文章目录
- 一、Stream API vs 集合
- 二、Stream 使用的执行流程
- 2.1、创建Stream
- 2.1、中间操作
- 2.1.1. filter
- 2.1.2. limit
- 2.1.3. skip
- 2.1.4. distinct
- 2.1.5. map
- 2.1.6. sorted
一、Stream API vs 集合
- Stream API 关注的是多个数据的
计算(排序、查找、过滤、映射、遍历等),面向CPU。集合关注的是数据的存储,面向内存。 - Stream API 之于 集合,类似于 SQL 之于 数据表的查询。
二、Stream 使用的执行流程
- 1.创建Stream
一个数据源(如:集合、数组),获取一个流
- 2.中间操作
- 3.终止操作
2.1、创建Stream
- 1.通过集合
@Test
public void test(){
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
//JDK1.8中,Collection系列集合增加了方法
Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();
}
Java8 中的 Collection 接口被扩展,提供了两个获取流的方法
1.default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流 2.default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
- 2.通过数组
@Test
public void test(){
String[] arr = {"hello","world"};
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
}
- 3.通过Stream的of()
@Test
public void test04(){
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5);
}
2.1、中间操作
2.1.1. filter
从流中排除某些元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
Person p1 = new Person(1,"xixi");
Person p2 = new Person(3,"haha");
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.stream().filter(person -> person.getAge() > 2).forEach(System.out :: println);
}
2.1.2. limit
使元素不超过指定数量
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
Person p1 = new Person(1,"xixi");
Person p2 = new Person(3,"haha");
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.stream().limit(1).forEach(System.out :: println);
}
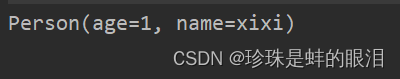
2.1.3. skip
跳过前面n个元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();
Person p1 = new Person(1,"xixi");
Person p2 = new Person(3,"haha");
Person p3 = new Person(5,"yiyi");
list.add(p1);
list.add(p2);
list.add(p3);
list.stream().skip(2).forEach(System.out :: println);
}
2.1.4. distinct
通过流中元素的hashCode()和equals()方法,去除重复元素
2.1.5. map
映射,将元素转换为其他形式或提取信息
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc");
/* 1.lmabda表达式 */
list.stream().map(item -> item.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out :: println);
/* 2.方法引用 */
list.stream().map(String :: toUpperCase).forEach(System.out :: println);
}

2.1.6. sorted
排序