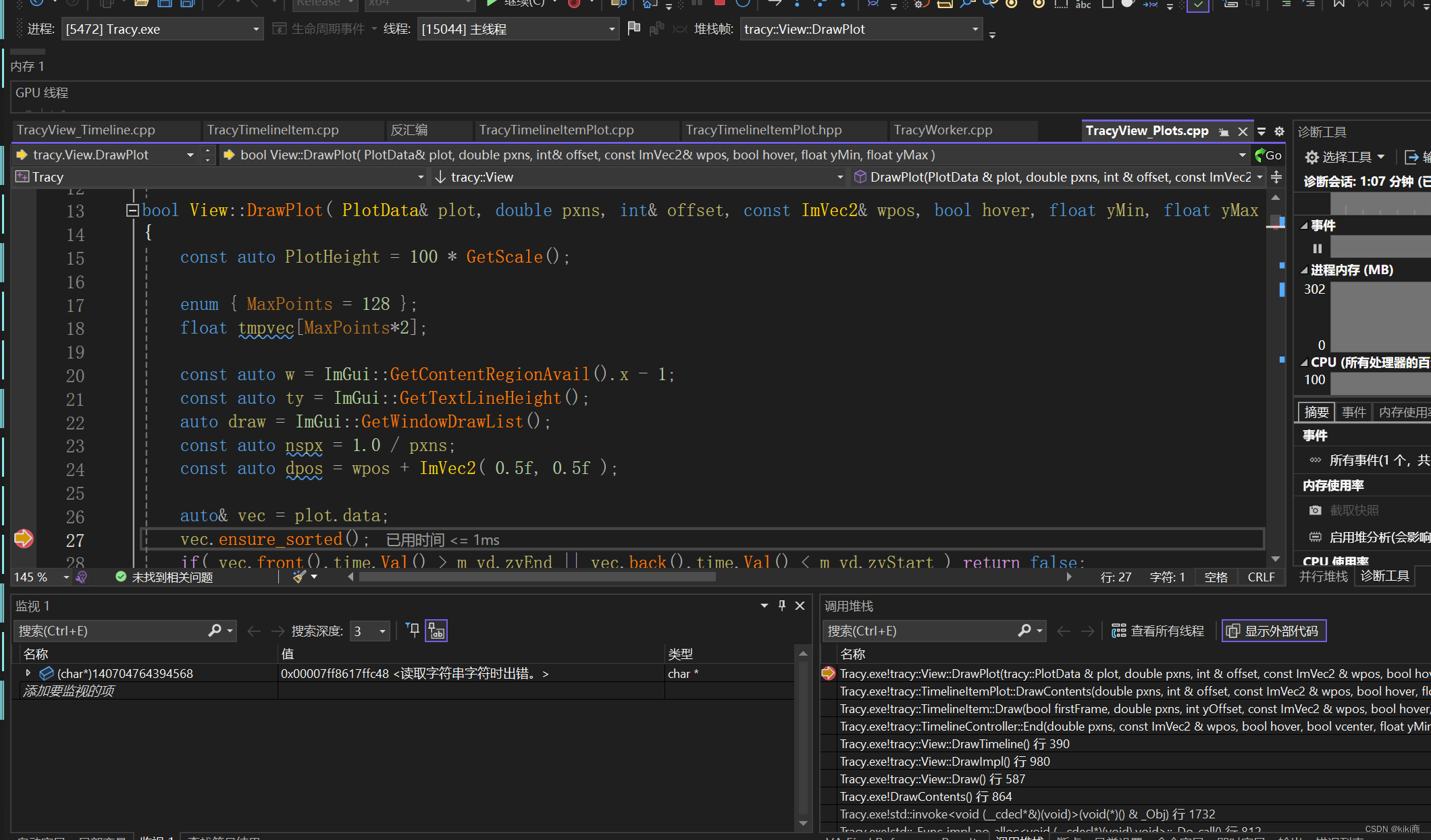
一、Defects4j数据集安装
在Ubuntu系统上进行操作,具体的在:Defects4j数据集安装
二、Defects4j数据集的使用
1. 常用命令
Getting started
----------------
#### Setting up Defects4J
1. Clone Defects4J:
- `git clone https://github.com/rjust/defects4j`
2. Initialize Defects4J (download the project repositories and external libraries, which are not included in the git repository for size purposes and to avoid redundancies):
- `cd defects4j`
- `./init.sh`
3. Add Defects4J's executables to your PATH:
- `export PATH=$PATH:"path2defects4j"/framework/bin`
#### Using Defects4J
4. Check installation and get information for a specific project (commons lang):
- `defects4j info -p Lang`
- `defects4j info -p Math`
5. Get information for a specific bug (commons lang, bug 1):
- `defects4j info -p Lang -b 1`
6. Checkout a buggy source code version (commons lang, bug 1, buggy version):
- `defects4j checkout -p Lang -v 1b -w /tmp/lang_1_buggy`
7. Change to the working directory, compile sources and tests, and run tests:
- `cd /tmp/lang_1_buggy`
- `defects4j compile`
- `defects4j test`
8. More examples of how to use the framework are available in `framework/test`
2. 框架
defects4j
|
|--- project_repos: The version control repositories of the provided projects.
|
|--- major: The Major mutation framework.
|
|--- framework: Libraries and executables of the database abstraction and
| test execution framework.
|
|--- bin: Command line interface to Defects4J.
|
|--- core: The modules of the core framework.
|
|--- lib: Libraries used in the core framework.
|
|--- util: Util scripts used by Defects4J.
|
|--- projects: Project-specific resource files.
|
|--- test: Scripts to test the framework.
首先看一下文件结构,首先是project_repos,指提供的含有故障的项目的版本控制库,之后是major,是主要的变异框架,再framework中存在我们比较需要的各种信息,重点关注projects,里面是各种真实故障的项目。
以Lang为例,讲解一下里面的目录结构
Lang
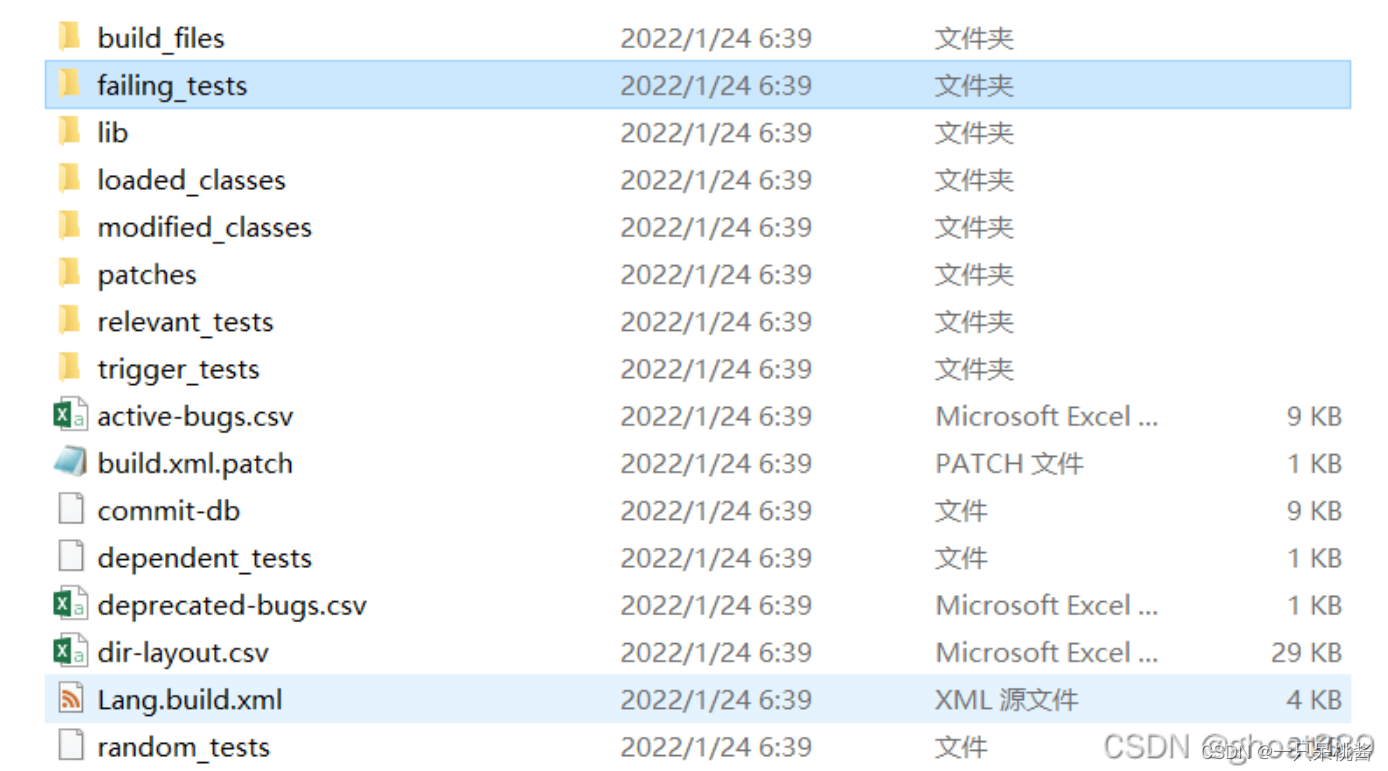
逻辑是这样的,对每个defects4j项目来有很多测试类,每个测试类里面有很多测试用例,如果全通过了就说明程序没有问题,但有些情况下测试可能不通过,可能只是某一两个测试方法不通过,难道要把所有的程序再重新加载,进行实验吗?西门子故障程序是那么做的,不同版本的故障程序之间只有一两行不一样,所有的测试用例也都是一样的,测试用例对在运行不同版本的故障程序时结果是不同的。这种情况在defects4j上行不通,因为西门子程序太小了,这里动辄上万行的代码。
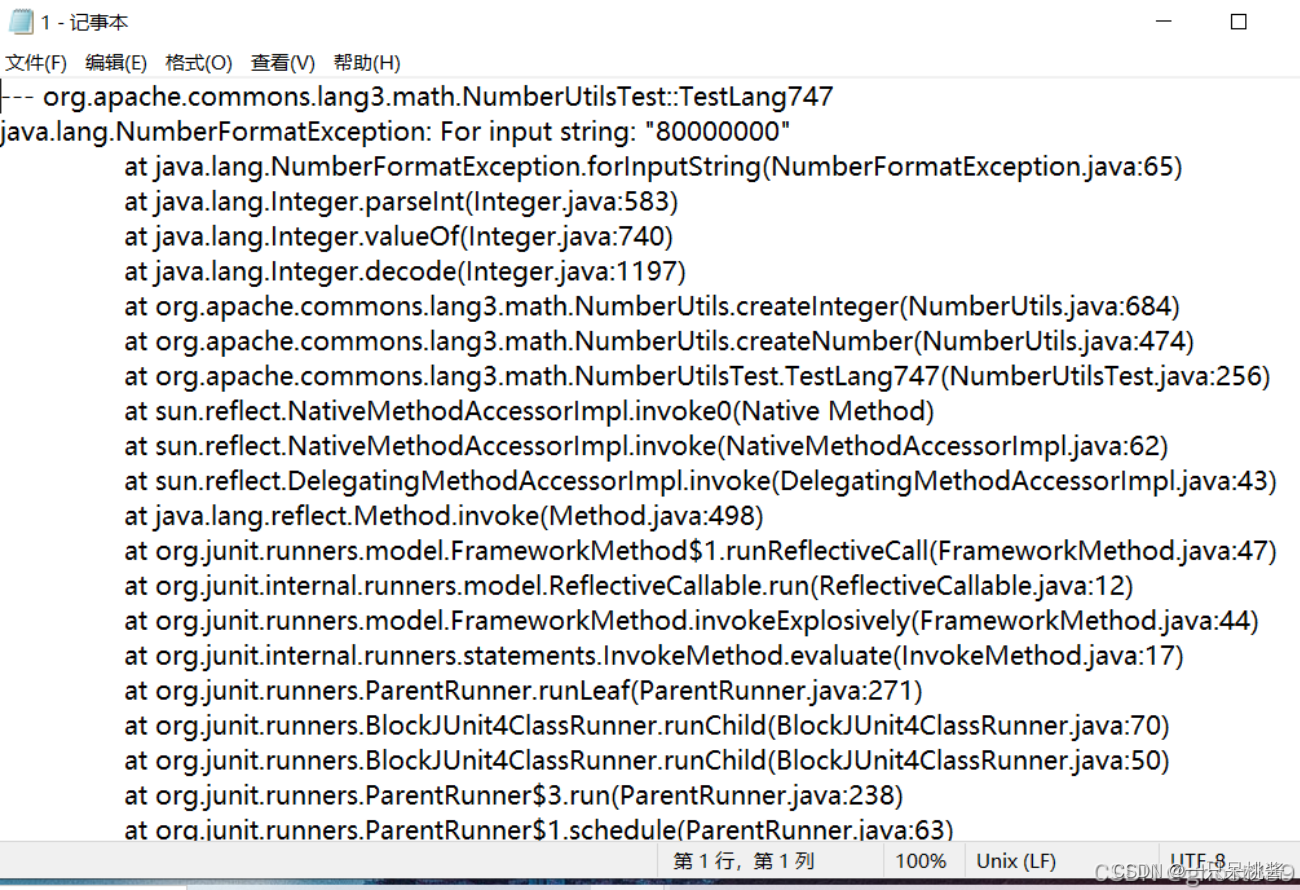
- trigger tests
每个故障版本都对应个一个trigger test,这个trigger test里面包含了一些引发了程序bug的测试方法。
-
modified classes
既然有了trigger test ,那么就必然有bug,那么文件夹modified_classes里面装的就是将bug修复时,需要改动源程序中的哪些类。
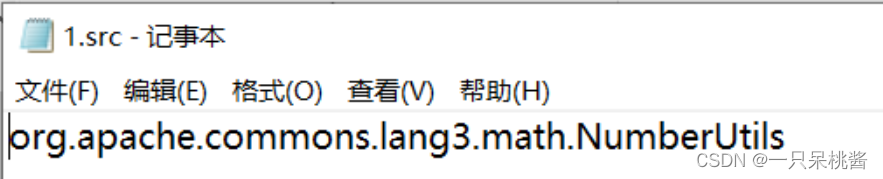
如图,Lang项目的第一个故障版本需要改动NumberUtils类即可修复。 -
loaded classes/relevant classes
虽然bug只和这一个类有关,但程序是一个整体,只有这一个类跑不起来呀,想要跑起来需要很多relevant classes,在项目里是loaded_classes文件夹下,只有将这些类都加载进JVM中,trigger test方法才能跑起来。 -
relevant tests
既然trigger test的运行,说明了程序中存在bug,只是在trigger_test中引发了bug,其他的测试程序中可能也跑了故障代码(modified classes),但是没有引发故障,所以relevent tests里面记录的就是所有的相关测试类。所谓相关测试类就是指当执行测试方法时,JVM中加载了modified classes,这样就保证了所有相关的测试都包含在内。 -
patches
最后就是patches,其中src.patch记录了故障应该怎么修复,比如说,按照github的教程上执行了
defects4j checkout -p Lang -v 1b -w /tmp/lang_1_buggy
这行代码后,实际上就是在/tmp/lang_1_buggy文件夹下将这个Lang 1 版本编译,测试所需要所有类和测试类都写进去了,在src文件夹下,我们再执行
cd /tmp/lang_1_buggy
defects4j compile
defects4j test
注意,这里可以直接在linux中使用命令进行编译和测试,如果想在IDEA中进行运行测试,我这里用的环境是jdk1.7和maven3.8.1,注意:亲测maven3.6不行
这时候我们编译的是含有故障的代码,运行后
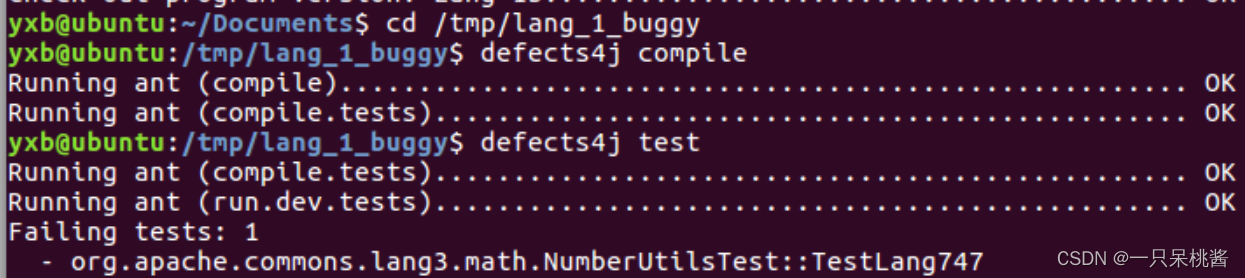
它就会显示trigger test中记录的故障代号。
如果我们想要一个没有故障的版本怎么办呢,就对defects4j checkout后,/tmp/lang_1_buggy中的源码进行更改即可,按照src.patch更改源码,其中@@后是代码在NumberUtils.java中的行数,每行代码前面没有符号时,代表代码无需改动,- 代表是新加的正确代码,+ 代表是错误代码,注释掉即可。
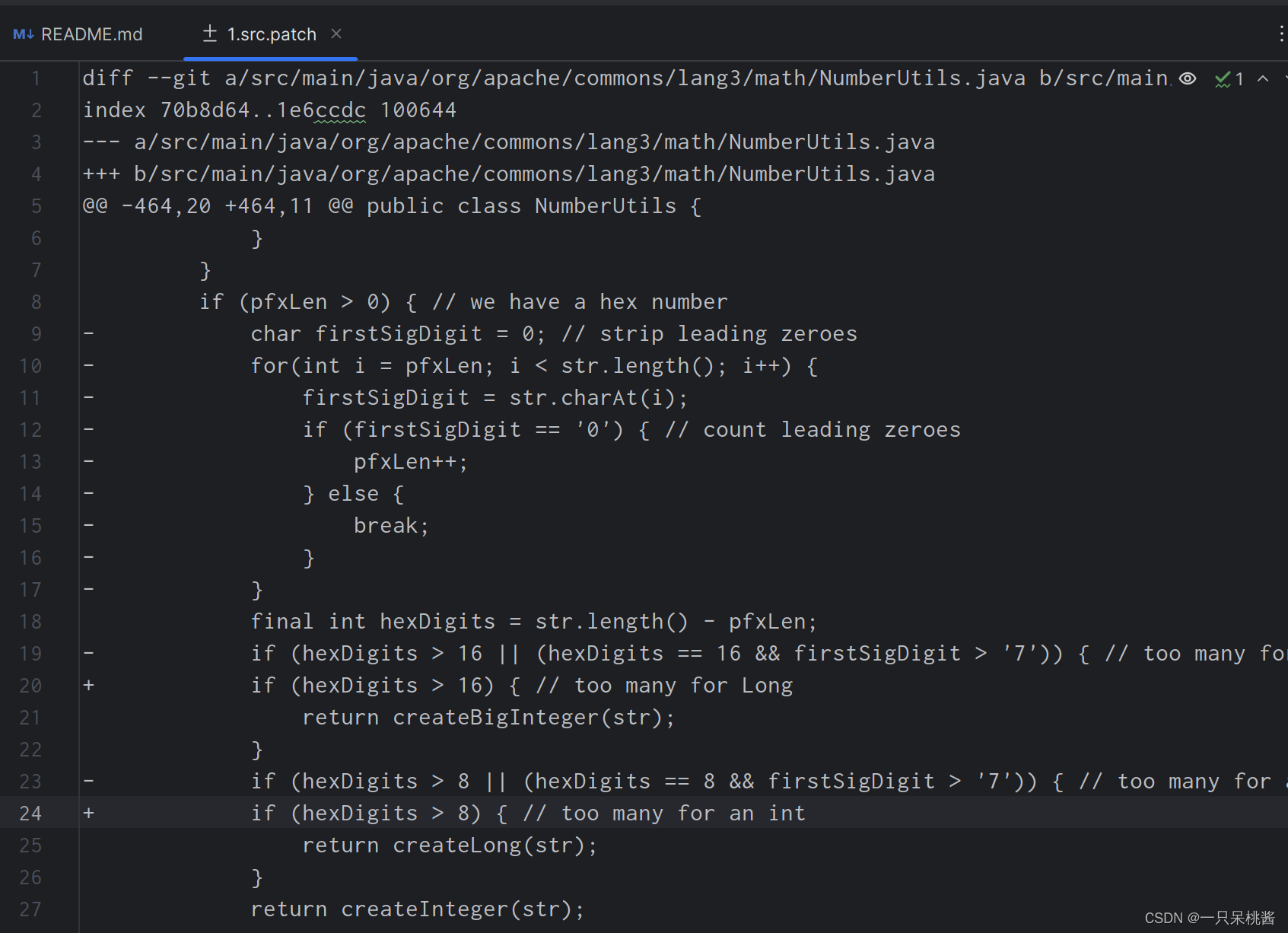
更改完代码后,我们再执行defexts4j test 就没有错误了。
这种方法可以帮助我们获取无故障的源码,以及为程序中插入故障提供思路。