LVGL_文件系统FS
前言:
LVG 内置支持以下文件系统:
1、FATFS
2、STDIO (Linux 和 Windows 都可以使用的 C 标准函数接口,比如:fopen, fread…)
3、POSIX (Linux 和 Windows 都可以使用的 POSIX 函数接口,比如:open, read…)
4、WIN32 (Windows 使用 Win32 API 函数接口比如:CreateFileA, ReadFile…)
1、在lv_conf.h中配置
/*---------------------
* 3rd party libraries
*--------------------*/
/*File system interfaces for common APIs */
/*API for fopen, fread, etc*/
#define LV_USE_FS_STDIO 0
#if LV_USE_FS_STDIO
#define LV_FS_STDIO_LETTER '\0' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/
#define LV_FS_STDIO_PATH "" /*Set the working directory. File/directory paths will be appended to it.*/
#define LV_FS_STDIO_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/
#endif
/*API for open, read, etc*/
#define LV_USE_FS_POSIX 0
#if LV_USE_FS_POSIX
#define LV_FS_POSIX_LETTER '\0' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/
#define LV_FS_POSIX_PATH "" /*Set the working directory. File/directory paths will be appended to it.*/
#define LV_FS_POSIX_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/
#endif
/*API for CreateFile, ReadFile, etc*/
#define LV_USE_FS_WIN32 1
#if LV_USE_FS_WIN32
#define LV_FS_WIN32_LETTER 'E' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/
#define LV_FS_WIN32_PATH "" /*Set the working directory. File/directory paths will be appended to it.*/
#define LV_FS_WIN32_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/
#endif
/*API for FATFS (needs to be added separately). Uses f_open, f_read, etc*/
#define LV_USE_FS_FATFS 0
#if LV_USE_FS_FATFS
#define LV_FS_FATFS_LETTER '\0' /*Set an upper cased letter on which the drive will accessible (e.g. 'A')*/
#define LV_FS_FATFS_CACHE_SIZE 0 /*>0 to cache this number of bytes in lv_fs_read()*/
#endif
2、使用示例
在电脑的E盘中新建测试文件
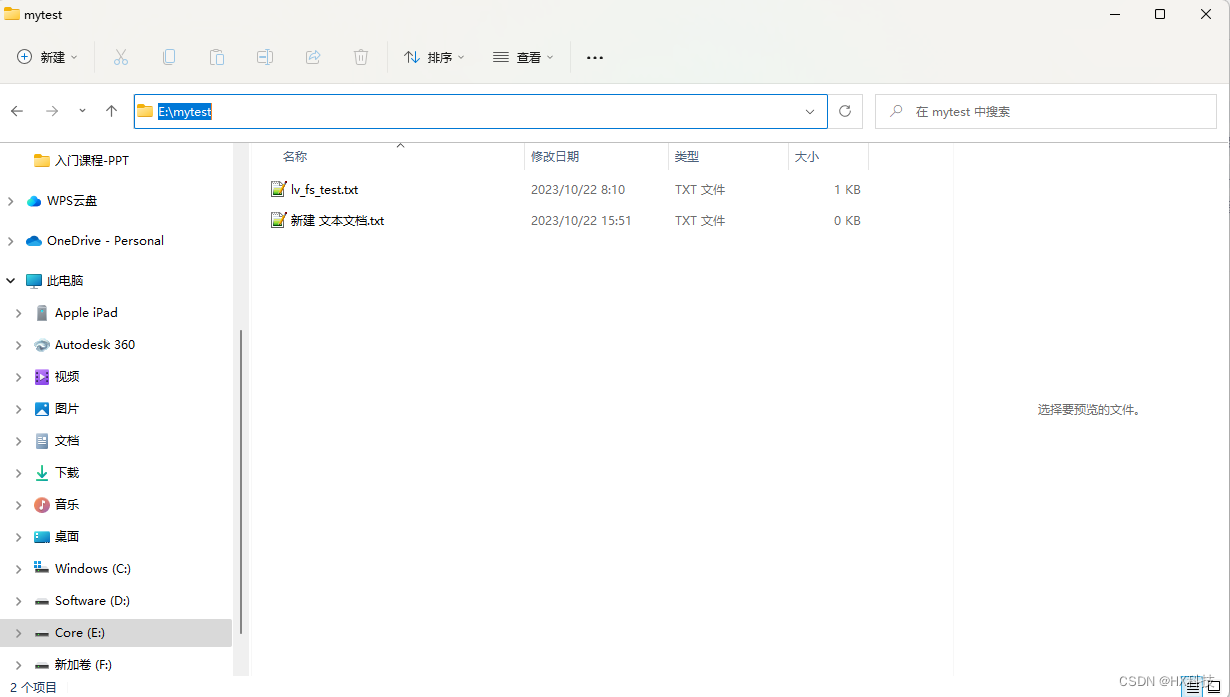
// 要打开的文件
#define FILE_NAME "E:/mytest/lv_fs_test.txt"
// 要读取的目录
#define DIR_PATH "E:/mytest/"
/* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取文件 */
static void lv_fs_read_dir(char * fn);
/* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取目录内容 */
static void lv_fs_read_file(char * path);
void lv_100ask_demo_course_6_1_1(void)
{
// 读取文件
lv_fs_read_file(FILE_NAME);
// 读取目录内容
lv_fs_read_dir(DIR_PATH);
}
/* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取文件 */
static void lv_fs_read_file(char * fn)
{
lv_fs_file_t f;
lv_fs_res_t res;
// 打开文件有两个模式: LV_FS_MODE_RD(只读) 和 LV_FS_MODE_WR(写)
res = lv_fs_open(&f, fn, LV_FS_MODE_RD);
// 如果一切正常会返回 LV_FS_RES_OK ,其他错误代码请看 lv_fs.h 中的 lv_fs_res_t 定义
if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK) {
LV_LOG_USER("Open error! Error code: %d", res);
return;
}
/* 每次实际读取到的数据大小(byte) */
uint32_t read_num;
/* 数据缓冲区 */
uint8_t buf[8];
/* 读取整个文件并打印内容 */
while (1) {
res = lv_fs_read(&f, buf, 8, &read_num);
if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK) {
LV_LOG_USER("Read error! Error code: %d", res);
break;
}
/* 将读取到数据打印出来 */
printf("%s", buf);
if (read_num != 8) break;
}
lv_fs_close(&f);
}
/* 通过LVGL文件系统接口统一不同的文件系统并读取目录内容 */
static void lv_fs_read_dir(char * path)
{
lv_fs_dir_t dir;
lv_fs_res_t res;
res = lv_fs_dir_open(&dir, path);
if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK){
LV_LOG_USER("Open DIR error! Error code: %d", res);
return;
}
char fn[256]; // 缓冲区
while(1) {
res = lv_fs_dir_read(&dir, fn);
if(res != LV_FS_RES_OK) {
LV_LOG_USER("Read DIR error! Error code: %d", res);
break;
}
/* 如果没有更多文件可以读取时 fn 就为空 */
if(strlen(fn) == 0) {
LV_LOG_USER("Fn is empty, if not more files to read.");
break;
}
printf("%s\n", fn);
}
lv_fs_dir_close(&dir);
}
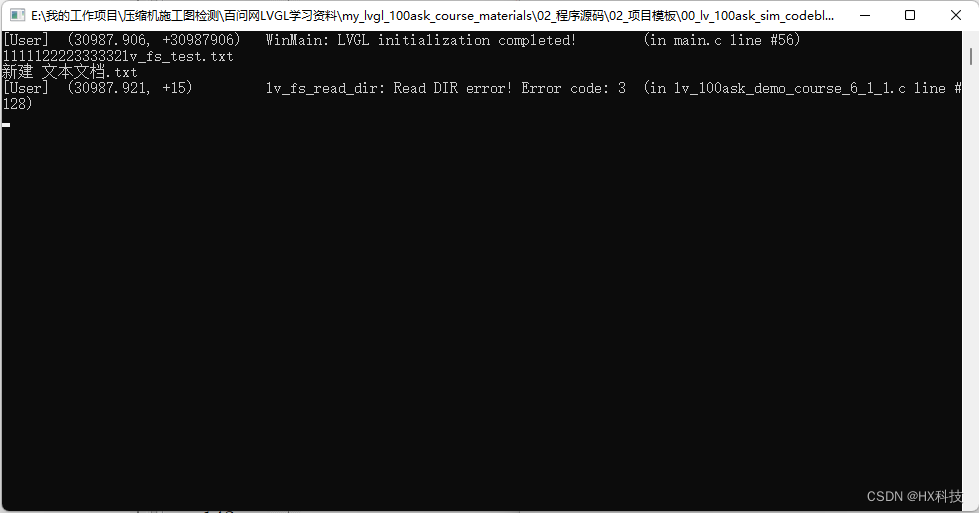
运行上述代码结果如下(打印出文件内容,文件夹的内容)