nn.MSELoss均方损失函数

LPIPS感知损失
学习感知图像块相似度(Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity, LPIPS)也称为“感知损失”(perceptual loss),用于度量两张图像之间的差别,来源于论文《The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric》。
论文地址:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1801.03924.pdf
代码地址:
pytorch:https://github.com/richzhang/PerceptualSimilarity
计算相似度需逐层计算网络输出的对应channel的Cos Distance,然后对得到的distance进行平均(所有层,空间维度),LPIPS主要是把两个Cos Distance作为网络的输入,然后用Cross Entropy Loss训练网络学习2AFC。
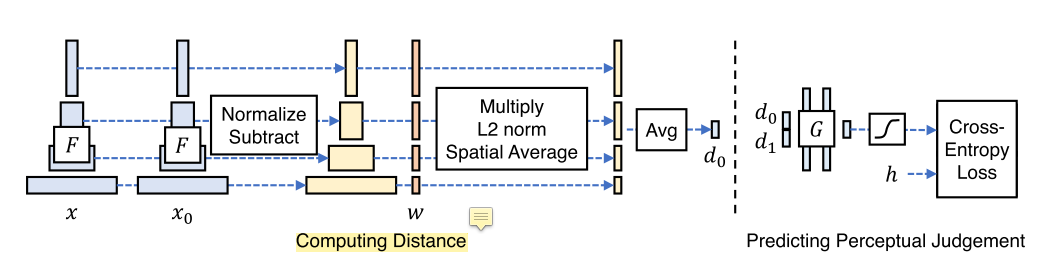
计算x与x0 之间的距离d0:给定不同的BaseNet F,首先计算深度嵌入,规格化通道维度中的激活,用向量w缩放每个通道,取L2距离,然后对空间维度和所有层次求平均。
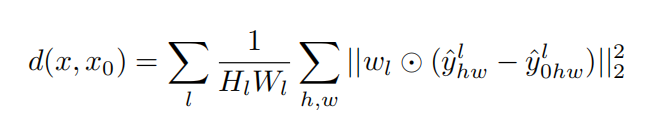
从层提取特征堆并在通道维度中进行单元标准化。通过
缩放激活通道维并计算
距离
,在空间上取平均,在层上求和。
# pytorch 求LPIPS
import torch
import lpips
import os
use_gpu = False # Whether to use GPU
spatial = True # 返回感知距离的空间图
# 线性校准模型 Linearly calibrated models (LPIPS)
loss_fn = lpips.LPIPS(net='alex', spatial=spatial) # Can also set net = 'squeeze' or 'vgg'
# loss_fn = lpips.LPIPS(net='alex', spatial=spatial, lpips=False) # Can also set net = 'squeeze' or 'vgg'
if (use_gpu):
loss_fn.cuda()
# 使用伪张量的实例 Example usage with dummy tensors
rood_path = r'D:\Project\results\faces'
img0_path_list = []
img1_path_list = []
## path in net is already exist
'''
for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(rood_path, followlinks=True)):
for fname in fnames:
path = os.path.join(root, fname)
if '_generated' in fname:
im0_path_list.append(path)
elif '_real' in fname:
im1_path_list.append(path)
'''
dist_ = []
for i in range(len(img0_path_list)):
dummy_img0 = lpips.im2tensor(lpips.load_image(img0_path_list[i]))
dummy_img1 = lpips.im2tensor(lpips.load_image(img1_path_list[i]))
if (use_gpu):
dummy_img0 = dummy_img0.cuda()
dummy_img1 = dummy_img1.cuda()
dist = loss_fn.forward(dummy_img0, dummy_img1)
dist_.append(dist.mean().item())
print('Avarage Distances: %.3f' % (sum(dist_) / len(img0_path_list)))