0. 简介
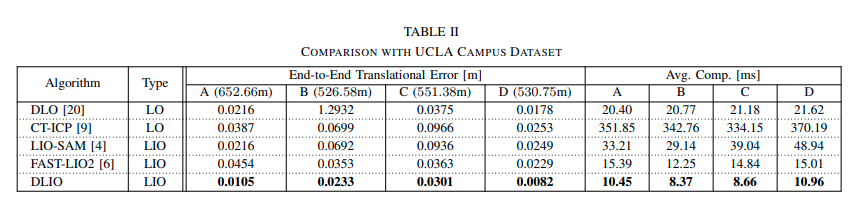
我们刚刚了解过DLIO的整个流程,我们发现相比于Point-LIO而言,这个方法更适合我们去学习理解,同时官方给出的结果来看DLIO的结果明显好于现在的主流方法,当然指的一提的是,这个DLIO是必须需要六轴IMU的,所以如果没有IMU的画,那只有DLO可以使用了。
1. OdomNode–DLIO构造函数
OdomNode是一个ROS节点的构造函数,主要用于初始化节点的参数、订阅和发布的话题以及一些算法所需的参数和数据结构。在构造函数中,首先通过调用getParams()函数获得节点的参数,然后获取最大的线程数。接着初始化一些标志位和数据结构,例如dlio标定是否初始化、第一帧有效观测、第一帧IMU数据等。之后通过ros::NodeHandle订阅和发布话题,其中包括点云、IMU数据、odom、pose、path、关键帧位姿、关键帧点云和去畸变的点云。然后通过创建timer定时发布pose。接下来初始化位姿、lidar位置、IMU数据以及点云数据结构等。之后设置一些算法所需的参数,例如gicp的参数、voxel的参数等。最后获取CPU的信息并初始化一些度量指标和CPU时间。整个构造函数的主要作用是初始化节点的参数、订阅和发布话题以及一些算法所需的参数和数据结构,为后续的节点运行做好准备。
dlio::OdomNode::OdomNode(ros::NodeHandle node_handle) : nh(node_handle) {
this->getParams(); //获得参数,主要是在cfg中读取的
this->num_threads_ = omp_get_max_threads(); //获取最大的thread线程
this->dlio_initialized = false; // dlio标定是否初始化
this->first_valid_scan = false; //第一帧有效观测
this->first_imu_received = false; //第一帧IMU数据
if (this->imu_calibrate_) { // IMU是否已经标定,设置为true时候直接从cfg中读取
this->imu_calibrated = false;
} else {
this->imu_calibrated = true;
}
this->deskew_status = false; //是否进行去畸变
this->deskew_size = 0; //去畸变的点云数量
this->lidar_sub =
this->nh.subscribe("pointcloud", 1, &dlio::OdomNode::callbackPointCloud,
this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
this->imu_sub = this->nh.subscribe("imu", 1000, &dlio::OdomNode::callbackImu,
this, ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay());
this->odom_pub =
this->nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odom", 1, true); //发布odom
this->pose_pub = this->nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped>(
"pose", 1, true); //发布pose
this->path_pub =
this->nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>("path", 1, true); //发布path
this->kf_pose_pub = this->nh.advertise<geometry_msgs::PoseArray>(
"kf_pose", 1, true); //发布关键帧的位姿
this->kf_cloud_pub = this->nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(
"kf_cloud", 1, true); //发布关键帧的点云
this->deskewed_pub = this->nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(
"deskewed", 1, true); //发布去畸变的点云
this->publish_timer =
this->nh.createTimer(ros::Duration(0.01), &dlio::OdomNode::publishPose,
this); //根据timer,发布pose
this->T = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(); //初始化T
this->T_prior = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(); //初始化T_prior,上一帧位姿
this->T_corr = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(); //初始化T_corr,当前位姿
this->origin = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化原点
this->state.p = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化位置
this->state.q = Eigen::Quaternionf(1., 0., 0., 0.); //初始化四元数
this->state.v.lin.b = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化线速度,机体坐标系下
this->state.v.lin.w = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化线速度,世界坐标系下
this->state.v.ang.b = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化角速度,机体坐标系下
this->state.v.ang.w = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化角速度,世界坐标系下
this->lidarPose.p = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化lidar位置
this->lidarPose.q = Eigen::Quaternionf(1., 0., 0., 0.); //初始化lidar四元数
this->imu_meas.stamp = 0.;
this->imu_meas.ang_vel[0] = 0.; //初始化IMU的角速度
this->imu_meas.ang_vel[1] = 0.;
this->imu_meas.ang_vel[2] = 0.;
this->imu_meas.lin_accel[0] = 0.; //初始化IMU的线加速度
this->imu_meas.lin_accel[1] = 0.;
this->imu_meas.lin_accel[2] = 0.;
this->imu_buffer.set_capacity(this->imu_buffer_size_); //设置IMU的buffer
this->first_imu_stamp = 0.;
this->prev_imu_stamp = 0.;
this->original_scan = pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr(
boost::make_shared<const pcl::PointCloud<PointType>>()); //初始化原始点云
this->deskewed_scan = pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr(
boost::make_shared<
const pcl::PointCloud<PointType>>()); //初始化去畸变点云
this->current_scan = pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr(
boost::make_shared<const pcl::PointCloud<PointType>>()); //初始化当前点云
this->submap_cloud = pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr(
boost::make_shared<const pcl::PointCloud<PointType>>()); //初始化子图点云
this->num_processed_keyframes = 0; //初始化处理的关键帧数量
this->submap_hasChanged = true; //初始化子图是否改变,第一帧肯定改变
this->submap_kf_idx_prev.clear(); //初始化上一帧的关键帧索引
this->first_scan_stamp = 0.; //初始化第一帧点云的时间戳
this->elapsed_time = 0.; //初始化时间
this->length_traversed; //初始化长度
this->convex_hull.setDimension(3); //设置凸包的维度
this->concave_hull.setDimension(3); //设置凹包的维度
this->concave_hull.setAlpha(this->keyframe_thresh_dist_); //设置凹包的阈值
this->concave_hull.setKeepInformation(true); //设置凹包保留信息
this->gicp.setCorrespondenceRandomness(
this->gicp_k_correspondences_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表每次迭代时,随机选择的点对的数量
this->gicp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(
this->gicp_max_corr_dist_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表两个点云中对应点之间的最大距离
this->gicp.setMaximumIterations(
this->gicp_max_iter_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表最大迭代次数
this->gicp.setTransformationEpsilon(
this->gicp_transformation_ep_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表两次迭代之间的最小差异
this->gicp.setRotationEpsilon(
this->gicp_rotation_ep_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表两次迭代之间的最小旋转差异
this->gicp.setInitialLambdaFactor(
this->gicp_init_lambda_factor_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表初始lambda因子
this->gicp_temp.setCorrespondenceRandomness(
this->gicp_k_correspondences_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表每次迭代时,随机选择的点对的数量
this->gicp_temp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(
this->gicp_max_corr_dist_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表两个点云中对应点之间的最大距离
this->gicp_temp.setMaximumIterations(
this->gicp_max_iter_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表最大迭代次数
this->gicp_temp.setTransformationEpsilon(
this->gicp_transformation_ep_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表两次迭代之间的最小差异
this->gicp_temp.setRotationEpsilon(
this->gicp_rotation_ep_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表两次迭代之间的最小旋转差异
this->gicp_temp.setInitialLambdaFactor(
this->gicp_init_lambda_factor_); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表初始lambda因子
pcl::Registration<PointType, PointType>::KdTreeReciprocalPtr temp;
this->gicp.setSearchMethodSource(
temp, true); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表搜索源点的方法
this->gicp.setSearchMethodTarget(
temp, true); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表搜索目标点的方法
this->gicp_temp.setSearchMethodSource(
temp, true); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表搜索源点的方法
this->gicp_temp.setSearchMethodTarget(
temp, true); //设置gicp的参数,这个值代表搜索目标点的方法
this->geo.first_opt_done = false; //初始化几何观测的第一次优化
this->geo.prev_vel = Eigen::Vector3f(0., 0., 0.); //初始化几何观测的上一次速度
pcl::console::setVerbosityLevel(pcl::console::L_ERROR);
this->crop.setNegative(true); //设置crop的参数,让所有内部的点都被删除
this->crop.setMin(Eigen::Vector4f(-this->crop_size_, -this->crop_size_,
-this->crop_size_, 1.0));
this->crop.setMax(Eigen::Vector4f(this->crop_size_, this->crop_size_,
this->crop_size_, 1.0));
this->voxel.setLeafSize(this->vf_res_, this->vf_res_,
this->vf_res_); //设置voxel的参数,这个值代表体素的大小
this->metrics.spaciousness.push_back(0.); //初始化度量指标
this->metrics.density.push_back(this->gicp_max_corr_dist_); //初始化度量指标
// CPU Specs
char CPUBrandString[0x40];
memset(CPUBrandString, 0, sizeof(CPUBrandString));
this->cpu_type = "";
#ifdef HAS_CPUID //如果有cpuid
unsigned int CPUInfo[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
__cpuid(0x80000000, CPUInfo[0], CPUInfo[1], CPUInfo[2],
CPUInfo[3]); //获取CPU的信息
unsigned int nExIds = CPUInfo[0];
for (unsigned int i = 0x80000000; i <= nExIds; ++i) {
__cpuid(i, CPUInfo[0], CPUInfo[1], CPUInfo[2], CPUInfo[3]);
if (i == 0x80000002) //获取CPU的型号
memcpy(CPUBrandString, CPUInfo, sizeof(CPUInfo));
else if (i == 0x80000003)
memcpy(CPUBrandString + 16, CPUInfo, sizeof(CPUInfo));
else if (i == 0x80000004)
memcpy(CPUBrandString + 32, CPUInfo, sizeof(CPUInfo));
}
this->cpu_type = CPUBrandString;
boost::trim(this->cpu_type);
#endif
FILE *file;
struct tms timeSample;
char line[128];
this->lastCPU = times(&timeSample); //获取CPU的时间
this->lastSysCPU = timeSample.tms_stime; //获取CPU的系统时间
this->lastUserCPU = timeSample.tms_utime; //获取CPU的用户时间
file = fopen("/proc/cpuinfo", "r");
this->numProcessors = 0;
while (fgets(line, 128, file) != nullptr) {
if (strncmp(line, "processor", 9) == 0)
this->numProcessors++;
}
fclose(file);
}
2. callbackPointCloud–DLIO主要进程输入
这个代码是基本DLIO所有主要函数的调用渠道,用于处理传感器数据并进行实时SLAM。具体来说,该函数接收一个类型为sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr的指针,并对其进行一系列处理。以下是该函数的主要步骤:
- 获取当前时间戳,用于计算处理时间。
- 如果是第一次处理,则记录第一个扫描的时间戳。
- 进行DLIO的初始化,包括IMU校准和重力校准。
- 将传入的点云数据转换为DLIO格式。
- 预处理点云。
- 检查点云是否有效,如果点数过少则返回错误。
- 计算度量指标,并在单独的线程中进行。
- 如果开启了自适应参数,则设置自适应参数。
- 将当前扫描设置为输入源,并传入GICP算法进行配准。
- 如果当前没有关键帧,则将初始帧设置为第一关键帧,并在单独的线程中构建子地图和关键帧。
- 通过IMU、S2M和GEO方法获取下一个姿态。
- 更新当前关键帧姿态和地图。
- 如果需要,构建关键帧法线和子地图。
- 更新轨迹和时间戳。
- 将处理后的点云发布到ROS。
- 更新一些统计数据。
- 发布自定义DLIO消息。
该代码段中的函数主要使用了多线程技术,并涉及到大量的SLAM算法和数据处理操作,如GICP配准、IMU校准、重力校准、位姿估计、轨迹更新等。
void dlio::OdomNode::callbackPointCloud(
const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr &pc) {
std::unique_lock<decltype(this->main_loop_running_mutex)> lock(
main_loop_running_mutex);
this->main_loop_running = true;
lock.unlock();
double then = ros::Time::now().toSec();
if (this->first_scan_stamp == 0.) {
this->first_scan_stamp = pc->header.stamp.toSec();
}
// DLIO Initialization procedures (IMU calib, gravity align)
if (!this->dlio_initialized) {
this->initializeDLIO();
}
// 将传入的扫描转换为DLIO格式
this->getScanFromROS(pc);
// 预处理点云
this->preprocessPoints();
if (!this->first_valid_scan) {
return;
}
if (this->current_scan->points.size() <= this->gicp_min_num_points_) {
ROS_FATAL("Low number of points in the cloud!");
return;
}
// 计算度量指标
this->metrics_thread = std::thread(&dlio::OdomNode::computeMetrics, this);
this->metrics_thread.detach();
// 设置自适应参数
if (this->adaptive_params_) {
this->setAdaptiveParams();
}
// 将新帧设置为输入源,并传入GICP
this->setInputSource();
// 将初始帧设置为第一关键帧
if (this->keyframes.size() == 0) {
this->initializeInputTarget();
this->main_loop_running = false;
this->submap_future =
std::async(std::launch::async, &dlio::OdomNode::buildKeyframesAndSubmap,
this, this->state);
this->submap_future.wait(); // 等待任务完成
return;
}
// 通过IMU + S2M + GEO获取下一个姿态
this->getNextPose();
// 更新当前关键帧姿态和地图
this->updateKeyframes();
// 如果需要,构建关键帧法线和子地图(如果我们还没有在等待中)
if (this->new_submap_is_ready) {
this->main_loop_running = false;
this->submap_future =
std::async(std::launch::async, &dlio::OdomNode::buildKeyframesAndSubmap,
this, this->state);
} else {
lock.lock();
this->main_loop_running = false;
lock.unlock();
this->submap_build_cv.notify_one();
}
// 更新轨迹
this->trajectory.push_back(std::make_pair(this->state.p, this->state.q));
// 更新时间戳
this->lidar_rates.push_back(1. / (this->scan_stamp - this->prev_scan_stamp));
this->prev_scan_stamp = this->scan_stamp;
this->elapsed_time = this->scan_stamp - this->first_scan_stamp;
// 将信息发布到ROS
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::ConstPtr published_cloud;
if (this->densemap_filtered_) {
published_cloud = this->current_scan;
} else {
published_cloud = this->deskewed_scan;
}
this->publish_thread = std::thread(&dlio::OdomNode::publishToROS, this,
published_cloud, this->T_corr);
this->publish_thread.detach();
// 更新一些统计数据
this->comp_times.push_back(ros::Time::now().toSec() - then);
this->gicp_hasConverged = this->gicp.hasConverged();
// 调试语句和发布自定义DLIO消息
this->debug_thread = std::thread(&dlio::OdomNode::debug, this);
this->debug_thread.detach();
this->geo.first_opt_done = true; //第一次优化完成
}
3. callbackImu—DLIO的IMU状态传播
下面的函数主要用于处理传感器数据,进行IMU校准,并将校准后的IMU测量值存储到IMU缓冲区中。该函数接收一个sensor_msgs::Imu类型的指针作为输入参数,并将该指针转换为sensor_msgs::Imu::Ptr类型的指针,以便进行操作。
函数首先将接收到的IMU数据标记为已接收状态,然后获取该数据的角速度和线性加速度信息。如果是第一次接收到IMU数据,则记录第一次接收到的时间戳。接下来进行IMU校准程序,该程序持续三秒钟,期间会记录一段时间内的陀螺仪和加速度计数据,并计算它们的平均值。如果需要进行重力校准,则会通过估计重力向量,计算出重力对齐方向,并更新状态量。如果需要进行加速度计校准,则会将重力从平均加速度中减去以得到偏差,并更新状态量。如果需要进行陀螺仪校准,则会计算陀螺仪的偏差,并更新状态量。最后,将IMU校准完成标记为真。