请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可
示例 1:
输入:
[“MyQueue”, “push”, “push”, “peek”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
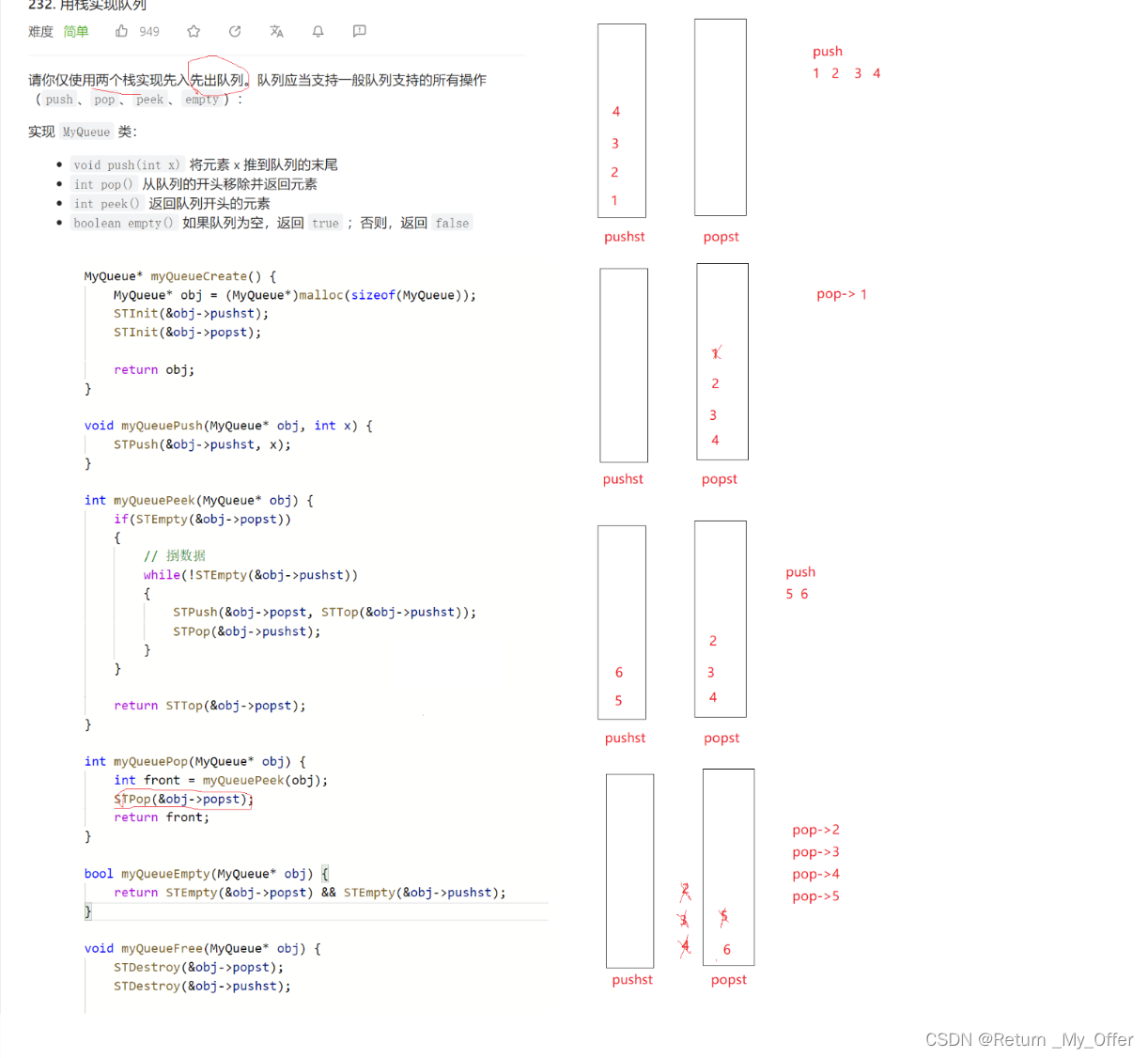
将一个栈当作输入栈,用于压入 push 传入的数据;另一个栈当作输出栈,用于 pop和 peek 操作
每次 pop或 peek 时,若输出栈为空则将输入栈的全部数据依次弹出并压入输出栈,这样输出栈从栈顶往栈底的顺序就是队列从队首往队尾的顺序
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* ps);
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
STDataType STSize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a=NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,
sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
STDataType STSize(ST* ps)/*.....*/
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top ==0;//0;
}
typedef struct {
ST Pushst;
ST Popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue*obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&obj->Pushst);
STInit(&obj->Popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->Pushst, x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->Popst);
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(STEmpty(&obj->Popst)){
while(!STEmpty(&obj->Pushst)){
STPush(&obj->Popst,STTop(&obj->Pushst));
STPop(&obj->Pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->Popst);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->Popst)&&STEmpty(&obj->Pushst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->Popst);
STDestroy(&obj->Pushst);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/



![[架构之路-238]:目标系统 - 纵向分层 - 网络通信 - 网络规划与设计框架](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/40fd6973ef404b59bd5fb31bc3ece5e8.png)