目录
- 🌈前言
- 🌸1、System V共享内存
- 🍡1.1、概念
- 🍢1.2、原理
- 🌺2、共享内存相关函数和指令
- 🍡2.1、shmget函数(创建)
- 🍢2.2、shmctl函数(控制)
- 🍧2.3、shmat函数(挂接)
- 🍨2.4、shmdt(去挂接)
- 🍀3、共享内存的使用
- 🍡3.1、测试
- 🍢3.2、共享内存与管道的区别
- 🍧3.3、基于共享内存+管道实现访问控制
🌈前言
这篇文章给大家带来进程间通信中共享内存的学习!!!
🌸1、System V共享内存
🍡1.1、概念
概念:
-
共享内存是与管道不同的一种进程间通信方式
-
它们都是先让多个进程先看到一份相同的资源,所以必须提供存储数据的空间
-
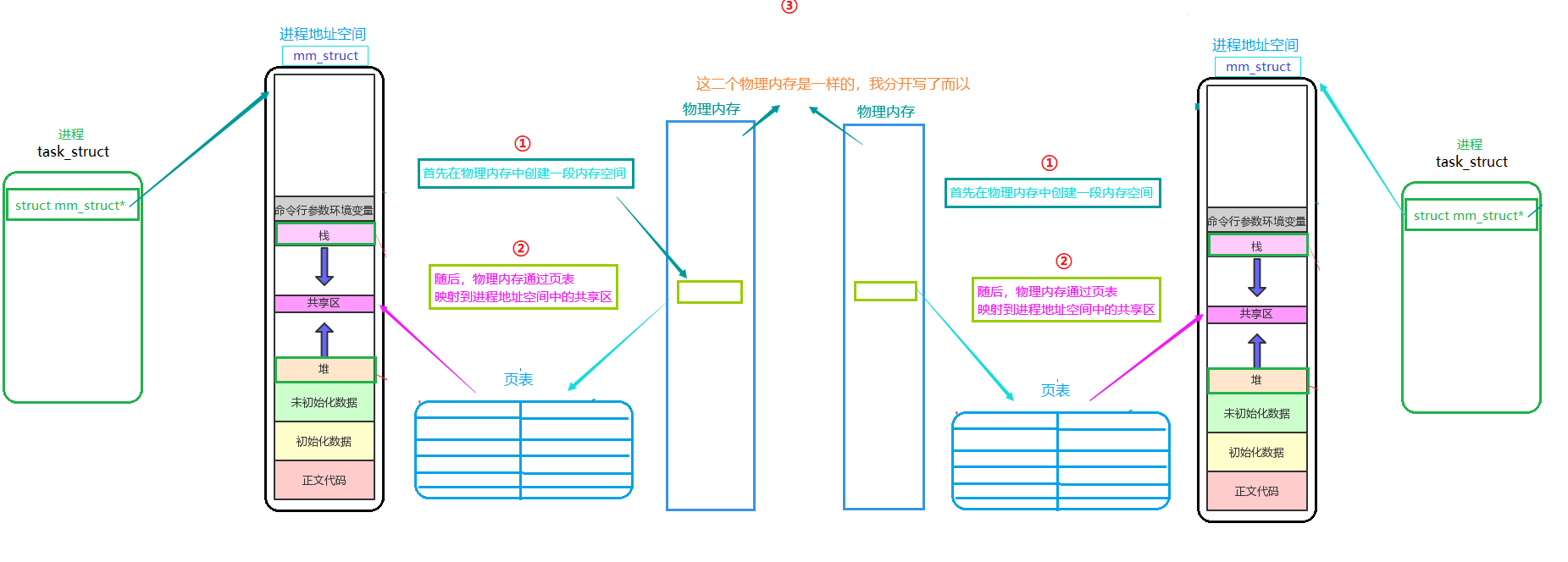
管道是在磁盘中创建文件,每次要加载到内存;共享内存是通过在物理内存创建一段内存,然后映射到共享区进行数据交互(只要创建一次,后面都会存在,因为共享内存是内核维护的)
🍢1.2、原理
进程间通信的前提是:让二个或多个不同的进程看到相同的资源(FIFO或pipe)!!!
-
进程地址空间中有一个共享区:该区域除了映射动态库以外,还能映射其他数据(共享内存)
-
共享内存(Shared Memory):允许不同进程访问同一段的空间,常用于多进程间的通信
-
共享内存被某个进程创建后,在物理内存中通过页表映射到该进程的进程地址空间的共享区中
-
最后返回一个key值(标识这段空间的唯一性,key是一个整形),其他进程想要映射到相同的内存空间,必须通过key值!!!
左边是进程1,右边是进程2!!!
-
共享内存区是最快的进程间通信方式,它不用在磁盘中创建管道文件,而是直接在物理内存映射到进程空间中进行数据交互即可
-
一旦这样的内存映射到共享它的进程的地址空间,这些进程间数据传递不再涉及到内核,换句话说是进程不再通过执行进入内核的系统调用来传递彼此的数据
-
共享内存是内核级的数据结构,进程退出后,共享内存不会被释放
🌺2、共享内存相关函数和指令
🍡2.1、shmget函数(创建)
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);
-
函数解析:
-
- 功能:用于创建共享内存,并返回共享内存的标识符
-
- 返回值:成功返回一个非负整数,即该共享内存段的标识码;失败返回-1
参数:size
-
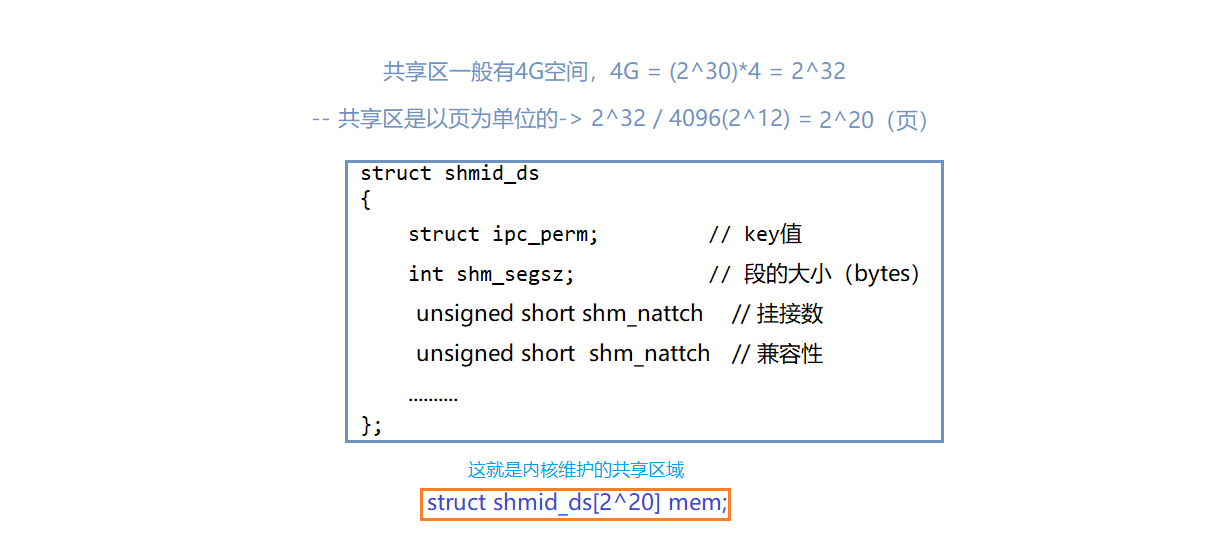
- size:共享内存大小。共享内存是以页(4KB = 4096Bytes)为单位的,建议设置成页的整数倍,共享内存是由内核数据结构(struct shmid_ds)维护的
-
参数:shmflg
-
- 由九个权限标记位构成,它们的用法和创建文件(open)时使用的mode模式标志是一样的
-
- 该参数传参的是一个宏,创建共享内存一般传二个标记位(IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL)
-
- 其他进程想要获取共享内存,只需要传一个标记位(IPC_CREAT)即可
-
- 想要正常使用共享内存时,必须设置共享内存的权限,(… | 0666)
IPC_EXCL和IPC_CREAT配合使用,是因为如果shmget调用成功后,保证创建的是一个全新的共享内存
| 宏 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| IPC_CREAT | 创建共享内存,如果已经存在,就获取它,不存在,就创建它 |
| IPC_EXCL | 不单独使用,必须和IPC_CREAT配合(按位或)使用,如果不存在指定的共享内存,就创建,如果存在,就报错返回 |
-
共享内存存在哪里?
-
- 存在内核中,内核会给我们维护共享内存的结构,该结构也要被OS管理起来
-
- OS对共享内存的管理,就是对描述共享内存的数据结构的数组进行管理(增删查改)
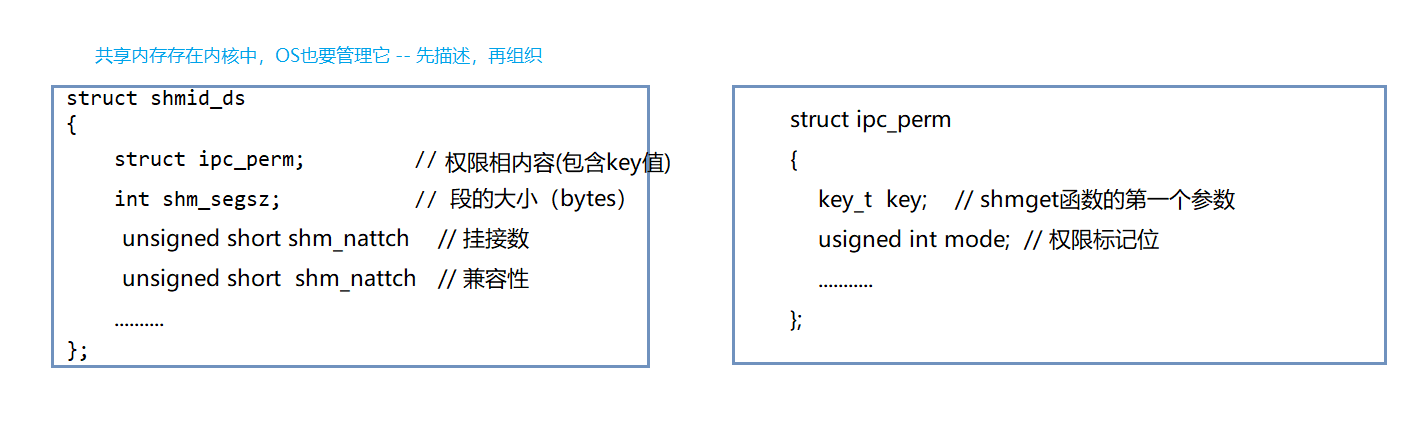
凡是涉及管理:都是先描述事物的属性(struct shmid_ds),然后对其进行组织(数据结构)
struct shmid_ds
{
struct ipc_perm shm_perm; /* operation perms */
int shm_segsz; /* size of segment (bytes) */
__kernel_time_t shm_atime; /* last attach time */
__kernel_time_t shm_dtime; /* last detach time */
__kernel_time_t shm_ctime; /* last change time */
__kernel_ipc_pid_t shm_cpid; /* pid of creator */
__kernel_ipc_pid_t shm_lpid; /* pid of last operator */
unsigned short shm_nattch; /* no. of current attaches */
unsigned short shm_unused; /* compatibility */
void *shm_unused2; /* ditto - used by DIPC */
void *shm_unused3; /* unused */
};
struct ipc_perm
{
key_t __key; /* Key supplied to shmget(2) */
uid_t uid; /* Effective UID of owner */
gid_t gid; /* Effective GID of owner */
uid_t cuid; /* Effective UID of creator */
gid_t cgid; /* Effective GID of creator */
unsigned short mode; /* Permissions + SHM_DEST and
SHM_LOCKED flags */
unsigned short __seq; /* Sequence number */
};
这个key值就是共享内存再内核数据结构中的唯一标识符的值(整形)-- 唯一性:只有一个
结论:
-
共享内存要被管理,需要在struct shmid_ds[]中找到某一页内部中的struct ipc_perm中的key值(共享内存在内核数据结构中唯一的标识符的值)
-
共享内存,在内核中,让不同的进程看到同一份资源,做法是”让它们拥有相同的key值“即可
-
参数:key
-
- 共享内存段的名字(唯一标识符),该参数由用户设置
-
- key值需要用户通过ftok系统调用获取
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
key_t ftok(const char* pathname, int proj_id)
-
pathname:指定一个文件或目录的路径,主要是文件和目录都有一个唯一的inode值
-
proj_id:项目id,取值范围是【0,255】
-
返回值:生成成功返回一个key值,失败返回-1
-
作用:通过指定路径的文件/目录的inode值和项目id生成一个唯一性的key值!!!
shmget的使用:
comm.hpp – hpp文件:函数声明和定义可以混合使用
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cerrno>
// 在某个路径下的某个文件或目录
#define PATH_NAME "/home/lyh/Linux_Study"
// 项目id
#define PROJ_ID 0x12
key_t CreateKey()
{
key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID);
if (key < 0)
{
std::cout << "ftok errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1); // key值冲突,结束调用该函数的进程
}
return key;
}
// 用于调试打印消息 -- 该函数返回一个ostream& 可充当左值进行使用
std::ostream& Log()
{
return std::cout << "Fot Debug | " << "timestamp: " << (long long)time(nullptr)
<< " | ";
}
IpcShmSer.cpp – 该文件创建共享内存
#include "comm.hpp"
// 设置共享内存的大小
#define MIN_SIZE 4096
// 共享内存的状态标记位(创建全新的,如果存在则设置errno,并且返回-1)
const int shmflags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL;
// 该文件创建共享内存
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值(共享内存的唯一标识符)
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
// 2、创建共享内存 -- 0666是共享内存的权限,标识谁能使用
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, shmflags | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}
[lyh@192 lesson4(共享内存)]$ pwd
/home/lyh/Linux_Study/lesson4(共享内存)
[lyh@192 lesson4(共享内存)]$ ./IpcShmSer
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671720131 | key: 302207089
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671720131 | shmget sucess!!! | shmid: 31
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671720131 | shmctl sucess!!! | shmid: 31
验证OS是否存在共享内存 – ipcs -m指令(查看共享内存的信息)
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ./IpcShmSer
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671799258 | key: 302207089
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671799258 | shmget sucess!!! | shmid: 31
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ipsc -m
bash: ipsc: command not found...
Similar command is: 'ipcs'
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ipcs -m
------ Shared Memory Segments --------
key shmid owner perms bytes nattch status
0x00000000 9 lyh 777 16384 1 dest
0x00000000 10 lyh 777 6193152 2 dest
0x00000000 16 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 17 lyh 777 6193152 2 dest
0x00000000 20 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 24 lyh 600 16777216 2 dest
0x00000000 25 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 26 lyh 777 2064384 2 dest
0x00000000 27 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x12035071 31 lyh 666 4096 0
-
key是共享内存唯一标识符;shmid是共享内存标识符;owner是创建者;perms是共享内存的权限;nattch是挂接的(映射到指定的进程)数量
-
System V共享内存下的生命周期是随内核的(只能关机重启或显示调用函数或使用指令来进行删除),进程退出后也没有释放!
🍢2.2、shmctl函数(控制)
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);
-
函数解析:
-
- 功能:用于控制共享内存,在System V共享内存段上执行cmd指定的控制操作,该段的标识符在shmid中给出
-
- 返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1,并且设置errno(错误码)
参数shmid:
-
- 由shmget函数创建共享内存返回的标识符
参数cmd:
-
- 将要采取的动作(有三个可取值)
-
- 该函数主要用于显示删除共享内存段,只需要IPC_RMID(宏)进行删除
注意:cmd参数中的值都是标记位,可以通过按位或进行结合使用

-
参数shmid_ds *buf:
-
- 指向一个保存着共享内存的模式状态和访问权限的数据结构(struct shmid_ds)
-
- 该参数一般设置为nullptr
shmctl函数的使用:
comm.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cerrno>
#define PATH_NAME "/home/lyh/Linux_Study"
#define PROJ_ID 0x12
key_t CreateKey()
{
key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID);
if (key < 0)
{
std::cout << "ftok errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1); // key值冲突,结束调用该函数的进程
}
return key;
}
// 该函数返回一个ostream& 可充当左值进行使用
std::ostream& Log()
{
return std::cout << "Fot Debug | " << "timestamp: " << (long long)time(nullptr)
<< " | ";
}
IpcShmSer.cpp
#include "comm.hpp"
// 设置共享内存的大小
#define MIN_SIZE 4096
// 共享内存的状态(创建全新的,如果存在则设置errno,并且返回-1)
const int shmflags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL;
// 该文件创建共享内存
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值(共享内存的唯一标识符)
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
// 2、创建共享内存
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, shmflags);
if (shmid < 0)
{
sleep(5);
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
// 使用共享内存
// 删除共享内存
sleep(5);
int RM = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
if (RM < 0)
{
Log() << "shmctl errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
}
Log() << "shmctl sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}
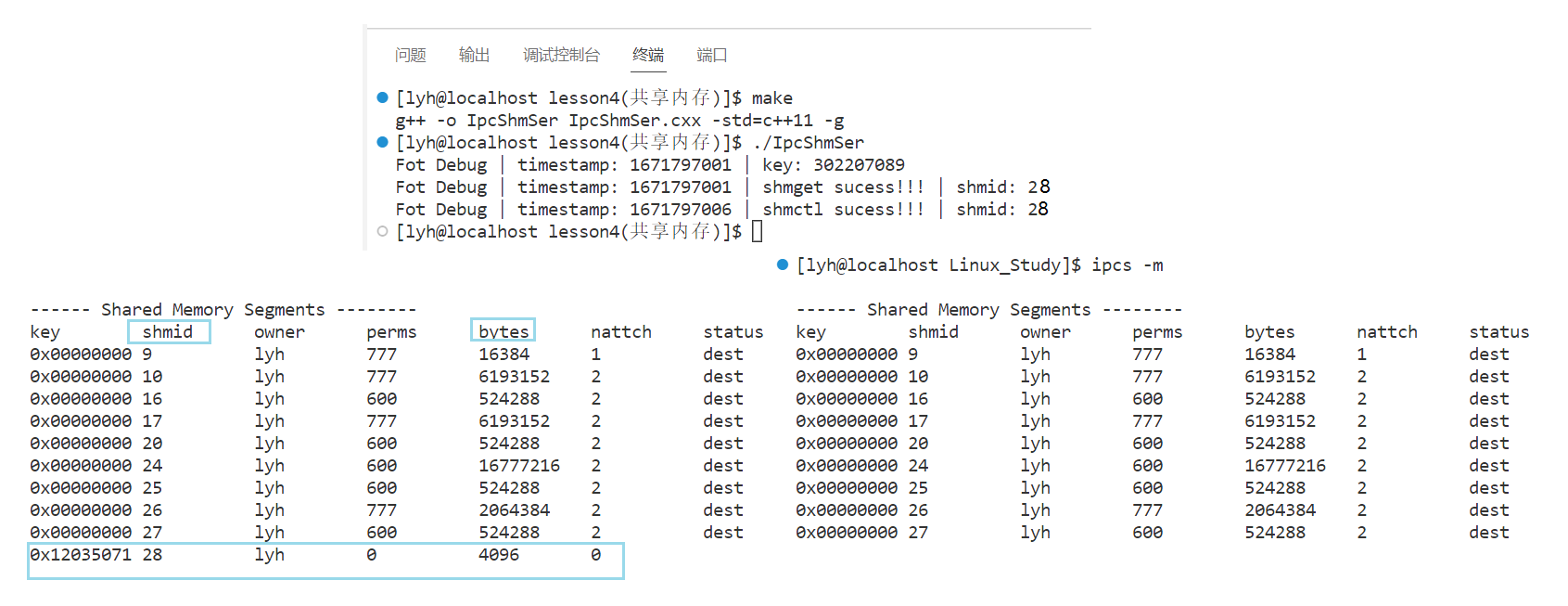
- 还可以使用指令进行删除 – ipcrm -m shmid
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ make
g++ -o IpcShmSer IpcShmSer.cxx -std=c++11 -g
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ./IpcShmSer
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671797310 | key: 302207089
Fot Debug | timestamp: 1671797310 | shmget sucess!!! | shmid: 30
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ipcs -m
------ Shared Memory Segments --------
key shmid owner perms bytes nattch status
0x00000000 9 lyh 777 16384 1 dest
0x00000000 10 lyh 777 6193152 2 dest
0x00000000 16 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 17 lyh 777 6193152 2 dest
0x00000000 20 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 24 lyh 600 16777216 2 dest
0x00000000 25 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 26 lyh 777 2064384 2 dest
0x00000000 27 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x12035071 30 lyh 0 4096 0
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ipcrm -m 30
[lyh@localhost lesson4(共享内存)]$ ipcs -m
------ Shared Memory Segments --------
key shmid owner perms bytes nattch status
0x00000000 9 lyh 777 16384 1 dest
0x00000000 10 lyh 777 6193152 2 dest
0x00000000 16 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 17 lyh 777 6193152 2 dest
0x00000000 20 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 24 lyh 600 16777216 2 dest
0x00000000 25 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
0x00000000 26 lyh 777 2064384 2 dest
0x00000000 27 lyh 600 524288 2 dest
🍧2.3、shmat函数(挂接)
-
共享内虽然在进程中被创建,但是不属于进程,它是由OS进行管理的
-
我们想要使用共享内存,必须将共享内存与进程关联(共享内存映射到当前进程的共享区)起来
shmat函数:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);
-
函数解析:
-
- 功能:将shmid标识的SystemV共享内存段附加到调用进程的地址空间
-
- 返回值:成功时返回0;错误时返回-1,并设置errno以指示错误的原因。该返回值的使用与C语言的malloc一样!!!
参数shmid:
-
- 由shmget函数创建共享内存返回的标识符
参数shmflg:
-
- 它的两个可能取值是SHM_RND和SHM_RDONLY,一般为0,详细内容查man手册
参数shmaddr:
-
- 该参数传递一个地址,表示我们需要将共享内存附加到进程地址空间的某一个位置
-
- 如果shaddr为NULL,系统将选择一个合适的(未使用的)地址来附加段
-
- shmaddr不为NULL且shmflg无SHM_RND标记,则以shmaddr为连接地址
-
- shmaddr不为NULL且shmflg设置了SHM_RND标记,则连接的地址会自动向下调整为SHMLBA的整数倍。公式:shmaddr - (shmaddr % SHMLBA)
-
- shmflg = SHM_RDONLY,表示连接操作用来只读共享内存
挂接共享内存:
comm.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cerrno>
#define PATH_NAME "/home/lyh/Linux_Study"
#define PROJ_ID 0x12
key_t CreateKey()
{
key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID);
if (key < 0)
{
std::cout << "ftok errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1); // key值冲突,结束调用该函数的进程
}
return key;
}
// 该函数返回一个ostream& 可充当左值进行使用
std::ostream& Log()
{
return std::cout << "Fot Debug | " << "timestamp: " << (long long)time(nullptr)
<< " | ";
}
IpcShmSer.cpp
#include "comm.hpp"
// 设置共享内存的大小
#define MIN_SIZE 4096
// 共享内存的状态(创建全新的,如果存在则设置errno,并且返回-1)
const int shmflags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL;
// 该文件创建共享内存
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值(共享内存的唯一标识符)
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
// 2、创建共享内存 -- 0666是共享内存的权限,标识谁能使用
sleep(5);
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, shmflags | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
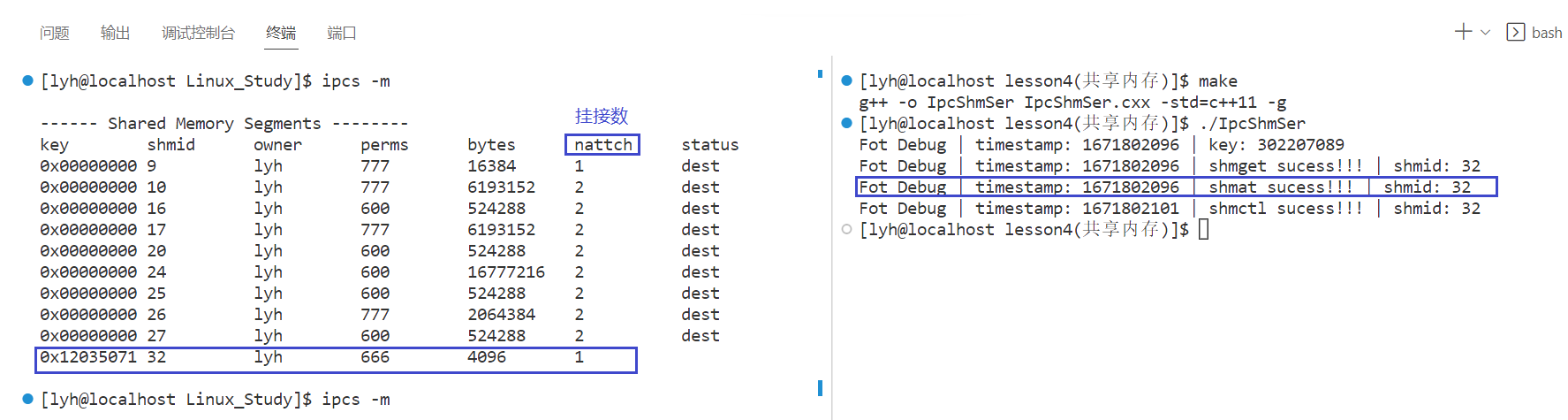
// 3、挂接共享内存
sleep(5);
char *pIps = (char *)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if (pIps < 0)
{
Log() << "shmat errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 3;
}
Log() << "shmat sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
// 删除共享内存
sleep(5);
int RM = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
if (RM < 0)
{
Log() << "shmctl errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 4;
}
Log() << "shmctl sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}
🍨2.4、shmdt(去挂接)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
-
函数解析:
-
- 功能:将共享内存段与当前进程脱离(去除共享内存与进程地址空间的映射)
-
- 返回值:成功时shmdt()返回0;错误时返回-1,并设置errno以指示错误的原因
参数shmaddr:
-
- shmaddr:由shmat所返回的指针,与C语言中使用free释放堆空间类似
IpcShmSer.cpp
#include "comm.hpp"
// 设置共享内存的大小
#define MIN_SIZE 4096
// 共享内存的状态(创建全新的,如果存在则设置errno,并且返回-1)
const int shmflags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL;
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值(共享内存的唯一标识符)
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
// 2、创建共享内存 -- 0666是用户访问共享内存的权限,标识谁能读、写、执行
sleep(5);
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, shmflags | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
// 3、挂接共享内存
sleep(5);
char *pIps = (char *)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if (pIps < 0)
{
Log() << "shmat errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 3;
}
Log() << "shmat sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
// 4、使用共享内存
// 5、去挂接
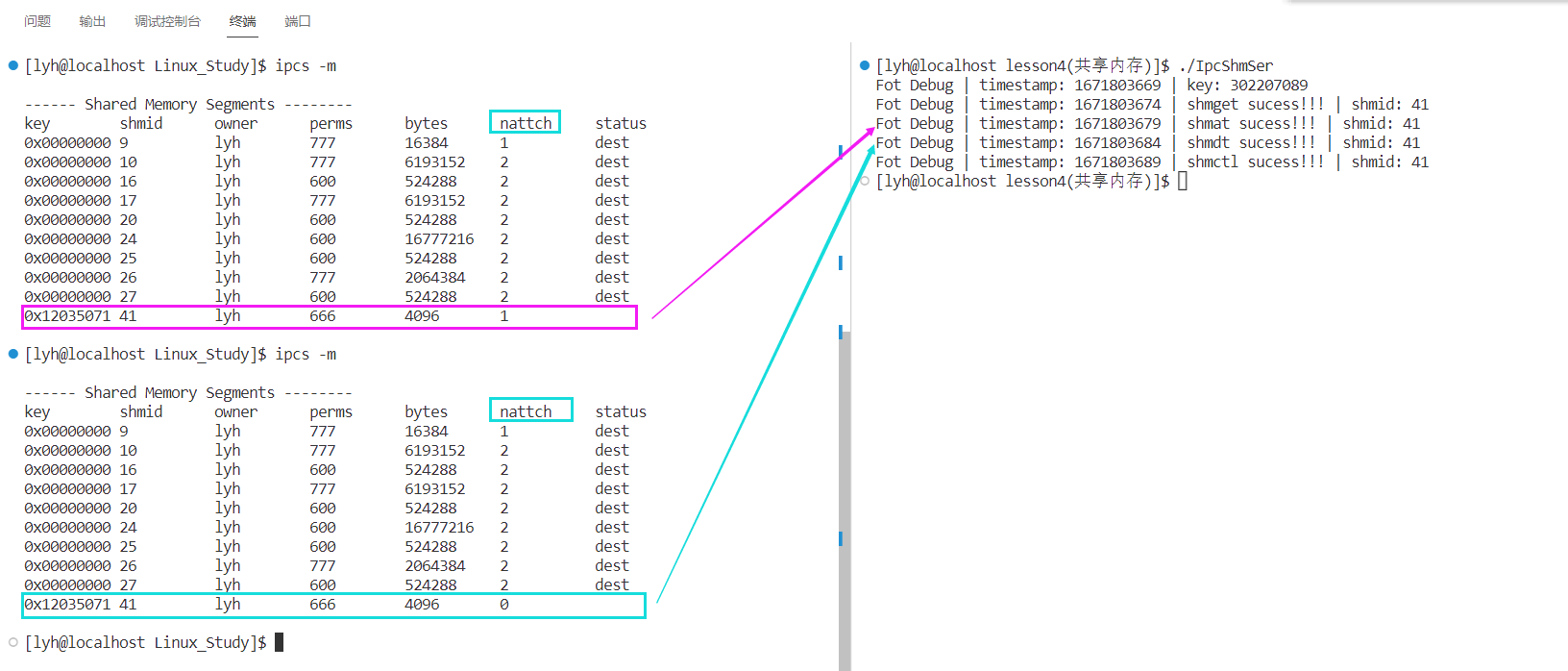
sleep(5);
int flag = shmdt(pIps);
if (flag < 0)
{
Log() << "shmdt errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmdt sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
// 5、删除共享内存
sleep(5);
int RM = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
if (RM < 0)
{
Log() << "shmctl errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 4;
}
Log() << "shmctl sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}
🍀3、共享内存的使用
🍡3.1、测试
-
我们上面所讲的内容,只完成了共享内存的创建、挂接、去挂接和删除共享内存
-
共享内存实际上是映射到进程地址空间的用户空间(堆、栈之间)
-
对于每个进程而言,挂接到自己上下文当中的共享内存,是属于自己的空间,可以被用户直接使用
-
共享内存被映射到进程地址空间后类似于堆、栈空间,可以直接被使用
comm.hpp – 头文件和定义混编
-
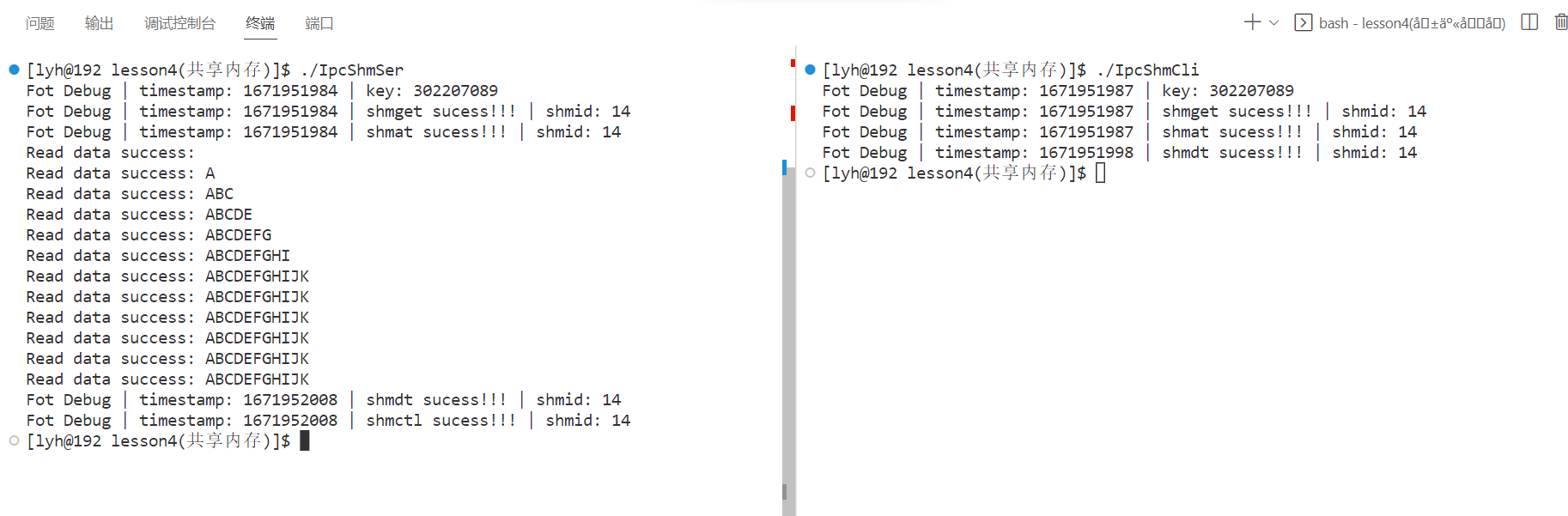
测试:服务器文件(IpcShmCli)写入数据,客户端文件(IpcShmSer)读取数据
-
每次写入一个字节的数据,查看共享内存的读写顺序(是否存在同步与互斥)
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <cerrno>
#define PATH_NAME "/home/lyh/Linux_Study"
#define PROJ_ID 0x12
#define MIN_SIZE 4096
// 获取key值
key_t CreateKey()
{
key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID);
if (key < 0)
{
std::cout << "ftok errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1); // key值冲突,结束调用该函数的进程
}
return key;
}
// 该函数返回一个ostream& 可充当左值进行使用 -- 用于debug
std::ostream& Log()
{
return std::cout << "Fot Debug | " << "timestamp: " << (long long)time(nullptr) << " | ";
}
IpcShmSer – 客户端创建共享内存并且读取共享内存的数据
-
使用共享内存时,shmat跟malloc一样,返回的是引用共享内存块/堆块的虚拟地址
-
我们可以对这些地址进行解引用写入数据
#include "comm.hpp"
// 共享内存的状态(创建全新的,如果存在则设置errno,并且返回-1)
const int shmflags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL;
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 2、创建共享内存 -- 0666是用户访问共享内存的权限,标识谁能读、写、执行
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, shmflags | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 3、挂接
char *pIps = (char *)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if (pIps < 0)
{
Log() << "shmat errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 3;
}
Log() << "shmat sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 4、使用共享内存 -- 读取数据
int cnt = 0;
while (true)
{
sleep(2);
std::cout << "Read data success: " << pIps << std::endl;
if (cnt > CNT)
break;
++cnt;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 5、去挂接
int flag = shmdt(pIps);
if (flag < 0)
{
Log() << "shmdt errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmdt sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 6、删除共享内存
int RM = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
if (RM < 0)
{
Log() << "shmctl errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 4;
}
Log() << "shmctl sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}
IpcShmCli – 服务器写入数据
#include "comm.hpp"
// 该文件使用共享内存
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 2、获取共享内存标id
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 3、挂接
char *pIps = (char *)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if (pIps < 0)
{
Log() << "shmat errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 3;
}
Log() << "shmat sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 4、使用共享内存 -- 写入数据
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt <= CNT)
{
pIps[cnt] = 'A' + cnt;
++cnt;
pIps[cnt] = '\0';
sleep(1);
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 5、去挂接
int flag = shmdt(pIps);
if (flag < 0)
{
Log() << "shmdt errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmdt sucess!!! | " << "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}
每次读取等待两秒,每次写入等待一秒,A->ABC->ABCDE…
🍢3.2、共享内存与管道的区别
通过上面的测试,我们知道:
-
共享内存,因为它自身的特性,没有任何访问控制(同步与互斥)
-
共享内存可以直接被二个或多个进程看到,属于二个或多个进程的用户空间,可以直接通信
-
可以直接通信意味着:多个进程可以各自随便写入和读取(不安全,没有访问控制)
-
共享内存,是所有IPC中,速度最快的
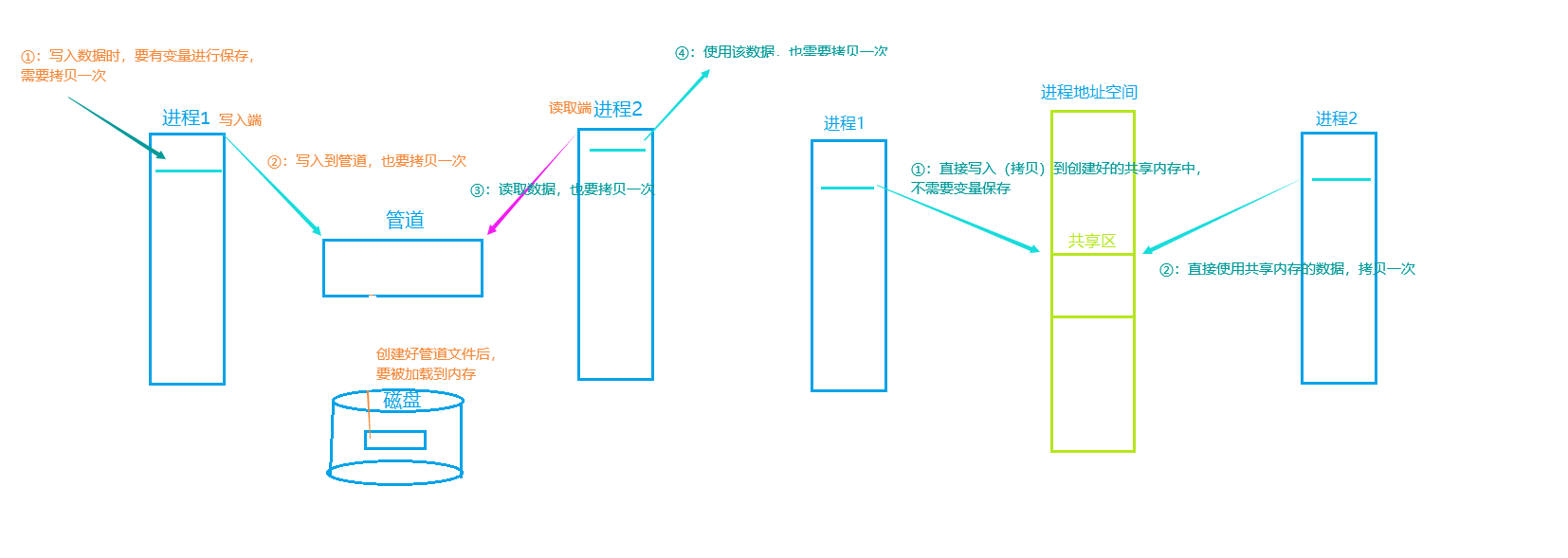
管道与共享内存中进程通信所拷贝数据次数的对比
🍧3.3、基于共享内存+管道实现访问控制
前言:
-
虽然共享内存不能同步和互斥,但是我们可以通过管道的特性(访问控制)来间接的让共享内存获得访问控制这一特性!
-
首先,前面的代码不变,我们还需增加命名管道的代码
-
注意:命名管道只是辅助共享内存,主要是共享内存进行通信!!!
comm.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cerrno>
#define PATH_NAME "/home/lyh/Linux_Study"
#define PROJ_ID 0x12
#define MIN_SIZE 4096
const int CNT = 5;
// 获取key值
key_t CreateKey()
{
key_t key = ftok(PATH_NAME, PROJ_ID);
if (key < 0)
{
std::cout << "ftok errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1); // key值冲突,结束调用该函数的进程
}
return key;
}
// 该函数返回一个ostream& 可充当左值进行使用 -- 用于debug
std::ostream& Log()
{
return std::cout << "Fot Debug | " << "timestamp: " << (long long)time(nullptr) << " | ";
}
// 创建命名管道
void CreateName_Fifo()
{
umask(0);
// 在当前进程cwd下创建名为fifo的管道文件
if (mkfifo("./fifo", 0666) == -1)
{
Log() << "fifo errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
Log() << "fifo success!!!" << std::endl;
}
// 向命名管道写入任务码
void Write_Data()
{
int fifofd = open("./fifo", O_WRONLY);
if (fifofd == -1)
{
Log() << "fifofd errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// 写入任务码为:"1"的数据 -- 随便写,命名管道是辅助共享内存
uint32_t taskcode = 1;
write(fifofd, &taskcode, sizeof(uint32_t));
}
// 读取命名管道的任务码
ssize_t Read_Data()
{
int fifofd = open("./fifo", O_RDONLY);
if (fifofd == -1)
{
Log() << "fifofd errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
uint32_t taskcode = 0;
ssize_t s = read(fifofd, &taskcode, sizeof(uint32_t));
return s;
}
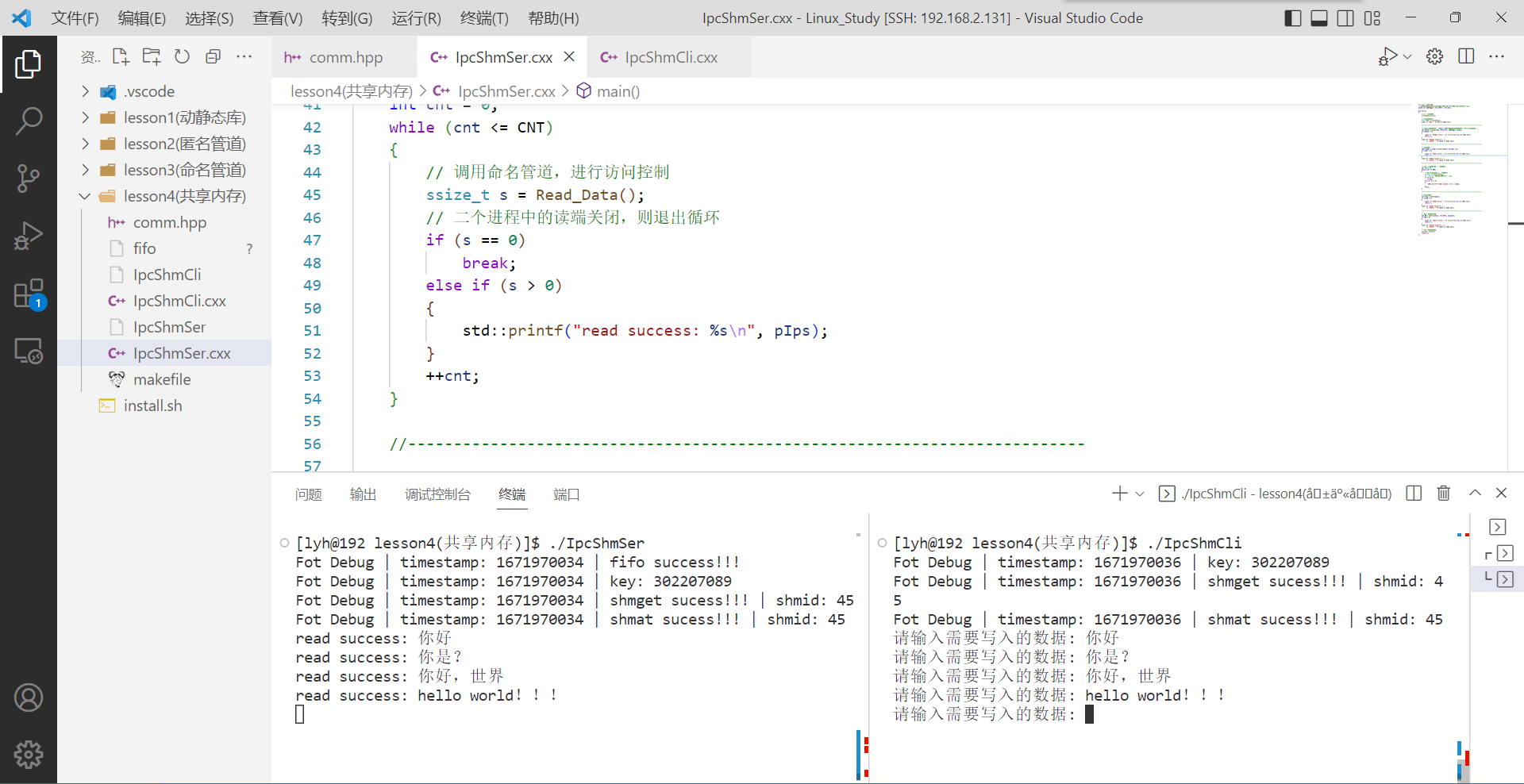
IpcShmSer – 增加命名管道访问控制代码(读端)
#include "comm.hpp"
// 共享内存的状态(创建全新的,如果存在则设置errno,并且返回-1)
const int shmflags = IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL;
int main()
{
// 打开命名管道
CreateName_Fifo();
// 1、获取key值
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 2、创建共享内存 -- 0666是用户访问共享内存的权限,标识谁能读、写、执行
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, shmflags | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 3、挂接
char *pIps = (char *)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if (pIps < 0)
{
Log() << "shmat errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 3;
}
Log() << "shmat sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 4、使用共享内存 -- 读取数据
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt <= CNT)
{
// 调用命名管道,进行访问控制
ssize_t s = Read_Data();
// 二个进程中的读端关闭,则退出循环
if (s == 0)
break;
else if (s > 0)
{
std::printf("read success: %s\n", pIps);
}
++cnt;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 5、去挂接
int flag = shmdt(pIps);
if (flag < 0)
{
Log() << "shmdt errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmdt sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 6、删除共享内存
int RM = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, nullptr);
if (RM < 0)
{
Log() << "shmctl errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 4;
}
Log() << "shmctl sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
// 7、删除管道文件
unlink("./fifo");
return 0;
}
IpcShmCli – 增加命名管道访问控制代码(写端)
#include "comm.hpp"
// 该文件使用共享内存
int main()
{
// 1、获取key值
key_t key = CreateKey();
Log() << "key: " << key << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 2、获取共享内存标id
int shmid = shmget(key, MIN_SIZE, IPC_CREAT | 0666);
if (shmid < 0)
{
Log() << "shmget errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmget sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 3、挂接
char *pIps = (char *)shmat(shmid, nullptr, 0);
if (pIps < 0)
{
Log() << "shmat errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 3;
}
Log() << "shmat sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 4、使用共享内存 -- 写入数据
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt <= CNT)
{
std::string str;
std::cout << "请输入需要写入的数据: ";
std::fflush(stdout);
std::getline(std::cin, str);
// 调用命名管道,进行访问控制
Write_Data();
strcpy(pIps, str.c_str());
++cnt;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 5、去挂接
int flag = shmdt(pIps);
if (flag < 0)
{
Log() << "shmdt errno: " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;
return 2;
}
Log() << "shmdt sucess!!! | "
<< "shmid: " << shmid << std::endl;
return 0;
}