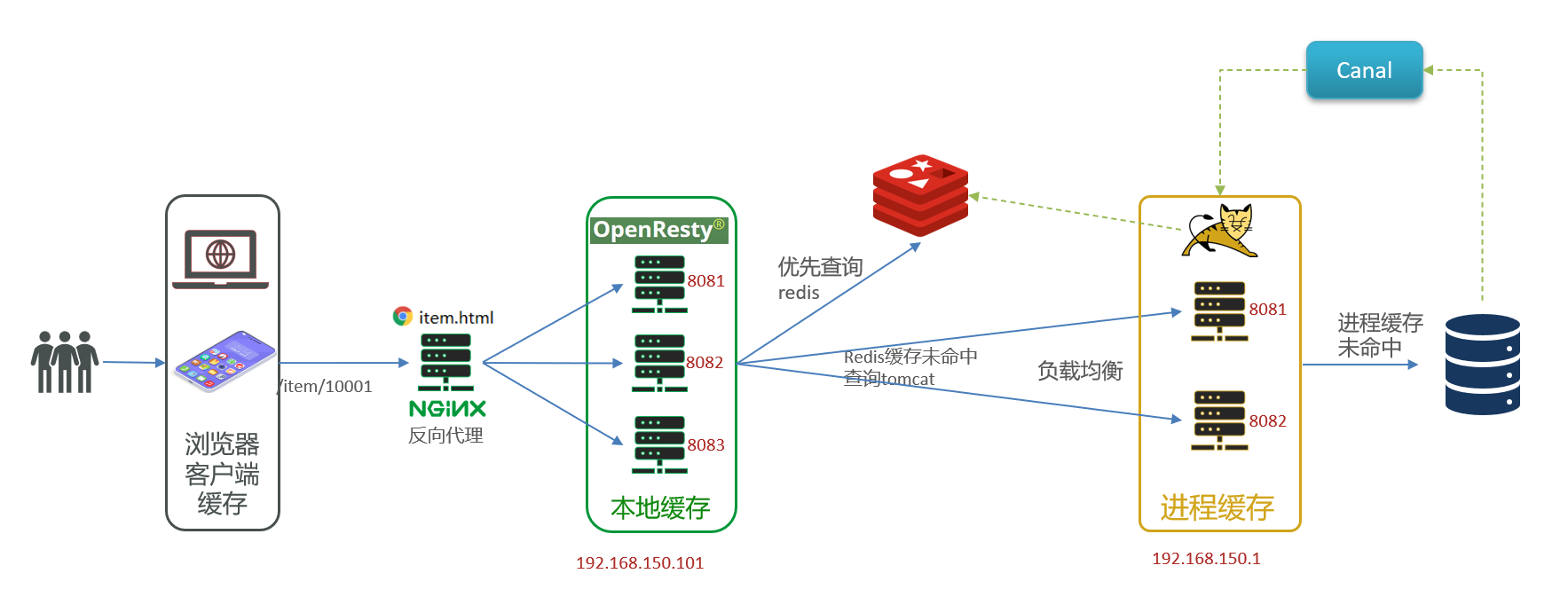
map 和 set 一起使用的场景其实也蛮多的,最近业务上就遇到了。需求是这样的,一条路径(mpls中的lsp)会申请多个 id,这个 id 是独一无二的。这里很显然就就一个”一对多“的情况,合适用这个容器不保存这些信息,如:std::map<uint32_t, std::set<bundle_set>> mLdpIdmMap; 下面为一个完成的可编译运行的代码,只是功能并不完善。
#include <mutex>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <string.h>
#define IDM_BUNDLE_SET 9 //一个bundle 9 个set
#define BUNDLE_SET_ID 8 //每个 set 8 个id
#define IDM_MALLOC_16 16 //一次 16 个id
#define IDM_MALLOC_32 32
int g_ECMP = 70;
struct bundle_set
{
uint32_t baseId;
uint32_t endId;
bool operator< (const bundle_set &a)const
{
return baseId < a.baseId;
}
};
struct bundle_data
{
uint32_t allocaNum; //一个bundle里已经分配的个数
bundle_set setId[IDM_BUNDLE_SET];
};
class idm_bundle_manager
{
public:
int assign(uint32_t baseId, uint32_t num, uint32_t ldpIdx);
int getLdpById(uint32_t idmId);
int getSetById(uint32_t idmId);
void dumpBundleAll() const;
void dumpBundleByIdx(uint32_t index) const;
void dumpLdpAll()const;
void dumpByLdpIdx(uint32_t ldpIdx)const;
static idm_bundle_manager *instance();
virtual ~idm_bundle_manager();
private:
uint32_t mBundleIdx; //第几个 bundle
uint32_t mSetIdx; //bundle里第几个set, 一共有9个set
uint32_t mIdInBundle; //一个bundle里id数,为 IDM_BUNDLE_SET * BUNDLE_SET_ID
uint32_t mBundleNum; //bundle总个数
std::mutex mtx;
bundle_data *mBundle;
std::map<uint32_t, std::set<bundle_set>> mLdpIdmMap;
private:
int32_t findIdleBundle(uint32_t bundleIdx, uint32_t num);
bool insertLdpIdm(uint32_t ldpIdx, uint32_t baseId, uint32_t num);
idm_bundle_manager();
idm_bundle_manager(const idm_bundle_manager&);
idm_bundle_manager& operator=(const idm_bundle_manager&);
};
idm_bundle_manager::idm_bundle_manager():
mBundleIdx(0),
mSetIdx(0),
mIdInBundle(IDM_BUNDLE_SET * BUNDLE_SET_ID),
mBundleNum(0),
mBundle(NULL)
{
mBundleNum = (g_ECMP % IDM_BUNDLE_SET == 0)? g_ECMP / IDM_BUNDLE_SET : (g_ECMP % IDM_BUNDLE_SET + 1);
mBundle = (bundle_data*)malloc(sizeof(bundle_data) * mBundleNum);
memset(mBundle, 0, sizeof(bundle_data) * mBundleNum);
}
idm_bundle_manager::~idm_bundle_manager()
{
if(mBundle)
{
free(mBundle);
mBundle = NULL;
}
}
int32_t idm_bundle_manager::findIdleBundle(uint32_t bundleIdx, uint32_t num)
{
uint32_t i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < mBundleNum; i++) //全部找一遍,因为分配的num不一样导致各个bundle剩余的空间也不一样
{
if(i == bundleIdx) //当前那个不找
{
continue;
}
if(mIdInBundle - mBundle[i].allocaNum >= num)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int idm_bundle_manager::assign(uint32_t baseId, uint32_t num, uint32_t ldpIdx)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mtx);
if(mBundleIdx >= mBundleNum) //bundle到最后一个时,重新从0开始
{
mBundleIdx = 0;
}
//当前的 bundle 已经不够容纳 num 个id,找一个空闲的 bundle
if(num > mIdInBundle - mBundle[mBundleIdx].allocaNum)
{
uint32_t idx = findIdleBundle(mBundleIdx, num);
if(-1 == idx)
{
return 0;//找不到能够容纳 num 的 bundle 了
}
mBundleIdx = idx;
}
//算出在bundle里的第几个set(0~8)
mSetIdx = (mBundle[mBundleIdx].allocaNum == 0) ? 0 : mBundle[mBundleIdx].allocaNum / 8;
if(IDM_MALLOC_32 == num)
{
}
else if(IDM_MALLOC_16 == num) //一次16个,跨两个 set
{
mBundle[mBundleIdx].setId[mSetIdx].baseId = baseId;
mBundle[mBundleIdx].setId[mSetIdx].endId = baseId + IDM_MALLOC_16 / 2;
mBundle[mBundleIdx].setId[mSetIdx + 1].baseId = baseId + IDM_MALLOC_16 / 2;
mBundle[mBundleIdx].setId[mSetIdx + 1].endId = baseId + num;
mBundle[mBundleIdx].allocaNum += num;
}
else
{
mBundle[mBundleIdx].setId[mSetIdx].baseId = baseId;
mBundle[mBundleIdx].setId[mSetIdx].endId = baseId + num;
mBundle[mBundleIdx].allocaNum += num;
}
mBundleIdx += 1;
//直接插入map,
if(!insertLdpIdm(ldpIdx, baseId, num))
{
printf("insert ldpIdx(%u) fail\n", ldpIdx);
}
return mSetIdx;
}
int idm_bundle_manager::getLdpById(uint32_t idmId)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mtx);
for(auto ite : mLdpIdmMap)
{
if(idmId >= ite.second.begin()->baseId && idmId <= ite.second.end()->endId)
{
return ite.first;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool idm_bundle_manager::insertLdpIdm(uint32_t ldpIdx, uint32_t baseId, uint32_t num)
{
bundle_set set{baseId, baseId + num -1 };
auto ret = mLdpIdmMap[ldpIdx].insert(set);
return ret.second;
}
int idm_bundle_manager::getSetById(uint32_t idmId)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mtx);
for(uint32_t bundleIdx = 0; bundleIdx < mBundleNum; bundleIdx++)
{
for(uint32_t setId = 0; setId < IDM_BUNDLE_SET; setId++)
{
if(idmId >= mBundle[bundleIdx].setId[setId].baseId && idmId <= mBundle[bundleIdx].setId[setId].endId)
{
return setId;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
void idm_bundle_manager::dumpBundleAll()const
{
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < mBundleNum; i++)
{
printf("bundle_index: %u\n", i);
dumpBundleByIdx(i);
}
}
void idm_bundle_manager::dumpBundleByIdx(uint32_t bundleIdx) const
{
if(bundleIdx >= mBundleNum)
{
return;
}
for(uint32_t i = 0; i < IDM_BUNDLE_SET; i++)
{
printf("\tset_index: %u\n", i);
if(mBundle[bundleIdx].setId[i].baseId)
{
for(uint32_t j = 0; j < BUNDLE_SET_ID; j++)
{
printf("\t %u ", mBundle[bundleIdx].setId[i].baseId + j);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void idm_bundle_manager::dumpByLdpIdx(uint32_t ldpIdx)const
{
if(!mLdpIdmMap.empty())
{
printf("ldpidx = %u\n", ldpIdx);
auto ret = mLdpIdmMap.find(ldpIdx);
if(ret != mLdpIdmMap.end())
{
for(auto ite : ret->second)
{
printf("%u %u\n", ite.baseId, ite.endId);
}
}
}
}
idm_bundle_manager *idm_bundle_manager::instance()
{
static idm_bundle_manager _instance;
return &_instance;
}
#define g_IdmBundleManager (*idm_bundle_manager::instance())
int main()
{
//每次分配8个,最多能分配72次
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
int baseId = 1024 + i * 8;
g_IdmBundleManager.assign(baseId, 8, 1073741832);
}
//每次分配16个,最多能分配 bundleNum * 4 次
// for(int i = 0; i < 33; i++)
// {
// int baseId = 10024 + i * 16;
// g_IdmBundleManager.assign(baseId, 16);
// }
g_IdmBundleManager.dumpBundleAll();
g_IdmBundleManager.dumpByLdpIdx(1073741832);
// int idm_id = 10808;
// int setId = g_IdmBundleManager.getSetById(idm_id);
// printf("setId of %d is %d\n", idm_id, setId);
return 0;
}这里主要借这个说明一下 set,set 里的元素是唯一的,且是有序的,它和 map 的底层实现同样的红黑树,所以如果 set 的元素类型是自定义类型的,则必须要实现 operator< 否则是无法编译的。如:
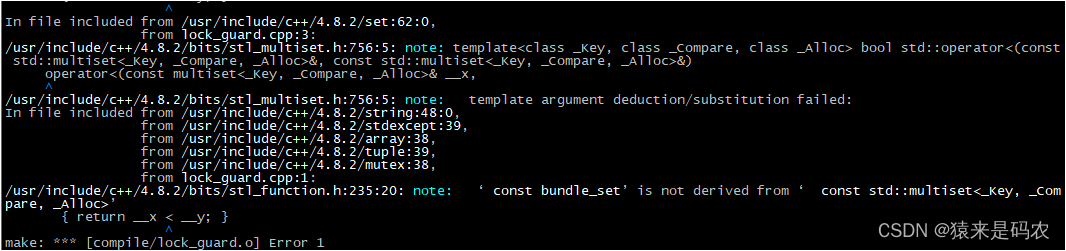
因为 set 的元素是有序的,所以每次插入元素都要进行比较。那实现 operator> 是否可行 ,反正都是比较,其实是不行的,因为它底层实现就是用的 小于号 < ,如错误所示。
使用 auto 进行插入及读取数据的代码:
int idm_bundle_manager::getLdpById(uint32_t idmId)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(mtx);
for(auto ite : mLdpIdmMap)
{
if(idmId >= ite.second.begin()->baseId && idmId <= ite.second.end()->endId)
{
return ite.first;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool idm_bundle_manager::insertLdpIdm(uint32_t ldpIdx, uint32_t baseId, uint32_t num)
{
bundle_set set{baseId, baseId + num -1};
auto ret = mLdpIdmMap[ldpIdx].insert(set);
return ret.second;
}