linux驱动开发-点亮第一个led灯
- 一.背景知识
- 二.如何写驱动程序
- 三.实战演练
- 3.1 查询原理图
- 3.2 配置引脚为gpio模式
- 3.3 配置引脚为输出模式
- 3.4 DR寄存器
- 四.代码实例
- 4.1 驱动层
- 4.2 应用层
一.背景知识
我们这里使用的是百问网的imx_6ullpro的开发板。这里和裸机不同的是,这类开发板可以运行linux操作系统,所以和裸机开发有点不同。
另外前面博主以及写过51,32单片机的技术博客,入门都是从点灯开始,这里也不例外。
二.如何写驱动程序
其实驱动程序和我们的裸机程序也类似。也需要操作寄存器来控制引脚。而不同的是程序是运行在操作系统之上的,可以调用标准c库以及内核提供的函数接口,且需要将文件编译为ko文件,加载进linux内核中才能运行。下面我通过实际代码来讲解驱动程序,这样才能更加理解驱动。
三.实战演练
3.1 查询原理图
我们可以看原理图得知,开发板上有一个led可以操控,引脚为GPIO5_3,这样我们只需要操作对应寄存器即可。
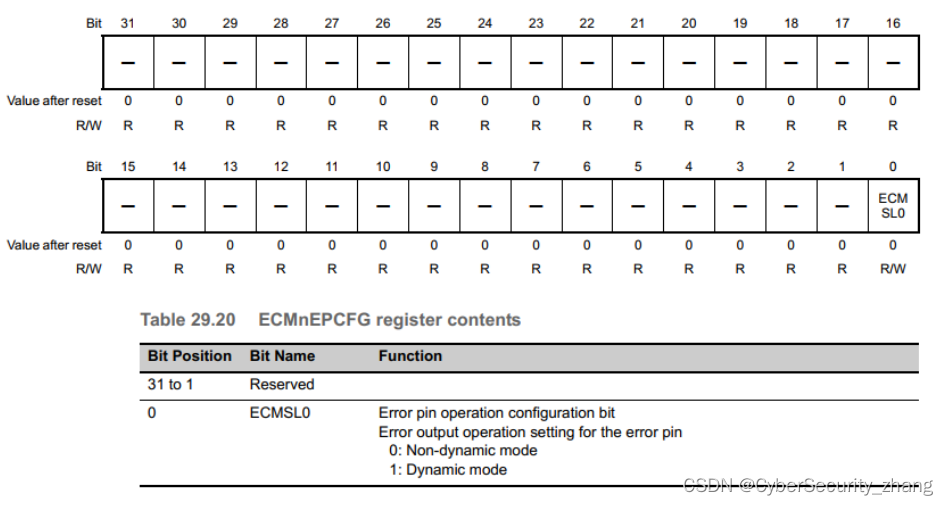
3.2 配置引脚为gpio模式
可以看到此寄存器地址:0x02290000+0x14,需要将此寄存器的MUX_MODE配置为101才能使用GPIO5_IO3。
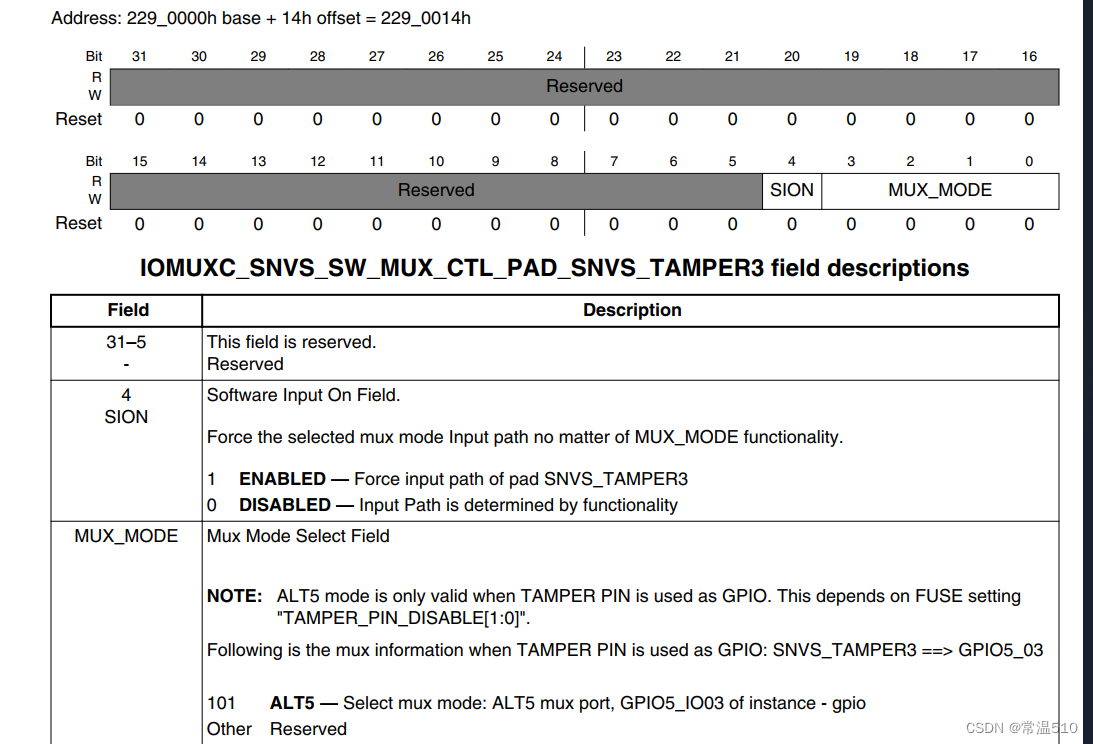
3.3 配置引脚为输出模式
可以看出地址为0x020A_C004,配置0为输入模式,配置1为输出模式
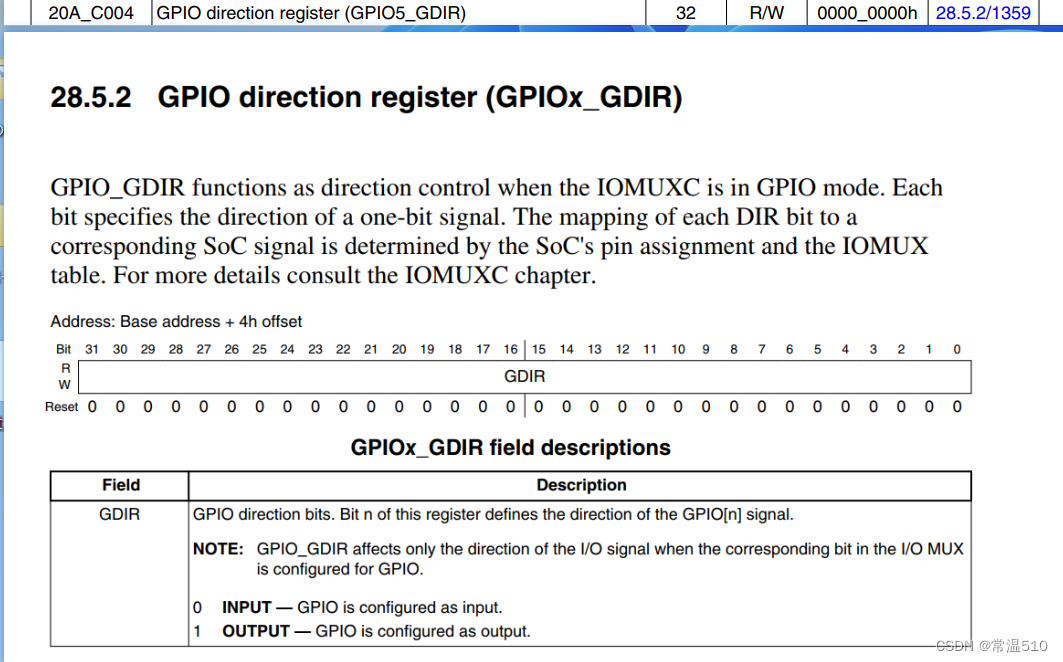
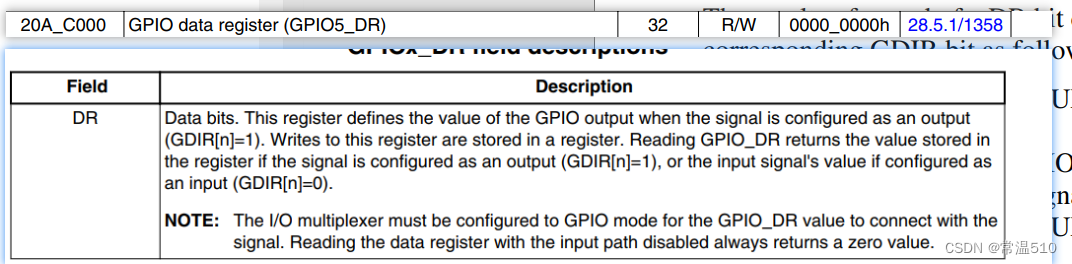
3.4 DR寄存器
DR寄存器也就是配置引脚输出电平是高电平还是低电平
四.代码实例
前面都是相关知识的介绍,包括原理图以及寄存器。下面我们进行代码的讲解。
4.1 驱动层
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
static int major;
static struct class *led_class;
/* registers */
// IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 地址:0x02290000 + 0x14
static volatile unsigned int *IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3;
// GPIO5_GDIR 地址:0x020AC004
static volatile unsigned int *GPIO5_GDIR;
//GPIO5_DR 地址:0x020AC000
static volatile unsigned int *GPIO5_DR;
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
char val;
int ret;
/* copy_from_user : get data from app */
ret = copy_from_user(&val, buf, 1);
/* to set gpio register: out 1/0 */
if (val)
{
/* set gpio to let led on */
*GPIO5_DR &= ~(1<<3);
}
else
{
/* set gpio to let led off */
*GPIO5_DR |= (1<<3);
}
return 1;
}
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
/* enable gpio5
* configure gpio5_io3 as gpio
* configure gpio5_io3 as output
*/
*IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 &= ~0xf;
*IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 |= 0x5;
*GPIO5_GDIR |= (1<<3);
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, //默认THIS_MOUDLE
.write = led_write, //绑定应用层write函数
.open = led_open,//绑定应用层open函数
};
/* 入口函数 */
static int __init led_init(void)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
//注册设备,返回主设备号
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_led", &led_fops);
/* ioremap */
//物理地址转换为裸机地址
IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3 = ioremap(0x02290000 + 0x14, 4);
// GPIO5_GDIR 地址:0x020AC004
GPIO5_GDIR = ioremap(0x020AC004, 4);
//GPIO5_DR 地址:0x020AC000
GPIO5_DR = ioremap(0x020AC000, 4);
//创建设备类
led_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myled");
//创建设备
device_create(led_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "myled"); /* /dev/myled */
return 0;
}
//出口函数
static void __exit led_exit(void)
{
iounmap(IOMUXC_SNVS_SW_MUX_CTL_PAD_SNVS_TAMPER3);
iounmap(GPIO5_GDIR);
iounmap(GPIO5_DR);
device_destroy(led_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(led_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_led");
}
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
4.2 应用层
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// ledtest /dev/myled on
// ledtest /dev/myled off
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char status = 0;
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev> <on|off>\n", argv[0]);
printf(" eg: %s /dev/myled on\n", argv[0]);
printf(" eg: %s /dev/myled off\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
// open
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can not open %s\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
// write
if (strcmp(argv[2], "on") == 0)
{
status = 1;
}
write(fd, &status, 1);
return 0;
}