文章目录
- 1. 代码仓库
- 2. 广度优先遍历图解
- 3.主要代码
- 4. 完整代码
1. 代码仓库
https://github.com/Chufeng-Jiang/Graph-Theory
2. 广度优先遍历图解

3.主要代码
- 原点入队列
- 原点出队列的同时,将与其相邻的顶点全部入队列
- 下一个顶点出队列
- 出队列的同时,将与其相邻的顶点全部入队列
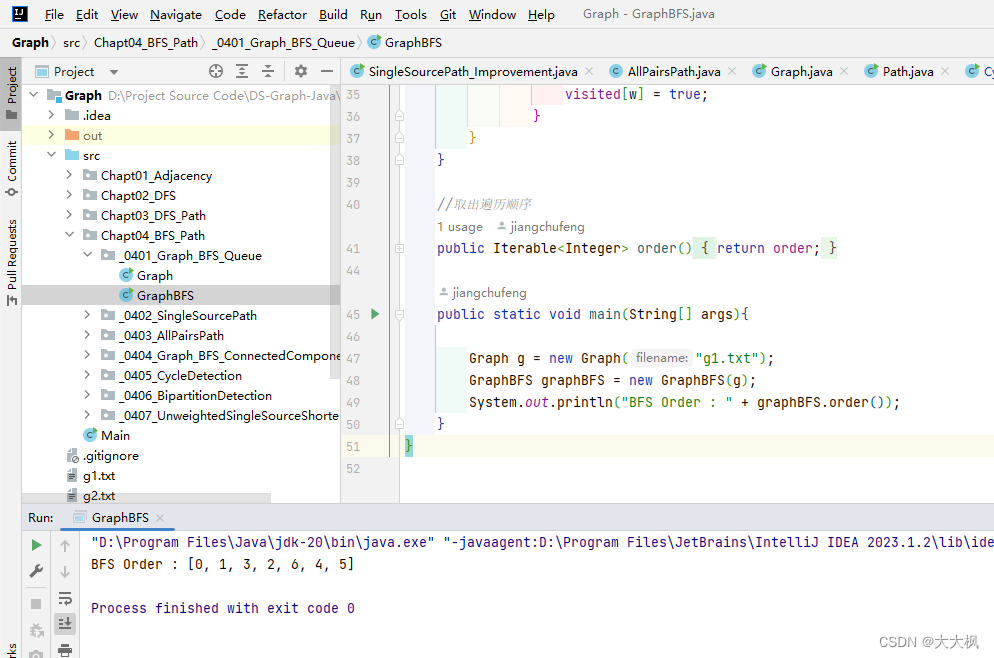
private void bfs(int s){ //使用循环
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //只要不是空就不停地出队
int v = queue.remove(); // v记录队首元素 | 相邻顶点入队后,重新进入while循环,队首出队
order.add(v); //添加到order数组中,order数组装的是按照BFS顺序遍历的顶点
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w); // 相邻的顶点入队列
visited[w] = true;
}
}
}
复杂度:O(V+E)
4. 完整代码
输入文件
7 9
0 1
0 3
1 2
1 6
2 3
2 5
3 4
4 5
5 6
package Chapt04_BFS_Path._0401_Graph_BFS_Queue;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class GraphBFS {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private ArrayList<Integer> order = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储遍历顺序
public GraphBFS(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
//遍历所有连通分量
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(!visited[v])
bfs(v);
}
private void bfs(int s){ //使用循环
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //只要不是空就不停地出队
int v = queue.remove(); // v记录队首元素 | 相邻顶点入队后,重新进入while循环,队首出队
order.add(v); //添加到order数组中,order数组装的是按照BFS顺序遍历的顶点
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w); // 相邻的顶点入队列
visited[w] = true;
}
}
}
//取出遍历顺序
public Iterable<Integer> order(){
return order;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g1.txt");
GraphBFS graphBFS = new GraphBFS(g);
System.out.println("BFS Order : " + graphBFS.order());
}
}