C++笔记之遍历vector的所有方式
—— 2023年4月15日 上海
code review
文章目录
- C++笔记之遍历vector的所有方式
- 1.普通for循环
- 2.迭代器版
- 3.const迭代器
- 4.C++11引入的范围for循环
- 5.使用auto关键字和迭代器
- 6.使用std::for_each算法
- 7.使用std::for_each和lambda表达式
- 8.普通版+vector::at()版
- 9.指针版
- 10.使用while循环
- 10.1.使用普通while循环和下标
- 10.2.使用普通while循环和迭代器
- 11.迭代器的声明通常使用auto it = v.begin();来替代std::vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
注意:不使用引用或指针来遍历的遍历方式都是只读操作,无法修改元素的值
1.普通for循环
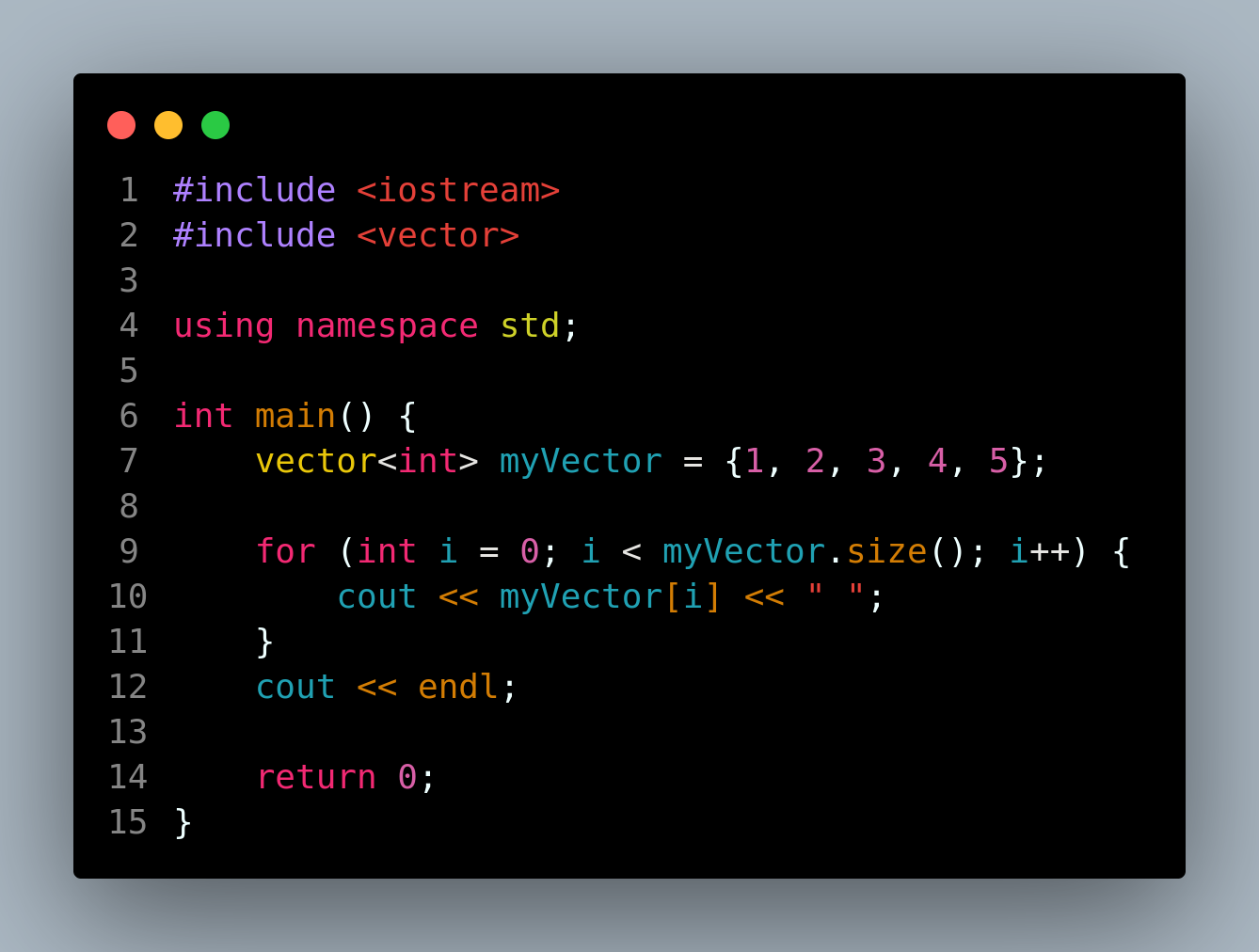
2.迭代器版
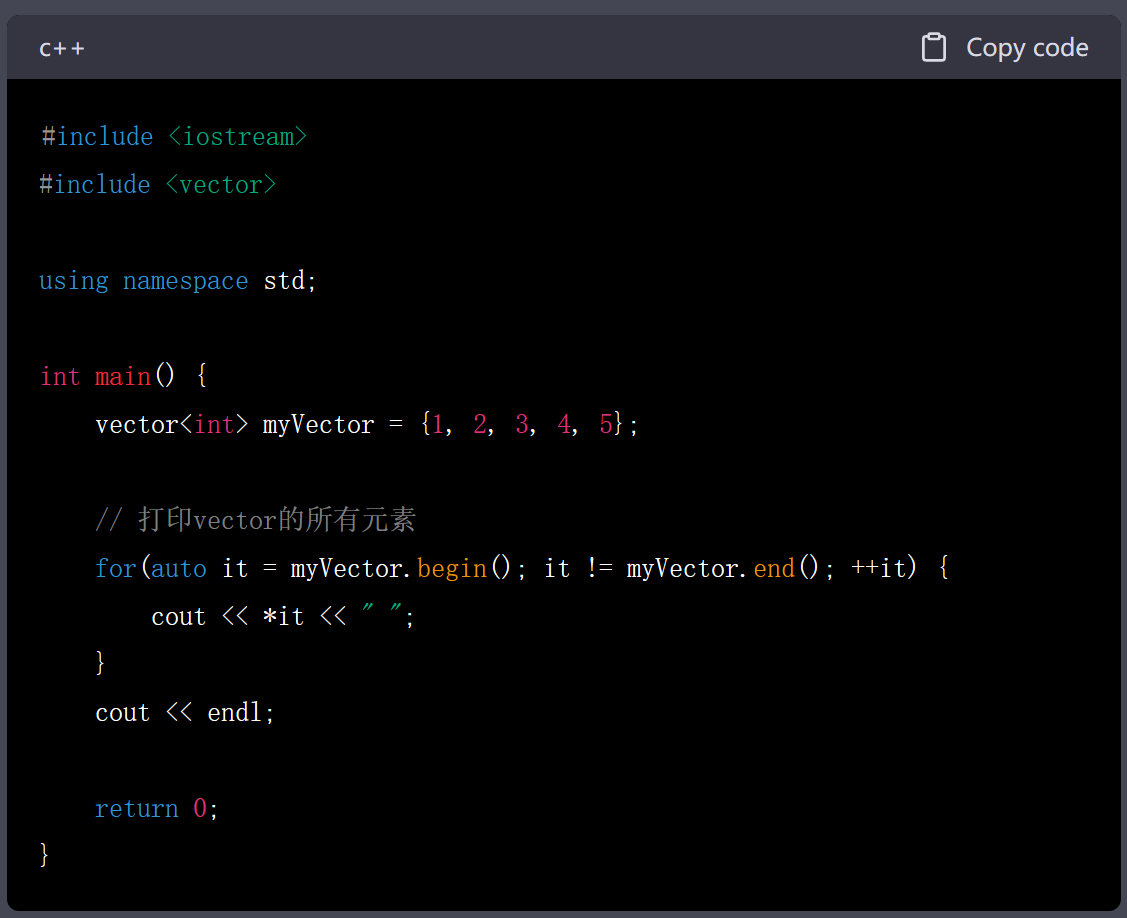
3.const迭代器

4.C++11引入的范围for循环
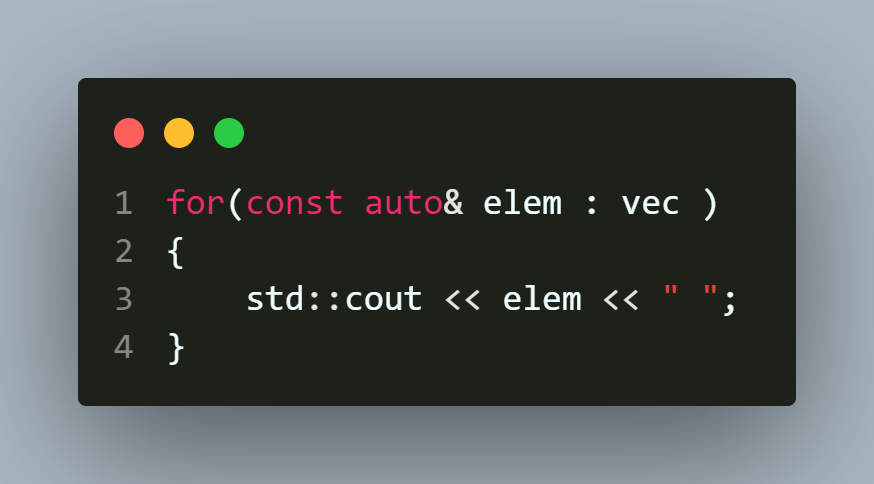
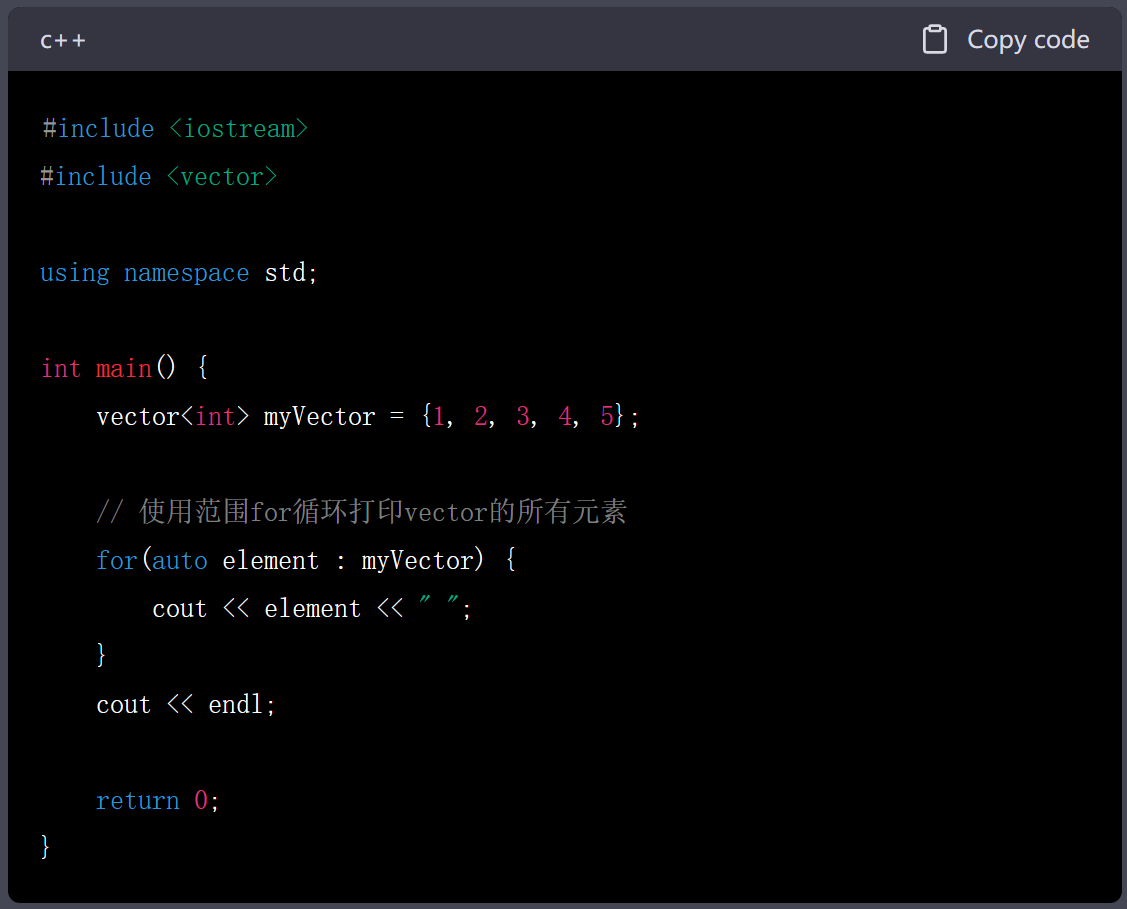
5.使用auto关键字和迭代器

6.使用std::for_each算法

7.使用std::for_each和lambda表达式

8.普通版+vector::at()版

9.指针版
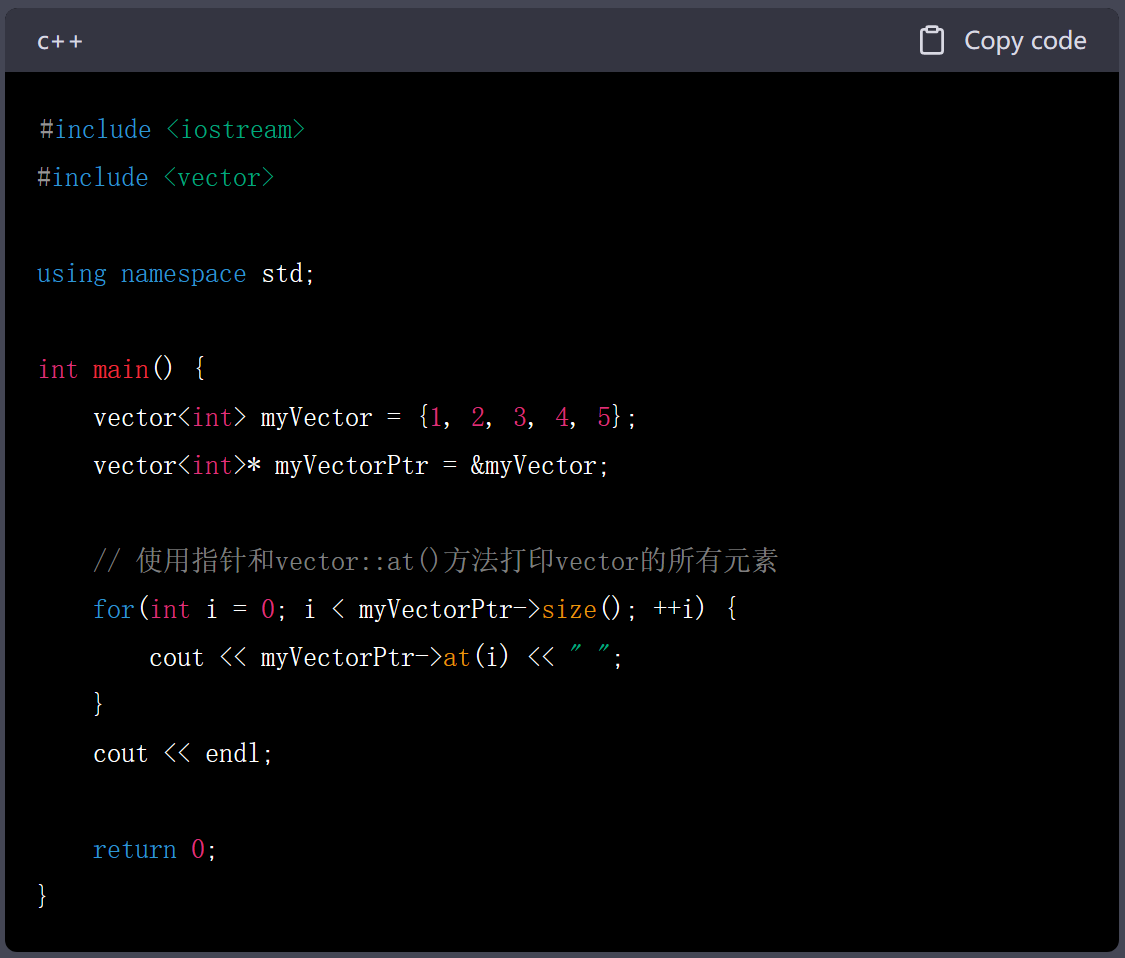
10.使用while循环
注意:使用while循环遍历时需要注意循环条件,遍历完成后一定要确保循环变量或迭代器指向std::vector的end()位置,否则可能会出现未定义的行为。
10.1.使用普通while循环和下标
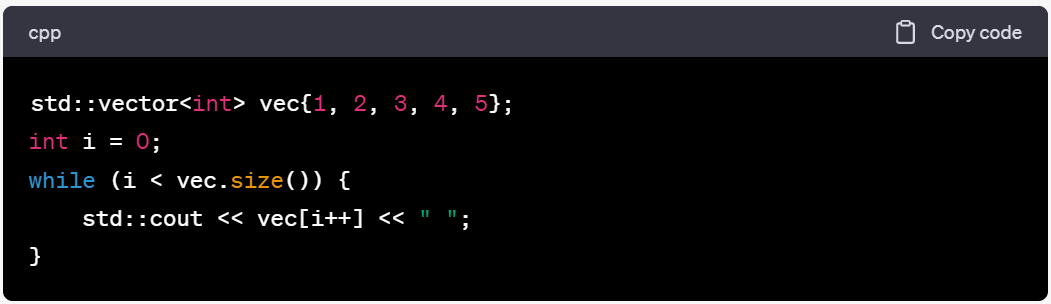
10.2.使用普通while循环和迭代器
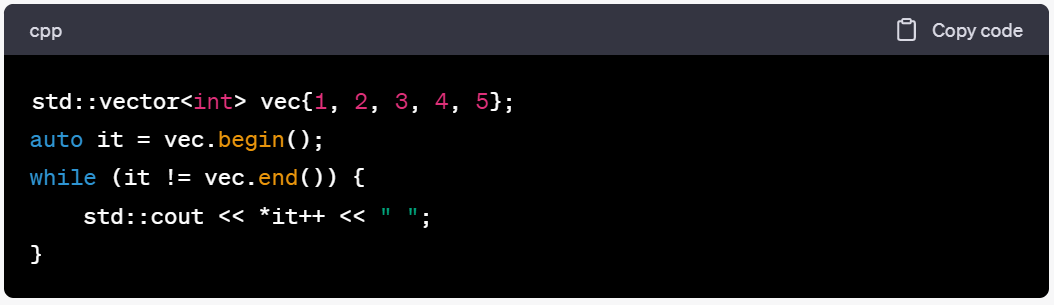
11.迭代器的声明通常使用auto it = v.begin();来替代std::vector::iterator it = v.begin();
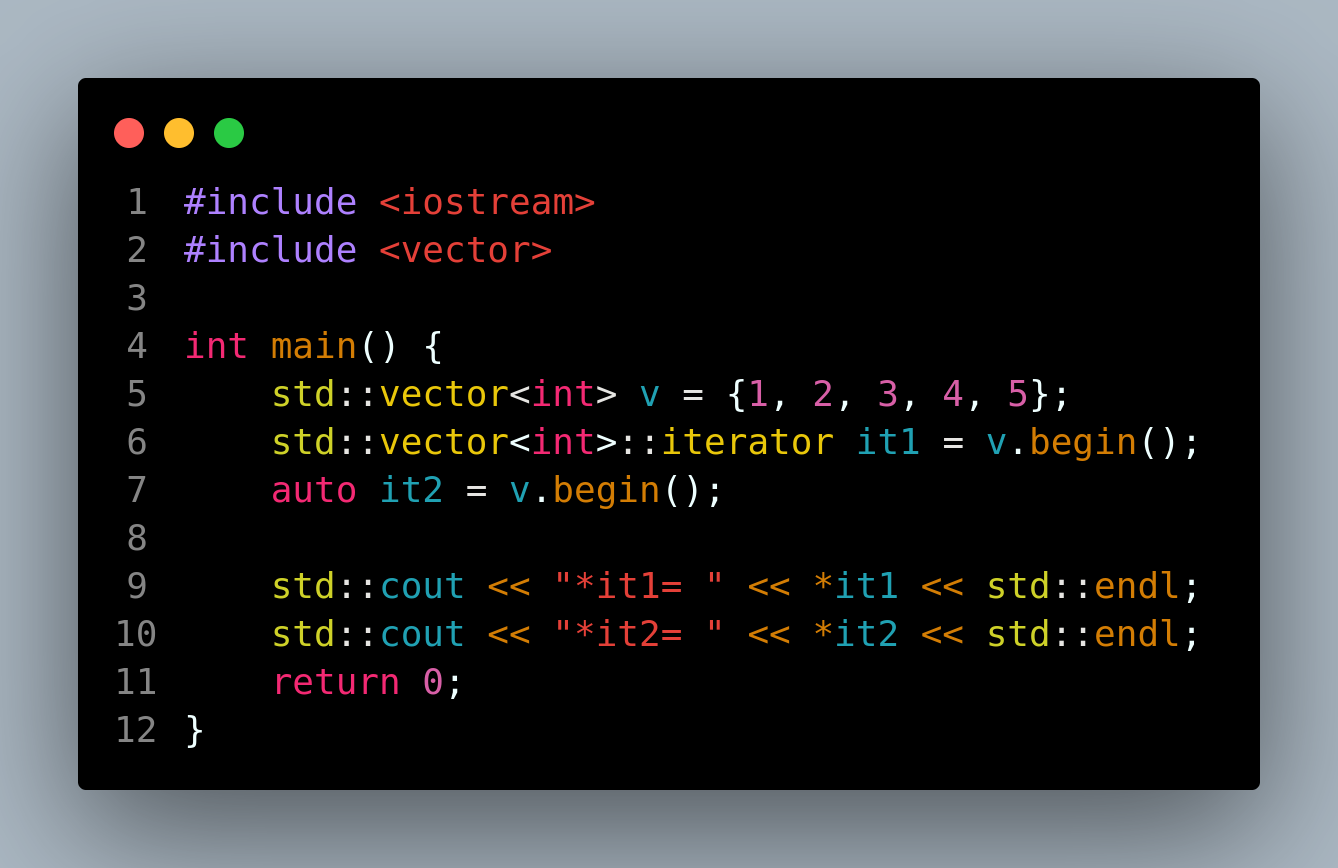
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::vector<int>::iterator it1 = v.begin();
auto it2 = v.begin();
std::cout << "*it1= " << *it1 << std::endl;
std::cout << "*it2= " << *it2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}