绘图元件,如Line2D、Rectangle、Text、AxesTmage等;容器类型可以包含许多简单类型的Artist组成一个整体,如Axis、Axes、Figure等。
步骤:
①创建Figure对象
②用Figure对象创建一个或多个Axes或者Subplot对象
③调用Axes等对象的方法创建各种简单类型的ArtistMatplotlib所绘制的图表中的每一个元素都由Artist控制,而每一个Artist对象包含很多属性来控制显示效果,常见属性:
alpha透明值,0完全透明,1完全不透明
animate布尔值,绘制动画效果是使用
axes此Artist对象所在的Axes对象,可能为None
figure此Artist对象所在的Figure对象,可能为None
label文本标签
picker控制Artist对象选取
zorder控制绘图顺序所有属性都可通过相应的get_*和set_*函数读写,如将alpha设置为当前值的一半:
fig.set_alpha(0.5*fig.get_alpha())若一句代码设置多个属性:
fig.set(alpha = 0.5,zorder = 2,label = '$sin(x)$')四、Pandas绘图
pandas是python最强大的数据分析和探索工具,包含高级的数据结构和精巧的工具。它构建在numpy之上,使得以numpy为中心的应用更便捷;支持类似于SQL的数据操作,具有丰富的数据处理函数;它的作图依赖于matplotlib,通常两者一起使用。
1、数据框(dataframe)&系列(series)
pandas带两个重要数据结构:数据框(dataframe)、系列(series)
①数据框
二维表,行列都有索引,面向行列的操作对称。创建数据框的方法很多,常用包含相等长度列表的字典或Numpy数组来创建数据库,行索引默认由0开始,列索引用户自定义(也可自定义行索引,列索引要与字典对应不然数据为空)
import pandas as pd
data = {'name':['小明','小红','小刚','小强','大壮'],
'age':[15,16,14,18,20],
'score':[88,99,65,95,67]
}
dataframe1 = pd.DataFrame(data)
dataframe2 = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['name','age','score'],index=['one','two','three','four','five'])
print(dataframe1)
print(dataframe2)
运行结果:
name age score
0 小明 15 88
1 小红 16 99
2 小刚 14 65
3 小强 18 95
4 大壮 20 67
name age score
one 小明 15 88
two 小红 16 99
three 小刚 14 65
four 小强 18 95
five 大壮 20 67②系列
对具有同一属性的值的统称,可理解为一维数组(退化了的数据框)
print(dataframe2['name'])
运行结果:
one 小明
two 小红
three 小刚
four 小强
five 大壮
Name: name, dtype: object2、pandas常用绘图函数
plot():绘制线性二维图(matplotlib/pandas库都有)
pie():绘制饼形图(matplotlib/pandas、库都有)
hist():绘制二维条形直方图(matplotlib/pandas库都有)
boxplot():绘制样本数据箱体图(pandas库)
plot(logy = True):绘制y轴的对数图(pandas库)
plot(yerr = error):绘制误差条形图(pandas库)