项目代码
https://github.com/yinhai1114/Java_Learning_Code/tree/main/IDEA_Chapter10/src/com/yinhai/final_
一、什么是设计模式
1.静态方法和属性的经典使用
2.设计模式是在大量的实践中总结和理论化之后优选的代码结构、编程风格以及解决问题的思考方式。设计模式就像是经典的棋谱,不同的棋局,我们用不同的棋谱,免去我们自己再思考和摸索
二、什么是单例模式
单例(单个的实例)
1.所谓类的单例设计模式,就是采取一定的方法保证在整个的软件系统中,对某
个类只能存在一个对象实例,并且该类只提供一个取得其对象实例的方法
2.单例模式有两种方式: 1) 饿汉式2)懒汉式
三、单例模式应用实例
演示 饿汉式和懒汉式单例模式的实现
步骤如下:
1.饿汉式 在类加载的时候就就创建对象了 所以可以造成创建了对象但是没有使用 资源的浪费
1)构造器私有化(防止直接new)
2)类的内部创建静态对象
3)向外暴露一个静态的公共方法。getInstance
4)代码实现
public class SingleTon01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// GirlFriend xiaohuang = new GirlFriend("xiaohuang");
// GirlFriend xiangwang = new GirlFriend("xiangwang");
//通过方法就可以获取对象
GirlFriend instance = GirlFriend.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance);
GirlFriend instance1 = GirlFriend.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance1);
System.out.println(instance == instance1);
}
}
class GirlFriend{
private String name;
//为了能够在静态方法中使用,需要static修饰
private static GirlFriend gf = new GirlFriend("hong");//2
//如何保障只能创建一个GirlFriend对象?
//1.私有化构造器
//2.在类的内部创建静态对象
//3.提供一个公共的静态static方法 返回gf对象
private GirlFriend(String name) {//1
this.name = name;
}
public static GirlFriend getInstance(){//3
return gf;
}
}2.懒汉式 在类被使用的时候才创建对象
1)仍然构造器私有化
2)定义一个static静态属性对象
3)提供一个public的static方法,可以返回一个Cat对象
public class SingleTon02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
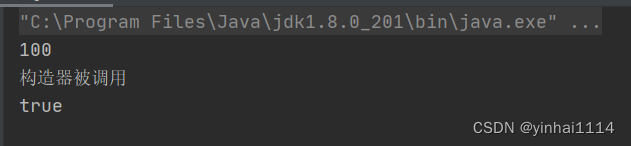
System.out.println(Cat.n1);//此时使用n1并没有创建cat对象
Cat instance = Cat.getInstance();//创建对象
Cat instance1 = Cat.getInstance();//因为对象不为空,所以只会创建一次
System.out.println(instance == instance1);
}
}
class Cat{
private String name;
public static int n1 = 100;
private static Cat cat;
//1)仍然构造器私有化
// 2)定义一个static静态属性对象
// 3)提供一个public的static方法,可以返回一个Cat对象
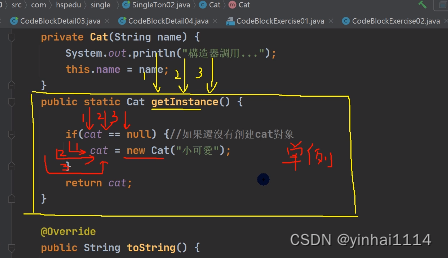
private Cat(String name){
System.out.println("构造器被调用");
this.name = name;
}
public static Cat getInstance(){
if(cat == null){//如果还没有创建cat对象
cat = new Cat("xiaohua");
}
return cat;
}
}
四、饿汉式和懒汉式的区别
1.二者的主要的区别在于创建对象的时机不同:饿汉式是在类加载就创建了对象实例,而懒汉式是在使用时创建
2.饿汉式不存在线程安全问题,懒汉式存在线程安全问题(后面学习线程后,会完善一把)
3.饿汉式存在浪费资源的可能,因为如果一个实例对象都没使用,那么饿汉式创建的对象就浪费了;但懒汉式是使用时才创建就不存在这个问题
4.在我们javaSE标准类中,java.lang.runtime就是经典的单例模式
public class Runtime {
private static Runtime currentRuntime = new Runtime();
/**
* Returns the runtime object associated with the current Java application.
* Most of the methods of class <code>Runtime</code> are instance
* methods and must be invoked with respect to the current runtime object.
*
* @return the <code>Runtime</code> object associated with the current
* Java application.
*/
public static Runtime getRuntime() {
return currentRuntime;
}