一、介绍:
1、定义:是一种行为设计模式,它允许将对象的内部状态保存在一个备忘录对象中,并在需要时恢复对象的状态,而不破坏对象的封装性。
2、使用场景:
(1)当需要保存和恢复对象的内部状态,并且希望封装状态的具体实现细节。备忘录模式将对象的状态保存在备忘录对象中,对外部对象隐藏了状态的实现细节,提高了对象的封装性。
(2)当需要在不破坏对象封装性的前提下保存和恢复对象的状态,以便进行撤销、回滚或者历史记录管理时。备忘录模式可以保存对象的历史状态,并在需要时恢复到指定的状态。
(3)当需要保存对象状态的快照,以便在将来某个时间点恢复到该状态时。备忘录模式可以捕获对象的当前状态并保存在备忘录对象中,以供后续恢复使用。
(4)当对象的状态变化频繁,但是希望能够随时回滚到之前的某个状态时。备忘录模式可以在每次状态变化时保存备忘录,以便在需要时进行状态的回滚。
(5)当需要实现多级撤销操作或者复杂的历史记录功能时。备忘录模式可以保存多个备忘录对象,实现多级撤销或者浏览历史记录的功能。
3、缺点:使用备忘录模式时需要考虑内存的使用情况和性能要求。
4、组成:备忘录模式的核心是备忘录(Memento)角色,它用于存储对象的内部状态,并提供对状态的访问方法。原发器(Originator)角色负责创建备忘录并将自身的状态保存到备忘录中。管理者(Caretaker)角色负责存储和恢复备忘录,但是它不能访问备忘录的内部状态。
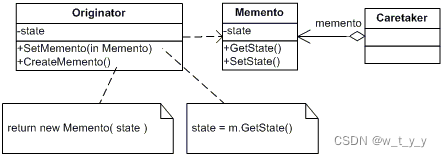
(1)备忘录类 Memento,用于存储对象的状态:
public class Memento {
private String state;
public Memento(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
}(2)原发器类 Originator,它包含了需要保存和恢复的状态,并提供了创建备忘录和从备忘录恢复状态的方法:
public class Originator {
private String state;
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public Memento createMemento() {
return new Memento(state);
}
public void restoreFromMemento(Memento memento) {
state = memento.getState();
}
}(3)管理者类 Caretaker,它负责存储和恢复备忘录对象:
public class Caretaker {
private Memento memento;
public void setMemento(Memento memento) {
this.memento = memento;
}
public Memento getMemento() {
return memento;
}
}客户端:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Originator originator = new Originator();
Caretaker caretaker = new Caretaker();
// 设置原发器的状态
originator.setState("State 1");
System.out.println("Initial state: " + originator.getState());
// 创建备忘录并保存到管理者
caretaker.setMemento(originator.createMemento());
// 修改原发器的状态
originator.setState("State 2");
System.out.println("Updated state: " + originator.getState());
// 从备忘录中恢复原发器的状态
originator.restoreFromMemento(caretaker.getMemento());
System.out.println("Restored state: " + originator.getState());
}
}二、demo:
1、文本编辑器撤销恢复功能:
(1)备忘录:
public class EditorMemento {
private String content;
public EditorMemento(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
}(2)原触发器:
public class Editor {
private String content;
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public EditorMemento createMemento() {
return new EditorMemento(content);
}
public void restoreFromMemento(EditorMemento memento) {
content = memento.getContent();
}
}(3)管理者类:
import java.util.Stack;
public class History {
private Stack<EditorMemento> mementos;
public History() {
mementos = new Stack<>();
}
public void pushMemento(EditorMemento memento) {
mementos.push(memento);
}
public EditorMemento popMemento() {
return mementos.pop();
}
}客户端:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Editor editor = new Editor();
History history = new History();
// 用户输入和编辑文本
editor.setContent("First version");
System.out.println("Current content: " + editor.getContent());
// 创建备忘录并保存到历史记录
history.pushMemento(editor.createMemento());
// 用户继续编辑文本
editor.setContent("Second version");
System.out.println("Current content: " + editor.getContent());
// 用户撤销操作,恢复到之前的状态
EditorMemento memento = history.popMemento();
editor.restoreFromMemento(memento);
System.out.println("Restored content: " + editor.getContent());
}
}