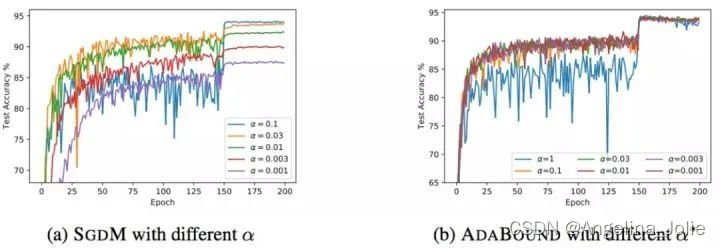
说明
一切节点的跟是 machine-root,同一个资源在不同链路会创建多个DefaultNode,但是在全局只会创建一个 ClusterNode
machine-root
/\
/ \
EntranceNode1 EntranceNode2
/ \
/ \
DefaultNode(nodeA) DefaultNode(nodeA)
| |
- - - - - - + - - - - - - - - - +- - - - - - -> ClusterNode(nodeA);如我们所见,在两个上下文中为“nodeA”创建了两个 DefaultNode,但只创建了一个 ClusterNode
一切的开始
DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC框架中的核心组件,它作为前置控制器,它拦截匹配的请求,并根据相应的规则分发到目标Controller来处理。当请求进入后,首先会执行DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch 方法
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
···
try {
try {
···
// 执行preHandle方法
// 会进入AbstractSentinelInterceptor 的 preHandle
// 会为当前访问的controller接口创建资源
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
// 最终会执行SentinelResourceAspect#invokeResourceWithSentinel(pjp);
// 为所有添加注解的方法创建资源
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
···
}
catch (Exception ex) {
···
}
}catch (Exception ex) {
···
}
}
}因此,从这里就可以知道,簇点链路中,默认使用 controller 创建的资源一定在使用注解创建的资源之前创建,也就是说,使用注解创建的资源只能作为使用 controller 创建的资源的子节点。
链路创建过程分析
创建 EntranceNode
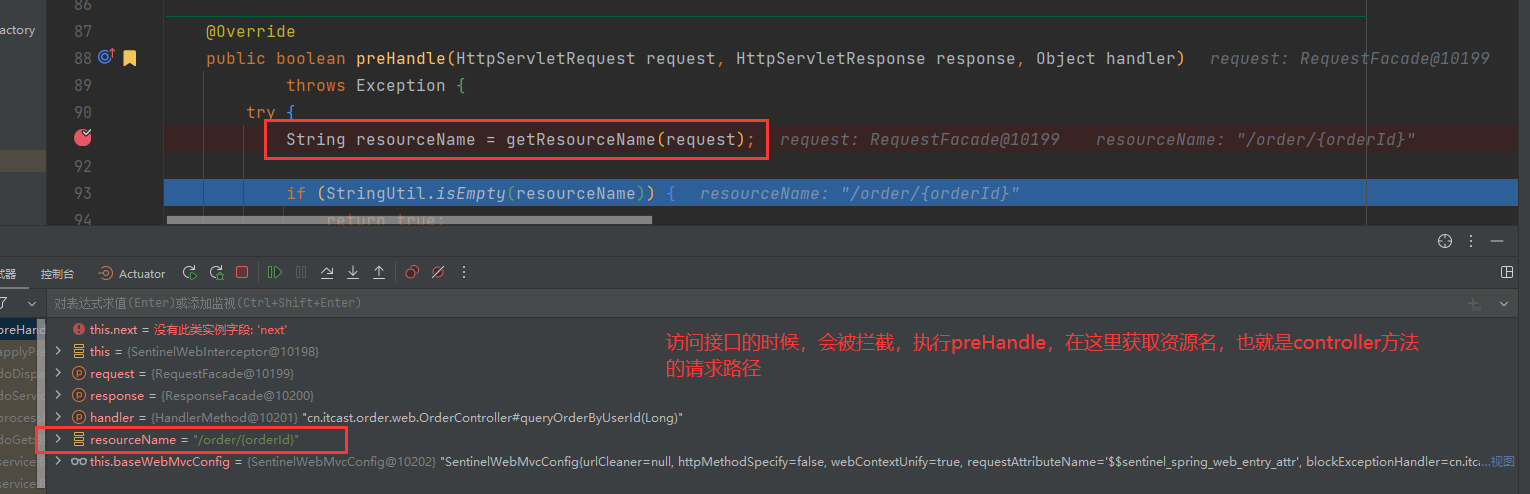
上面说到,执行会进入AbstractSentinelInterceptor 的 preHandle,进行资源创建
public abstract class AbstractSentinelInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
public static final String SENTINEL_SPRING_WEB_CONTEXT_NAME = "sentinel_spring_web_context";
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
try {
// 获取资源名,也就是 /order/{orderId}
String resourceName = getResourceName(request);
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(resourceName)) {
return true;
}
if (increaseReferece(request, this.baseWebMvcConfig.getRequestRefName(), 1) != 1) {
return true;
}
// Parse the request origin using registered origin parser.
String origin = parseOrigin(request);
// contextName默认是sentinel_spring_web_context,
// 如果不想使用这个,而是使用Controller接口路径作为contextName,则需要在application.yml文件中关闭context整合
// spring.cloud.sentinel.web-context-unify=false
String contextName = getContextName(request);
// 创建context
// Context初始化的过程中,会创建EntranceNode,contextName就是EntranceNode的名称
ContextUtil.enter(contextName, origin);
// 创建资源,簇点链路的形成就在里面
Entry entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, ResourceTypeConstants.COMMON_WEB, EntryType.IN);
request.setAttribute(baseWebMvcConfig.getRequestAttributeName(), entry);
return true;
} catch (BlockException e) {
···
}
}
}
在获取 contextName 时,会先判断有没有关闭 context 整合,然后选择返回默认的sentinel_spring_web_contex还是从接口中获取url
@Override
protected String getContextName(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (config.isWebContextUnify()) {
return super.getContextName(request);
}
return getResourceName(request);
}
@Override
protected String getResourceName(HttpServletRequest request) {
// Resolve the Spring Web URL pattern from the request attribute.
Object resourceNameObject = request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE);
if (resourceNameObject == null || !(resourceNameObject instanceof String)) {
return null;
}
String resourceName = (String) resourceNameObject;
UrlCleaner urlCleaner = config.getUrlCleaner();
if (urlCleaner != null) {
resourceName = urlCleaner.clean(resourceName);
}
// Add method specification if necessary
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(resourceName) && config.isHttpMethodSpecify()) {
resourceName = request.getMethod().toUpperCase() + ":" + resourceName;
}
return resourceName;
}然后会进行 context 的创建
protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
// 第一次肯定为空
Context context = contextHolder.get();
if (context == null) {
// contextNameNodeMap 有1个值(EntranceNode是DefaultNode的子类,是一种特殊的DefaultNode)
// 1. sentinel_default_context -> {EntranceNode@10330}
Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;
// 根据传入的contextName选择看有没有这个name的EntranceNode
DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);
// 如果没有就创建一个
if (node == null) {
if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
LOCK.lock();
try {
node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
// 创建一个新的EntranceNode
node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
// Add entrance node.
// Constants.ROOT是一个EntranceNode, id是machine-root
// 将当前创建的EntranceNode添加为Constants.ROOT的子节点
Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);
newMap.put(name, node);
contextNameNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
} finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
// 创建一个新的context
context = new Context(node, name);
context.setOrigin(origin);
contextHolder.set(context);
}
return context;
}创建 DefaultNode
创建资源时,首先会创建一个 slot 执行链,然后依次执行。
第一个节点是 NodeSelectSlot,在里面完成 DefaultNode 的创建。

当第一次访问时,NodeSelectorSlot 中
// volatile保证map多线程的可见性
// 非static变量,每次创建对象时都创建一个新的
private volatile Map<String, DefaultNode> map = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(10);
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 第一次一定是空,同一个链路中的资源之后的请求不为空
// 不同链路中的资源,后续的请求中,第一次访问还是空
DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
synchronized (this) {
node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
// 创建一个DefaultNode,将他放入到map中
node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
HashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());
cacheMap.putAll(map);
cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);
// 更新map
map = cacheMap;
// Build invocation tree
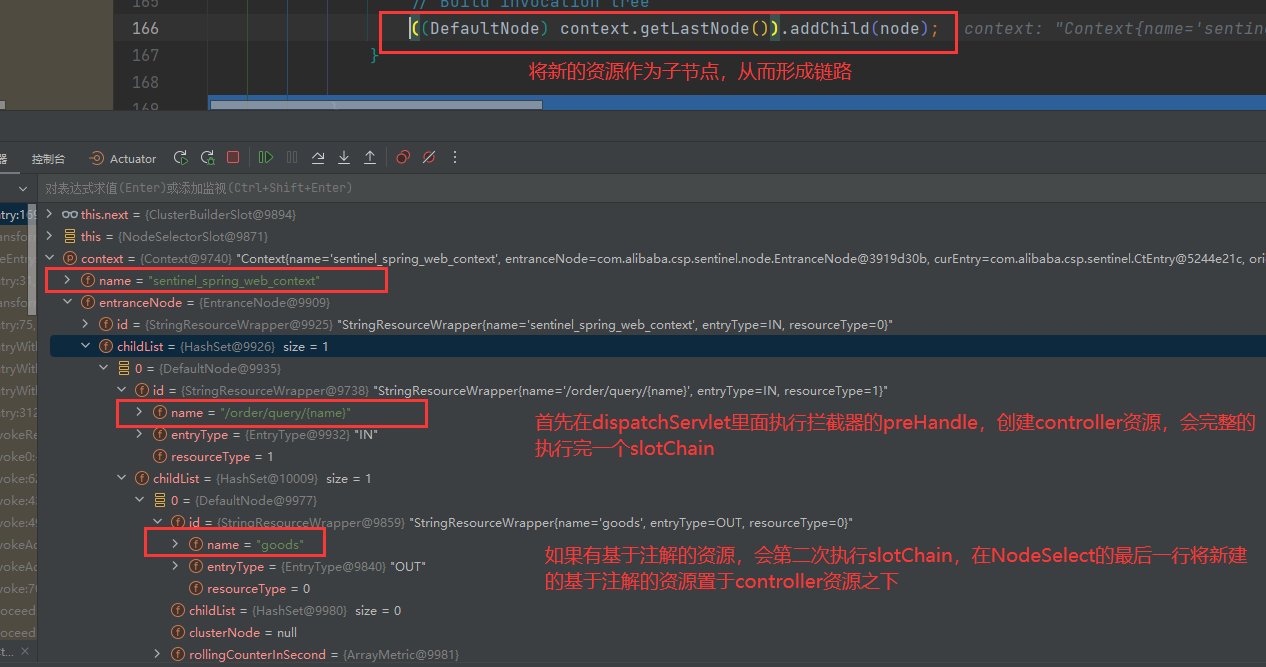
// 将刚创建的node设置为当前node的子节点
((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
}
}
}
// 设置当前节点为刚创建的节点
context.setCurNode(node);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
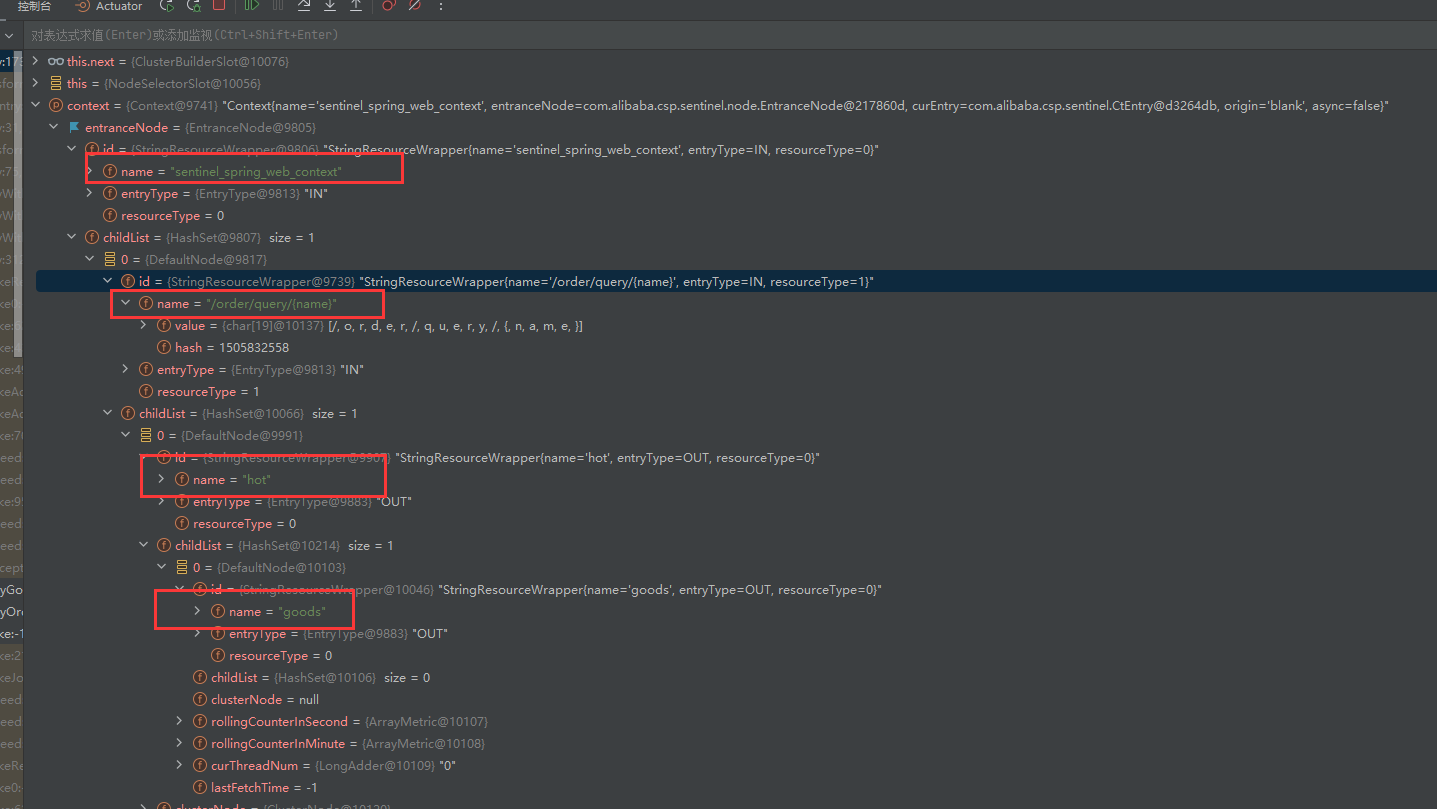
}下面的图是访问/order/query/{name}接口创建的资源

下面的图是访问/order/query/{name}接口创建的资源,不过在这个 Controller 接口里面又调用了 service 中添加了@SentinelResource注解的方法。根据上面的分析,基于注解的资源后创建,因此它作为基于 Controller 创建的资源的子节点
第二次访问/order/query/{name}接口,在NodeSelectorSlot中,node 会获取到,因此直接执行后边的操作

如果 controller 接口上加了@SentinelResource,还是先创建 controller 资源,然后创建 controller 基于注解的资源,然后是 service 的资源。下面的图中,在/order/query/{name}Controller 接口上添加了@SentinelResource注解。
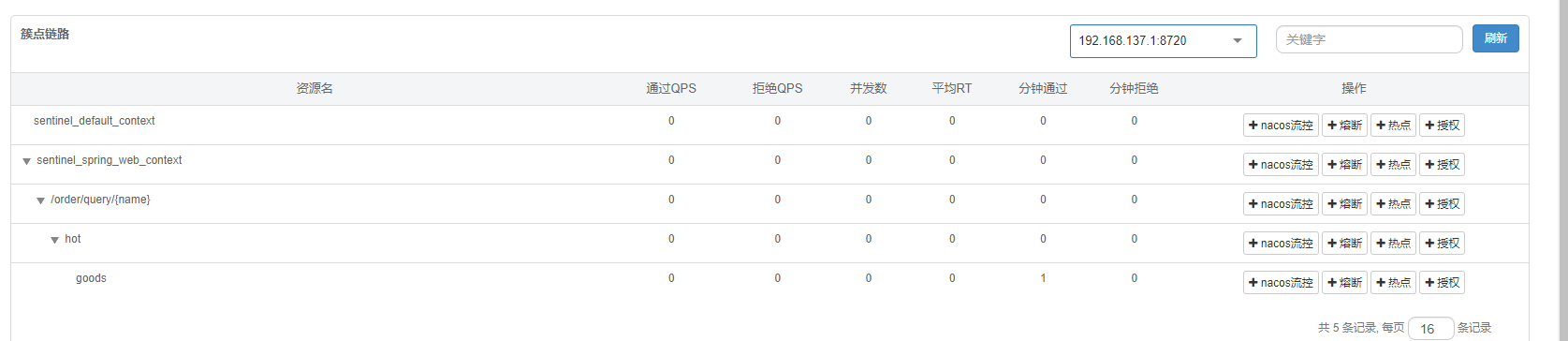
feign 对 Sentinel 支持
开启 feign 对 Sentinel 的支持后,Sentinel 会将 feign 的请求添加到簇点链路中
feign.sentinel.enabled=true在 Sentinel 的 jar 中,使用 spi 机制加载了一个类com.alibaba.cloud.sentinel.feign.SentinelFeignAutoConfiguration
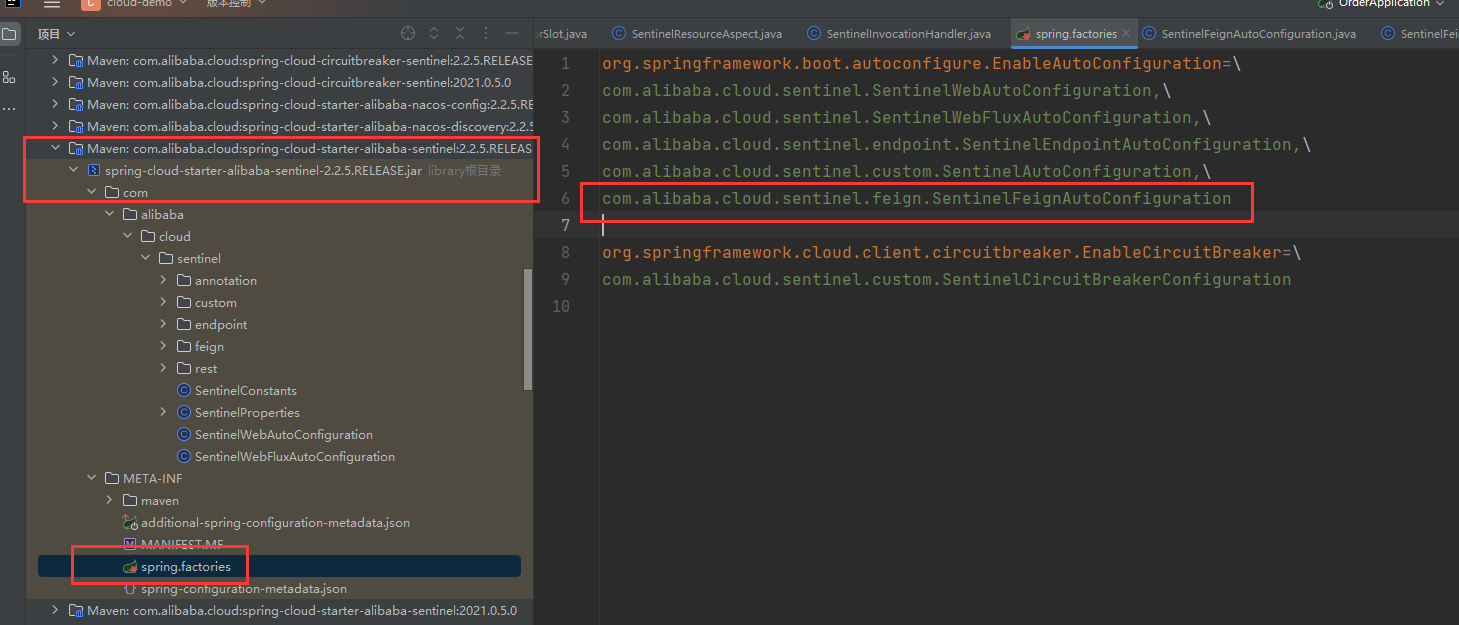
SentinelFeignAutoConfiguration 配置类里定义了Feign.Builder 的实现类 SentinelFeign.builder()
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ SphU.class, Feign.class })
public class SentinelFeignAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feign.sentinel.enabled") // 配置项为true时该bean生效
public Feign.Builder feignSentinelBuilder() {
return SentinelFeign.builder();
}
}SentinelFeign.builder( ) 的 build( ) 方法
主要作用是: 创建 invocationHandlerFactory,重写create( ) 方法;invocationHandlerFactory 用于创建 SentinelInvocationHandler ,代替前面的 FeignCircuitBreakerInvocationHandler。
public Feign build() {
super.invocationHandlerFactory(new InvocationHandlerFactory() {
public InvocationHandler create(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch) {
GenericApplicationContext gctx = (GenericApplicationContext)Builder.this.applicationContext;
BeanDefinition def = gctx.getBeanDefinition(target.type().getName());
FeignClientFactoryBean feignClientFactoryBean = (FeignClientFactoryBean)def.getAttribute("feignClientsRegistrarFactoryBean");
// 从BeanDefinition 里获取到 fallback、fallbackFactory
Class fallback = feignClientFactoryBean.getFallback();
Class fallbackFactory = feignClientFactoryBean.getFallbackFactory();
String beanName = feignClientFactoryBean.getContextId();
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
beanName = feignClientFactoryBean.getName();
}
if (Void.TYPE != fallback) {
// 创建 fallback 实例
Object fallbackInstance = this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallback", fallback, target.type());
// 创建 SentinelInvocationHandler
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, new org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FallbackFactory.Default(fallbackInstance));
} else if (Void.TYPE != fallbackFactory) {
FallbackFactory fallbackFactoryInstance = (FallbackFactory)this.getFromContext(beanName, "fallbackFactory", fallbackFactory, FallbackFactory.class);
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch, fallbackFactoryInstance);
} else {
return new SentinelInvocationHandler(target, dispatch);
}
}
private Object getFromContext(String name, String type, Class fallbackType, Class targetType) {
Object fallbackInstance = Builder.this.feignContext.getInstance(name, fallbackType);
if (fallbackInstance == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("No %s instance of type %s found for feign client %s", type, fallbackType, name));
} else if (!targetType.isAssignableFrom(fallbackType)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("Incompatible %s instance. Fallback/fallbackFactory of type %s is not assignable to %s for feign client %s", type, fallbackType, targetType, name));
} else {
return fallbackInstance;
}
}
});
super.contract(new SentinelContractHolder(this.contract));
return super.build();
}在 invoke 方法里面为feign请求创建资源创建资源
@Override
public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
Object otherHandler = args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0])
: null;
return equals(otherHandler);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
return false;
}
}
else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) {
return hashCode();
}
else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) {
return toString();
}
Object result;
MethodHandler methodHandler = this.dispatch.get(method);
// only handle by HardCodedTarget
if (target instanceof Target.HardCodedTarget) {
Target.HardCodedTarget hardCodedTarget = (Target.HardCodedTarget) target;
MethodMetadata methodMetadata = SentinelContractHolder.METADATA_MAP
.get(hardCodedTarget.type().getName()
+ Feign.configKey(hardCodedTarget.type(), method));
// resource default is HttpMethod:protocol://url
if (methodMetadata == null) {
result = methodHandler.invoke(args);
}
else {
String resourceName = methodMetadata.template().method().toUpperCase()
+ ":" + hardCodedTarget.url() + methodMetadata.template().path();
Entry entry = null;
try {
ContextUtil.enter(resourceName);
// 为feign请求创建资源
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, EntryType.OUT, 1, args);
// 调用服务端接口
result = methodHandler.invoke(args);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// fallback handle
if (!BlockException.isBlockException(ex)) {
Tracer.trace(ex);
}
if (fallbackFactory != null) {
try {
//异常时 调用熔断逻辑
Object fallbackResult = fallbackMethodMap.get(method)
.invoke(fallbackFactory.create(ex), args);
return fallbackResult;
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
····
}
}
else {
···
}
}
finally {
···
}
}
}
else {
result = methodHandler.invoke(args);
}
return result;
}如果 service 中使用 feign,则 feign 的调用 也会现实在链路中,他和使用注解创建的service 资源是同级的,但是先创建 feign,后创建 service 注解资源

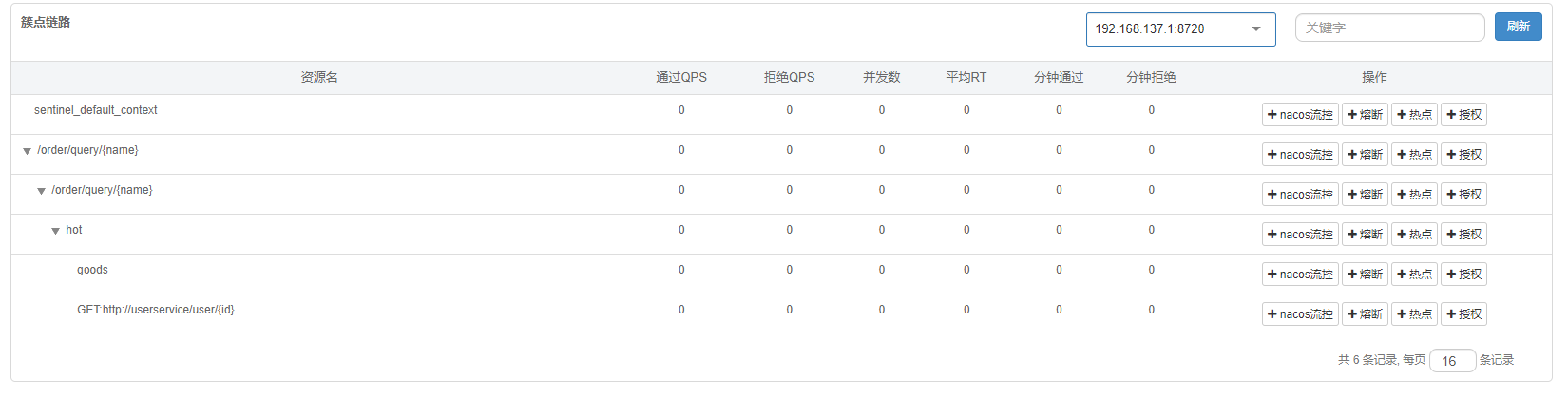
使用注解和 feign 创建的资源,EntryType 都是 OUT,只有 controller 资源的EntryType 是 IN。
EntryType:枚举标记资源调用方向。
创建ClusterNode
在创建 ClusterNode 时,使用 static 变量存储。将创建的 ClusterNode 与当前 node 进行关联。
/**
* 请记住,相同的资源(ResourceWrapper.equals(Object))将在全局范围内共享相同的ProcessorSlotChain,而与上下文无关。
* 因此,如果代码进入entry(Context,ResourceWrapper,DefaultNode,int,boolean,Object...),
* 则资源名称必须相同,但上下文名称可能不同。要获得不同上下文中相同资源的总统计数据,
* 相同的资源在全局范围内共享相同的ClusterNode。此映射在应用运行时间越长,就会变得越稳定。
* 因此,我们不使用并发映射,而是使用锁。因为此锁仅在开始时发生,而并发映射将始终保持锁定状态。
*/
private static volatile Map<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> clusterNodeMap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 如果不是第一次访问这个资源,则clusterNode是一定有的
// 所以直接将DefaultNode和ClusterNode进行关联
// 因为保存ClusterNode的map是static 的,因此全局共享,且创建后内容一直存在
// 因此一个资源只会创建一次ClusterNode
if (clusterNode == null) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (clusterNode == null) {
// Create the cluster node.
clusterNode = new ClusterNode(resourceWrapper.getName(), resourceWrapper.getResourceType());
HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ClusterNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(Math.max(clusterNodeMap.size(), 16));
newMap.putAll(clusterNodeMap);
newMap.put(node.getId(), clusterNode);
clusterNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
}
node.setClusterNode(clusterNode);
/*
* if context origin is set, we should get or create a new {@link Node} of
* the specific origin.
*/
if (!"".equals(context.getOrigin())) {
Node originNode = node.getClusterNode().getOrCreateOriginNode(context.getOrigin());
context.getCurEntry().setOriginNode(originNode);
}
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}说明
如果一个请求中要经过多个资源保护的方法(controller 资源*1,注解资源*n),则上面的流程会进行多次,分别根据资源创建类型执行对应的方法,从而将每次的资源添加到前面资源的字节的中,形成于给完整的簇点链路
后面就是限流的一些 slot