一、别名 Alias
1. 为什么使用别名
一般映射文件中会包含大量<select>标签, 每个<select>中都需要配置resultType="com.bjsxt.pojo.People",MyBatis提供了别名机制可以对某个类起别名或给某个包下所有类起别名,简化resultType取值的写法。
2. 明确指定别名
通过<typeAlias>标签明确设置类型的别名。
-
type:类型全限定路径。
-
alias:别名名称。
指定别名方式优点和缺点:
-
优点:别名可以设置为单个字母,以后使用别名时比较方便。
-
缺点:当需要定义别名的类比较多时,定义别名是个较大工程量。
在mybatis.cfg.xml全局配置文件中,添加下面配置
<typeAliases>
<!-- type 类型是 包名+类名 全限定名-->
<!-- alias 是指定的别名 -->
<!--
(1)一个类可以有多个别名
(2)设置别名后,类的全限定路径依然可以使用。
-->
<typeAlias type="com.sh.pojo.People" alias="a"/>
</typeAliases>别名定义后,可以在resultType中使用别名,类全限定路径方式还可以使用。
<!-- 配置SQL映射的文件 -->
<mapper namespace="a.b">
<select id="select1" resultType="a">
select * from people;
</select>
</mapper>(1)一个类可以有多个别名
(2)设置别名后,类的全限定路径依然可以使用。
尝试修改resultType="a"中a为大写的A,依然运行成功。说明在明确配置别名时不区分大小写。
3. 指定包中所有类的别名
当类个数较多时,明确指定别名工作量较大,可以通过<package>标签指定包下全部类的别名。
指定后所有类的别名就是类名。
<typeAliases>
<!-- 指定包名 -->
<package name="com.sh.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>在映射文件中测试,别名是否生效。
<!-- 在给包名进行别名设置后 ,resultType直接写类名 不区分大小写-->
<select id="select2" resultType="people">
select * from people;
</select>4. MyBatis内置别名
MyBatis框架中内置了一些常见类型的别名。这些别名不需要配置
| 别名 | 映射的类型 | 别名 | 映射的类型 | 别名 | 映射的类型 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| _byte | byte | string | String | date | Date | ||
| _long | long | byte | Byte | decimal | BigDecimal | ||
| _short | short | long | Long | bigdecimal | BigDecimal | ||
| _int | int | short | Short | object | Object | ||
| _integer | int | int | Integer | map | Map | ||
| _double | double | integer | Integer | hashmap | HashMap | ||
| _float | float | double | Double | list | List | ||
| _boolean | boolean | float | Float | arraylist | ArrayList | ||
| boolean | Boolean | collection | Collection | ||||
| iterator | Iterator |
二、SQL查询结果填充的几种方式(面试题)
1. 介绍
MyBatis会根据句映射关系把查询到的结果填充到指定结果集类型中。支持方式:
-
auto mapping:自动映射。当列名或列的别名与实体类属性名相同时不需要做额外配置。
-
resultMap:手动定义映射关系。
-
camel case:驼峰命名转换规则。
2. Auto Mapping
自定映射方式就是前面所讲的方式,只要保证数据库中列名和属性名相同,就可以自动进行映射。
自动映射到对象的属性中,如果表中的列名和属性不一样,可以在查询的时候添加别名,这样也能自动映射
select eid 'id',ename 'name',eaddr 'addr' from people;(单引号可以省略)
3. resultMap
当数据库列名和属性名不同时是无法进行自动映射的,这时需要手动指定映射关系。
举个例子
3.1 创建表
在数据库中创建表。
表名:无论哪种方式,表名和实体类名称是否相同都没有关系。
列名:列名和实体类名称不对应。

3.2 创建实体类
实体类的类名和表名不是必须相同的。
实体类中属性名和列名也不相同。
package com.sh.pojo;
public class People1 {
private int id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People1{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public People1(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public People1() {
}
}
3.3修改映射文件
在映射文件中需要注意的是<select>标签不再使用resultType属性,而是使用resultMap属性。
resultMap属性表示使用哪个<resultMap>作为结果映射配置
resultMap的作用是可以手动进行映射,表中的字段名和属性名不同时使用
注意:
<resultMap>标签的子标签的property属性必须和类的属性名严格对应,区分大小写。如果没有对应上,会出现反射异常.数据库查询结果填充到对应属性中优先使用setter方法,如果没有setter方法,通过反射直接对属性进行赋值。
column属性对应数据库列名,由于数据库是不区分大小写的,所以column的值也是不区分大小写的。
resultMap可以存在多个。只要id属性不重名就可以。
<!--
resultMap: 将表中字段和实体类中属性手动映射
id : resultMap的唯一标识
type : 手动映射返回的结果类型
-->
<!-- 这里的type 设置别名的话可以使用别名 -->
<resultMap id="abc" type="People1">
<!-- 主键 和 属性的 映射-->
<!--
column : 字段名
property : 属性名
-->
<!--如果有主键设置为id-->
<id column="pid" property="id"></id>
<!-- 其他的字段使用result -->
<result column="pname" property="name"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="select3" resultMap="abc">
select * from people1;
</select>4. 驼峰转换
在MySQL中列名命名规范是xxx_yyy,多个单词之间使用下划线进行分割。在Java中属性命名规范是xxxYyy,小驼峰的方式进行命名。这两种技术的命名习惯是不一样的,这就导致每次都需要手动配置映射关系。
MyBatis发现了这个问题,提供了驼峰转换的能力。通过全局配置文件开启驼峰转换功能后,就可以让xxx_yyy自动映射到xxxYyy上。例如:列名叫做peo_id,可以自动映射到peoId的属性上。转换时去掉列中的下划线,把下划线后面单词首字母变大写。
4.1 修改全局配置文件
要想使用驼峰转换,必须在全局配置文件中添加设置,开启驼峰转换功能。
<settings>
<!-- 开启驼峰转换 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>三、接口绑定方案
1. 接口绑定方案存在的意义
前面所学的方式都是通过SqlSession的方法调用指定的一个statement。在学习MyBatis之前,我们的习惯都是创建Dao对象,通过一个对象调用类中多个方法。这样的好处是一次创建,多次调用。显然要比前面所学的方式用起来更加方便。
MyBatis提供了也提供了一种接口绑定方案,通过SqlSession的getMapper方法产生接口的动态代理对象。然后通过对象调用接口中提供的功能。
2. 完整项目流程
数据库以ssm数据库的people为例。
2.1 创建项目并配置pom.xml
创建项目,命名为mybatis2。并配置pom.xml,配置的内容和之前一样,只需要导入MyBatis框架依赖和数据库驱动。
2.2 创建全局配置文件
在resources中创建mybatis.cfg.xml。
配置文件中保留了别名的配置,通过<mapper>的子标签换成了<mapper>和<package>标签j
<!-- 映射路径-->
<mappers>
<!-- 接口绑定 -->
<!--<!– 方式一 单独指定 mapper接口 –>
<mapper class="com.sh.mapper.PeopleMapper"></mapper>-->
<!-- 方式二 只需要指定包名 -->
<package name="com.sh.mapper"/>
</mappers>2.3 创建实体类
在src/main/java下新建com.bjsxt.pojo.People实体类。
package com.sh.pojo;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class People implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String addr;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", addr='" + addr + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddr() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(String addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
public People(int id, String name, String addr) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.addr = addr;
}
public People() {
}
}
2.4 创建映射文件(常用)
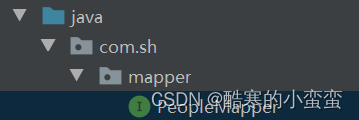
在接口绑定方案中,对于映射文件有几点强制要求:
映射文件和接口需要在同一个包中
映射文件名称要和接口名称相同
两种方法,一种是设置资源拷贝,还有一种就是下面图中的方法
设置相同的路径,在resources中设置路径,分层要使用/而不是.
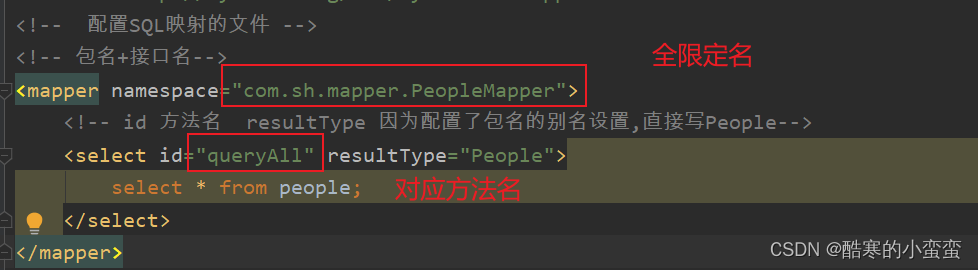
namespace取值必须是接口的全限定路径
id属性值必须和方法名对应
resultType必须和方法返回值类型对应。如果方法返回值是集合类型,resultType中写泛型的类型
2.5 添加资源拷贝插件的使用
由于映射文件添加到了com.bjsxt.mapper包中,所以需要添加资源拷贝插件,保证映射文件能被编译。
小提示:
资源拷贝插件配置的主要目的是为了让src/main/java下映射文件能被编译时包含。
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>2.6 编写测试类
创建测试类com.bjsxt.test.Test类
三、接口绑定方案下参数传递
接口绑定方式其底层调用的就是前面学习的SqlSession的相关方法。
接口中方法对应以前测试类中直接调用的SqlSession中的方法。
对于映射文件的使用还是和之前学习的相同。
| 接口中方法 | SqlSession的方法 |
|---|---|
| int insertPeople(People peo); | session.insert("insertPeople",peo); |
| int deleteById(int id); | session.delete("deleteById",id); |
| int updatePeople(People peo); | session.update("updatePeople",peo); |
| People selectById(int id); | session.selectOne("selectById",id); |
| List<People> selectAll(); | session.selectList("selectAll"); |
| List<People> selectByUnameAndAddr(String name,String address); | session.selectList("selectByUnameAndAddr",Map类型参数) |
在接口绑定方案中唯一需要重点注意的是:
当方法带有多个参数将使用session.selectList("",Map类型参数)或session.selectOne("",Map类型参数)作为底层调用。
通过前面的学习清楚的知道,Map类型当做参数时,在映射文件中通过Map的key进行获取value值。
Mybatis会自动创建Map的key:
-
如果接口中方法没有使用注解定义名称,MyBatis使用内置名称作为key。
规则:arg0、arg1、argM(M为从0开始的数字,和方法参数顺序对应)或param1、param2、paramN(N为从1开始的数字,和方法参数顺序对应)。
-
也可以在接口方法参数中通过@Param("key名称")的形式进行定义key。一定使用了注解argN的这种形式就不能使用了,但是paramN的方式还是可以使用。
增删改查
3.1 配置接口
package com.sh.mapper;
import com.sh.pojo.People;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface PeopleMapper {
List<People> selectAll();
//查询
//一个参数 根据姓名查询
List<People> select1(String name);
//两个参数 姓名,地址
List<People> select2(String name,String addr);
//两个参数 姓名,地址
List<People> select3(@Param("name") String name,@Param("addr") String addr);
//传递一个对象
List<People> select4(People people);
//增加
int insert1(People people);
//修改
int alter1(People people);
//删除
int del1(int id);
}
3.2 配置mapper映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- 配置SQL映射的文件 -->
<mapper namespace="com.sh.mapper.PeopleMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="People">
select * from people
</select>
<!-- 有参数的接口绑定-->
<!-- 1. 一个参数 -->
<select id="select1" resultType="People">
select * from people where name = #{name};
</select>
<!-- 2. 两个参数 -->
<select id="select2" resultType="People">
<!-- 这里的参数不能直接映射, 因为mybatis分不清楚 -->
<!--底层代码 使用了一个ParamMap集合进行了封装 */
/* 两组:
[arg0, arg1,
param1, param2]
*/-->
select * from people where name = #{arg0} and addr = #{arg1};
</select>
<!-- 3. 两个参数 -->
<select id="select3" resultType="People">
<!-- 这里的参数不能直接映射, 因为mybatis分不清楚 -->
<!-- /*也可以定义别名,在接口类中使用注解 @Param 定义自己想要的名字 */ -->
select * from people where name = #{name} and addr = #{addr};
</select>
<!-- 4. 两个参数 -->
<select id="select4" resultType="People">
<!-- 这里的参数不能直接映射, 因为mybatis分不清楚 -->
<!-- 使用类中的属性来传递参数 -->
<!-- 属性名必须一一对应 -->
select * from people where name = #{name} and addr = #{addr};
</select>
<!-- 添加操作 -->
<!-- 参数的传递和查询同理 -->
<insert id="insert1">
insert into people values (0,#{name},#{addr})
</insert>
<!-- 修改操作 -->
<update id="alter1">
update people set name = #{name},addr = #{addr} where id = #{id}
</update>
<!-- 删除操作 -->
<delete id="del1">
delete from people where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>3.3 配置测试类
import com.sh.mapper.PeopleMapper;
import com.sh.pojo.People;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class PeopleTest {
SqlSessionFactory factory;
//@Before在@Test方法执行前执行
@Before
public void before(){
//将流的操作放入try()中,可以自动关闭流
try(InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml")){
/*
* 解析mybatis-config.xml
* 1.读取db.properties,将结果存储到properties中
* 2.创建事务工厂
* 3.创建数据库连接池
* 4.读取指定包中所有的接口,因为在mapper中配置了package
* 获取每一个接口,获取 包名.接口名 + .xml
* 读取包名.接口名.xml的映射文件,完成映射文件的解析
* id : namespace.sql的id
* sqlSource : sql语句
* 5.把一些解析到的文件都存储到了一个叫configuration的类中
* */
factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//查询操作
//动态绑定的查询底层使用的还是 selectList()方法
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
//获取SqlSession对象
/*
* 1.事务控制
* 2.增删改查
* 3.ORM映射
* */
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//4.执行查询
//mybatis为PeopleMapper创建了实现类对象(动态代理对象)
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
List<People> list = mapper.selectAll();
/*
* 获取到 接口的 包名.接口名.方法名 com.zqwl.mapper.PeopleMapper.selectAll
*
* sqlSession.selectList("com.zqwl.mapper.PeopleMapper.selectAll");
*
* mapper映射文件中解析的内容:
* id: com.zqwl.mapper.PeopleMapper.selectAll
* sql: select * from people;
* */
System.out.println(list);
//5.资源释放
session.close();
}
//一个参数
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
List<People> list = mapper.select1("小明");
System.out.println(list);
session.close();
}
//两个参数 使用默认的map映射 /* 两组:
// [arg0, arg1,
// param1, param2]
// */
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
List<People> list = mapper.select2( "小明","北京");
System.out.println(list);
session.close();
}
// 两个参数 在接口类中使用@Param注解
@Test
public void test3(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
List<People> list = mapper.select3( "小明","北京");
System.out.println(list);
session.close();
}
//也可以使用对象传递参数
@Test
public void test4(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
People people = new People(0,"小明","北京");
List<People> list = mapper.select4(people);
System.out.println(list);
session.close();
}
//添加操作
@Test
public void test5(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
People people = new People(0,"小花","北京");
int i = mapper.insert1(people);
System.out.println(i);
//增删改查手动提交事务
session.commit();
session.close();
}
//修改操作
@Test
public void test6(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
People people = new People(9,"小","北京");
int i = mapper.alter1(people);
System.out.println(i);
//增删改查手动提交事务
session.commit();
session.close();
}
//删除操作
@Test
public void test7(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
int id = 9;
int i = mapper.del1(id);
System.out.println(i);
//增删改查手动提交事务
session.commit();
session.close();
}
}
四、主键回填
在一些特殊的需求中,需要执行完新增的SQL后立即知道新增时主键的值。如果主键的值是自己设置的固定值,可以知道主键的值。但是很多时候都是使用MySQL的主键自增,这时想要获取主键的值就需要通过特殊的方式获取了。
MyBatis中有两种方式可以获取到自增主键的值:
-
使用
<selectKey>子标签编写SQL进行回填属性值。 -
使用
<select>的useGeneratedKeys属性值进行自动回填。
4.1 mapper映射设置
<!-- 主键回填 -->
<insert id="getPrimaryKey">
<!-- 需要手动设置主键回填 -->
<!--
keyColumn 哪个字段是主键
keyProperty 回填到对象的哪个属性当中
resultType 返回结果的类型
order 在什么时候回填 我们肯定是after
-->
<selectKey keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select @@identity
</selectKey>
insert into people values(default, #{name}, #{addr});
</insert>
<!-- 主键回填简化操作 -->
<!-- selectKey 中的属性可以写在 insert 里面-->
<insert id="getPrimaryKey1" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id">
insert into people values(default, #{name}, #{addr});
</insert>4.2 接口类设置
//主键回填(自增长的主键值回填到指定的对象属性中)
//获取添加数据的主键自增值
int getPrimaryKey(People people);4.3 测试类设置
//获取主键自增值
@Test
public void test8(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
People people = new People(0,"小花","北京");
int i = mapper.getPrimaryKey(people);
//返回的是影响的行数,还是添加操作
System.out.println(i);
//回填的主键值存储在people对象当中
System.out.println(people);
//输出结果
/*
* 1
People{id=10, name='小花', addr='北京'}
* */
//增删改查手动提交事务
session.commit();
session.close();
}
五、动态SQL
1. 动态SQL引入
MyBatis在简化操作方法中提出了动态SQL功能,将使用Java代码拼接SQL语句,改变为在XML映射文件中截止标签拼接SQL语句。相比而言,大大减少了代码量,更灵活、高度可配置、利于后期维护。
MyBatis中动态SQL是编写在mapper.xml中的,其语法和JSTL类似,但是却是基于强大的OGNL表达式实现的。
为了查看动态SQL最终执行时的SQL,先把日志配置上。
2. if标签
通过if处理用户多变的查询条件
接口代码
List<People> selectIf(People people);
mapper映射文件通过if进行判断参数的属性是否为null。
<if>标签的test属性值为OGNL(对象导航图语言)表达式,通过对象属性名可以快速获取到对象属性值。
代码解释说明:
name!=null : OGNL 表达式,直接写属性名可以获取到属性值。不需要添加${}或#{}。
name=#{name} 中name是表中的列名。#{name}是MyBatis获取参数对象属性值的写法(之前学习的)。
where 1=1 中1=1是为了保证SQL语法的正确性。如果if成立没有1=1最后的SQL就是where and name=xxx 这种写法是不对的。
2.1 配置映射文件
<!-- 动态sql -->
<!-- if : 满足条件参与执行 相当于java中的if -->
<select id="select11" resultType="People">
select * from people where 1=1
<!--
因为两个if 中都带有 and ,当有一个为空时语句会变为
select * from people where and name = #{name}
语法错误,所以在前面拼接一个1=1
select * from people where 1=1 and name = #{name}
保证语句正确
-->
<if test="name != null">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="addr != null">
and addr = #{addr}
</if>
</select>2.2 配置接口类
//动态sql方法
//if
List<People> select11(@Param("name") String name,@Param("addr") String addr);2.3 配置测试类
//动态sql
//if
@Test
public void test9(){
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
PeopleMapper mapper = session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
List<People> list = mapper.select11( "小明","北京");
System.out.println(list);
session.close();
}3. choose
choose when otherwise 相当于 if else if else 注意:只有一个when 或 otherwise能够被执行
<select id="selectIf" resultType="People">
select * from people where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="name!=null">
and name=#{name}
</when>
<when test="address!=null">
and address=#{address}
</when>
<otherwise>
// do something
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>4. trim标签
上面的if标签中为了保证语法的正确性,需要在SQL中明确指定where 1=1,其中1=1存在的意义单纯为了保证语法的正确性,没有实际意义的。可以通过trim标签动态进行截取添加,省略where 1=1。
trim标签包含四个属性:
prefix:只要子内容不是空字符串(""),就在子内容前面添加特定字符串。
prefixOverrides:如果子内容是以某个内容开头,去掉这个内容。
suffix:只要内容不是空字符串(""),就在子内容后面添加特定字符串。
suffixOverrides:如果里面内容以某个内容结尾,就去掉这个内容。
小提示:
trim作为很多其它标签的底层。
无论是开头操作还是结尾的操作,都是先去掉内容,后添加。
trim只会对里面的子内容进行操作。如果子内容为空则不进行任何操作。
后添加的内容会有空格。
特例:
如果内部字符串为要去掉的字符串,去掉后认为内容不为空,prefix依然添加。
<select id="selectIf" resultType="People">
select * from people
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="name!=null">
and name=#{name}
</if>
<if test="address!=null">
and address=#{address}
</if>
</trim>
</select>5. where标签
where标签属于trim标签的简化版,被where标签包含的内容具备:
简化:<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
-
如果里面内容不为空串,在里面内容最前面添加where。
-
如果里面内容是以and开头,去掉最前面的and。
6. set标签
set标签是专门用在修改SQL中的,属于trim的简化版,带有下面功能:
简化:
<set> 简化 <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
-
如果子内容不为空串,在最前面添加set。
-
去掉最后一个逗号。
7. foreach标签
foreach标签表示循环,主要用在in查询或批量新增的情况。
foreach标签的属性解释说明:
collection:要遍历的数组或集合对象。
1. 如果参数没有使用@Param注解:arg0或array或list。
2. 如果使用@Param注解,使用注解的名称或param1。
open:遍历结束在前面添加的字符串。
close:遍历结束在后面添加的字符串。
item:迭代变量。在foreach标签里面#{迭代变量}获取到循环过程中迭代变量的值。
separator:分隔符。在每次循环中间添加的分割字符串。
index:迭代的索引。从0开始的数字。
nullable:是否允许数组或集合对象为null。如果设置为true,表示集合或数组允许为null。如果设置为false表示不允许数组或集合对象为null,一旦为null会出现:org.apache.ibatis.builder.BuilderException: The expression 'array' evaluated to a null value。
8. bind标签
bind标签表示对传递进来的参数重新赋值。最多的使用场景为模糊查询。通过bind可以不用在Java代码中对属性添加%。
拼接操作
<select id="selectLike" resultType="People">
<bind name="name" value="'%'+name+'%'"/>
select * from people where name like #{name}
</select>9. sql和include标签
在企业开发中的表可能都会有很多列,当使用多表联合查询时列的个数更多。
很多功能或SQL都需要使用这些列的话,其实在做很多重复工作。即使复制粘贴,一旦碰到表结构改变或添加、删除列的时候也需要修改很多SQL。
MyBatis的sql标签用于定义SQL片段,include标签用于引用sql标签定义的片段。
<sql id="mysqlpart">
id,name,address
</sql>
<select id="selectSQL" resultType="People">
select <include refid="mysqlpart"></include> from people
</select><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- 配置SQL映射的文件 -->
<mapper namespace="com.sh.mapper.PeopleMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="People">
select * from people
</select>
<!-- 有参数的接口绑定-->
<!-- 1. 一个参数 -->
<select id="select1" resultType="People">
select * from people where name = #{name};
</select>
<!-- 2. 两个参数 -->
<select id="select2" resultType="People">
<!-- 这里的参数不能直接映射, 因为mybatis分不清楚 -->
<!--底层代码 使用了一个ParamMap集合进行了封装 */
/* 两组:
[arg0, arg1,
param1, param2]
*/-->
select * from people where name = #{arg0} and addr = #{arg1};
</select>
<!-- 3. 两个参数 -->
<select id="select3" resultType="People">
<!-- 这里的参数不能直接映射, 因为mybatis分不清楚 -->
<!-- /*也可以定义别名,在接口类中使用注解 @Param 定义自己想要的名字 */ -->
select * from people where name = #{name} and addr = #{addr};
</select>
<!-- 4. 两个参数 -->
<select id="select4" resultType="People">
<!-- 这里的参数不能直接映射, 因为mybatis分不清楚 -->
<!-- 使用类中的属性来传递参数 -->
<!-- 属性名必须一一对应 -->
select * from people where name = #{name} and addr = #{addr};
</select>
<!-- 添加操作 -->
<!-- 参数的传递和查询同理 -->
<insert id="insert1">
insert into people values (0,#{name},#{addr})
</insert>
<!-- 修改操作 -->
<update id="alter1">
update people set name = #{name},addr = #{addr} where id = #{id}
</update>
<!-- 删除操作 -->
<delete id="del1">
delete from people where id = #{id}
</delete>
<!-- 主键回填 -->
<insert id="getPrimaryKey">
<!-- 需要手动设置主键回填 -->
<!--
keyColumn 哪个字段是主键
keyProperty 回填到对象的哪个属性当中
resultType 返回结果的类型
order 在什么时候回填 我们肯定是after
-->
<selectKey keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select @@identity
</selectKey>
insert into people values(default, #{name}, #{addr});
</insert>
<!-- 主键回填简化操作 -->
<!-- selectKey 中的属性可以写在 insert 里面-->
<insert id="getPrimaryKey1" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id">
insert into people values(default, #{name}, #{addr});
</insert>
<!-- 动态sql -->
<!-- if : 满足条件参与执行 相当于java中的if -->
<select id="select11" resultType="People">
select * from people where 1=1
<!--
因为两个if 中都带有 and ,当有一个为空时语句会变为
select * from people where and name = #{name}
语法错误,所以在前面拼接一个1=1
select * from people where 1=1 and name = #{name}
保证语句正确
-->
<if test="name != null">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="addr != null">
and addr = #{addr}
</if>
</select>
<!-- choose when otherwise-->
<!-- 相当于 if else if else -->
<select id="select12" resultType="People">
select * from people where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="name != null">
and name = #{name}
</when>
<when test="addr != null">
and addr = #{addr}
</when>
<!-- 所有when都不成立,执行 otherwise -->
<otherwise>
and 2 = 2
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
<!-- trim 简化if -->
<select id="select13" resultType="People">
select * from people
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="addr != null">
and addr = #{addr}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
<!-- trim 简化 choose -->
<!-- 简化操作有多种,只要能实现 -->
<select id="select14" resultType="People">
select * from people
<trim prefix="where" >
<choose>
<when test="name != null and addr != null">
name = #{name} and addr = #{addr}
</when>
<when test="name != null">
name = #{name}
</when>
<when test="addr != null">
addr = #{addr}
</when>
<!-- 所有when都不成立,执行 otherwise -->
<!-- otherwise 前面也会拼接where -->
<otherwise>
2 = 2
</otherwise>
</choose>
</trim>
</select>
<select id="select15" resultType="People">
select * from people
<where>
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="addr != null">
and addr = #{addr}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!-- where 也可以简化 choose -->
<!-- 更新操作 -->
<update id="update1" >
update people
<!-- prefix 只拼接一次 -->
<!-- 最后的语句 进行拼接 -->
<!--
比如当name,addr都不为空时
name = #{name},addr = #{addr},
prefix="set" 前面拼一个set
set name = #{name},addr = #{addr},
suffixOverrides="," 后面去掉逗号
set name = #{name},addr = #{addr}
-->
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="addr != null">
addr = #{addr},
</if>
<!--
因为拼接了一个where 如果name和addr都为空时
语句会变成
update people where id = ?
语法错误
所以要加一个 id = #{id}
相当于不修改
-->
id = #{id}
</trim>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!-- set 简化上面的操作 -->
<!--
<set> 简化 <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
作用:
1.子串不为空,添加set
2.子串以,结尾,去掉,
-->
<update id="update2" >
update people
<set>
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="addr != null">
addr = #{addr},
</if>
id = #{id}
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!-- 一次操作多条数据 -->
<!-- foreach 遍历 -->
<!-- 正常的删除多条数据 -->
<!--
delete from people where id in(7,10);
-->
<!-- 参数可以是数组 , 也可以是集合 -->
<!-- 数组 -->
<!--
数组类型参数:
没有注解:array, arg0
有注解: 注解中的值, param1
-->
<delete id="delMany" >
delete from people where id in
<!-- 因为我设置了ints的注解 -->
<!--
collection 参数传递过来的名字
open 以什么开头
separator 以什么分割
close 以什么结尾
item 遍历的元素叫什么 , 叫什么都行,下面要使用
#{num}
-->
<foreach collection="ints" open="(" separator="," close=")" item="num">
#{num}
</foreach>
</delete>
<delete id="delMany1" >
delete from people where id in
<!-- 因为我设置了list的注解 -->
<!--
delete from people where id in(7,8);
数组类型list集合:
没有注解:arg0, collection, list
有注解: 注解中的值, param1
-->
<foreach collection="list" open="(" separator="," close=")" item="num">
#{num}
</foreach>
</delete>
<!-- 模糊查询 -->
<!-- 正常模糊查询需要%%,如果想在sql这边操作 -->
<!-- 使用concat 单行函数 字符串拼接-->
<!--<select id="selectLike" resultType="People">
select * from people where name like concat('%', #{name}, '%');
</select>-->
<!-- 动态sql也封装了方法 -->
<!-- bind 标签-->
<select id="selectLike" resultType="People">
<bind name="abc" value="'%'+name+'%'"/>
select * from people where name like #{abc}
</select>
<!-- sql 片段 -->
<!--
一般在实际开发中我们不会使用*
而是使用 id , name , addr
-->
<!--
sql 标签来设置片段
include 来代替
-->
<sql id="a">
id , name , addr
</sql>
<select id="selectL" resultType="People">
select <include refid="a"/> from people;
</select>
</mapper>七、MyBatis中常用注解
在MyBatis中对于特别简单的SQL、尤其不需要定义resultMap的SQL可以使用注解进行实现。通过注解能简化映射文件的编写。
MyBatis的注解通过全局配置文件<mappers>进行加载。
-
如果一个Mapper接口中所有方法都使用注解定义SQL,可以在全局文件中配置。
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.bjsxt.mapper.PeopleMapper"></mapper>
</mappers>-
如果一个Mapper接口中既有注解又有mapper.xml定义SQL。可以在全局配置文件中通过
<package>进行加载。这种方式和之前的接口绑定方案的配置是一样的。也就是说MyBatis在扫描这个包的时候就可以加载到注解。
<mappers>
<package name="com.bjsxt.mapper"/>
</mappers>在MyBatis中注解都是写在Mapper接口的方法上中,所有的注解都在org.apache.ibatis.annotations包中,常见注解:
| 注解 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| @Select | 查询 |
| @Insert | 新增 |
| @Delete | 删除 |
| @Update | 修改 |
| @SelectKey | 主键回填 |
| @SelectProvider | 调用SQL构建器。查询专用 |
| @DeleteProvider | 调用SQL构建器。删除专用 |
| @UpdateProvider | 调用SQL构建器。修改专用 |
| @INSERTProvider | 调用SQL构建器。删除专用 |
| @Param | 定义参数的名称 |
2. 主键回填
使用注解时,主键回填需要通过@SelectKey注解。
该注解中:必有属性
keyProperty:表示回填属性名。
statement:执行的sql。
before:表示是否在@Insert的SQL之前执行。resultType:表示statement对应SQL执行结果。
@SelectKey(keyProperty = "id",statement = "select @@identity",before = false,resultType = Integer.class)3. SQL构建器(Provider)
在以后工作时,有的功能对应SQL可能会非常长,在Navicat中一页显示不下。对于这种情况可以使用映射文件没有什么太大问题。如果放在@Select注解的参数中,显然看起来不是太方便。如果还是希望使用注解,最好使用SQL构建器。
MyBatis的SQL构建器赋予了程序员在Java类中编写SQL的方式。把以前写在注解参数中的复杂SQL转移到了类的方法中进行书写。
3.1 直接写SQL方式代码演示
在接口中提供方法。并在方法上面添加@SelectProvider注解,注解中属性含义:
-
type:编写SQL的类。
-
method:类中哪个方法返回SQL。
@SelectProvider(type = MySQLProvider.class,method = "selectprovider")
List<People> select(People peo);新建MySQLProvider类,并在类中提供selectprovider方法。
下面SQL看起来写的不是特别费劲,但是一定要注意关键字前后都有空格。下面代码每行前面都有空格,其实这点非常不友好。
public class MySQLProvider {
public String selectprovider(){
return "select *" +
" from people" +
" where name=#{name} and address like #{address}" +
" order by id desc";
}
}3.2 使用SQL类
MyBatis提供了SQL类,该类中封装了很多方法,方法名称和SQL的关键字名称正好对应。
里面需要注意的点:
-
如果多个条件可以放在一个where中,也可以放在多个连续where中(放在多个where方法中不需要and关键字)。
-
最终需要调用toString()转换为字符串。
public class MySQLProvider {
public String selectprovider2(){
return "select *" +
"from people" +
"where name=#{name} and address like #{address}" +
"order by id desc";
}
public String selectprovider(){
return new SQL()
.SELECT("*")
.FROM("people")
.WHERE("name=#{name}")
// 没有and,多个并列条件使用WHERE方法
.WHERE("address like #{address}")
.ORDER_BY("id desc")
.toString();
}
}4.使用注解进行结果映射
@Results的value属性类型Result[]。
@Result注解:
column:数据库列
property:属性名
id:是否为主键,默认false
@Results(value = {
@Result(column = "peo_id",property = "id",id = true),
@Result(column = "peo_name",property = "name")
})
@Select("select * from tb_people where peo_name=#{name}")
List<People> select2(People peo);